PHARMA EXAM 20-23
1/195
Earn XP
Description and Tags
newest - from document 2020-2023 (kull 2019 - alt fra 2020), exam 26.05.21, 11.06.20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
Calculate the single dose (number of tbl.) of an MPP Panacur tbl for a dog weighing 15 kg. Dosage: 50 mg/kg. Administration 1x per day for 3 days. 1 tbl contains 0.25 g of AS. Choose the correct answer:
a. 3 tablets
b. 1 tablet
c. 9 tablets
d. 6 tablets
c. 9 tablets
Explanation:
Dog weight: 15 kg
Dosage: 50 mg/kg
Total dosage required: 15 \text{ kg} \times 50 \text{ mg/kg} = 750 \text{ mg}
Each tablet contains 0.25 g = 250 mg
Number of tablets: 750 \text{ mg} / 250 \text{ mg/tablet} = 3 \text{ tablets}
3 tablets x 3 days = 9 tbl. (total)
weight units:
1T → kg →g?
1q → kg → g?
1kg → g?
1g → mg?
1dag → g?
1dg → g → mg?
1cg → g? → mg?
1mg → g?
1ug → g?
1ml H20 → g?
1L → ml?
1T → 1000kg →1 000 000g
1q → 100kg → 100 000g
1kg → 1000g
1g → 1000mg
1dag (dekagram) → 10g
1dg (desigram) → 0.1g → 100mg
1cg (centigram) → 0.01g → 10mg
1mg → 0.001g
1ug (microgram) → 0.000001g
1ml H2O → 1g
1L = 1000ml.

how to calculate making a volume of a concentration, out of another concentration? ex 100ml. 10% when we have 2%?
To calculate the volume of a concentration needed to achieve another concentration, you can use the formula: V1×C1=V2×C2
V1: volume of initial conc.
C1: concentration of initial
V2: volume of final conc. we want to achieve
C2: desired conc. of final solution
Thus: V1 × 10% = 100ml x 2%
V1 = 100ml x 2% /10% = 20ml
To make 100ml of a 2% solution, we would take 20ml of the 10% solution, and add 80ml of diluent (water) to reach final volume of 100ml.

Coumarine anticoagulants are competitive antagonist of vitamin k. True or False?
True
Aminoglycosides inhibit the synthesis of nucleic acids in bacteria. True or False?
False
Diaveridine, ormetroprim and trimethoprim potentiate amoxicillin. True or False?
False
As the emulsifiers are used
a. Acacia gum, tragacanth, methylcellulose
b. Liquid paraffin, caffeinum cum natrio benzoico, spiritus dilutes
c. White clay, glycerol, oleum cacao
d. Talc, wheat, starch, sucrose
a. Acacia gum, tragacanth, methylcellulose
Choose the appropriate indications to the following mass-produced preparations:
Willcain sol for inj
Buscopan compastium inj
Antisedan inj
Willcain sol for inj: Local anesthetic used in field block or peripheral administration, for minor surgical procedures like disbudding and dehorning in cattle
Buscopan compastium inj: Spastic colic, obstipation of esophagus, bloat, gallstone colic
Antisedan inj: Reversal of sedative and analgesic effects of medetomidine or dexmedetomidine in dogs and cats
Transform 40.6 cg into g
a. 0.406 g
b. 4.06 g
c. 0.0406 g
d. 40.6 g
a. 0.406 g
Explanation:
- 1 cg (centigram) = 0.01 g (gram)
- 40.6 \text{ cg} \times 0.01 \text{ g/cg} = 0.406 \text{ g}
- Therefore, 40.6 cg is equal to 0.406 g.
Calculate how many ml of an MPP Genabil sol, for inj, are needed for 2 pigs weighing 80 kg each for the whole treatment. Dosage: 25 mg of AS/kg. It is applied 2x in an interval of 24 h. The preparation contains 10% of the active substance
a. 40 ml
b. 20 ml
c. 160 ml
d. 80 ml
d. 80 ml
Explanation:
2 × 80kg = 160 kg
25 mg/kg x 160 = 4000mg
10%: 10g —— 100ml / 4g —— xml
x = 4 × 100 / 10 = 40ml
40ml x 2 = 80ml
How many mg of 100% methylviolet is needed for preparing 150 ml of 2‰ solution
a. 3000 mg
b. 750 mg
c. 300 mg
d. 75 mg
c. 300 mg
Explanation:
- 2‰ solution means 2 parts per 1000, or 2 g in 1000 ml, which is 0.002 g/ml or 2 mg/ml.
- For 150 ml of 2‰ solution, the amount of methylviolet needed is: 150 \text{ ml} \times 2 \text{ mg/ml} = 300 \text{ mg}
Choose the appropriate active substances to the following
ESB3 30% plv. Sol. auv
Neopen inj.auv.
Surolan susp. auv
ESB3 30% plv. Sol. auv: Sulfaclozine
Neopen inj.auv: Neomycine + procaine
Surolan susp. auv: Miconazole nitrate + prednisolone acetate
Choose the appropriate indication to the following MPPs
ESB3 30% plv. Sol. auv
Neopen inj.auv.
Surolan susp. auv
ESB3 30% plv. Sol. auv: Coccidiosis of chicken, turkey and rabbits, bacterial diseases of poultry and rabbits
Neopen inj.auv: Infectious diseases caused by susceptible agents
Surolan susp. auv: For the topical treatment of otitis externa and skin infections in dogs and cats caused by Gr+ bacteria, Gr- bacteria, fungi and yeasts. Anti-inflammatory and anti pruritic activity.
Convert 132 mg into grams
a. 0.132 g
b. 0.000132 g
c. 0.00132 g
d. 1.32 g
a. 0.132 g
Explanation:
- 1 g = 1000 mg
- 132 \text{ mg} / 1000 = 0.132 \text{ g}
Transform 5.23 dag (dkg) into g
a. 52.3 g
b. 5.23 g
c. 0.523 g
d. 523 g
a. 52.3 g
Explanation:
- 1 dag (decagram) = 10 g
- 5.23 \text{ dag} \times 10 = 52.3 \text{ g}
How many g of NaCl do you need for preparing 500 ml of 0.9% solution
a. 450 g
b. 0.45 g
c. 45 g
d. 4.5 g
d. 4.5 g
Explanation:
- 0. 9% solution means 0.9 g in 100 ml.
- If you have 500ml, then that multiplies the amount of NaCl needed by 5.
- This gives: 0.9 * 5 = 4.5
The part “subscription” in the prescription of individually prepared preparations contains
a. The required form of the medicine, number of required doses, used utensils, medicine packing
b. The number of doses per day, the dose, the route or location of application, the animal species
c. The name and address of the animal owner, the signature and stamp of the veterinary surgeon, the place and the date on which the prescription is written
d. The basic medicament, auxiliary medication, substance adjusting the taste of the medicine indifferent substance
a. The required form of the medicine, number of required doses, used utensils, medicine packing
Calculate the single dose (mL) of Linco-Spectin 15% inj. A.u.v. needed for administration to a pig weighing 90 kg. Dosage: 15 mg/kg bw. It is administered once a day for 5 days. Injection solution contains 50 mg of as in 1 ml
a. 2.7 ml
b. 135 ml
c. 1350 ml
d. 27 ml
a. 2.7 ml
Explanation:
- The pig weighs 90 kg, and the dosage is 15 mg/kgbw: 90kg \times 15mg/kg = 1350mg
- You have a 15% solution, which has 150 mg per ml.
- As the injection solution contains 50 mg of active substance in 1 ml, the amount of solution is: 1350 \text{ mg} / 50 \text{ mg/ml} = 27 \text{ ml}
Calculate how many ml of a preparation Baycox 2.5% sol. A.u.v. is needed for treatment of 10 turkeys, Dosage: 25 ppm of as is administered in water for 2 days. The daily consumption of water is 2 L for 10 turkeys. Preparation contains 25 mg of as in 1 ml of solution
a. 20 ml
b. 40 ml
c. 4 ml
d. 2 ml
c. 4 ml
Explanation:
Dosage: 25 ppm, which means 25 mg of active substance per liter of water.
Daily water consumption for 10 turkeys is 2 liters.
Total active substance needed per day: 25 \text{ mg/L} \times 2 \text{ L} = 50 \text{ mg}
The preparation contains 25 mg of active substance in 1 ml of solution.
Total ml of Baycox needed: 50 \text{ mg} / 25 \text{ mg/ml} = 2 \text{ ml}
Since the treatment is administered for 2 days: 2 \text{ ml/day} \times 2 \text{ days} = 4 \text{ ml}
Select “true” or “false” to the statement: Procaine salt of benzylpenicilline is a beta-lactam antibiotic with the longest duration of action
False (longest is: benzathine penicillin)
Select “true” or “false” to the statement: Enflurane can induce epilepsy-like seizures
True
Select “true” or “false” to the statement: Stimulation of nicotinic receptor causes hypersecretion
False
Which of the following statements concerning the intravenous route of drug administration is true
a. It bypasses absorption to give an immediate effect with 100% bioavailability
b. It cannot be used for drugs that must be given in large volumes
c. It cannot be used for drugs that are inactivated by gastric acid, for drugs that have a large first-pass effect or for drugs that irritate the gut
d. Absorption is similar to the intramuscular route but is usually somewhat slower
a. It bypasses absorption to give an immediate effect with 100% bioavailability
What is the goal of the P450 system (microsomes pinched off from endoplasmic reticulum)
a. Decreasing pH of compartments containing substances
b. Metabolism of substances
c. Detoxification of substances
d. Increasing pH of compartments containing substances
b. Metabolism of substances
c. Detoxification of substances
A prodrug is
a. A drug that is stored in body tissues and is then gradually released in the circulation
b. The oldest member of a class of drug
c. The prototype member of a class of drugs
d. An inactive drug that is transformed in the body to an active metabolite
d. An inactive drug that is transformed in the body to an active metabolite
Which of the following is the most important for movement through capillary wall
a. pKa
b. pH
c. Diffusion constant
d. Molecular size
e. Lipid solubility
c. diffusion constant
Which of the following can produce a therapeutic response
a. Not absorbed from the GI tract
b. Concentrated in the urine
c. Bound to plasma albumin
d. Concentrated in bile
e. Unbound to plasma proteins
e. Unbound to plasma proteins
Intrinsic activity is a drugs ability to elicit
a. Response
b. Weak receptor binding
c. Distribution
d. Strong receptor binding
e. Excretion
a. Response
What is the type of drug-to-drug interaction which is the result of interaction at receptor, cell, enzyme or organ level
a. Pharmacodynamic interaction
b. Pharmaceutical interaction
c. Pharmacokinetic interaction
d. Physical and chemical interaction
pharmacodynamic interaction

Idiosyncratic reaction of a drug is
a. Quantitatively exaggerated response
b. A type of drug antagonism
c. A type of hypersensitivity reaction
d. Unpredictable, inherent, qualitatively abnormal reaction to a drug
d. Unpredictable, inherent, qualitatively abnormal reaction to a drug
Which of the following is not a pharmacokinetic process
a. Drug metabolites are removed in the urine
b. Movement of the drug from the gut into general circulation
c. The drug causes dilation of coronary vessels
d. Alteration of the drug by liver enzymes
c. The drug causes dilation of coronary vessels
Which of the following can be used as a relative indicator of the margin of safety of a drug? a. LD50 b. EC50 c. T.I. d. TD50? e. ED50
c. T.I.
Most drugs are either _____acids or _____ bases
a. Weak; strong
b. Weak; weak
c. Strong; weak
d. Strong; strong
b. Weak; weak
The dose which cause death of 50% (one half) of a group of test animals is
a. Maximum therapeutic dose
b. Toxic dose
c. Median toxic dose
d. Median lethal dose
d. Median lethal dose
Drug distribution can be defined as
a. The process by which a drug is eliminated from the body through the kidneys or intestine
b. The metabolism of drugs (especially in the liver)
c. A simple passive diffusion of a drug molecule from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
d. The process by which a drug is carried from its site of absorption to its site of action
d. The process by which a drug is carried from its site of absorption to its site of action
The term “biotransformation” includes the following
a. Accumulation of substances in a fat tissue
b. Accumulation of substances in a tissue
c. Binding of substances with plasma proteins
d. Process of physicochemical and biochemical alteration of a drug in the body
d. Process of physicochemical and biochemical alteration of a drug in the body
Elimination of drug is the best quantified as follows
a. A time required to decrease the amount of drug in plasma by one half
b. Clearance of an organism from a drug
c. Rate of tubular reabsorption
d. Clearance speed of some volume of blood from substance
clearance of an organism from a drug
Pharmacodynamics involves the study of
a. Biotransformation of drugs in the organism
b. Distribution of drugs in the organism
c. Excretion of drug from the organism
d. Mechanism of drug action
d. Mechanism of drug action
Which answer is the most appropriate to the term “receptor”
a. Carriers activated by a drug
b. Active macromolecular components of the body tissue with which a drug interacts to elicit its specific effect
c. Enzymes of oxidizing-reducing reactions activated by a drug
d. All types of ion channels modulated by a drug
b. Active macromolecular components of the body tissue with which a drug interacts to elicit its specific effect
An antagonist is a substance that
a. Binds to the receptor without directly altering their functions
b. Binds to the receptor and initiates changes in cell function, producing
submaximal effect
c. Interacts with plasma proteins and doesn’t produce any effects
d. Binds to the receptors and initiates changes in cell function, producing
maximal effect
a. Binds to the receptor without directly altering their functions
What is the type of drug-to-drug interaction which is connected with process of absorption, biotransformation, distribution and excretion
a. Physical and chemical interaction
b. Pharmacokinetic interaction
c. Pharmacodynamic interaction
d. Pharmaceutical interaction
Pharmacokinetic interaction
Valnemulin is used for treatment of:
a. Dysentery in swine
b. Enzootic pneumonia in pigs
c. Acute mastitis in cow
d. Vulvovaginitis in mares
Dysentery in swine, enzootic pneumonia in pigs
The resistance of gram-positive organism to macrolide antibiotics results from
a. Formation of drug-inactivating acetyltransferases
b. Formation of esterases that hydrolyze the lactone ring
c. Decreased drug permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane
d. Alterations in ribosomal structure (target site methylation or mutation)?
Alterations in ribosomal structure (target site methylation or mutation)
Select the appropriate pharmacotherapeutic group used as antiparasitic to the following active substances:
i. Netobimin
ii. Halofuginone
iii. Amitraz
iv. Rafoxanisde
v. Oxibendazole
vi. Morantel
i. Netobimin = Probenzimidazoles (antinematodal)
ii. Halofuginone = Quinolone (anticoccidial)
iii. Amitraz = other ectoparasiticides
iv. Rafoxanisde = halogenated salicyanilides (antitrematodal)
v. Oxibendazole = Benzimidazole (imidazole, antinematodal)
vi. Morantel = tetrahydropyrimidine (antinematodal)
Which of the following is a steroidal antibiotic
a. Nitrofurantoin b. Fusidic acid c. Spectinomycin d. Nalidixic acid
b. Fusidic acid
The mode of action of antiparasitic drugs include
a. Alteration of reproduction cycle of parasite
b. Interfering with polarization of muscle cells
c. Interfering with energy production in the parasite
d. All of the presented options
all of the presented options

Select the drug belonging to aminoglycosides
a. Tilmicosin b. Gamithromycin c. Clindamycin d. Gentamicin
d. Gentamicin
Which of the listed sulfonamides is used for the treatment of intestinal infections
a. Sulfadiazine
b. Sulfadimethoxine
c. Phtalylsulphathiazole
d. Sulfadimidine
e. Sulfisoxazole
c. Phtalylsulphathiazole

The effect of fluoroquinolone is
a. In low doses bacteriostatic
b. In high doses bactericidal
c. Bactericidal
d. Bacteriostatic
c. Bactericidal
Amphenicols used for the treatment of respiratory and gastrointestinal infections are
a. Azidamphenicol b. Florphenicol c. Tiamphenicol d. Chloramphenicol
florphenicol, tiamphenicol
Select the fluoroquinolone derivative is
a. Enrofloxacine
b. Orbifloxacine
c. Cepquinone
d. Cefadroxil
e. Nitrofurantoin
f. Thiamphenicol
g. Florfenicol
a. Enrofloxacine b. Orbifloxacine

The anti-bacterial activity of amoxicillin can be enhanced by addition of a. Sulbactam
b. Clavulanic acid
c. Trimethoprime
d. Diaveridine
b. Clavulanic acid
Oral administration of aminoglycosides used for the treatment of dysentery in is preferred because
a. They are least absorbed from the oral route
b. They are least toxic to GIT
c. The peak concentration in blood is achieved quickly
d. None of the answers is correct
a. They are least absorbed from the oral route
Which of the following antibiotics possess neuromuscular blocking action
a. Tylosin b. Ampicillin c. Chloramphenicol d. Streptomycin
streptomycin
Antibacterial agents with bacteriostatic effect are
a. Macrolides b. Sulfonamides c. Aminoglycosides d. Fluoroquinolones
macrolides, sulfonamides
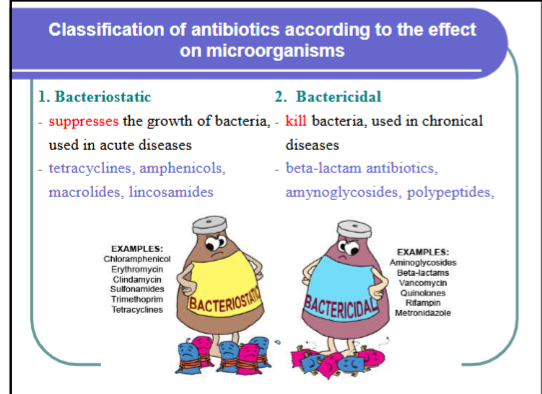
Antibiotics that inhibit bacterial nucleic acid synthesis are
a. Tylosin b. Rifampin c. Rifaximin d. Cloxacillin
rifampin, rifaximin
Considering the mechanism of action of penicillins all of the following are true except for
a. They activate Murein Hydrolases in the cell wall which stimulates the breakdown of the peptidoglycan layer
b. They bind reversibly to the 50S ribosomal subunit, blocking formation of peptide bonds
c. They irreversibly inhibit transpeptidase which leads to the inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis
d. They bind to penicillin-binding protein (PBPs) in the bacterial cell wall
They bind reversibly to the 50S ribosomal subunit, blocking formation of peptide bonds
Antibiotics inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis are
a. Macrolides b. Aminoglycosides c. Beta-lactam antibiotics d. Tetracyclines
Beta-lactam antibiotics
The drugs belonging to tetracyclines are
a. Doxycycline b. Tylosin c. Chlorotetracycline d. Streptomycin
Doxycycline, Chlorotetracycline
The drugs belonging to macrolides are
a. Tylosin b. Neomycin c. Tilmicosin d. Doxycycline
Tylosin, Tilmicosin
Aminoglycosides cause the following unwanted effect
a. Hepatotoxicity b. Pancytopenia c. Ototoxicity d. Nephrotoxicity
c. Ototoxicity d. Nephrotoxicity
The effect of lincosamides is
a. In low doses bacteriostatic
b. Bacteriostatic
c. In high doses bactericidal
d. Bactericidal
b. Bacteriostatic
The drugs belonging to ansamycins are
a. Rifaximin b. Rifampicin c. Spiramycin d. Spectinomycin
a. Rifaximin b. Rifampicin
Sulfonamides have the following unwanted effects
a. All of the listed options
b. Crystalluria
c. Hematopoietic disturbances
d. Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
a. All of the listed options
The drugs belonging to quinolones are
a. Oxacillin b. Flumequine c. Orbifloxacin d. Cefquinone
b. Flumequine c. Orbifloxacin
Ionophores are effective against
a. Roundworms b. Flukes c. Tapeworm d. Coccidia
d. Coccidia
Levamisole, netobimin and febantel are
a. Antiprotozoal drugs
b. Antinematodal drugs
c. Antitrematodal drugs
d. Anticestodal drugs
b. Antinematodal drugs
The drugs used for treatment of trematodosis (fluke invasion) is
a. Monensin b. Ivermectin c. Bithionol d. Pyrantel
c. Bithionol
Which of the following are not macrocyclic lactones
a. Closantel b. Netobimin c. Selamectin d. Doramectin
a. Closantel b. Netobimin
Carbaryl and propoxur are used against
a. Ectoparasites b. Nematodes c. Cest
a. Ectoparasites
Which of the following anticoagulant belong to vitamin K antagonists?
a. Heparin b. Ethyl biscousmacetate c. Warfarin d. Sodium citrate
Ethyl biscousmacetate, Warfarin

Codeine is indicated
a. For treatment of productive cough
b. To stimulate respiration after anesthesia
c. For cough suppression
d. In the management of intrathoracic collapsing trachea
c. For cough suppression
Direct effect on the heart are determined largely by
a. Beta2 receptor b. Beta1 receptor c. Alfa1 receptor d. Alfa2 receptor
b. Beta1 receptor
Atropine causes
a. Intestinal hypermotility
. Stimulation of contraction in the gut
c. Stimulation of secretory activity
d. Spasmolytic activity
d. Spasmolytic activity
All of the following drugs are antiemetic except for
a. Ondansetron b. Metoclopramide c. Apomorphine hydrochloride d. Maropitant
c. Apomorphine hydrochloride
Most of non-steroid analgesic have
a. All the answers are correct
b. Analgesic effect
c. Anti-inflammatory effect
d. Antipyretic effect
a. All the answers are correct
Which of the following vitamins is also known as an antisterility factor
a. Pyridoxine hydrochloride b. Tocopherol c. Menadione d. Thiamine
b. Tocopherol
Select the drug belonging to proton pump inhibitors
a. Omeprazole b. Misoprostol c. Cimetidine d. Ranitidine
a. Omeprazole
Select the main halothane adverse reactions
a. Crystalluria b. Hepatotoxicity c. Diarrhea d. Malignant hyperthermia
hepatotoxicity, Malignant hyperthermia
An oxidative disinfectant and antiseptic is used
a. Acriflavine b. Chlorhexidine c. Potassium permanganate d. Hydrogen peroxide
b. Chlorhexidine c. Potassium permanganate d. Hydrogen peroxide
Parasympathomimetic drugs cause
a. Bronchodilation b. Urinary retention c. Miosis d. Constipation
c. Miosis
Select the appropriate pharmacotherapeutic groups influencing the CNS to the following active substances
Azaperone
Prednisolone
Carprofen
Trimecaine
Fentanyl
Phenylbutazone
Sevoflurane
Flunixin
Tiletamine
Romifidin
Azaperone = butyrophenone (Major tranquilizer/neuroleptic)
Prednisolone = corticosteroid
Carprofen = NSAID
Trimecaine = local anaesthetic (amide)
Fentanyl = opioid analgesic
Phenylbutazone = anti-pyretic analgesic anti-inflammatory drug
Sevoflurane = liquid inhalation anesthetic
Flunixin = anti-pyretic analgesic anti-inflammatory drug
Tiletamine = dissociative anesthetics
Romifidin = alpha2-adrenergic agonist
The major natural progestin is
a. Estriol b. Estron c. Progesterone d. Estradiol
c. Progesterone
Select the appropriate pharmacological group to the active substances
i. Demebrexine
ii. Altrenogest
iii. Spiramycin
iv. Clenbuterol
v. Riboflavin
vi. Doxycycline
vii. Posaconazole
viii. Neomycin
ix. Acepromazine
x. Nafcillin
i. Demebrexine = mucolytic
ii. Altrenogest = progestogen
iii. Spiramycin = macrolides
iv. Clenbuterol = beta-agonist
v. Riboflavin = vitamin B2 given to cattle
vi. Doxycycline = tetracyclines
vii. Posaconazole = antifungals
viii. Neomycin = aminoglycosides
ix. Acepromazine = Phenothiazine
x. Nafcillin = beta-lactams (penicillins)
Match the appropriate pharmacological group to the active substance
i. N-acetylcysteine
ii. Danofloxacin
iii. Itraconazole
iv. Medetomidine
v. Gamithromycin
vi. Robenidine
vii. Gentamycin
viii. Cefacetrile
ix. Flunixin meglumine
x. Dinoprost
Groups:
NSAID
aminoglycoside
cephalosporin
mucolytic
quinolone, 2nd gen
guanidines - anticoccidial
prostaglandin
antifungal
azalides
a2 adrenergic agonist
i. N-acetylcysteine = mucolytic
ii. Danofloxacin = quinolone, 2nd generation
iii. Itraconazole = antifungal
iv. Medetomidine = a2 adrenergic agonist
v. Gamithromycin = azalides
vi. Robenidine = guanidines – anticoccidial
vii. Gentamycin = aminoglycosides
viii. Cefacetrile = cephalosporin
ix. Flunixin meglumine = NSAID
x. Dinoprost = prostaglandin
The state of “general anesthesia” usually includes
a. Amnesia
b. Analgesia
c. Loss of consciousness, inhibition of sensory and autonomic reflexes
d. All of the listed options
d. All of the listed options
Most serious toxic reaction to local anesthetics is
a. Respiratory failure
b. Seizures
c. Cardiovascular collapse
d. All of the listed options
d. All of the listed options
Which of the following general anesthetics belong to inhalants
a. Ketamine b. Desflurane c. Propofol d. Thiopental
b. Desflurane
What two ophtalmological results are caused by atropine
a. Miosis and increased lacrimation
b. Mydriasis and cycloplegia
c. Mydriasis (iris dilation) and increased lacrimation
d. Cycloplegia (ciliary paralysis) and miosis (iris contraction)
b. Mydriasis and cycloplegia
Pancuronium and vecuronium produce
a. Muscle relaxation
b. Bronchoconstriction
c. Motility of GIT
d. Stimulation of lacrimal secretion
a. Muscle relaxation
Indicate the sedative drug which is a phenothiazine derivative
a. Acepromazine b. Xylazine c. Romifidine d. Azaperone
a. Acepromazine
Morphine causes the following except for
a. Coronary vasoconstriction b. Dilatation of the biliary duct c. Miosis d. Constipation
a. Coronary vasoconstriction
What of the following agent is not a non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory drug a. Triamcinolone b. Meloxicam c. Carprofen d. Ketoprofen
a. Triamcinolone
Which of the diuretic agent is used for treatment of hypertension a. Hydrochlorothiazide b. Benazepril c. Enalapril d. Captopril
a. Hydrochlorothiazide
Theophylline is indicated
a. In the management of intrathoracic collapsing trachea
b. To stimulate respiration after anesthesia
c. For cough suppression
d. For treatment of productive cough
c. For cough suppression
The laxative drug belonging to neuromuscular purgatives
a. Neostigmine
b. Carbachol
c. Dihydroxyantraquinone
d. Magnesium sulphate
carbachol, neostigmine

All of the following are estrogens except for
a. Estradiol b. Mestranol c. Diethyl stilbosterol d. Altrenogest
d. Altrenogest
Select a fat-soluble (lipophilic vitamin)
a. Riboflavin b. Thiamine c. Tocopherol d. Ascorbic acid
c. Tocopherol
Write “true” or “false” to the statement: Penteterazole exerts anesthetic effect
False (Penteterazole = analeptics, excites the CNS)
Write “true” or “false” to the statement: Acepromazine is used as an anticonvulsant agent
False
