Week 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Pharmacokinetics
what the body does to the drug (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion)
Pharmacodynamics
what the drug does to the body
the biochemical effects and physiological effects of drugs and the mechanisms by which those effects are produced
what is a receptor?
a receptor is a molecule to which a drug binds to initiate its effect
agonist
binds tightly to a receptor to produce a desired effect
antagonist
competes with other molecules and blocks a specific action or response
four basic pharmacokinetic processes
absorption
distribution
metabolism
excretion
adverse drug reaction
any harmful, unintended and undesired effect that occurs at normal drug doses
frequency distribution curve
graphical representations of the number of people who respond to a drug at various doses
what is the peak of a frequency distribution curve called?
median effective dose (ED50)
what is the median effective dose (ED50)?
the largest number of people responding to a given drug
what is the median lethal dose (LD50)?
the dose required to kill 50% of the subjects
therapeutic index
used to examine the safety of a drug by comparing the median lethal dose and the median effective dose.
TI = median lethal dose / median effective dose
what is the graded dose response curve?
graphically show the relationship between the effect of the drug and the amount given
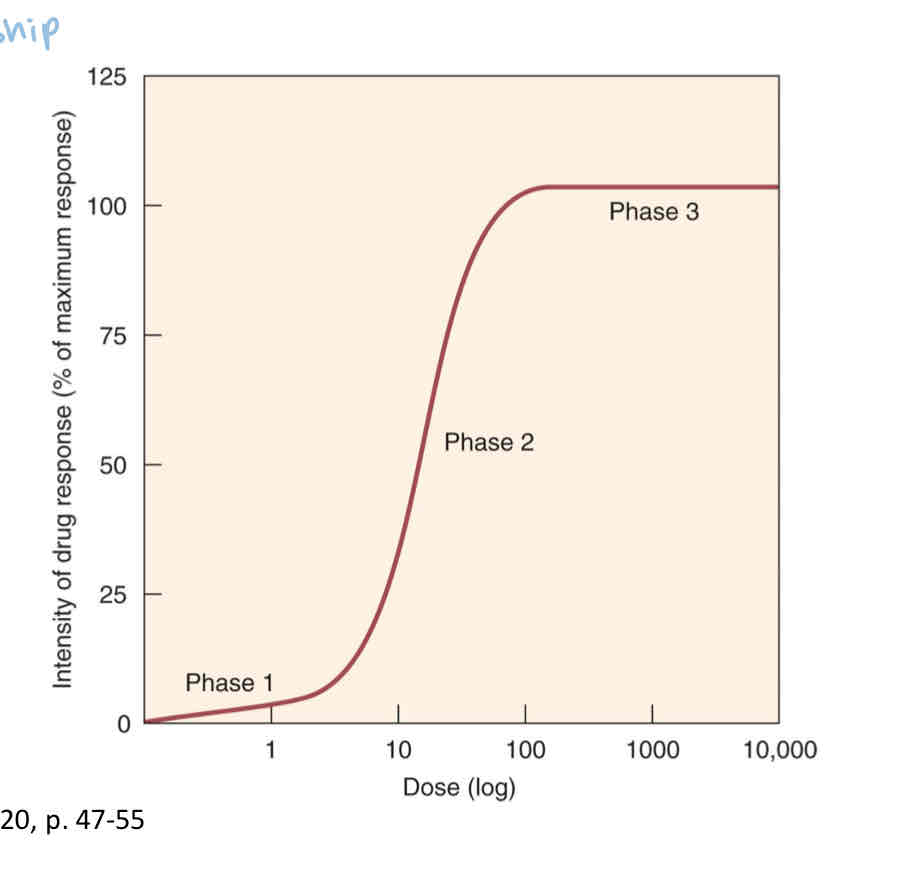
what is phase 1 of the graded dose response curve?
occurs at lowest dose ; few target cells effected by drug
affinity
how well the drug binds to the receptor site
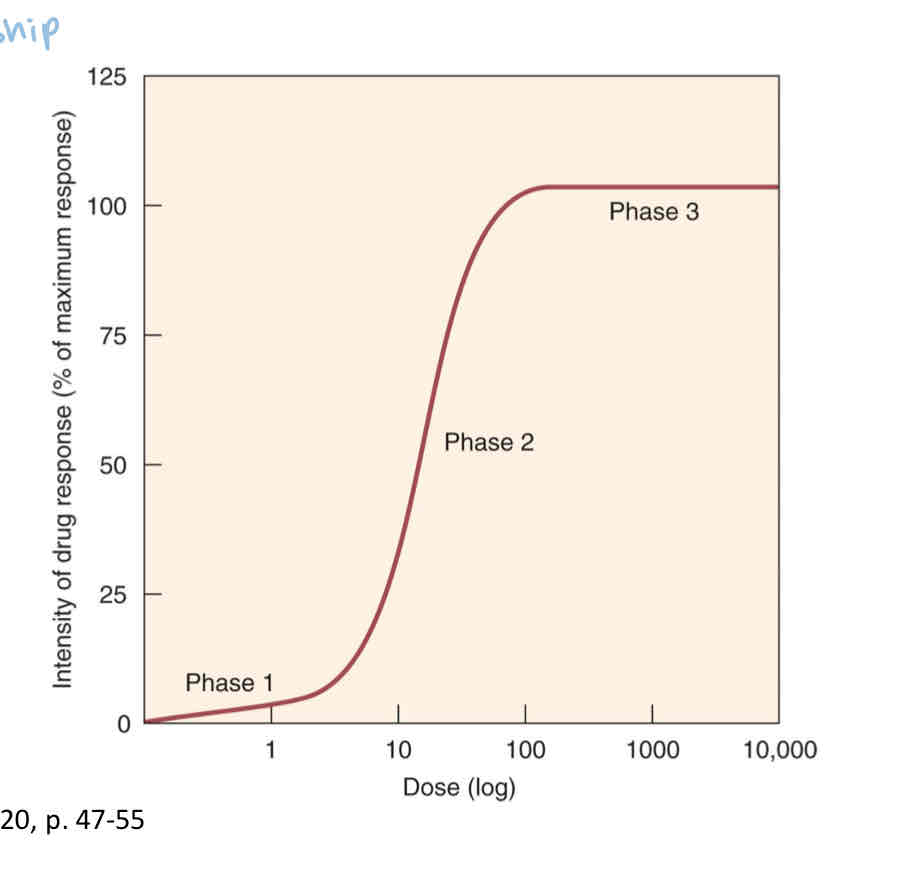
what is phase 2 of the graded dose response curve?
slope ; most desirable range
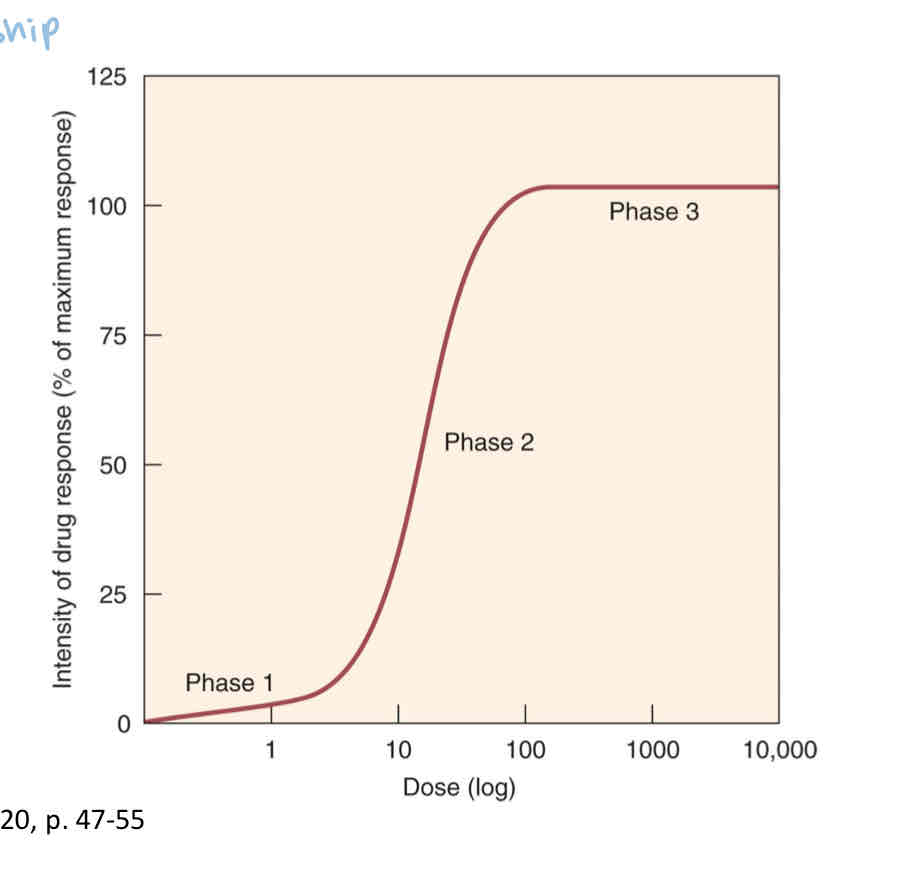
what is phase 3 of the graded dose response curve?
maximal efficacy or ceiling effect ; greatest attainable response, higher dose has no therapeutic effect, but may produce adverse effects
what is the ceiling effect?
a drug reaches a maximum effect, so that increasing the dosage does not increase its effectiveness
potency
the amount of drug required to produce the desired effect
a drug with high potency requires a lower dose to produce the desired effect
efficacy
the magnitude of maximum response that can be produced from a particular drug
side effect
drug effects that are predictable, caused by the drug binding to other sites in addition to the target site
idiosyncratic reaction
unusual responses to drugs caused by differences between patients (not related to the action of the drug)
what is a drug interaction
when a substance increases or decreases a drug’s actions
additive drug interaction
effect of two or more agents acting together
synergic drug interaction
effect of two drugs is greater than would be expected from simply adding the two individual drug responses
antagonistic drug interaction
effects of drugs actions “cancelled”
absorption
movement from site of admininstration, across body membranes, to circulating fluids
what is the primary factor in determining length of time for effect of drugs to occur?
absorption: the more rapid the absorption, the faster the onset
what are 4 different ways a drug can be absorbed?
passive diffusion
facilitated diffusion
endocytosis
active transport
passive diffusion (3)
most common way drugs are absorbed.
higher to lower concentration.
usually small, non-ionized or lipid soluble molecules.
facilitated diffusion (2)
higher to lower concentration.
carrier proteins (to help molecules pass through membrane).
endocytosis (2)
transports large molecules.
involves engulfment of a drug molecule by the cell membrane and transport into the cell by pinching off the drug filled vesicle
active transport (2)
needs energy (ATP) to work.
transports molecules fromm low to high concentration.
distribution
the transport of drugs throughout the body
what are the 2 special barriers in the body
blood brain barrier
fetal placental barrier
what is the simplest factor for determining distribution of medication?
amount of blood flow to body tissues
what is the blood brain barrier?
capillaries of the CNS have tight junctions that prevent free diffusion
what molecules can pass through the blood brain barrier?
only drugs that are lipid soluble or that have a transport system can cross the blood brain barrier
drugs exist in what 2 forms?
free drug molecules
drug-protein complex
what happens when a drug molecule forms a drug-protein complex?
drugs bind reversibly to plasma proteins, and thus never reach target cells (too big to cross membranes)
what is the significance of malnourishment to drug distribution?
malnourished people have less albumin, and therefore have more free drug molceules, making them very sensitive to medications
what is the most important protein for protein binding?
plasma albumin
where does drug metabolism take place?
in the liver: the body’s chemical processing plant
what is an important enzyme for the metabolism of medications?
Cytochrome P450
what is the first pass effect?
medications absorbed through the GI tract pass through the portal vein to the liver, which means some of the drug will be metabolized by the liver before it reaches circulation
metabolism
drugs are broken down by the liver by liver enzymes
elimination
remaining drug metabolites in the bloodstream are filtered by the kidney. a portion is reabsorbed into the bloodstream, and the remainder is excreted out of the body
what are the routes of excretion? (4)
urine - kidneys.
feces - bile from liver.
exhalation - lungs.
sweat, tears - glands.
xenobiotic metabolism
the process of biotransforming less polar compounds into more polar compounds that can be excreted more easily
liver transforms lipid soluble drugs into water soluble drugs so it can be excreted via the kidneys.
minimum effective concentration
amount of drug required to produce a therapeutic effect
toxic concentration
level of drug that will result in serious adverse effects
therapeutic range
plasma drug concentration between the minimum effective concentration and the toxic concentration
half life
amount of time needed to reduce the drug concentration by half
loading dose
if there is not enough time to build up a drug to the therapeutic range, a loading dose is given, which is a bigger dose upfront
what causes an allergic reaction?
hyper-response of the immune system
what are characteristics of a drug allergy (3)
small amount of drug
symptoms unrelated to action of drug
previous exposure to drug
what are the drugs / drug classes that are most likely to cause an allergic reaction? (6)
penicillin
iodine
insulin
NSAIDS
preservatives (sulphites and paraben)
antiseizure drugs
teratogen
drugs that cause birth defects
what is the most common cardiotoxic drug?
antineoplastics