A+P II Chp 27: Reproductive Cycles
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What are the 4 steps of the human life cycle?
1) haploid gametes (egg + sperm)
2) fertilization: diploid zygote
3) mitosis: multicellular diploid adults
4) meiosis: haploid gametes
Most body cells are ________________.
diploid (2n)
What do most body cells contain?
- 2 sets of chromosomes: one maternal, one paternal
- 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes
Gametes are ____________ and contain _____ chromosomes.
haploid; 23
Regarding meiosis,
a) what is it
b) what does it consist of
c) what are the products
d) what the point of meiosis (as opposed to mitosis)
a) nuclear division in the gonads: halves the number of chromosomes (2n to n)
b) after DNA replication, 2 consecutive cell divisions (meiosis I and II)
c) 4 daughter cells
d) introduces genetic variation
What are the 4 steps of meiosis I and II?
1) prophase I or II
2) metaphse I or II
3) anaphase I or II
4) telophase I or II
For meiosis I, what happens during...
a) prophase I
b) metaphase I
c) anaphase I
d) telophase I
a) synpasis (tetrads form) /crossing over
b) tetrads align randomly in spindle equator
c) homologous chromosomes separate
d) nuclear membranes re-form and 2 haploid daughter cells are produced
Why is synapsis in prophase I important?
for genetic variation
For meiosis II, what happens during...
a) prophase II
b) metaphase II
c) anaphase II
d) telophase II + cytokinesis
a) 2 haploid daughter cells: chromosomes condense, etc.
b) chromosomes align at equator
c) chromatids separate
d) 4 haploid cells produced
What is spermatogenesis?
sequence of events that produce sperm in the seminiferous tubules of the testes
What is the general process of spermatogenesis? (3 steps/phases)
1) mitosis: spermatogonia form spermatocytes
2) meiosis: spermatocytes form spermatids
3) spermiogenesis: spermatids become sperm
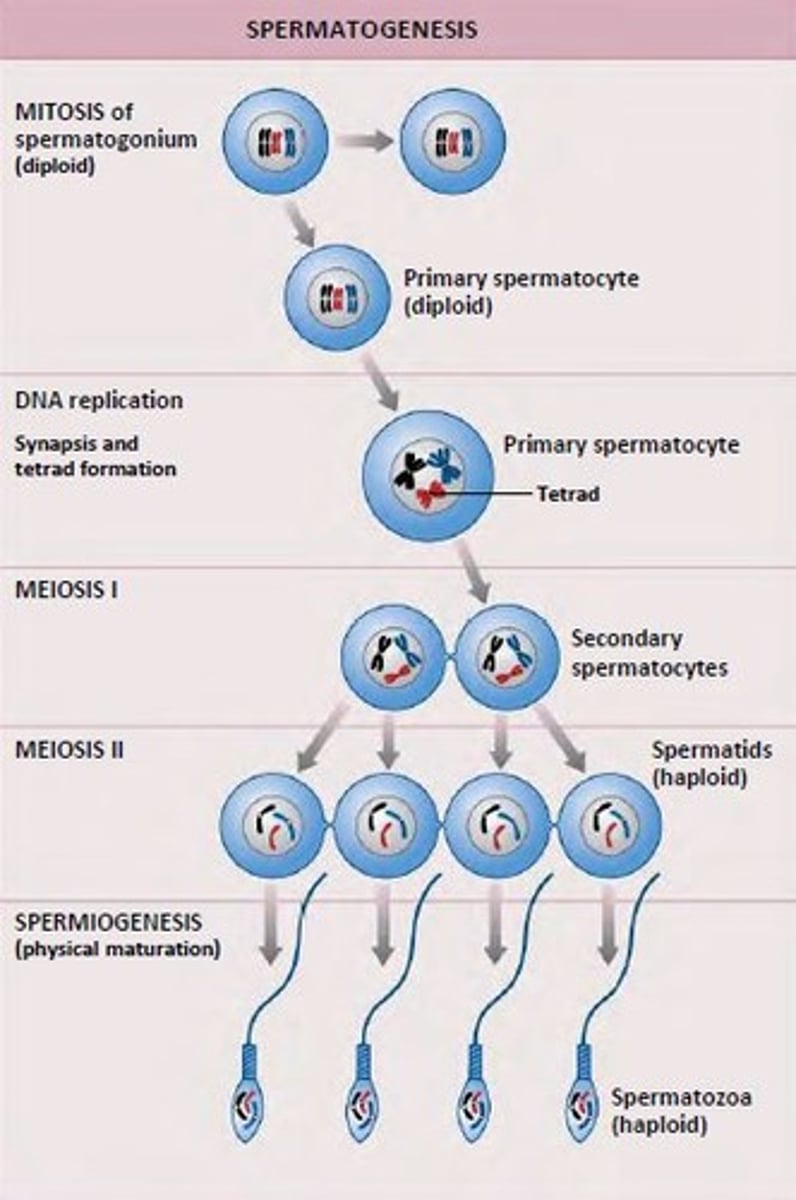
When does spermatogenesis begin?
at puberty
What are spermatogonia?
stem cells at basal lamina
What happens during each mitotic division of spermatogenesis?
- some daughter cells remain as stem cell
- others develop into primary spermatocytes
What happens in meiosis I of spermatogenesis?
primary spermatocyte (2n) --> 2 secondary spermatocytes (n)
What happens in meiosis II of spermatogenesis?
- each secondary spermatocyte (n) --> 2 spermatids (n)
- total: 4 spermatids (n)
What is a spermatid?
small nonmotile cells close to lumen of tubule
What happens in spermiogenesis?
spermatids lose excess cytoplasm and form a tail, becoming spermatozoa (sperm)
What are the 3 major regions of sperm?
1) head
2) midpiece
3) tail
Regarding the head of the sperm,
a) what is its functional region
b) what does it have
a) genetic region
b) nucleus and helmetlike acrosome contains hydrolytic enzymes: enable sperm to penetrate egg
What is the functional region of each? What feature does each have?
a) midpiece
b) tail
a) metabolic region: mitochondria
b) locomotor region: flagellum
Just to summarize, what happens in each phase of spermatogenesis?
a) mitosis
b) meiosis I
c) meiosis II
d) spermiogenesis
a) spermatogonia (2n) --> primary spermatocyte (2n)
b) primary spermatocyte (2n) --> secondary spermatocytes (n)
c) secondary spermatocytes (n) --> spermatids (n)
d) spermatids (n) --> sperms (n)
What regulates male reproductive function?
the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
Which hormones regulate male reproductive function? How are they activated? (pathway)
hypothalamus --> GnRH --> anterior pituitary --> FSH and LH
What is the function of each (when it comes to testicular function)?
a) FSH
b) LH
a) causes sustentacular cells to release androgen binding protein (ABP) in seminiferous tubules
b) stimulates interstitial cells to release testosterone
How is testosterone the final trigger for spermatogenesis?
testosterone binds to ABP, enhancing spermatogenesis
Feedback inhibition on the hypothalamus and pituitary results from ___________________________________.
rising levels of testosterone
What are 4 effects of testosterone activity?
1) prompts spermatogenesis
2) targets all accessory organs: deficiency leads to atrophy
3) multiple anabolic effects throughout body
4) basis of sex drive (libido) in males
What are male secondary sex characteristics?
features induced in the nonreproductive organs by male sex hormones (testosterone)
What are 5 examples of male secondary sex characteristics?
1) pubic, axillary, facial hair
2) chest growth + deep voice
3) skin thickens and becomes oily
4) bones grow
5) skeletal muscles grow
What is oogenesis and when does it begin?
- production of female gametes
- begins in fetal period
What are oogonia?
ovarian stem cells (2n)
What happens in mitosis of oogenesis?
- oogonia (2n) multiply and store nutrients
- primary oocytes (2n) develop in primordial follicles
What happens in meiosis I of oogenesis? What are the products at the end?
- primary oocytes (2n) begin meiosis I, but arrest in prophase I
- each month after puberty, a few primary oocytes are activated
- one primary oocyte resumes and completes meiosis I
- products: first polar body (n) + secondary oocyte (n)
Regarding the secondary oocyte (n),
a) what phase does it arrest in
b) what happens to it when penetrated by sperm
c) what happens to it when not penetrated
a) arrests in metaphase II and is ovulated
b) completes meiosis II: yields ovum (functional gamete) + second polar body
c) degenerates
What happens to the first polar body?
it may go through meiosis II and make 2 polar bodies
Which meiotic event(s) corresponds to each follicle development stage in the ovary?
a) primordial follicle
b) primary follicle
c) secondary follicle
d) vesicular (Graafian) follicle
a) primary oocyte: growth/development
b) primary oocyte arrested in prophase I
c) primary oocyte activated and completes meiosis I
d) secondary oocyte arrested in metaphase II: right before ovulation
What is the ovarian cycle?
monthly series of events associated with the maturation of an egg
What are the 3 phases of the ovarian cycle and when does each occur?
1) follicular phase: days 1-14
2) ovulation: midcycle
3) luteal phase: days 14-28
What happens in each phase?
a) follicular phase
b) luteal phase
a) period of follicle growth
b) period of corpus luteum activity
In the luteal phase, the ruptured follicle collapses and granulosa cells form _______________.
corpus luteum
In the luteal phase, what does the corpus luteum...
a) secrete
b) do when there's no pregnancy
c) do when there is pregnancy
a) progesterone + estrogen
b) degenerates into corpus albicans in 10 days
c) produces hormones until placenta takes over (at ~3 mo.)
What are the levels of each hormone in each phase of the ovarian cycle?
a) follicular phase
b) ovulation
c) luteal phase
a) high levels of FSH+LH at first, but then lower due to rising estrogen levels
b) very high levels of estrogen causes LH surge
c) increased estrogen and progesterone + decreased levels of FSH and LH
How does luteal activity end?
- estrogen and progesterone shut off FSH and LH
- declining LH ends luteal activity
What happens in days 26-28 of the ovarian cycle?
- ovarian hormones (estrogen, progesterone) decline
- blockade of FSH and LH ends
- cycle starts anew
How is the ovarian cycle established? What happens...
a) during childhood
b) as puberty nears
a) ovaries grow and secrete small amounts of estrogens, which inhibit GnRH release
b) GnRH released --> pituitary releases FSH + LH --> act on ovaries
These events continue until an adult cyclic pattern is achieved and _________ occurs.
menarche (first menstrual cycle)
What is the uterine/menstrual cycle?
series of cyclic changes in the endometrium in response to ovarian hormones
What are the 3 phases of the uterine/menstrual cycle and on which days do they occur?
1) menstrual phase: 1-5
2) proliferative (preovulatory) phase: 6-14
3) secretory (postovulatory) phase: 15-28
What happens in each phase of the uterine/menstrual cycle?
a) menstrual phase
b) proliferative/preovulatory phase
c) secretory/postovulatory phase
a) shedding stratum functionalis
b) rebuilding of stratum functionalis
c) endometrium prepares for embryo implantation
If fertilization doesn't occur during the secretory phase, what 4 things happen?
1) progesterone levels fall, depriving endometrium of hormonal support
2) spiral arteries kink/spasm: endometrial cells die
3) functional layer digests itself
4) capillary beds weaken: functional layer sloughs
Estrogen levels rise during puberty. What 2 things does this cause in the ovary?
1) oogenesis
2) follicle growth
What are 4 estrogen-induced secondary sex characteristics?
1) breast growth
2) subcutaneous fat in hips + breasts
3) widening of pelvis
4) growth of axillary and pubic hair
The follicle phase of the ovarian cycle corresponds to which phases of the uterine/menstrual cycle?
menstrual phase + proliferative phase
In the follicle phase/menstrual phase/proliferative phase, what hormones are there?
FSH, LH, estrogen
In the follicle phase, what happens to the uterus?
the stratum functionalis sheds and is then rebuilt
The luteal phase of the ovarian cycle correponds to which phase in the uterine/menstrual cycle?
secretory phase
Which hormones support the luteal/secretory phase?
estrogen, progesterone
What happens to FSH and LH in the secretory or luteal phase?
the levels go down due to rising levels of estrogen and progesterone
During the luteal phase, what happens in the uterus?
it becomes more glandular and blood vessels are enhanced
What is the stage the oocyte is in at birth?
primary oocytes arrested in prophase I
What is the stage the oocyte is in at ovulation?
secondary oocyte arrested in metaphase II
What is the stage called when the sperm meets ovum?
secondary oocyte arrested in metaphase II