Modules 2/3 Review: Motion, Forces, Newton's Laws
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
force
a push or pull upon an object
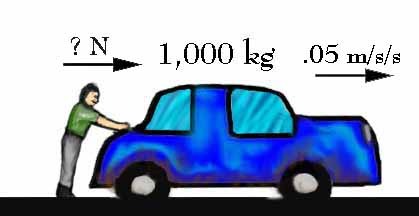


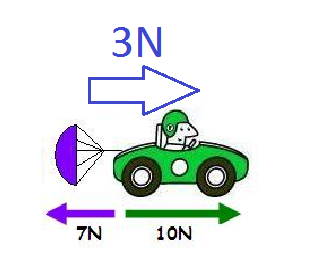




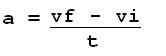
You are riding a bike, you hit a rock and you fly off the bike into the mud in front of the bike.
Example of Newton's 1st Law; inertia
A little kid and his dad are skipping pebbles on the pond. The pebbles that the dad throws accelerate faster than the little kid's pebbles.
Example of Newton's 2nd Law
Normal Force (Fn)
a force that acts on a surface in a direction perpendicular to the surface

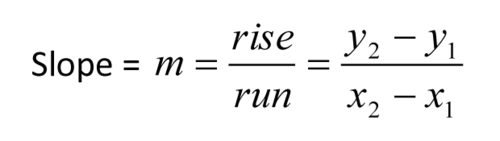
acceleration
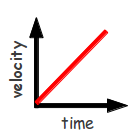
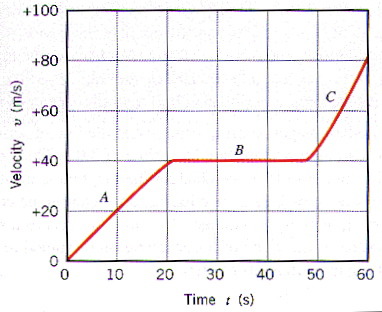
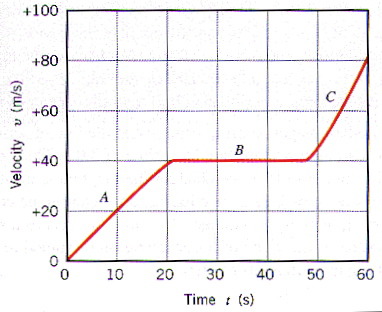
final velocity - initial velocity/time; slope of a velocity vs time graph
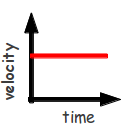
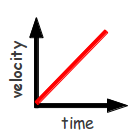
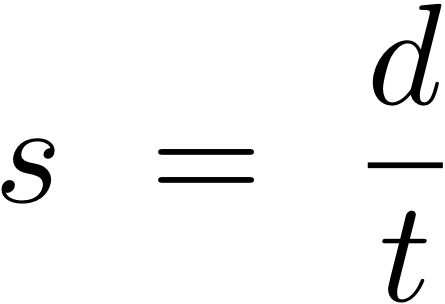


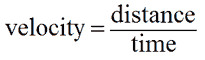
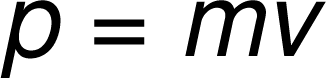
15 cm/s
An ant travels 75 cm in 5 s. What was the ant's average speed?
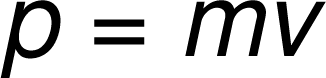
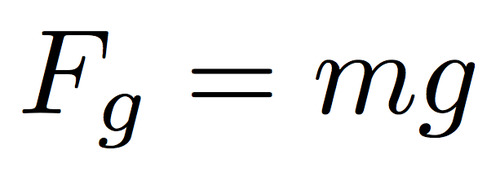


velocity
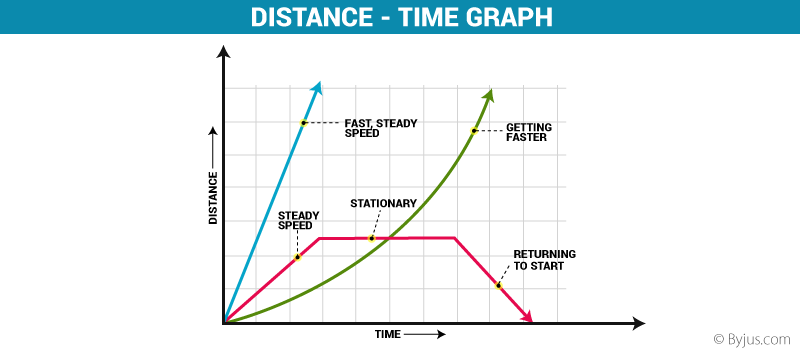
slope of a distance vs time graph
weight
(mass)(acceleration due to gravity); this is a force
unit of velocity
m/s
unit of acceleration
m/s2
Law of Conservation of Momentum
the total momentum of two objects before they collide equals the total momentum of the two objects after they collide
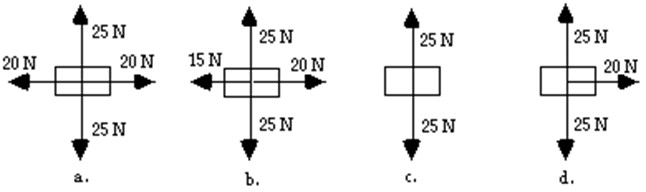
Free Body Diagram
a diagram of all the forces acting on an object; arrows show direction and magnitude of the forces
4800 m
A drone is traveling 72 km/hour. How many meters will it go in 4.0 minutes?
3.5 min
A runner is running at a constant speed of 4.8 m/s. How many minutes does it take the runner to travel 1.0 km?
22 m/s
Find the speed in meters per second of a baseball thrown 38 m from third base to first base in 1.7 s.
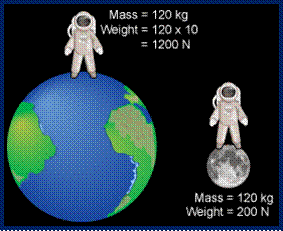
the gravitational force is greater; weighs more than on Earth
Jupiter is much more massive than Earth. How does the gravitational force between an object near the surface of Jupiter compare to that object near the surface of Earth?
the gravitational force is less; weighs less than on Earth;
The moon is much less massive than Earth. How does the gravitational force between an object near the surface of the moon compare to that object near the surface of Earth?
0.09 m/s
A 0.015 kg marble moves to the right at 0.225 m/s makes a head on collision with a 0.03 kg marble moving to the left at 0.180 m/s. After the collision, the smaller marble moves to the left at 0.315 m/s. What is the velocity of the 0.03 kg marble after the collision? Hint: use the Law of Conservation of Momentum
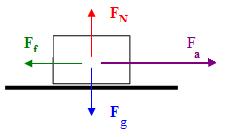
free body diagram of an object with 4 forces acting upon it; accelerating to the right
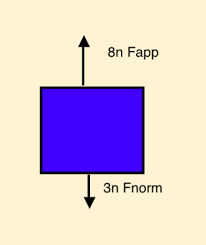
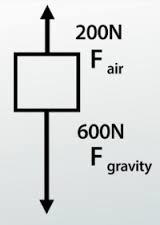
free body diagram of an object with 2 unbalanced forces acting upon it; accelerating upward
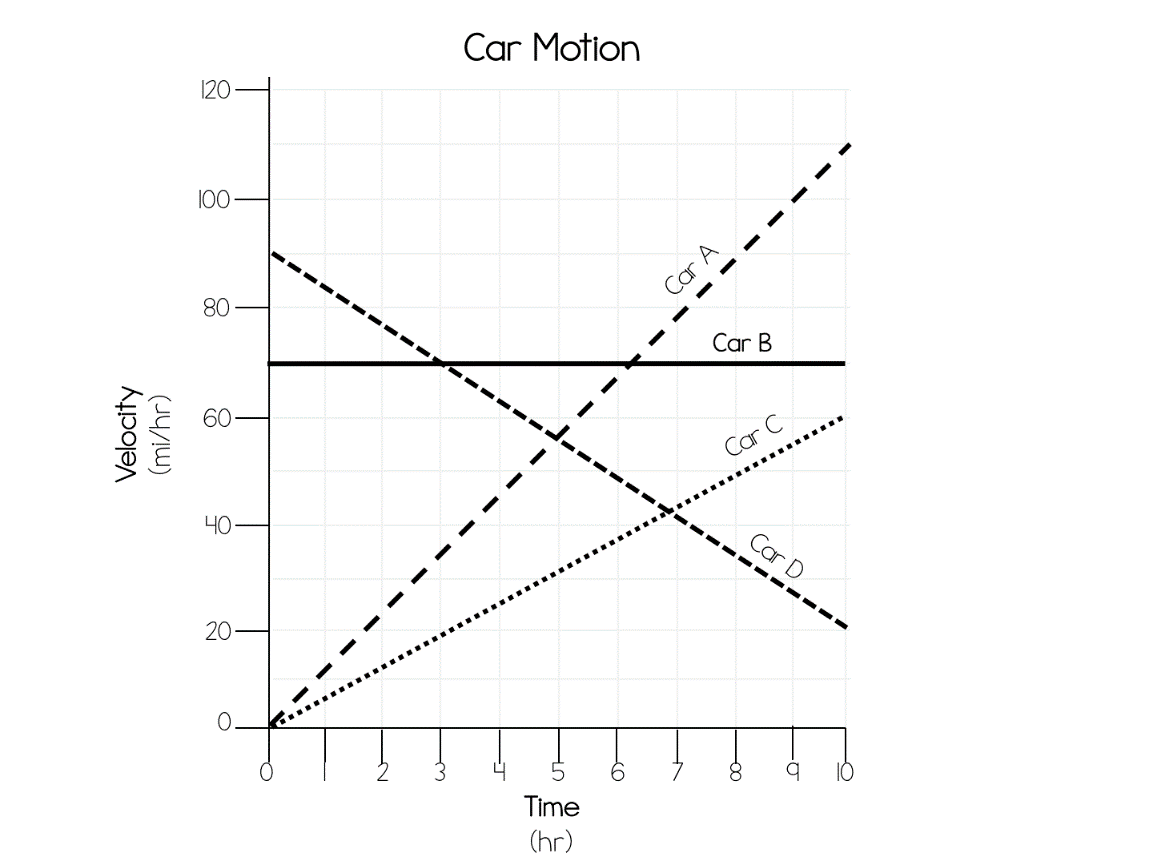
Car A
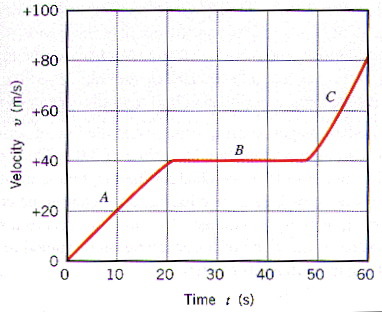
Which car has the greatest acceleration?
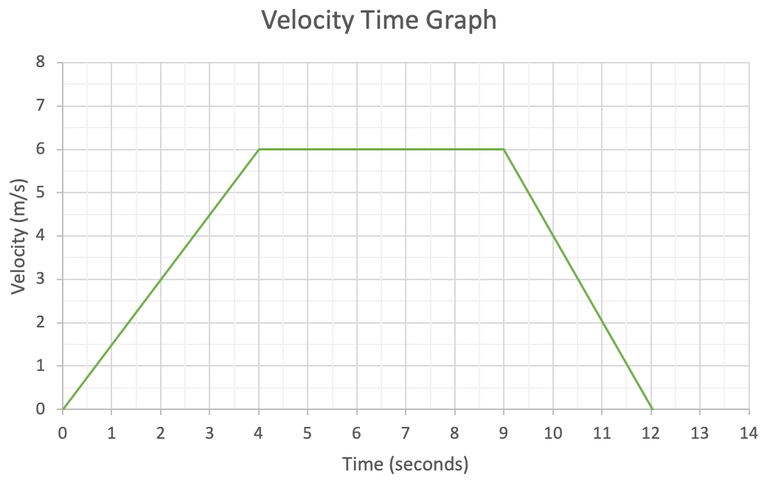
-2 m/s2
What is the acceleration from 9 s to 12 s?
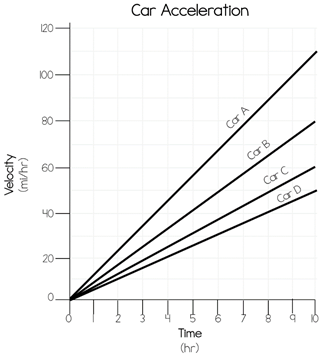
Car D
Which car has the greatest mass?
A 4 kg ball moving eastward at a speed of 5 m/s strikes a 2 kg ball at rest. After the collision, the 2 kg ball has a speed of 6.67 m/s. What is the speed of the 4 kg ball? hint: use the law of conservation of momentum
1.67 m/s
What would cause the gravitational force between two objects to increase?
greater mass of one or both of the objects; ex: bigger planet