ACTIVITY 2: Preparation of Wet, Fixed smear, and the gram staining method.
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
3 glass slides and coverslips
1 wire loop
1 alcohol lamp
2 clean toothpick
2 droppers, Marthylene blue, 0.85% NaCl and reagents for gram staining
Materials used in Activity 2
Crystal violet
Gram’s iodine
Ethyl Alcohol
Safranin
Reagents for gram staining used
purple
crystal violet
amber
Gram’s iodine
clear
Ethanol
red/ pink
safranin
Fixed Smear Method
Step 1: Teeth Scraping/Buccal Swab
Step 2: Place Sample on a Glass Slide
Step 3: Fix the sample Using Heat
Step 4: Staining with Methylene Blue
Step 5: Prepare slide for microscopy
Step 6: Examine the Slide Using the Microscope
Inside the cheek
Where should we rub the toothpick to get the buccal cells?
glass slide in a thin layer
After getting the buccal cells, we will spread it to the
alcohol lamp
what material will be using when heating the glass slide?
Quickly for 5 times to avoid overheating
how frequent we will pass the slide to the alcohol lamp.
covering it using the cover slip and adding immersion oil on top
After heating the glass slide, the next step will be
Scanner 4x (40x)
Low Power Objective 10x (100x)
High Power Objective 40x (400x)
what objectives will be using to examine the slide?
Wet Smear Method
Step 1: Teeth Scraping/Buccal Swab
Step 2: Place Sample on a Glass Slide
Step 3: Drop of 0.85 NACL (Sodium Chloride) solution
Step 4: Covering the sample
Step 5: Examine the Slide Using the Microscope
O.85% NaCl
What reagent used in the wet smear method
It uses heat
What is the unique steps in fixed smear method?
Gram Staining Method
Step 1: Teeth Scraping/Buccal Swab
Step 2: Place Sample on a Glass Slide
Step 3: Fix the sample Using Heat
Step 4: Staining (Crystal Violet)
Step 5: Staining ( Gram’s iodine)
Step 6: Staining ( Ethyl Alcohol)
Step 7: Staining ( Safranin)
Step 8: Prepare slide for microscopy
Step 9: Examine the Slide Using the Microscope
Crystal Violet
What is the primary stain that color all cells with a purple hue
1 minute
How many minute to let it sit before wash and dry for crystal violet, gram’s iodine and safranin?
10-15 secs
time to let it sit before wash and dry for Gram’s iodine
Iodine
Acts as a mordant, forming a complex with the crystal violet dye within the bacterial cells
Ethyl Alcohol
decolorizes the smear, allowing differentiation between gram positive and gram negative based on their cell wall structure
Safranin
stains the decolonized gram negative bacteria and gram positive
pink
gram negative color
purple
gram positive color
Buccal cells under HPO
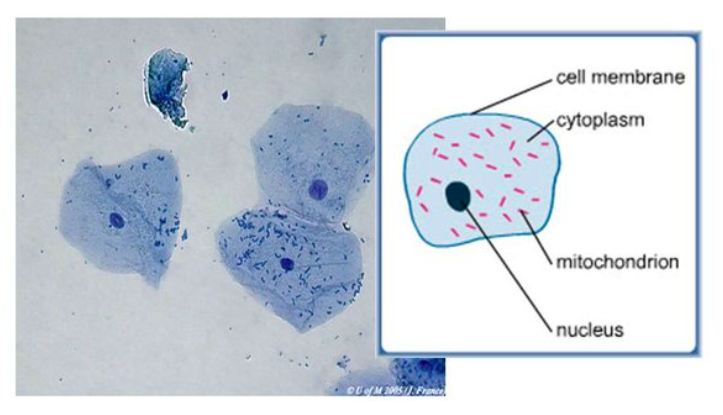
Before: Transparent
After: All positive and negative become purple
Crystal Violet (Primary stain) before and after color of bacteria
Before: Purple
After: remain purple
Gram’s iodine (mordant) before and after color of bacteria
Before: Purple
After: (+)- stay purple
(-) colorless
Ethyl Alcohol ( Decolorizer) before and after color of bacterias
Before: (+) still purple
(-) colorless
After: (+) remain purple
(-) pink/red
Safranin before and after color of bacterias
Squamous cell ae present
Motile bacterias are present
Wet smear result
- Squamous cells are present. More defined and clear image was seen under OIO.
- Non-motile bacteria were present.
Fixed smear result
Fixation process
is a process where the sample is fixed by agitating the slide over a heat for 5 times. This ensures that bacterias are killed.
Inclined
…, and slowly drop. If bubbles are present, slowly press down to eliminate bubbles.)
- Gram Positive Cells (Purple) were present
- Gram Negative Cells (Red) were present
- Non-motile Bacteria were present
Gram staining result
Hans Christian Gram
who first introduced gram staining in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.
Gram Positive Organisms
retain the primary color and appear purple-brown (Squamous epithelial cells)
Gram Negative Organisms
do not take the primary color and appear as red (WBC and Macrophages)