bromination of e-stilbene
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
when bromine is added to an alkene, what is the result
addition reaction with one or more brominated products
the number of brominated products depends on what
structure of starting alkene
3 isomers formed
meso, D,L
meso stilbene and D/L
diastereomers
D/L
enantiomers
distribution of isomers in reaction depends on what
cation intermediate
two possible cations
cyclic bromonium
acyclic carbocation
acyclic carbocation
50% meso
50% D/L
cyclic bromonium cation forms_
meso product
why do we not get expected extremes of products
both cations are formed and exist in equilibrium w one another
E- stilbene
E-1,2-diphenylethene
meso-stilbene dibromide
(1R,2S)-1,2-dibromo-1,2-diphenylethane
D stilbene dibromide
(1S,2S)-1,2-dibromo-1,2-diphenylethane
L-stilbene dibromide
(1R,2R)-1,2-dibromo-1,20diphenylethane
what are we doing with e-stilbene
brominating e-stilbene
isolating meso product
capping reaction
with glass stopper using keck clip
make sure it isn’t sealed
what is in the flask
silbene, DCM, stir bar, (bromine 1M added later)
how long does reaction stir
10-15 mins
until orange color has disappeared and white solid has formed
what do we do after reaction precipitate is formed
buchner funnel washed with cold DCM
bromine spill
sodium thiosulfate then pick up
bromine safety points
mucous, irritation, burns, vision loss, discoloration of mouth
DCM safety
slight fire hazard, irritation, burns, GI ulceration
D,L- stilbene dibromide safety
toxic fumes under flames
eye irritant
E-stilbene safety
slight fire hazard
skin and eye irritation
harmful if swallowed
meso-stilbene dibromide safety
toxic fumes under fire
may be harmful if inhaled or swallowed
eye and skin irritation
carcinogens and mutagens
C: DCM
M: DCM, e-stilbene
alkene halogenation results in
vicinal dihalide
what makes the halogen ion
pi bond attacks halogen
why is additiona nti
halogen must attack opposite of bridge so it can reach carbon
functional group
atom(s) that govern chemical and physical properties of family of compounds
what is the most common way to make CC pi bond
elimination reaction
why does addition occur across the pi bond
exothermic process (strength of CC pi bond is lower than sigma bonds that will be formed)
pi electrons are more loosely held (more polarizable)
qualitative analysis of alkyl halids
alcoholic silver nitrate solution
sodium iodide in acetone
stereospecificity of rxn
anti addition
diastereomers and properties
diff physical and chemical properties
for cyclic cation, what happens when you attack either carbon
forms meso
why can acyclic attack from above or below
no restriction
how much meso is expected?
90% but can change based on temperature and solvent
what do we do with meso product
isolate solid
rinse
get MP and percent yield
what is good percent yield for this reaction
70% but most students get 50-60
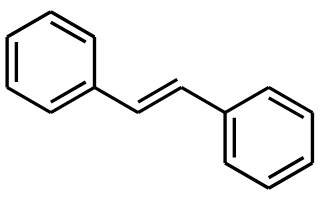
E-stilbene
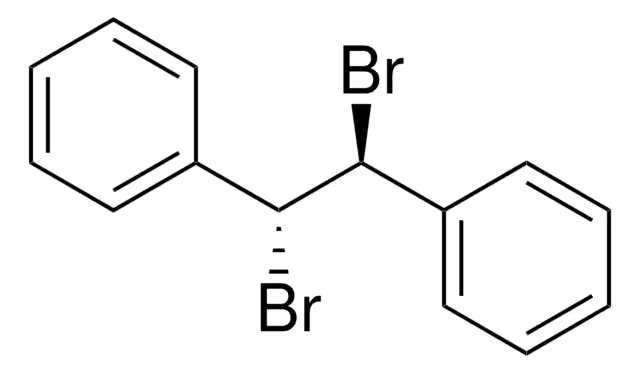
meso-stilbene dibromide
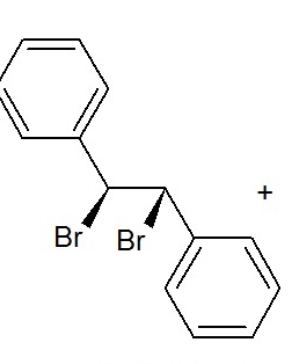
d-stilbene dibromide
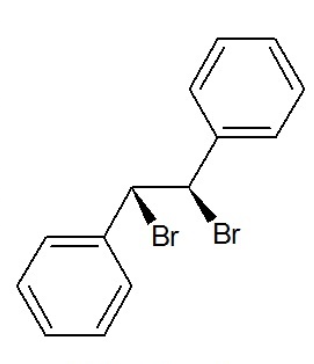
L-stilbene dibromide
meso numbering chiral centers
1R,2S
D
1S,2S
L
1R,2R
diastereomers
stereoisomers that aren’t nonsuperimposable mirror images
enantiomers
stereoisomers that are non-superimposable mirror images
meso compound
multiple stereocenters but optically inactive
has internal plane of symmetry
what are we doing w product at end of the lab
save product for dehydrobromination