probability math
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Theoretical Probability
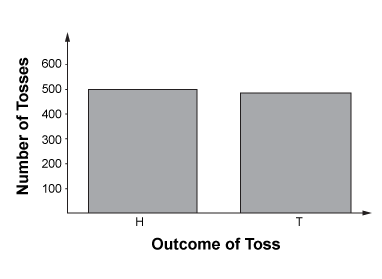
what we expect to happen in theory.
Example.
When flipping a coin several times, half should be Heads and half Tails.
Dependent Events
the outcome of one event affects the outcome of the second.
Example.
drawing colored balls from a bag, when you do NOT put them back after each draw P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B|A)
Probability of 0
an impossible outcome
Example.
P(7) = 0 because it is impossible to roll a 7 on a single standard six-sided die
Probability
the likelihood of an event occurring. Compares the successful outcomes to the total outcomes.
Example.
Probability = number of successful outcomes possible / total number of outcomes possible
The probability of rolling a 4 is 1/6 ("one out of 6")
Placebo
something that looks like the actual treatment but designed to have no effect on the subject
Independent Events
two or more events that have no influence on each other.
Example.
drawing colored balls from a bag, when you put them back after each draw P(A and B) = P(A) × P(B)
Bias
when incorrect conclusions are made because some parts of the population are over-represented in the sample and some parts are under-represented
Population (in stats)
all members of a defined group
Example.
Every doctor in America
Experimental Investigation
Researchers assign subjects in the sample to certain treatments, then observe the effects of the treatment. Can show causation (cause and effect).
Example.
Does using algebra tiles during instruction help freshman students learn how to solve equations?
Experimental Probability / Empirical Probability
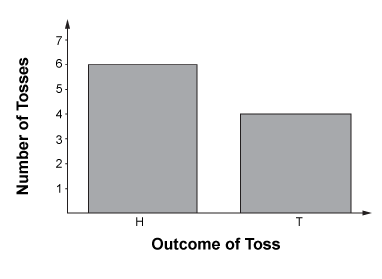
what actually occurs during a simulation or trial
Example.
When flipping a coin a few times, more are Heads than Tails.
Geometric Probability
interpreting one part of an area as a “successful” or “favorable” outcome, compared with the entire area
Margin of Error
a number that represents how far above or below the actual mean may be from the experimental mean in a study
Conditional Probability / Compound Event
occurs when two or more simple events are performed together so that one event happens and so does another
Sample
a subset of the population
Example.
The 250 doctors polled in a survey
Probability of 1
a guaranteed outcome
Example.
P (a number less than 10) = 1 because any roll on a standard six-sided die will guarantee a number smaller than 10
Observational Study
researchers observe and record data for the subjects in the sample (they do NOT assign treatments). Can only show correlation.
Example.
What percent of students at this university are involved in at least one extracurricular activity?
Probability Model
a mathematical representation of a random phenomenon
Sample Space
a list or set of all possible outcomes
Example.
tree diagram
Control Group
a group of specimens in an experiment to which no change is made; does not receive the experimental treatment
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of talk therapy on alleviating depression, the group receiving only the medicine would be the control group.
Simple Random Sample / Random Sample
a sample in which each member of the subset has an equal probability of being chosen
Example.
Every member is assigned a number and a random number generator is used to select the sample.
Experimental Group
a group of specimens in an experiment to which a change is made; receives the experimental treatment
Example.
In an experiment investigating the effect of talk therapy on alleviating depression, the group receiving the medicine and the therapy would be the experimental group.
Simulation
imitation of a real-world process or system
Example.
using a flight simulator to train pilots