Physics Class 5 - DC Circuits, Oscillators, Waves, and Sound
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What are Kirchhoff’s rules?
Currents into and out of any point in a circuit must equal one another
Continuity
Conservation of charge
Elements in series have equal current
Sum of voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must be equal to zero
Conservation of energy
Elements in parallel have same voltage
What is the equation for power?
P = IV = IR² = V²/R
P = power
I = current
V = voltage
R = resistor
How is energy dissipated by resistors?
Thermal energy
What is the form of power output by a battery?
Electrical energy
What is the rule for currents through elements of a series?
Elements in a series experience the same current running through them
What is the total resistance for elements in parallel?
(RaRb)/(Ra + Rb)
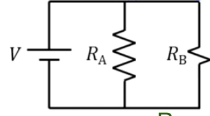
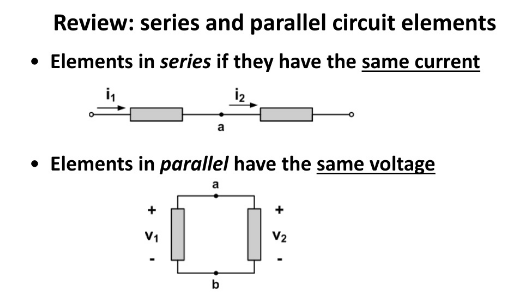
What are elements in series? Parallel?
Series: in a line, same current
Parallel: in parallel sides of a loop, same voltage
What is a voltmeter?
Measures voltage
Connect in parallel to circuit segment of interest
High internal resistance
What does high internal resistance do in voltmeters?
Minimizes impact of measurement on the circuit
What is an ammeter?
Measures current
Connect in series to the circuit segment of interest
Low internal resistance
Why do you want low internal resistance on an ammeter?
It is in series, so you want it not to affect how the current flows through it
What is the equation for force exerted by a magnetic field?
T = teslas
q = absolute value of the charge
v = speed
B = magnitude of magnetic field
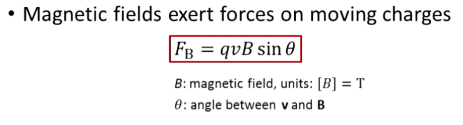
What is the magnetic field if theta is 0 or 180 degrees?
0
How do you use the right hand rule for magnetic fields?
Thumb points in direction of v
Fingers in the direction of B (fingers = field)
Palm gives direction of FB for a positive charge
Back of hand gives direction of FB for negative charge
What is FB perpendicular to?
v (speed) and B (magnetic field)
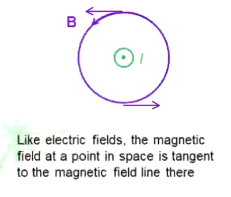
What does a circle with a dot mean in terms of magnetic field?
It is pointing out of the screen, towards me
What is work done by a magnetic field?
A charge entering a magnetic field will move in a circular path = centripetal force
Work done will be 0, as it is always when considering centripetal force
What are magnetic fields?
Created by moving charges
What is a current?
Motion of positive charges
How do you find the direction of a magnetic field using currents?
Point thumb of right hand in direction of current
Fingers curl in direction of magnetic field
The magnetic field at a point in space is tangent to the magnetic field there
What does a circle with a cross through it mean in magnetic field vectors?
The vector is pointing away from you, into the field
How are large magnetic fields created?
By permanent magnets made of materials like iron, cobalt, and nickel that create large magnetic fields due to alignments of their electron spin
Produces magnetic field without having a current applied to it
How do magnetic field lines relate to the North and South poles of a permanent magnet?
Magnetic field lines enter the south pole and exit the north pole

What is simple harmonic movement?
Back and forth motion
Force is proportional to the negative of the displacement
What is Hooke’s law?
F = -kx
F = restoring force
k = spring constant
x = displacement from equilibrium
What is amplitude?
Greatest displacement from equilibrium during oscillation
What is a period?
Time to complete one cycle
Constant for simple harmonic motion
Independent of amplitude for simple harmonic motion
What is frequency?
Number of cycles per second
f = 1/T
f = frequency
T = period
For springs: f = (1/2pi) sqrt (k/m)
k = spring constant
m = mass
What is the energy stored in a compressed spring?
PEelastic = ½ kx²
What is the Work done by a spring?
W = - (change in PE)
How do you figure out the energy in a spring system?
KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf
In absence of non-conservative forces
How does Vmax of a spring system relate to amplitude?
Vmax = sqrt (k/m) A
Directly proportional
What is the frequency of a pendulum?
f = 1/2pi (sqrt (g/L))
L = length
Angle in radians measured from vertical
String is massless and frictionless
What is the restoring force of a pendulum?
mg sin theta = Frestore
In radians
sin theta ~ theta when the angle is small, therefore force is proportional to force
What is a wave?
Propagating oscillations that transfer energy
What is wavelength, amplitude, wave speed, and period for a wave?
Wavelength (lambda) = length of one cycle
Amplitude (A) = max displacement from equilibrium
Wave speed (v) = speed of wave energy propagation
Period (T) = time required for one oscillation
What are trasverse waves?
Oscillations perpendicular to direction of wave propagation
Ex: ocean waves, wave on a string, electromagnetic waves
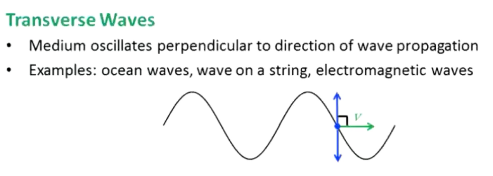
What are longitudinal waves?
Oscillation parallel to wave propagation
Ex: sound (longitudinal pressure waves)
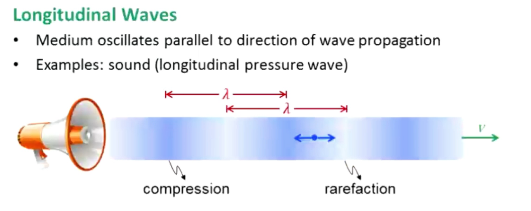
What is a compression, rarefaction?
Compression: in longitudinal wave, when a bunch of particles are oscillating so they are close together
Rarefaction: in longitudinal waves, when a bunch of particles are oscillating far apart
Wavelength is distance between compressions or rarefactions
What is wave speed?
v = (wavelength) (frequency)
What are the two big rules for waves?
Speed of a wave in a medium depends on the type of wave and physical properties of medium
v is constant in the same medium, regardless of frequency of wavelength
A wave moving form one medium to another will maintain the same frequency
f is constant between media
If a wave crosses a boundary, what must be true?
Some is reflected backwards, while some continues travelling through
Some energy is not transmitted, some is reflected back
What is constructive interference?
Waves are in phase
When two + waves combine, their displacements add
Final amplitude is greater than that of either wave
d + d = A
What is destructive interference?
When two or more waves combine, displacements add
Waves are out of phase (by half a cycle)
Final amplitude is smaller than that of both waves
d - d = A
What is beat frequency?
Two waves with different frequencies combine
Cycles between constructive and destructive interference are beats
fB = |f1 - f2|
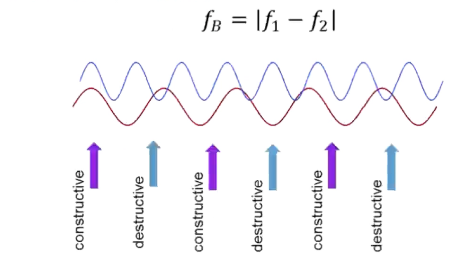
What is a standing wave?
Waves are trapped
Wave interferes with its own reflection → does not propagate (move left/right)
What is a node? Antinode? In terms of pressure and displacement
Pressure node: where pressure is zero
Displacement node: displacement is zero (point of zero oscillation)
Pressure antinode: pressure is max
Displacement antinode: displacement is max (max oscillation)
Pressure node = displacement antinode and vice versa
In a pipe with one end open, what nodes are always true?
Closed end is always a displacement node, pressure antinode
Open end is always a pressure node, displacement antinode
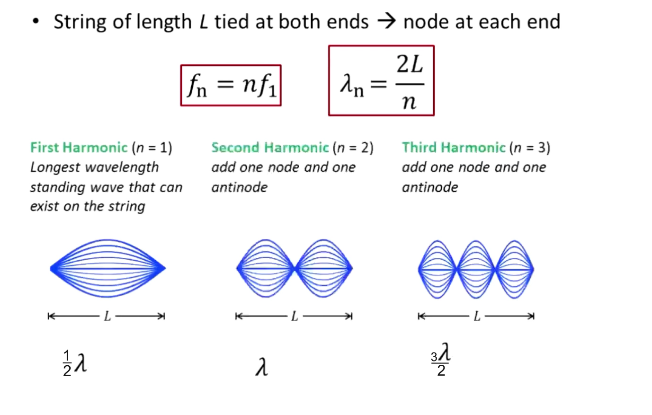
If a string is tied at both ends, what is the frequency, wavelength?
fn = nf1
Wavelength n = 2L/n
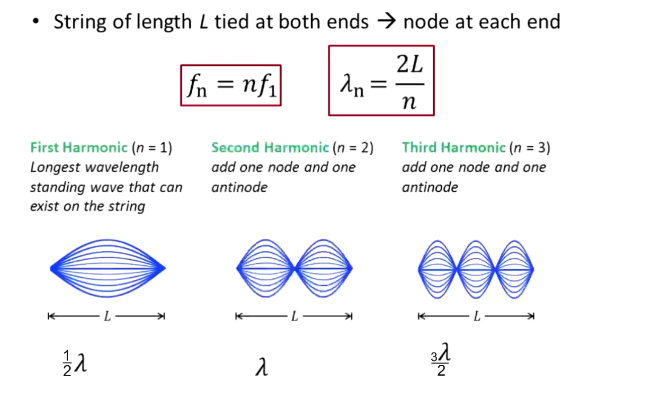
What is the first harmonic?
Longest wavelength standing wave that can exist on a string tied on both ends
n = 1
½ wave
1 displacement node, 2 displacement antinodes
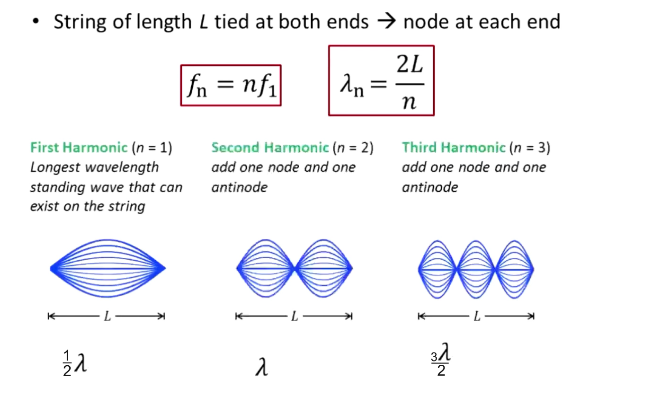
What is a second harmonic? Third?
Second: n = 2; two displacement nodes and three antinodes; 1 wave
Third: n = 3; three displacement nodes, four antinodes; 1.5 waves
What is intensity?
Energy of a wave incident per unit area per unit time
I = power/area
Units = [I] = Watts/m²
What is the intensity of a spherical wave?
I = P/(4pi*r²)
I is proportional to 1/r²
I is proportional to amplitude²
Spherical waves are those going in all directions (ex: sound from a speaker)
What is sound intensity equation? What is the threshold of human hearing?
B = 10 log10 I/Io
Io = 10-12 W/m²
Units: [B] = dB (decibels)
How do you work logarithms related to human hearing?
For every increase in the I by a factor of 10, add 10 to B (ex: if increases by factor of 100, add 20 b/c 10 + 10)
For every decrease of I by factor of 10, subtract 10 from B
What is the doppler effect?
Shift in detected frequency of a wave due to relative motion between detector and sound source
Detector and sound source move closer → higher detected frequency and vice versa
This does not mean frequency is increasing/decreasing → velocities are constant, so detected frequency is constant
How is doppler shift calculated?
fD = fs (v ± vD)/(v -/+ vS)
Use top sign when motion is toward
fD = frequency detected
vD = speed of detector
vS = speed of sound source
v = speed of sound wave (350 in air)
What is the speed of sound in air?
350 m/s ish