Ankle and Foot Kinesiology Overview
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Stability
A function of the foot that provides support and balance.
Mobility
A function of the foot that allows for movement and flexibility.
Protection
A function of the foot that safeguards against injury.
Rigid lever for walking
The foot acts as a stiff structure to assist in locomotion.
Absorbs shock
The foot mitigates impact forces during activities such as walking or running.
Sensation of sole
The foot provides sensory feedback from the ground.
Base for weight bearing
The foot supports the body's weight during standing and movement.
Propels body forward
The foot aids in advancing the body during locomotion.
Prevent injury
The foot's structure and function help to reduce the risk of harm.
Bones of the Foot
The foot consists of 26 bones plus 2 sesamoids.
Forefoot
Contains 5 Metatarsals and 14 Phalanges.
Midfoot
Contains Navicular, Cuboid, and 3 Cuneiforms.
Hindfoot
Contains Talus and Calcaneus.
Talocrural joint
A hinge joint that allows dorsiflexion and plantarflexion.
Subtalar joint
Allows inversion and eversion, important for adapting to uneven surfaces.
Transverse Tarsal Joint
Adds flexibility and transitions between hindfoot and forefoot.
Dorsiflexion
Movement of the foot upwards, with a range of motion of 0-20°.
Plantarflexion
Movement of the foot downwards, with a range of motion of 0-50°.
Open-Packed Position (OPP)
Position of the ankle at 10° plantarflexion.
Closed-Packed Position (CPP)
Position of the ankle at full dorsiflexion.
Capsular Pattern (CP)
Pattern of restriction where plantarflexion is greater than dorsiflexion.
Enthesitis
Inflammation of tendon attachment.
Anterior Compartment
Dorsiflexion; Muscles: TA, EHL, EDL, PT
Lateral Compartment
Pronation; Muscles: PL, PB
Posterior Compartment
Plantarflexion; Muscles: GS, Soleus, TP, FHL, FDL
Medial Compartment
Supination; Muscles: TP, FHL, FDL
Dorsiflexors
Muscles in the anterior compartment responsible for dorsiflexion.
Tibialis Anterior
Dorsiflexion, Inversion; Origin: Medial cuneiform & base of 1st MT; Insertion: Lateral condyle & lateral surface of tibia; Nerve: Deep Fibular.
EHL
Dorsiflexion, Extends hallux; Origin: Middle anterior fibula; Insertion: Distal phalanx of big toe; Nerve: Deep Fibular.
EDL
Dorsiflexion, Extends toes 2-5; Origin: Lateral condyle of tibia, anterior fibula; Insertion: Distal phalanges 2-5; Nerve: Deep Fibular.
Peroneus Tertius
Dorsiflexion, Eversion; Origin: Distal anterior fibula.
Plantarflexors
Muscles in the posterior compartment responsible for plantarflexion.
Gastrocnemius
Plantarflexion, Knee flexion; Origin: Femoral condyles; Insertion: Calcaneus via Achilles tendon; Nerve: Tibial.
Soleus
Plantarflexion; Origin: Posterior fibula & tibia; Insertion: Calcaneus via Achilles tendon; Nerve: Tibial.
Plantaris
Weak plantarflexion; Origin: Lateral supracondylar line (femur); Nerve: Tibial.
Tibialis Posterior
Plantarflexion, Inversion; Origin: Posterior tibia/fibula; Insertion: Navicular, cuneiforms, 2-4 MTs; Nerve: Tibial.
FDL
Plantarflexion, Toe flexion; Origin: Posterior tibia; Insertion: Distal phalanges 2-5; Nerve: Tibial.
FHL
Plantarflexion, Big toe flexion; Origin: Posterior fibula; Insertion: Distal phalanx of big toe.
Evertors
Muscles in the lateral compartment responsible for eversion.
Peroneus Longus
Eversion, Plantarflexion; Origin: Head & upper fibula; Insertion: Base of 1st MT & medial cuneiform; Nerve: Superficial Fibular.
Peroneus Brevis
Eversion, Plantarflexion; Origin: Lower lateral fibula; Insertion: Base of 5th MT; Nerve: Superficial Fibular.
Invertors
Muscles that perform inversion.
Intrinsic Foot Muscles
Muscles located within the foot, divided into dorsal and plantar groups.
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Extends toes 2-4; Nerve: Deep Fibular.
Abductor hallucis
Muscle in the plantar group; Nerve: Medial Plantar.
Lumbricals
Muscles in the plantar group; 1st = MP; 2-4 = LP; Nerve: Medial & Lateral Plantar.
Tricep Surae
Strongest plantar flexion; consists of Gastrocnemius and Soleus.
Mitered Joint
Two pieces cut at an angle (usually 45°) to form a corner, often used in frames and trims.
Mortise and Tenon Joint
A tongue-like tenon fits into a hole-like mortise, forming a strong right-angle joint.
Kinestia
Movement awareness.
Proprioception
Position awareness.
Talocrural joint
Refers to the talocrural (ankle) joint where the talus fits into the mortise of tibia & fibula.
Keystone of the medial longitudinal arch
Talus.
Subtalar joint motion
Primarily allows Inversion/Eversion.
Strongest inverter of the foot
Tibialis posterior.
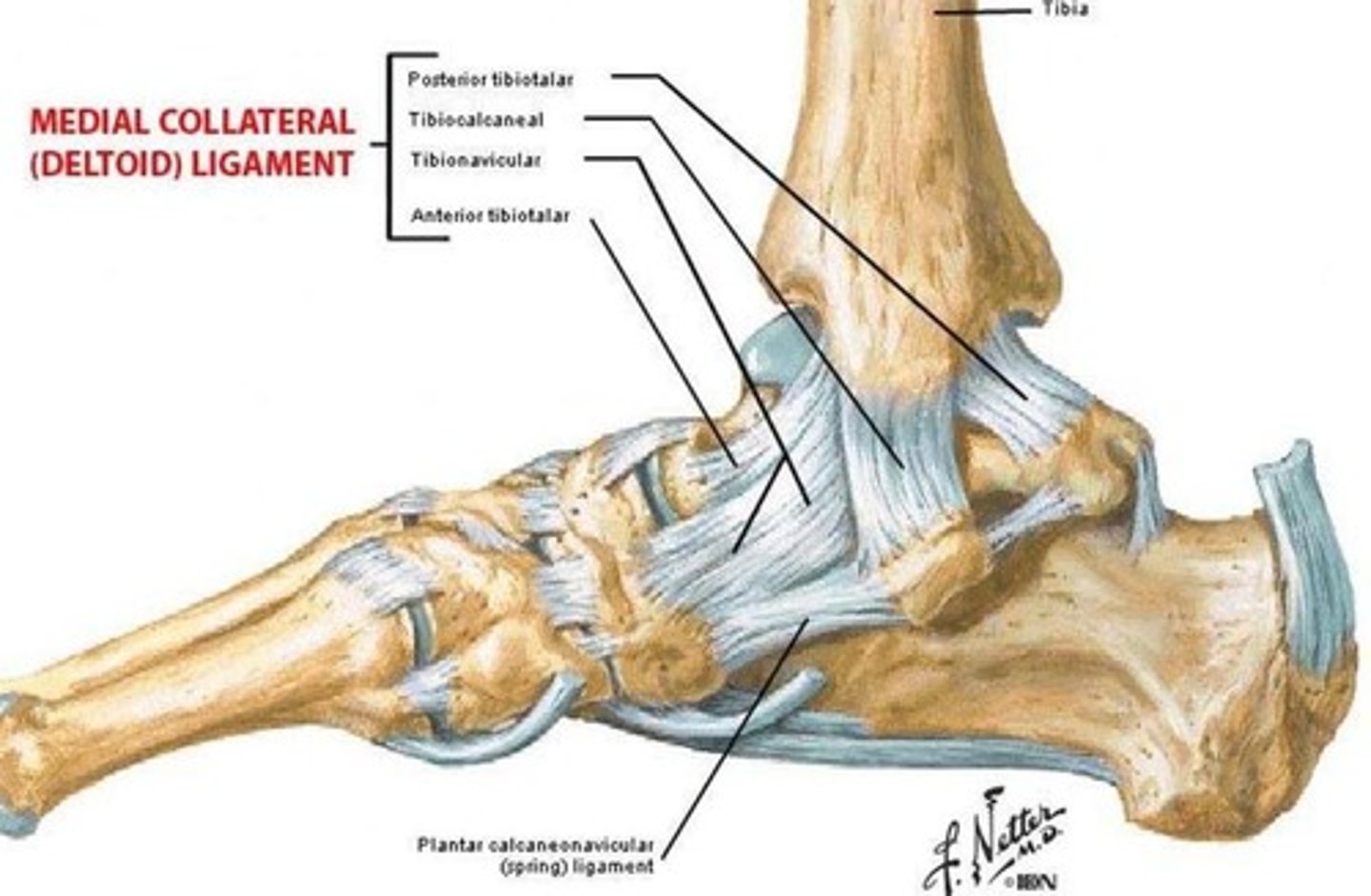
Ligament supporting the medial longitudinal arch
Spring ligament (plantar calcaneonavicular).
Primary function of the plantar fascia
Maintain arch height.
Close-packed position of the talocrural joint
Full dorsiflexion.
Muscles forming the stirrup support of the foot
Tibialis anterior and fibularis longus.
Phase when the foot becomes rigid during gait
Terminal stance.
Axis of rotation for the talocrural joint
Mediolateral.
Muscle assisting with both plantarflexion and knee flexion
Gastrocnemius.
Joint contributing most to foot supination and pronation
Subtalar.
Muscle supporting the transverse arch of the foot
Adductor hallucis (transverse head).
Muscle that dorsiflexes the ankle and inverts the foot
Tibialis anterior.
Nerve innervating the intrinsic foot muscles (except EDB/EHB)
Tibial nerve (via medial and lateral plantar branches).
Role of the fibularis longus during stance phase
Evert the foot and support lateral arch.
Muscle with a pulley around the lateral malleolus
Fibularis longus.
Weight-bearing axis of the leg passes through which bone
Talus.
Ligament preventing excessive eversion of the foot
Deltoid ligament.
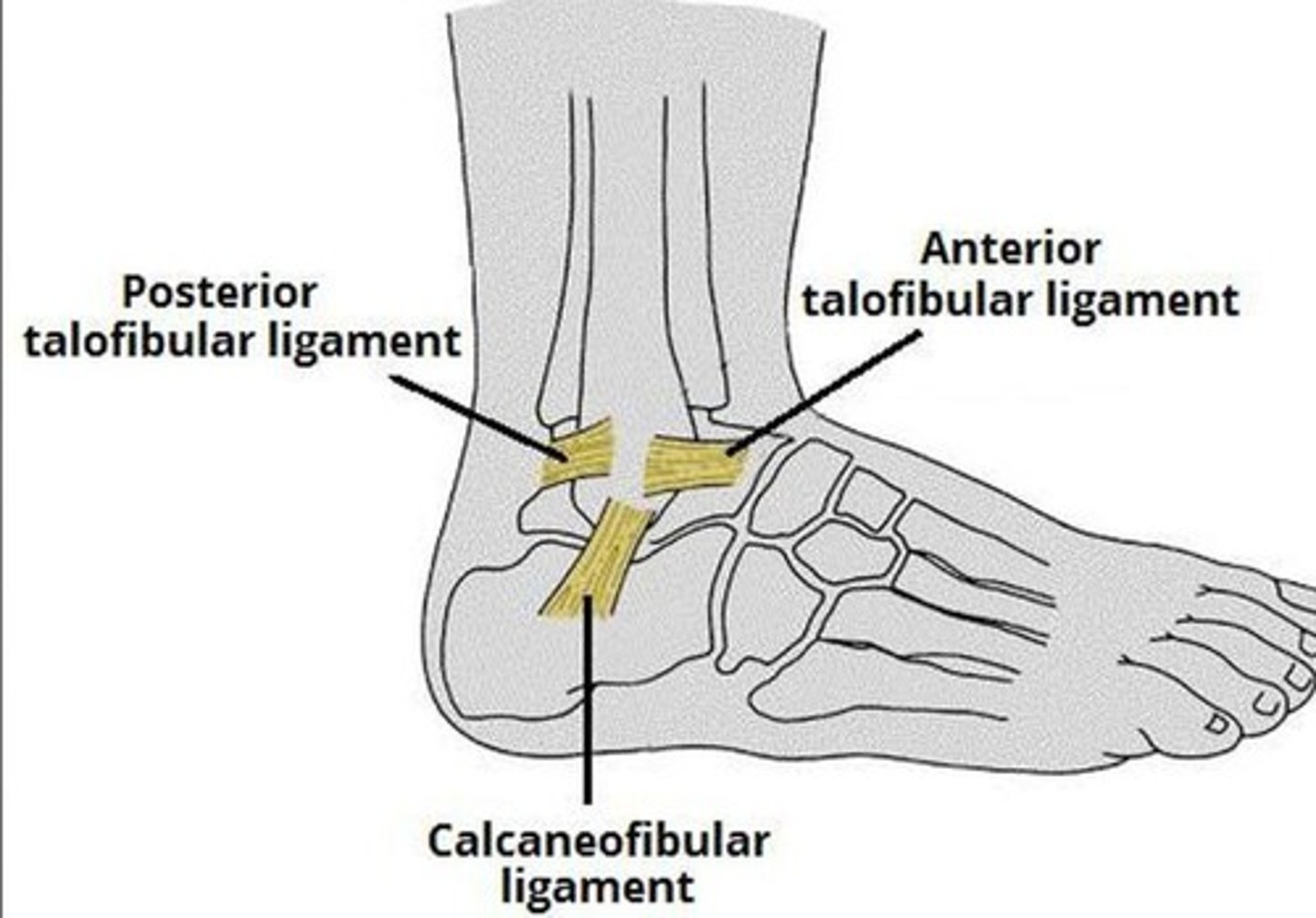
Structure at greatest risk during an inversion sprain
Not provided.
Deltoid ligament
A ligament that is at risk during an inversion sprain.
Anterior talofibular ligament
The structure at greatest risk during an inversion sprain.
Cuboid
The bone that does NOT articulate with the navicular.
Quadratus plantae
A muscle that assists FDL by redirecting pull.
Subtalar joint movement
Best described by the oblique axis.
2nd metatarsal
The most common site of foot stress fractures.
Tarsal tunnel
Contains the tibial nerve.
Calcaneocuboid joint
Forms the transverse tarsal joint along with the talonavicular joint.
Deep fibular nerve
The nerve damaged in a patient with foot drop.
Dorsal interossei
The main action is to abduct toes.
Calcaneus
Transmits body weight to the ground via the heel (posterior tuberosity).
Soleus
The muscle that lies immediately deep to the gastrocnemius.
Plantaris
Not part of the triceps surae.