Primitive Fish Orders
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Amphioxiforms
LANCELETES
→ nonvertebrate
No cranium complex (Acranniates)
protocercal tail
No cerebral, heart, respiration strucutres hemoglobin, red blood cells
25 gonands
one epidermal layer
PREY:
→ mostly diatoms and small food items
→ feed via cilla that transport water throuhg mucus mouth and pharnyx
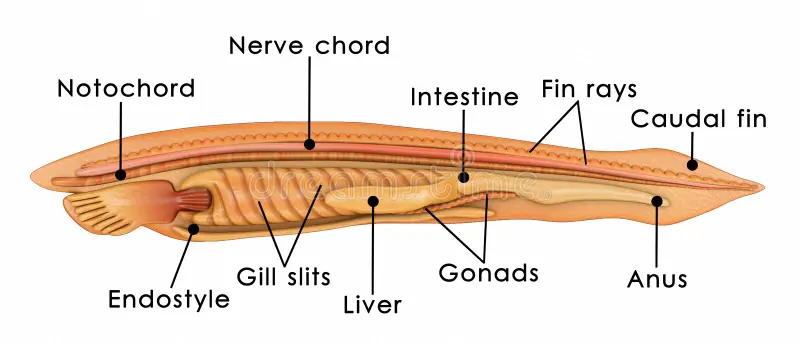
Amphioxiforms
what order is the sister group to all verebrates
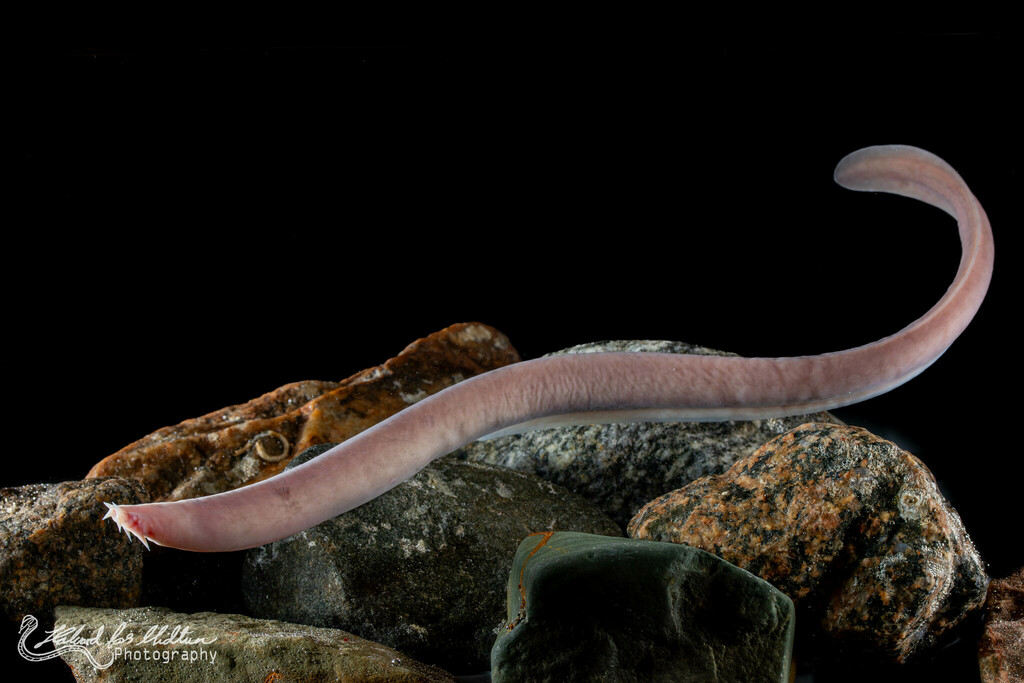
Myxiniformes
Order of Hagfish
→ Non-vertebrate
→ sister group to vertebrates and the basal craniate taxon
→ Stenohaline
→ Isomotic blood w/ the salinity of the surrounding water
→ Anatomy:
four rudimentary hearts
→ Oxygen uptake
water uptake through nostrils and run pass gills
Capillary beds at skin: contribute to cutaneous respiration; aids in forgaging behavior
→ metabolism:
low basal metabolic rates→ advantageous for deep sea environments, where prey encounters are low
→ Digestive System:
Lack a true stomach
Intestine begins at the pharynx and ends at anus w/ anterior muscular division
Cloacal region
→ Sensory system:
Photosensitive receptors: DERIVED characteristic
Barbels: find food via touch and olfaction

Variable lymphocyte receptors
primitive proteins that respond to infectious agents; found in Myxiniformes and Petromyzontiformes
stenohaline
organism with a narrow range of salinity tolerance
ex: Myxiniformes
Petromyzontiformes
order of LAMPREYS
Anatomy:
→ Notochord supported by primitive vertebrate made of cartilage, lacks a constructed vertebrate
→ Elongated dorsal fin
→ Single Nostril
→ Separate dorsal and ventral roots of nerves
→ “Open” Circulatory system: sinuses connecting arterial and venous system in the brachial region help in gas exchange
largest diploid chromosome of any vertebrate: 140-170
Ammocete
larval stage of petromyzontiformes, characterized by a blind toothless stage.
→ burrows in bed of silty streams or rivers
→ head protrudes from the bottom and filter feeds through pharnyx produced muscus the
Gnathastomes
unranked taxonomic order of jawed verebrates
Cartilaginous skeleton
ceratotrichial fins
spiral valve intestine
oil-filled liver, instead of gas bladder
no larval stage
sutureless skull
male intromittent organs
multiple gill slits
Chondrichthyans Characteristics
Subclass Holocephali
Type of Chondrichthyan containing superorder holocephalimorpha with one extant order: chimaeriformes
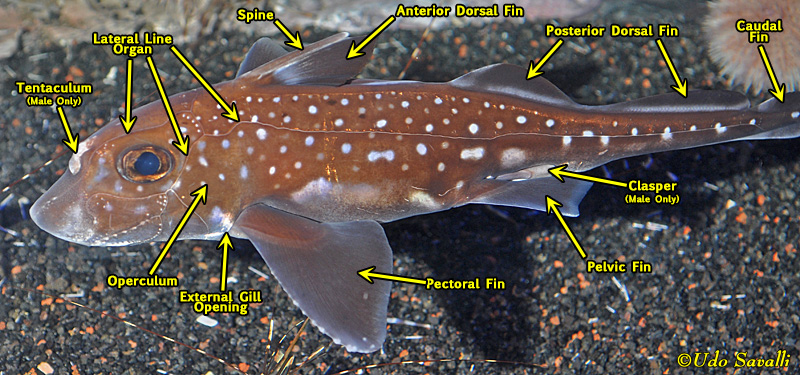
Chimaeriformes
Order of the modern Chimaera
Anatomy:
→ Upper Jaws immovably attached to braincase
→ Denticles, Placoid Scales along the midline of the back, naked rest of the way
→ Single gill flap that cover four internal gill openings
→ Leptocercal caudal fin
Teeth:
→ 3 pairs of hypermineralized toothplates
Reproduction:
→ oviparous
Cartilaginous skeleton
Placoid Scales
Internal Fertilization
Replacement dentition
Multiple gill slits
Calcified skeleton
Calcified verbal Centra
Sutureless skull
Upper Jaw of Palaoquadtre cartilage, free from braincase
Unsegmented certotrichia
Oil livers
Spiral valve intestine
soft fin rays
Spiracle
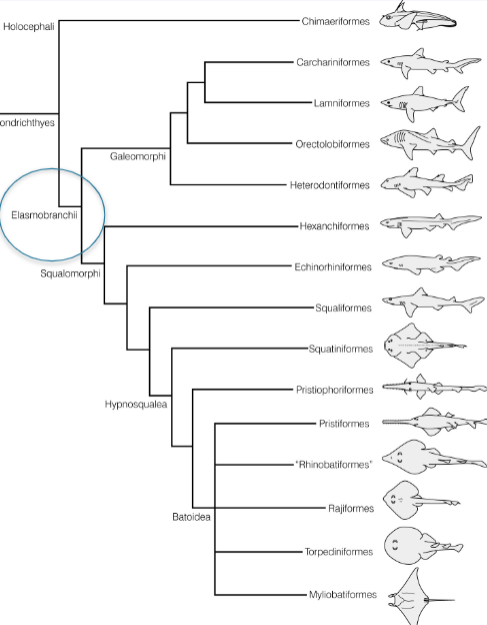
Characteristics of SUBDIVSION ELASMOBRANCHI
Spiracle
first functional gill arch supported by the hyoid bone in Elasmobranchs

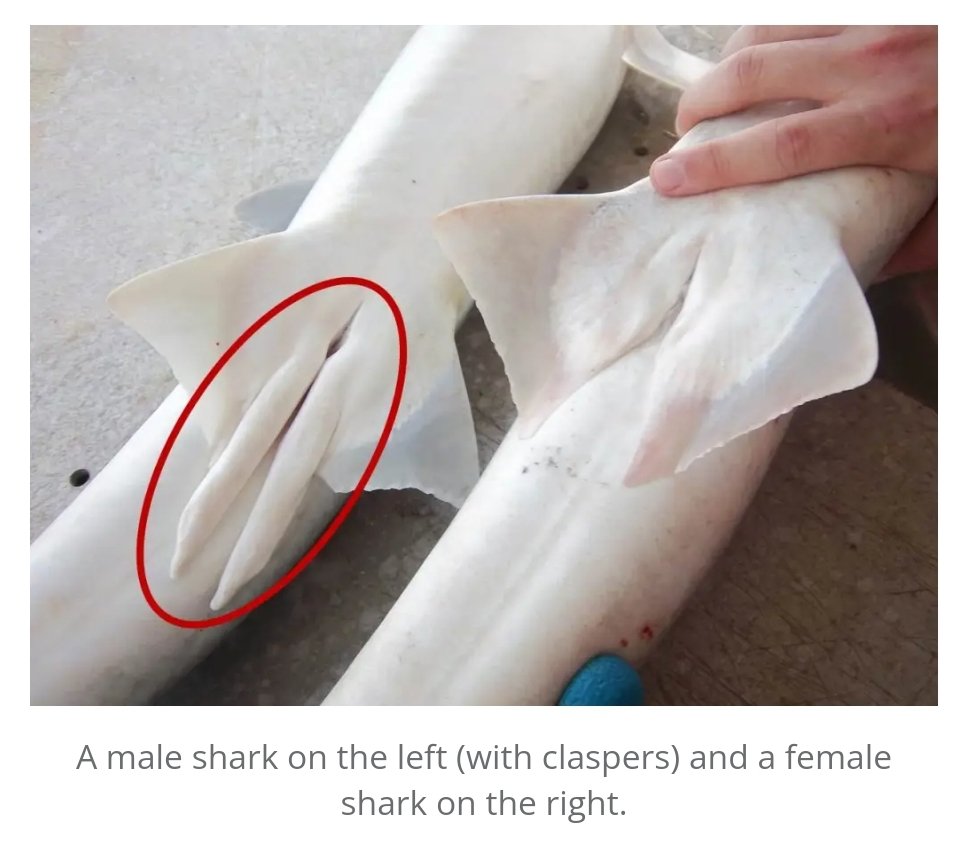
Myxoptergia (or claspers)
intromittent male sex organs on Chondrithyes

order heterodontiformes
order of bullhead and horn sharks
reproduction: oviparous
dorsal fin: 2, spine in frontal dorsal fin
Anal fin: Present
teeth: sharp front teeth, flat rounded back teeth
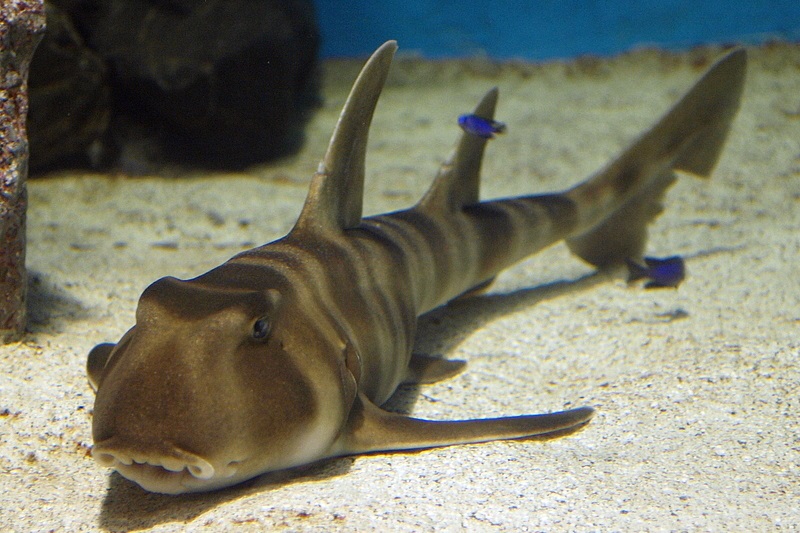

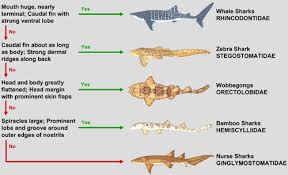
Orectolobiforms
order of carpet, blind, zebra, nurse, whale, and wobbegongs sharks
dorsal fins: 2
Gill slits: five with fifth overlapping the fourth
anal fin: present
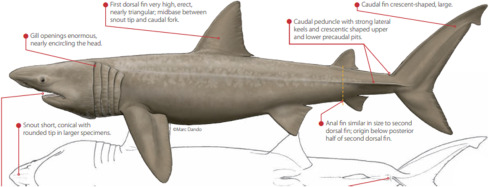
Lamniformes
Order of mackerel sharks
large plegaic sharks
Dorsal fin: 2
Anal fin: present
reproduction: moslty ovoviviparous; eggs fertilized and hatched internally
→ evidence of oophagy occurring in families of Tiger Sharks
Some families capable of countercurrent exchange to maintain body heat
Carcharhiniformes
order of ground sharks
40% of all shark species
dorsal fine: 1
Reprodction: (mostly) viviparous
Anala fin: present

Carcharhinus leucas
species of Carcharinifromes capable of entering into FW peridoically
Hexanchiformes
order of frilled and cow sharks
dorsal fin: 1
gill slits: 6-7
reproduction: ovovivparous
Deepwater dwelling, well over 2km

Echinorhiniformes
order of bramble sharks
dorsal fin: 2
anal fin: absent
reproduction: ovovivparous
Large placoid scales all over body
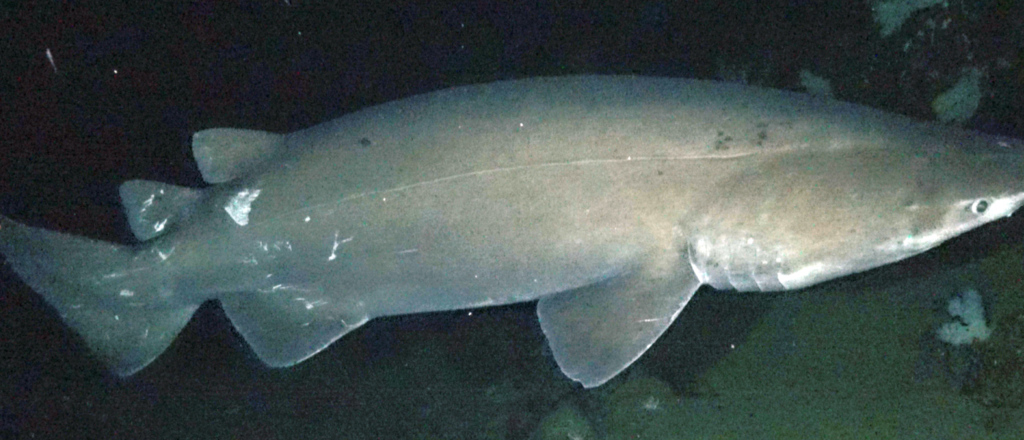

Squaliformes
order of dogfish, gulper, sleeper, and kitefins
dorsal fin: 2
anal fin: Absent
Reproduction: unkown, slow maturation period
Squalamine production in liver has antibacterial properties used in cancer treatments
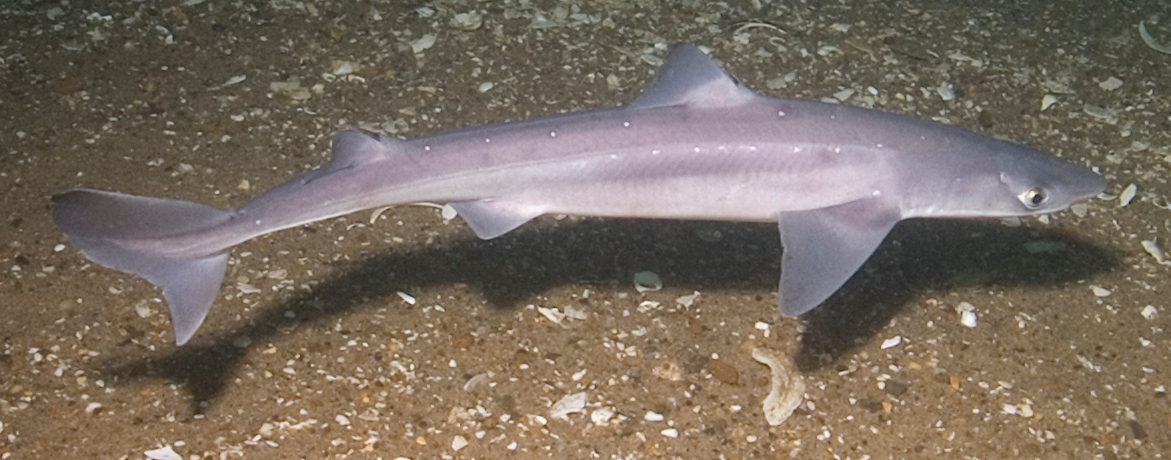

Squatiformes
order of angel sharks
flattened bodies, pectoreal and pelvic fins held horzonatally
dorsal fins: 2
reproduction: oboviviparous

Squalus acanthias
spiny dog fish
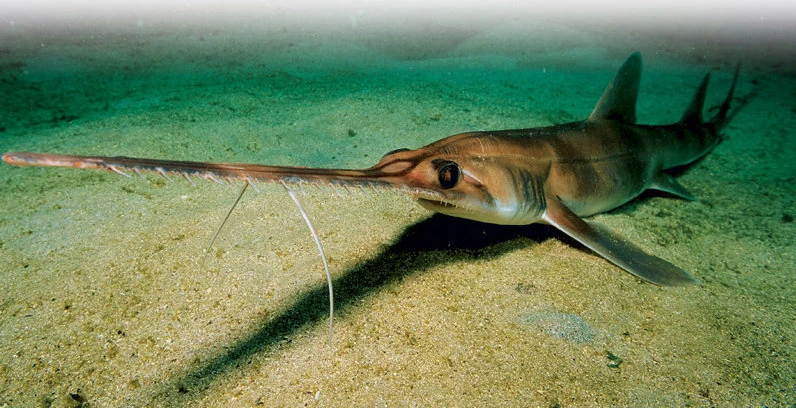
Prisitiophoriformes
order of saw sharks
dorsal: 2 fins
anal fin: absent
gill slits: 5-6
barbels for feeding

Batoidea
subdivision of skates and rays
→ ventral gill openings
→ anterior edge of enlarged pectoral fin attached to side of head
→ anal fin always absent
→ enlarged dorsal spiracles for water intake
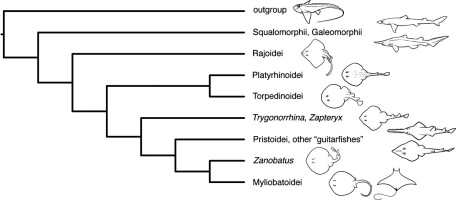
Torpendiniforms
Order of electric rays and numb fishes
59 species
produce electric discharge from 8-220 volts
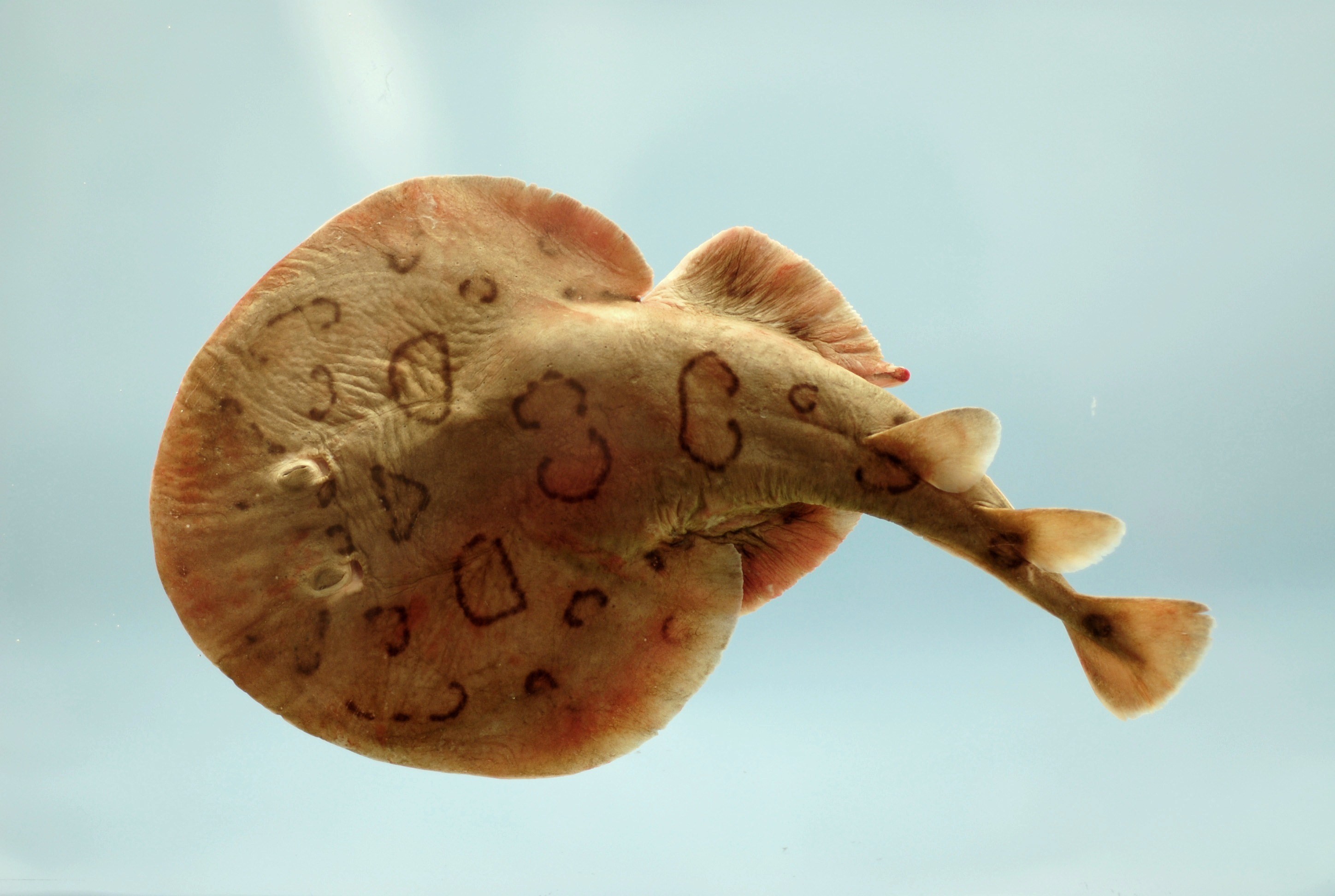

Pristiformes
Order of Sawfishes
7 marine and FW species
Respiration:
→ two large spiracles
→ ventral gills
Dorsal Fin: 2
Reproduction: ovoviviparous
No barbels
Fused pelvic fin

Rajiformes
ORder of skates, bowmouth guitarfishes, guitar fishes
dorsal fin: 2
large pectoral fins
285 marine species
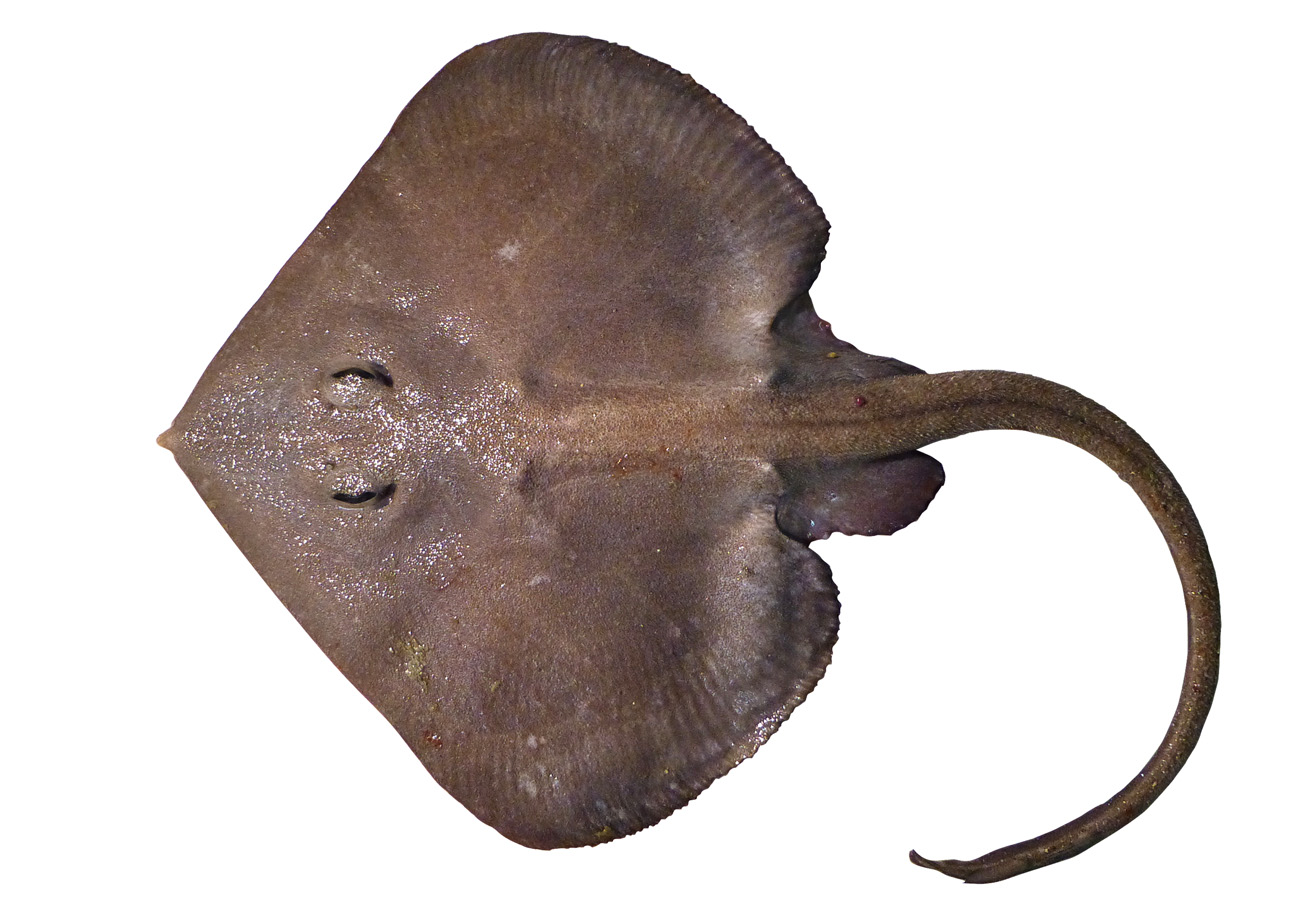

Myliobatiforms
stingrays, butterfly rays, and eagle rays
183 species, marine and FW
reproduction: ovoviviparous
no dorsal fins
Barbel on sting ray: modified placoid scale

Grade Teleostomi
Contains all bony fishes
Includes Classes Sacropterygii and Actinopterygii
Class Sacropterygii
Lobed fined fishes
basal group to all bony fishes
contains order Colecanthiforms and order Ceratdoniformes
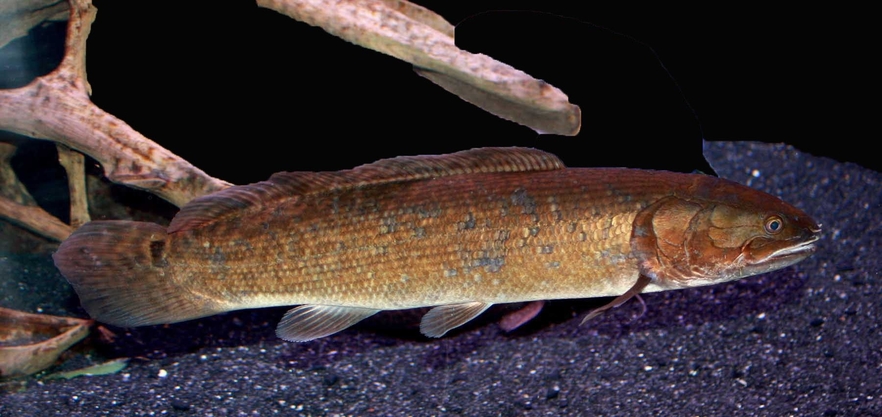
Coelacanthiforms
Order of Colecanths
Anatomy:
→ Uncsontricted and unossified modified notochord
→ fleshy lobed, paired and median fins
→ Diphyceral tail
→ thick bony scales
→ Gular plates on lower jaws
→ Thin bony layer vertebral spines and fin rays
→ No lungs
→ Fatfilled gas bladder
Reproduction: ovoviviparous; small clutch size, late maturation
→ Highly electrosenestive through rostral organs: series of pits and tubes in the snout that detects weak electrical currents

Ceratodonitoformes
Order of Lungfishes
apart of subclass Diponi
Anatomy:
→ Lungs and gills
→ Teeth not atttached to jaw margin, only occur on interior bone.
→ contain toothplates
All extant families are FW
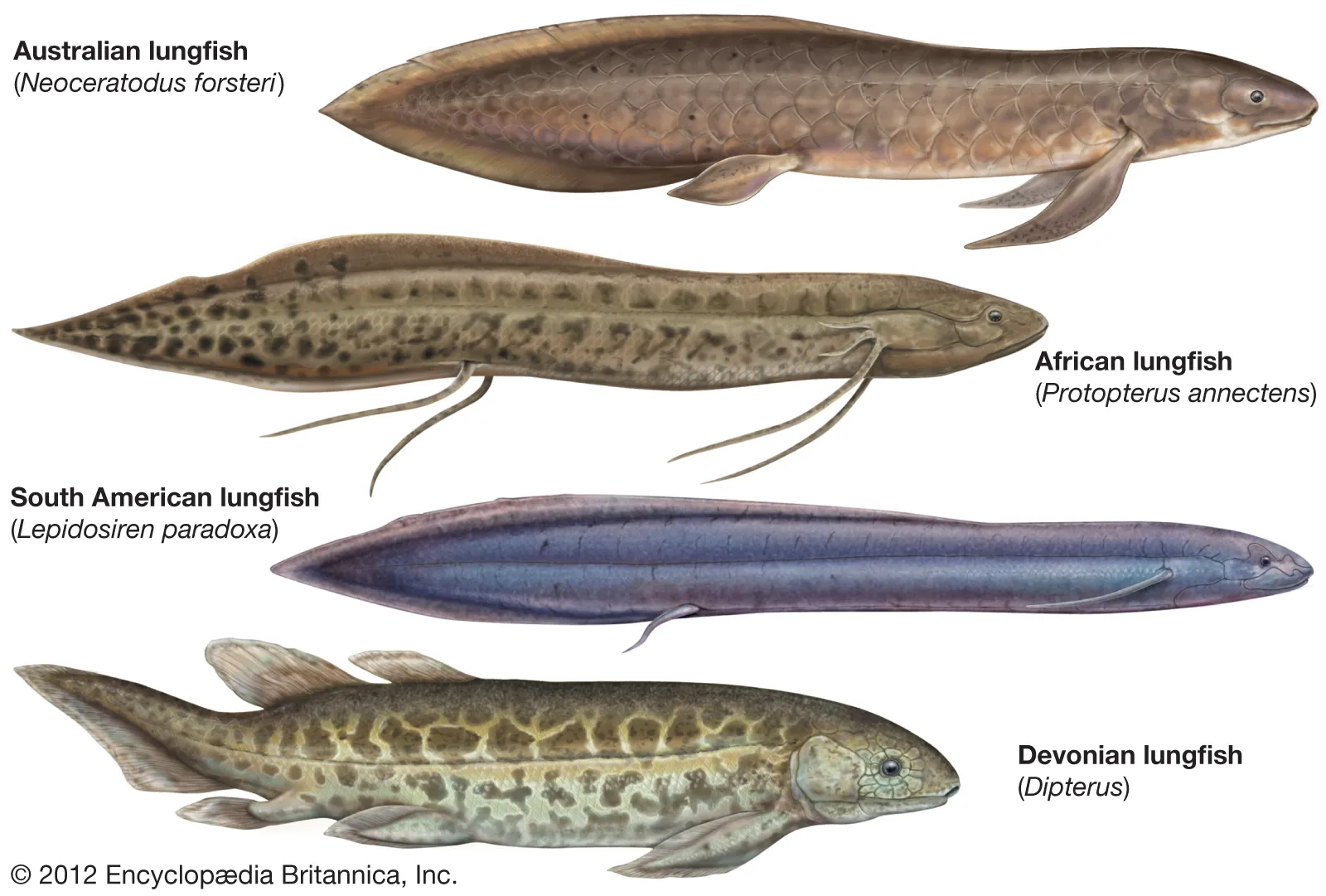
Estivation
state of dormany Ceratodontiformes enter during dry summer months
→ construction of an underground mud cocoon when ponds dry up where they rely enteriely on air breathing
→ heart rate drops
→ body proteins are metabolzied and rapid weight loss occurs `
Class Actinopterygii
Latimeria chalumnae
living specimens of coelacanth discovered in 1938
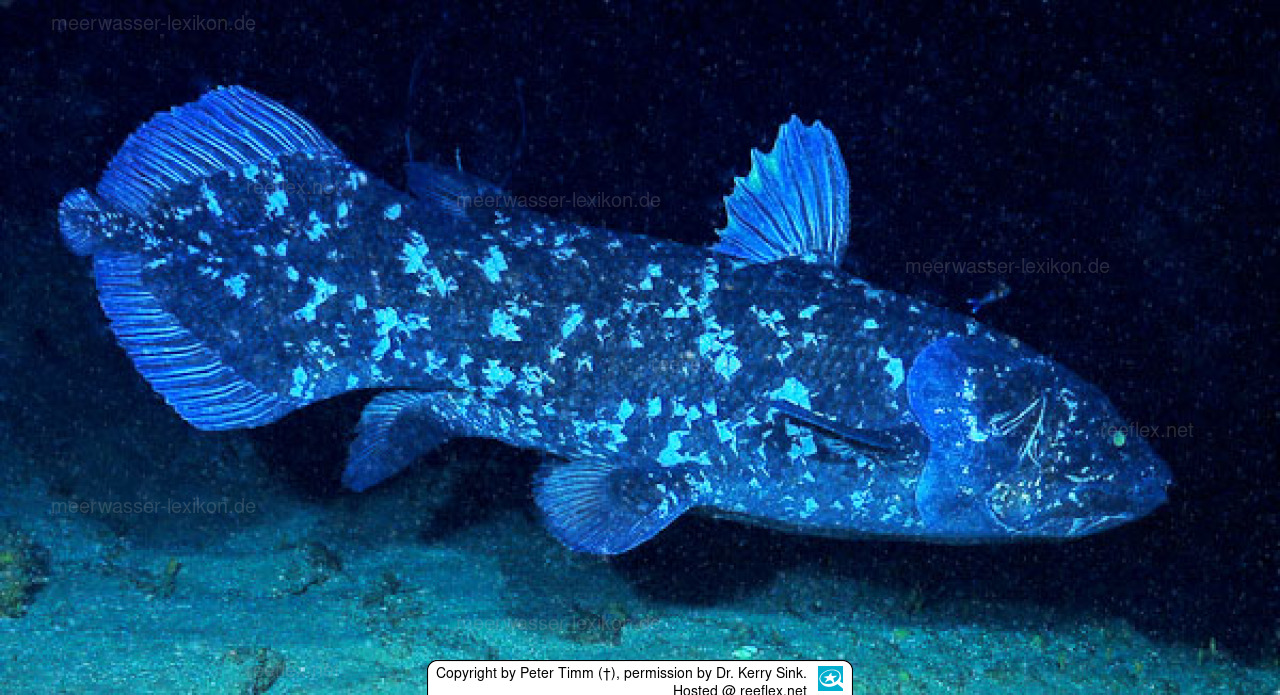

Subclass Cladista
subclass and basal group of Actinopterygii
contains order POlypteriformes
gular plate
ventral bony plate that lies between the two lower jaws, or in the anerior third of the space between lower jaws(bowfin)
→ found in elopiodae, colecathiformes, subclass cladista, ammiforms
Polypteriformes
order of bichirs and reedfishes
16 species of freshwater fish
→ Bichirs:
→ 5-18 dorsal finlets; vertical spines attached to horizontal rays
→ few chromosomes
→ 34 gill arches
→ obgliate air breathers; recoil aspiration

Acipenseriformes
order of Acipenseridae and Polydontidae
apart of subclass Chondrostei
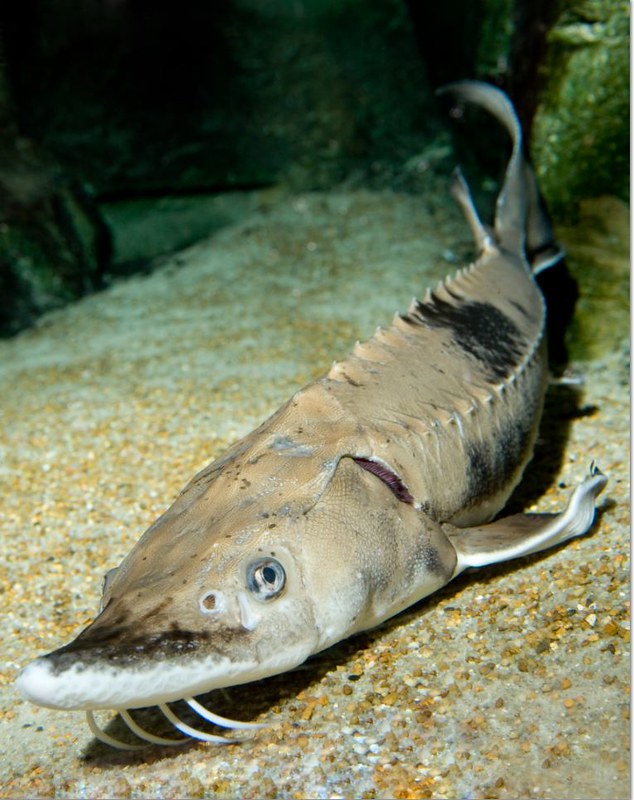
Acipenseridae
Family of Sturgeon
Anatomy:
→ Heterocercal tail
→ dorsal fin: 1
→ 5 rows of ganoid scutes
→ largley cartilaginous endoskelton
→ minute ossifications on body
→ protrusible mouth
→ barbels
→ spiracle
Reproduction:
→ all spawn in FW, leading to striclty FW species and anadromous species
→ high fecundity, but slow reproduction rates

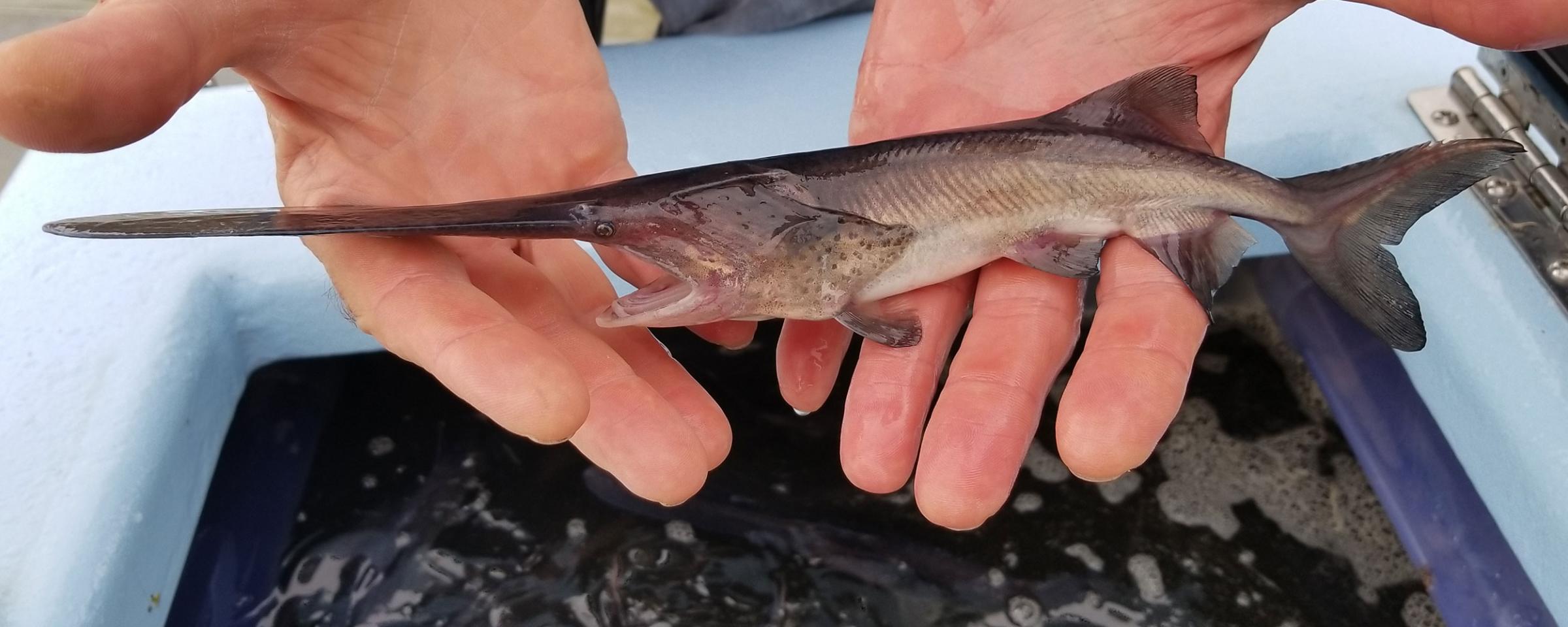
Polydontidae
family of paddlefish
2 extant species
Anatomy:
→ heterocercal tail
→ unrestricted notochord
→ Cartilaginous skeleton w/ osffiied headbones
→ two small barbels
→ no scutes or scales
Behavior:
→ pelagic feeders on zooplankton and fish
Sensory organ:
→ Rostral paddle: contains electroreceptors(Ampullae of Lorenzi) used to detect prey

subclass Neopterygi
subclass of Lepiosoteriformes, Amiiformes, and all Teleosts
Lepisosteriformes
Order of Gar
Anatomy:
→ Ossified skeleton
→ constricted notochord
→ vertebral centra: opisthoceolous arrangement
→ ganoid scales
→ abbreviated heterocercal tail
→ no electroreception tecnqhiues
apart of subclass neopterygi

Amiiformes
order of bowfins
primitive features:
→ abbreviated heterocercal tail
→ spiral valve intestine
→ gular plate on underside of head
Derived features:
→ vertebrate
→ cycloid scales
→ no electroreception
Anatomy:
→ one long dorsal fin used to swim through undulation

Amia calva
One species of of the order amiiformes
