Human Anatomy MIDTERM 1
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Longitudinal fissure
The cerebral hemispheres are separated by the
Diencephalon
Together the thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus are called the
between the dura mater and the arachnoid mater
The term subdural hematoma refers to blood accumulation (in)
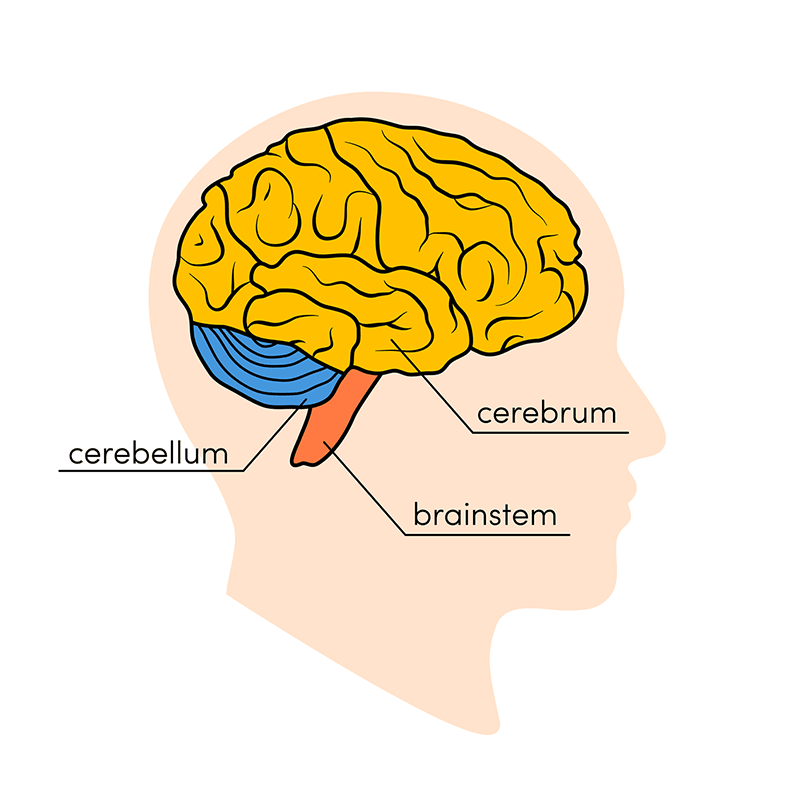
cerebrum
The largest region of the brain is the
Sulci (central, lateral, & parieto-occipital sulcus)
The cortical surface of the cerebral hemispheres forms a series of shallow grooves called
central sulcus
The groove between the frontal and parietal lobes of the brain is (the)
Septum Pellucidum of the Cerebrum
A 67-year-old female was admitted to a hospital after she reported to her primary care physician that she had been having very painful headaches. Further examination revealed the presence of significant increases in intracranial pressure. After viewing a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the neurologist concluded that the woman's condition was due to the presence of a tumor, which is developing along the rostral aspect of the medial wall of the lateral ventricle. Which area of the brain is likely to contain this tumor?
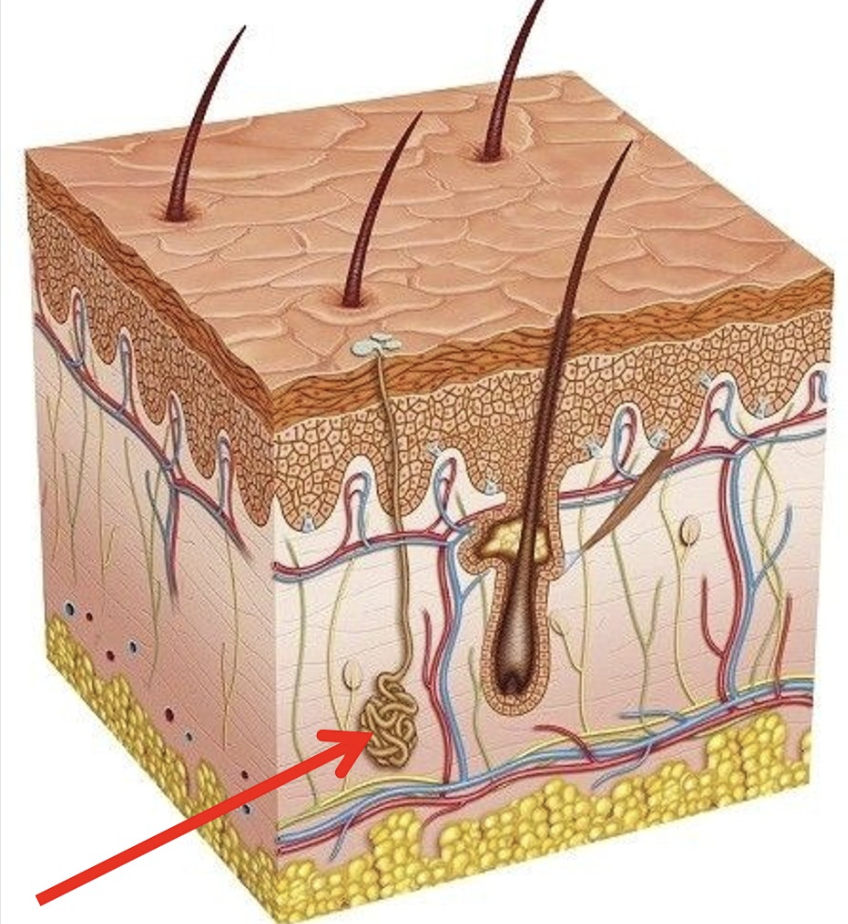
Sweat Gland of the Dermis
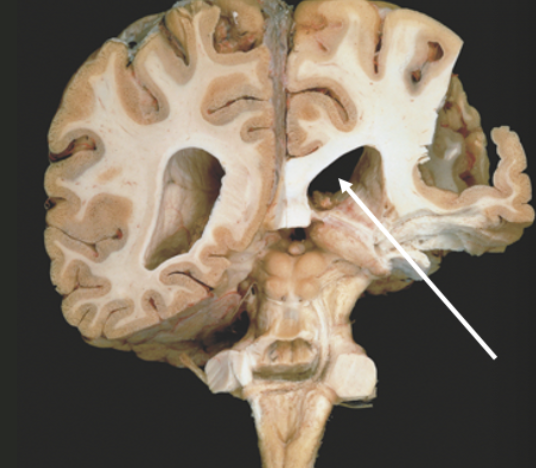
What is this?
Right lateral ventricle of the cerebrum
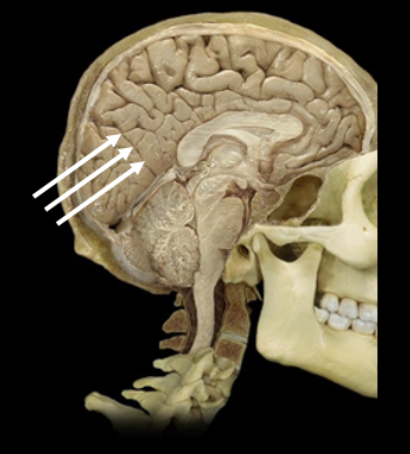
What is this?
left parieto-occipital sulcus of the cerebrum
What is this?
Inferior Nuchal Line of the Occipital Bone
What is this?
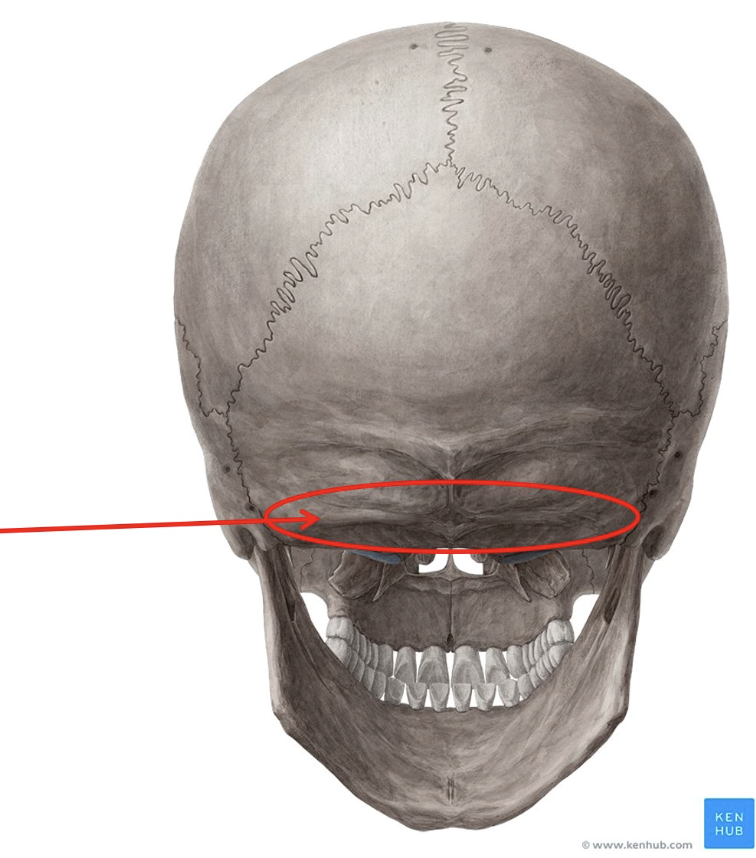
Right foramen spinosum of the sphenoid bone
What is this?
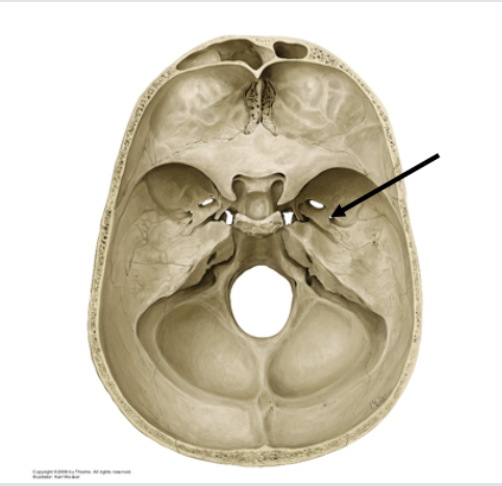
Right mastoid process of the temporal bone
What is this?
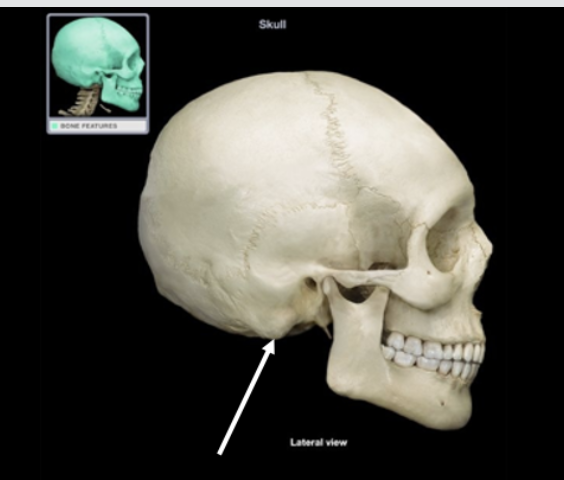
Simple Squamous of the Epithelium
A 53-year-old man with a known history of emphysema is examined in the emergency room. Laboratory findings along with examination indicate that the patient is unable to exchange oxygen in the air and carbon dioxide in the blood. This exchange occurs across which type of epithelium?
Cerebral Hemisphere
Location: The largest region of the brain, divided into left and right hemispheres
Function: Higher brain functions; reasoning, memory, sensory perception, movement, & language
Frontal Lobe
Location: Anterior portion of the cerebral hemisphere
Function: Controls voluntary movement, problem-solving, planning, decision-making, and aspects of personality
Precentral Gyrus
Location: Ridge immediately anterior to the central sulcus
Function: The Primary motor cortex initiates voluntary muscle movements
Parietal Lobe
Location: Posterior to the frontal lobe and superior to the occipital lobe
Function: Processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, pressure, and spatial awareness
Postcentral gyrus
Location: Ridge immediately posterior to the central sulcus in the parietal lobe
Function: Primary somatosensory cortex; receives sensory input from skin and proprioceptors
Temporal lobe
Location: Inferior to the lateral sulcus on each side of the brain
Function: involved in hearing, language comprehension, and memory
Superior temporal gyrus
Location: Uppermost ridge of this lobe, just below the lateral sulcus
Function: contains the primary auditory cortex; processes sound
Middle Temporal Gyrus
Location: between the superior & inferior ____ gyri
Function: involved in language processing & sematic memory
Inferior Temporal Gyrus
Location: Below middle ____ gyrus
Function: important for object recognition and visual processing
Occipital Lobe
Location: Posterior portion of the cerebral hemisphere
Function: Primary visual processing center of the brain
Insular Lobe of the cerebrum
Location: Deep within the lateral sulcus, beneath the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes
Function: Involved in taste, visceral sensation, emotional awareness, and homeostatic regulation
Cingulate (Limbic) Gyrus of the cerebrum
Location: Curves over the corpus callosum, part of the limbic system
Function: regulates emotion, motivation, a behavior
Corpus Callosum of the cerebrum
Location: Large C-shaped band of white matter connecting the left and right hemispheres
Function: Enables communication between the two hemispheres
Septum Pellucidum of the cerebrum
Location: thin membrane separating the left and right lateral ventricles, located beneath the corpus callosum
Function: Structural partition; may have a role in limbic system signaling
Fornix of the cerebrum
Location: Arched white matter tract beneath the corpus callosum
Function: connects the hippocampus to the hypothalamus
Lateral Ventricles of the