Moment of Inertia
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:58 AM on 11/24/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
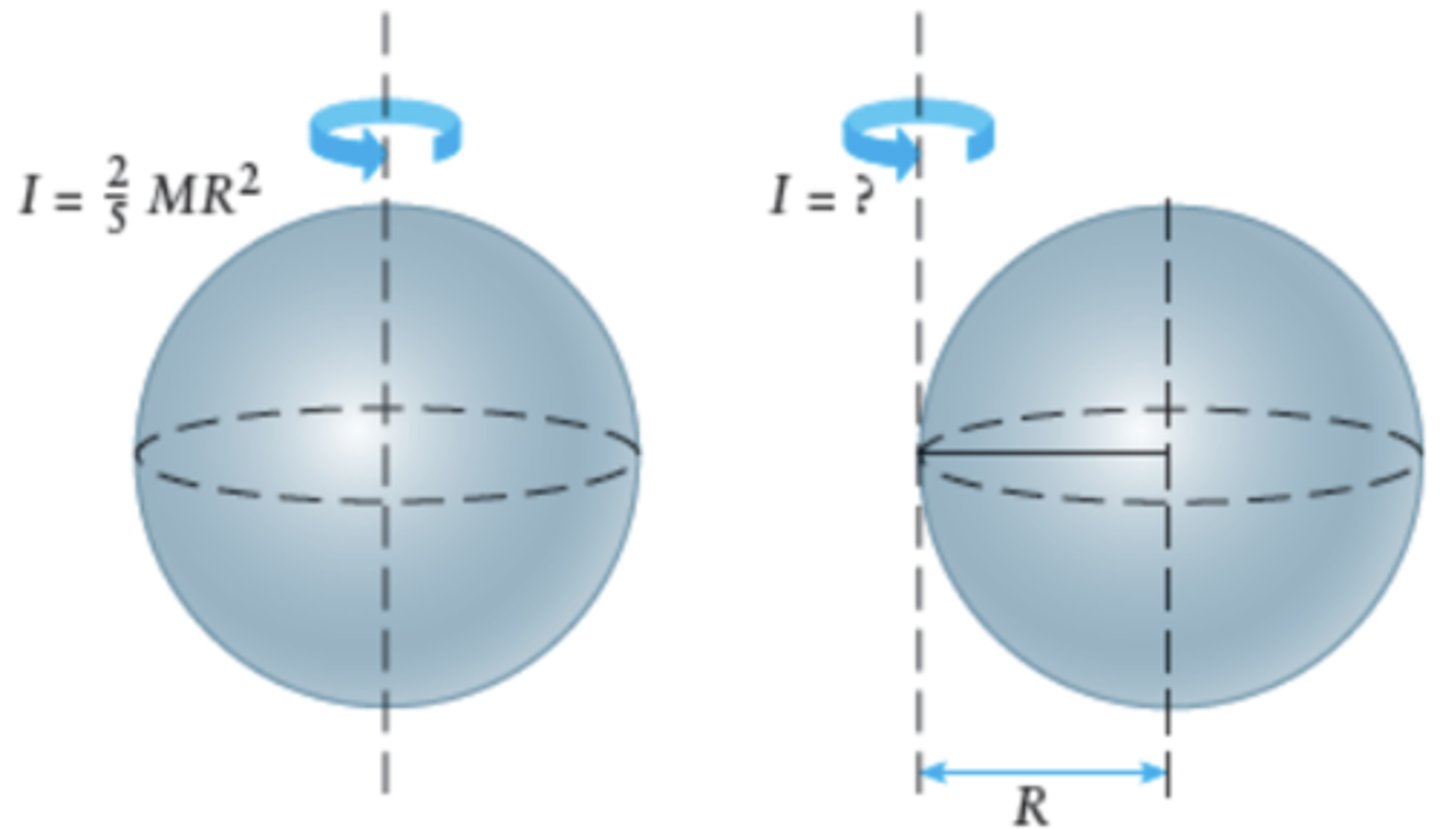
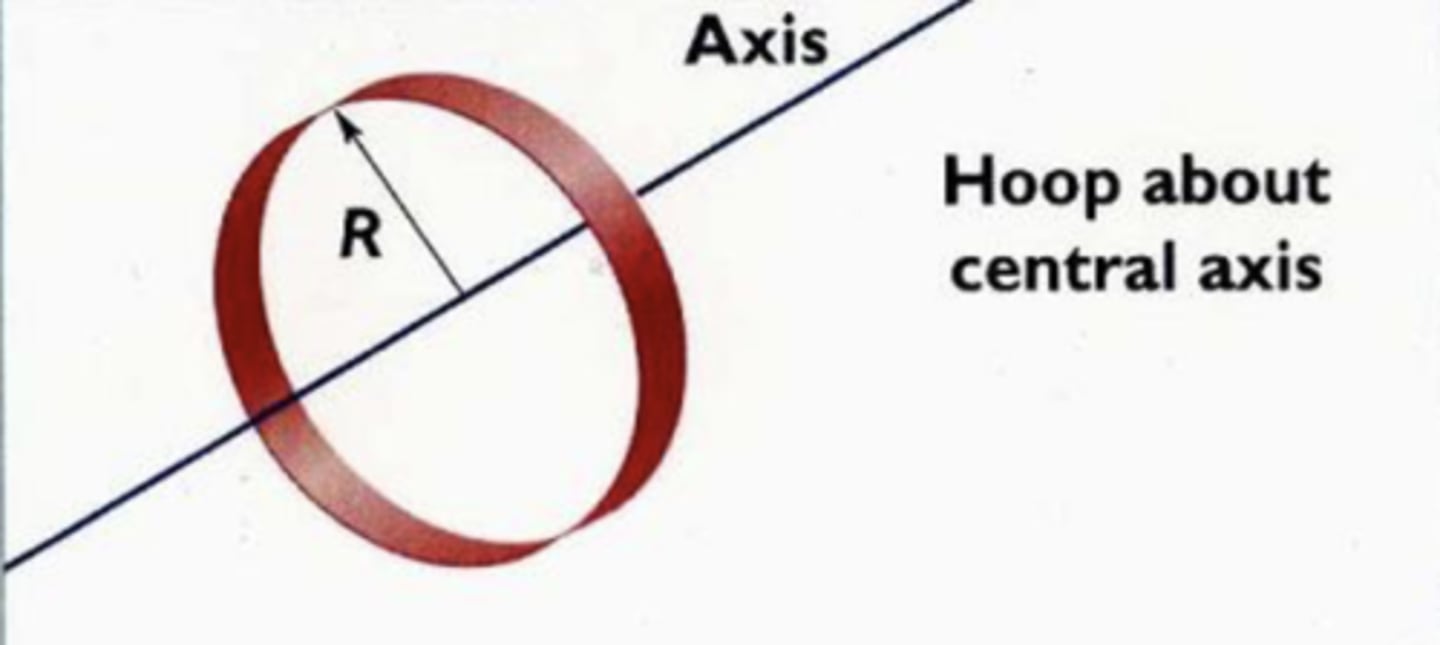
I = MR^2
2
New cards
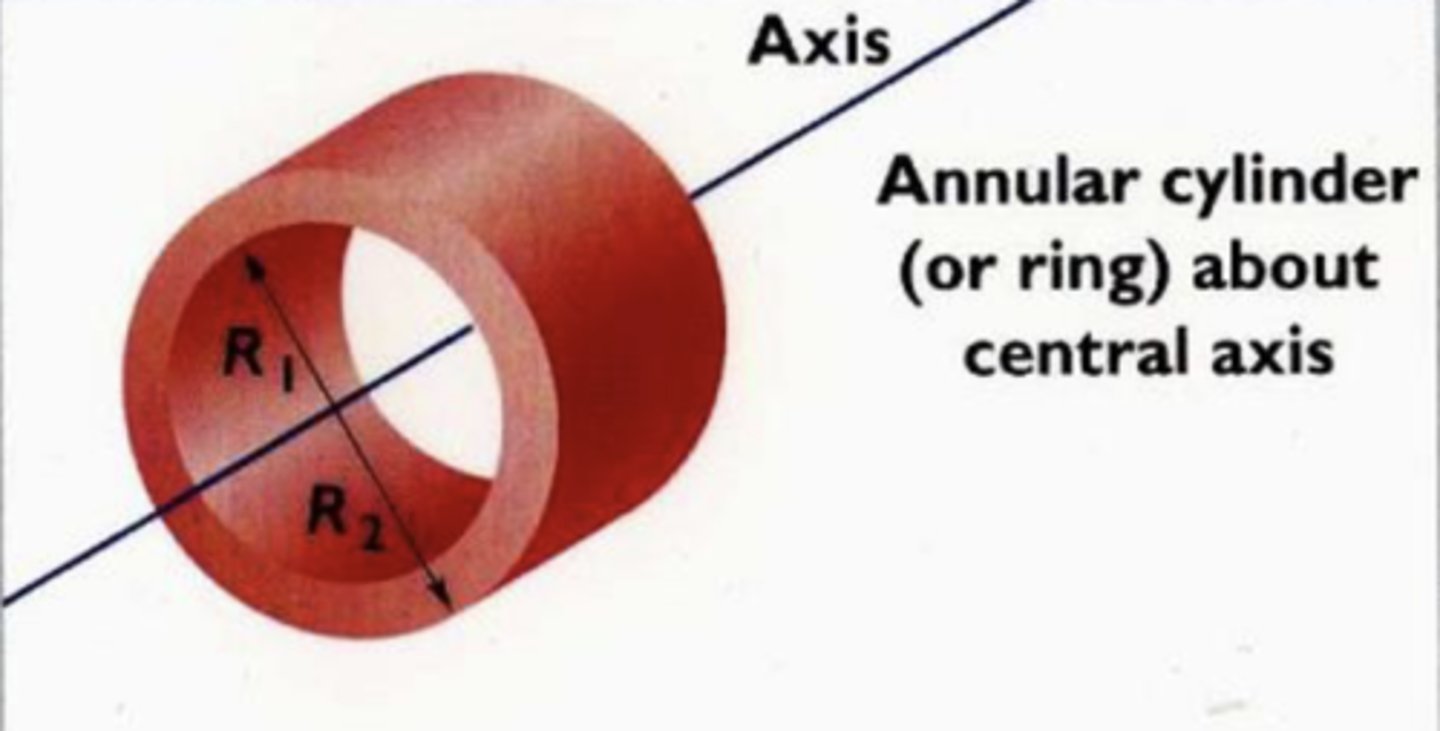
I = 1/2M(R1^2 + R2^2)
3
New cards
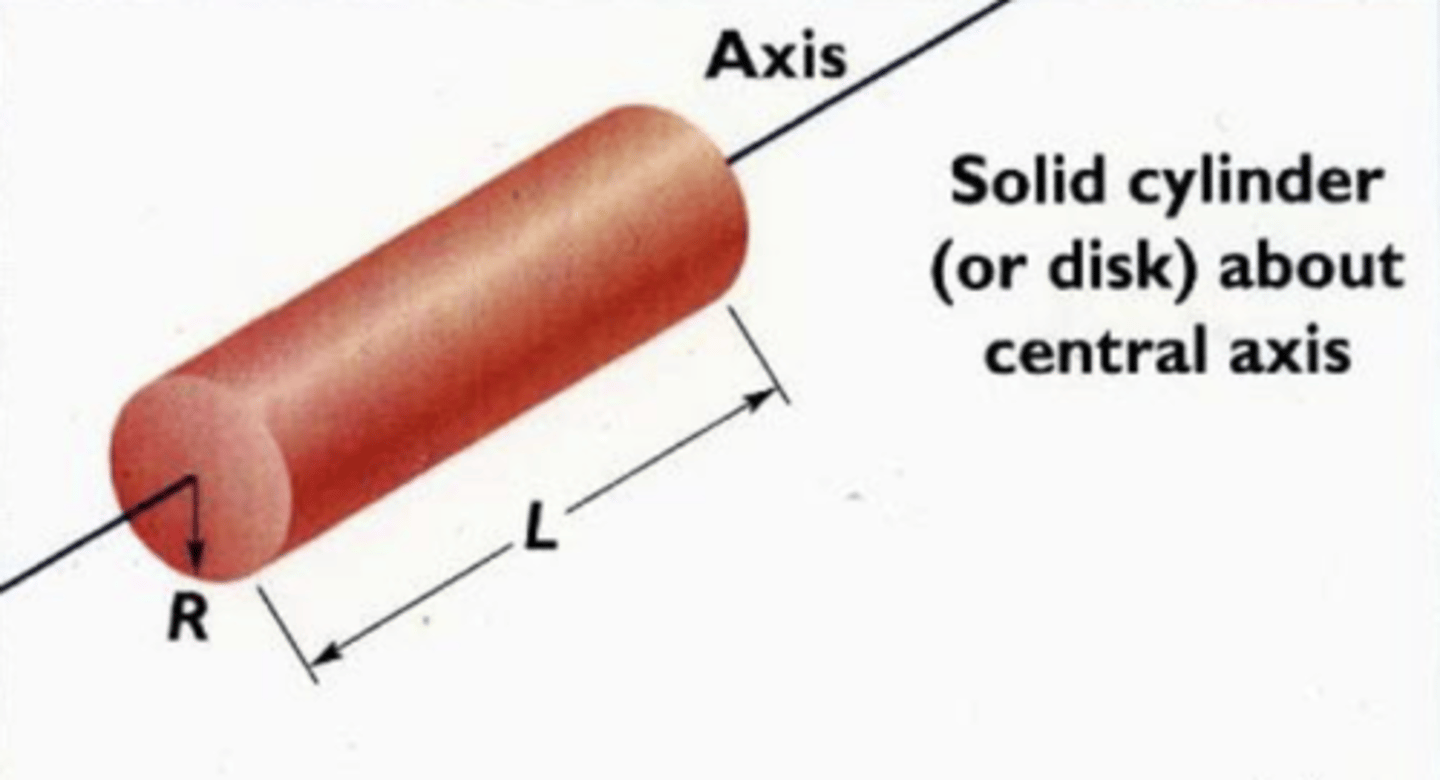
I = 1/2MR^2
(remember, this can include thin cylinders - ex. if a bike wheel is solid)
4
New cards
I = 1/4MR^2 + 1/12ML^2
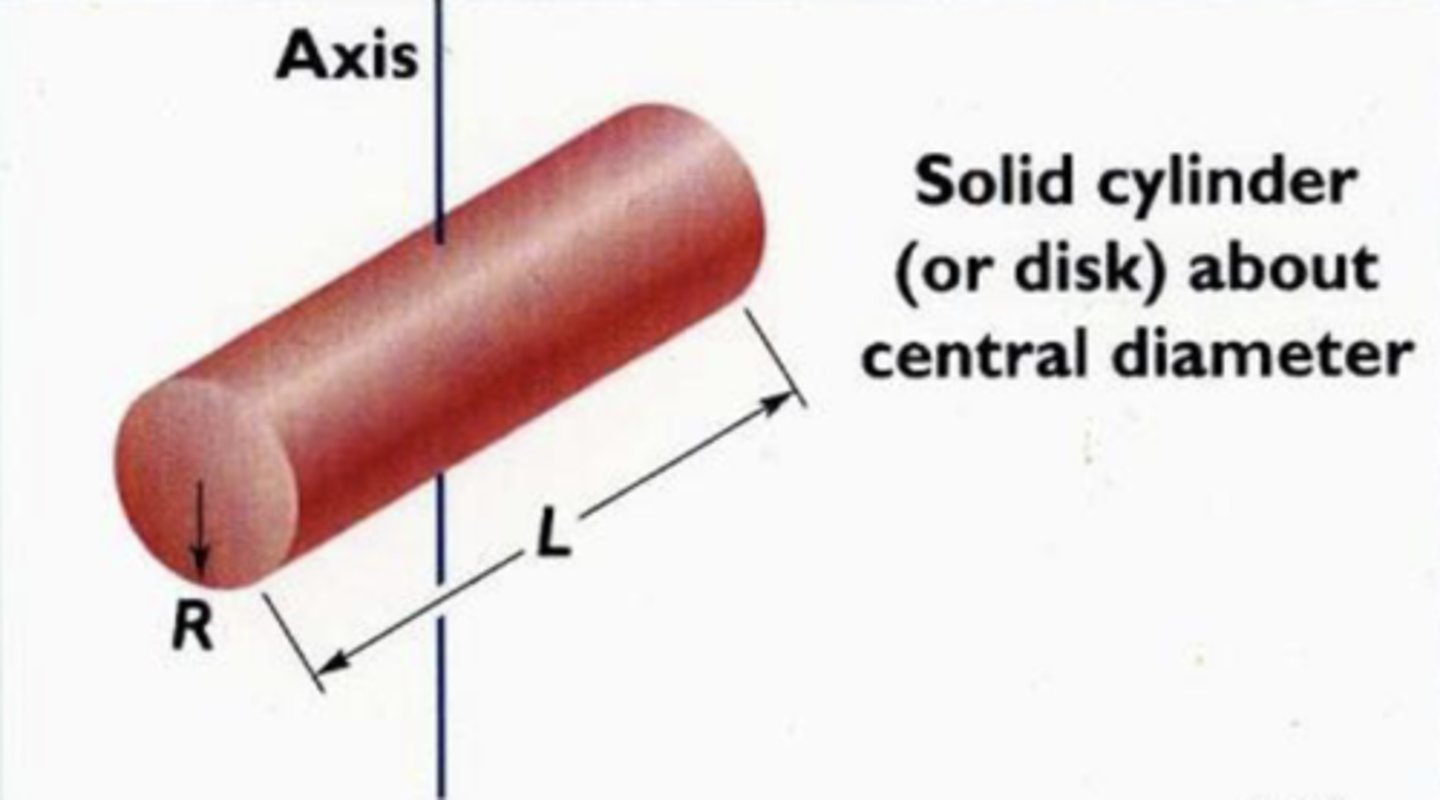
5
New cards
I = 1/12ML^2
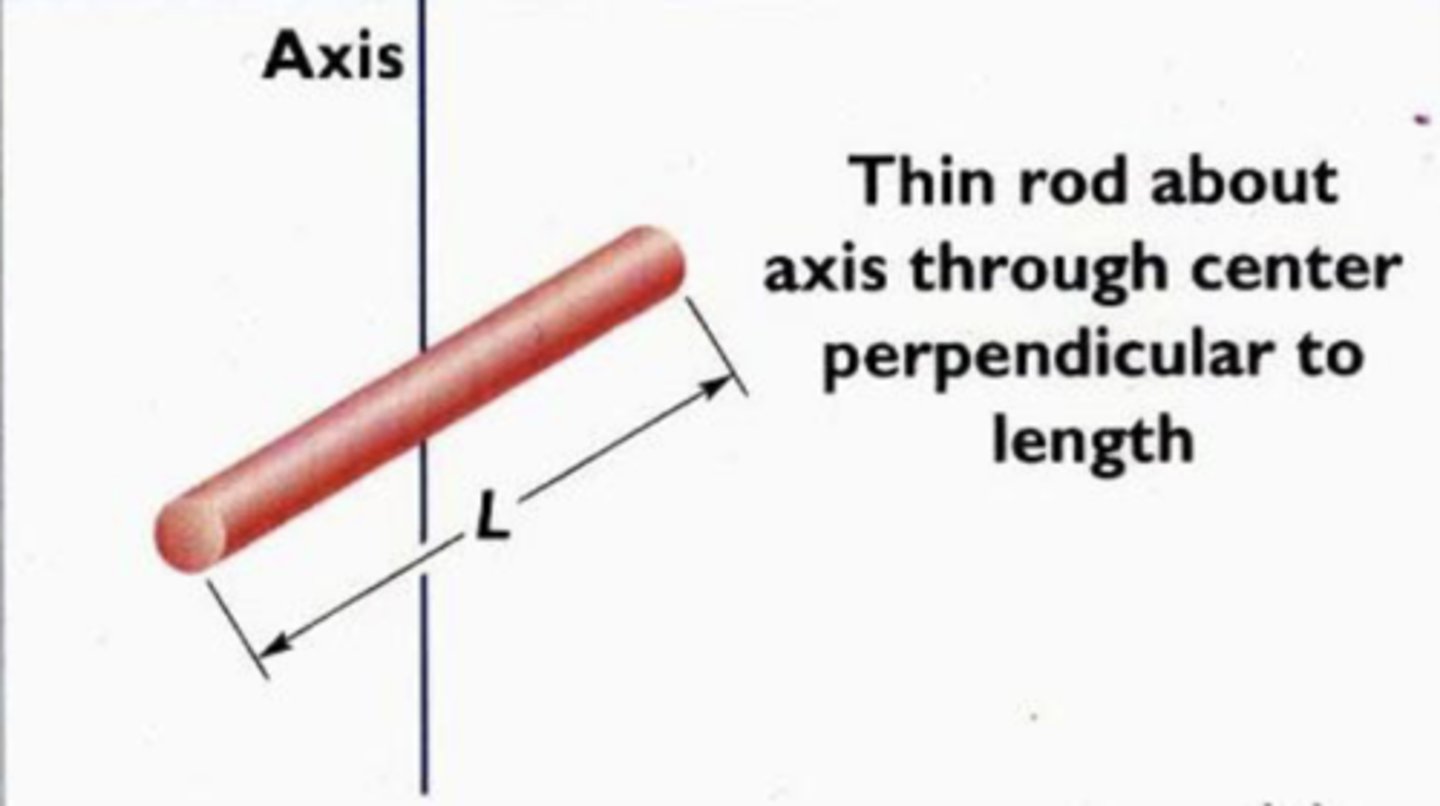
6
New cards
I = 2/5MR^2

7
New cards
I = 2/3MR^2
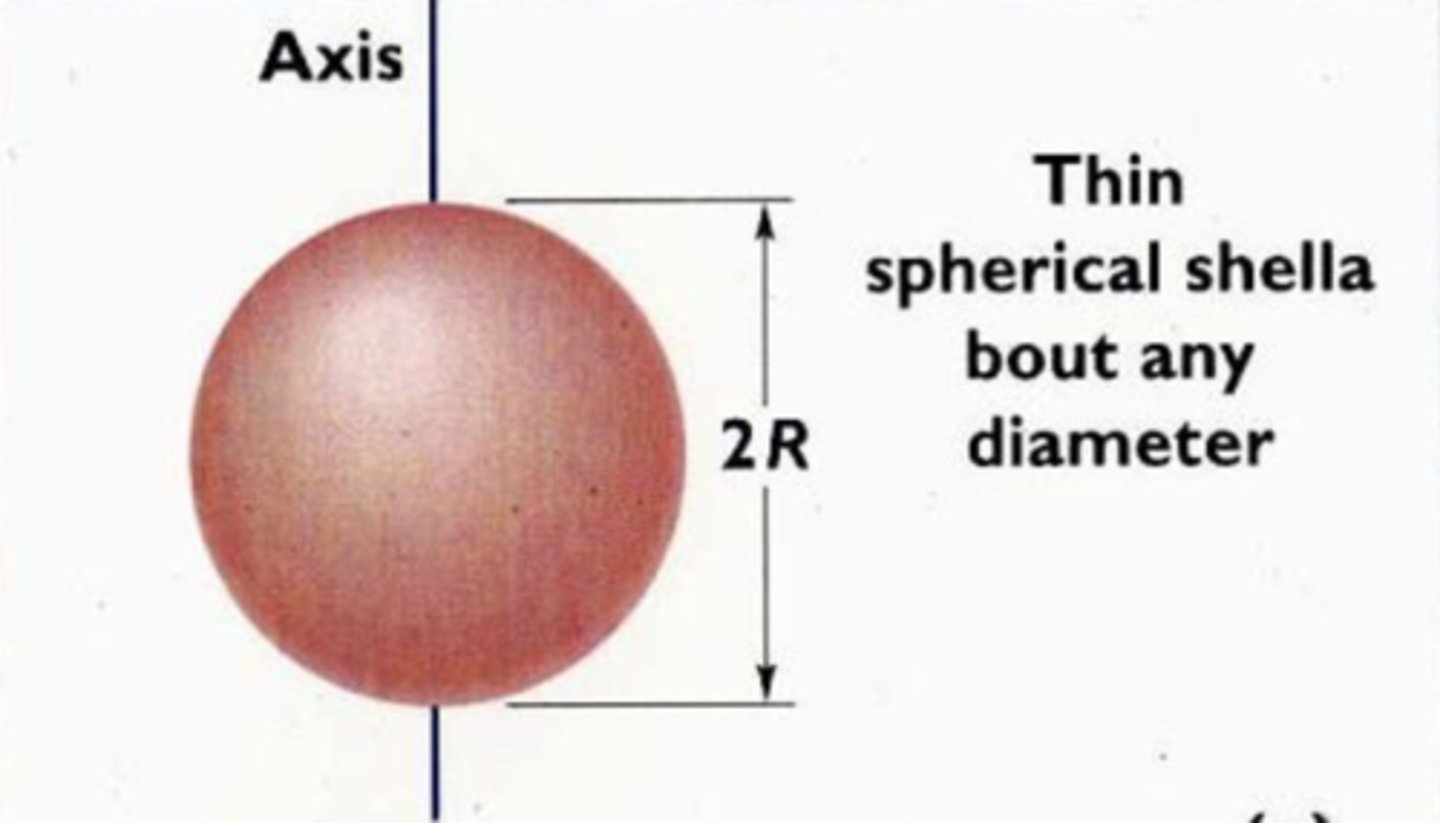
8
New cards
I = 1/2MR^2
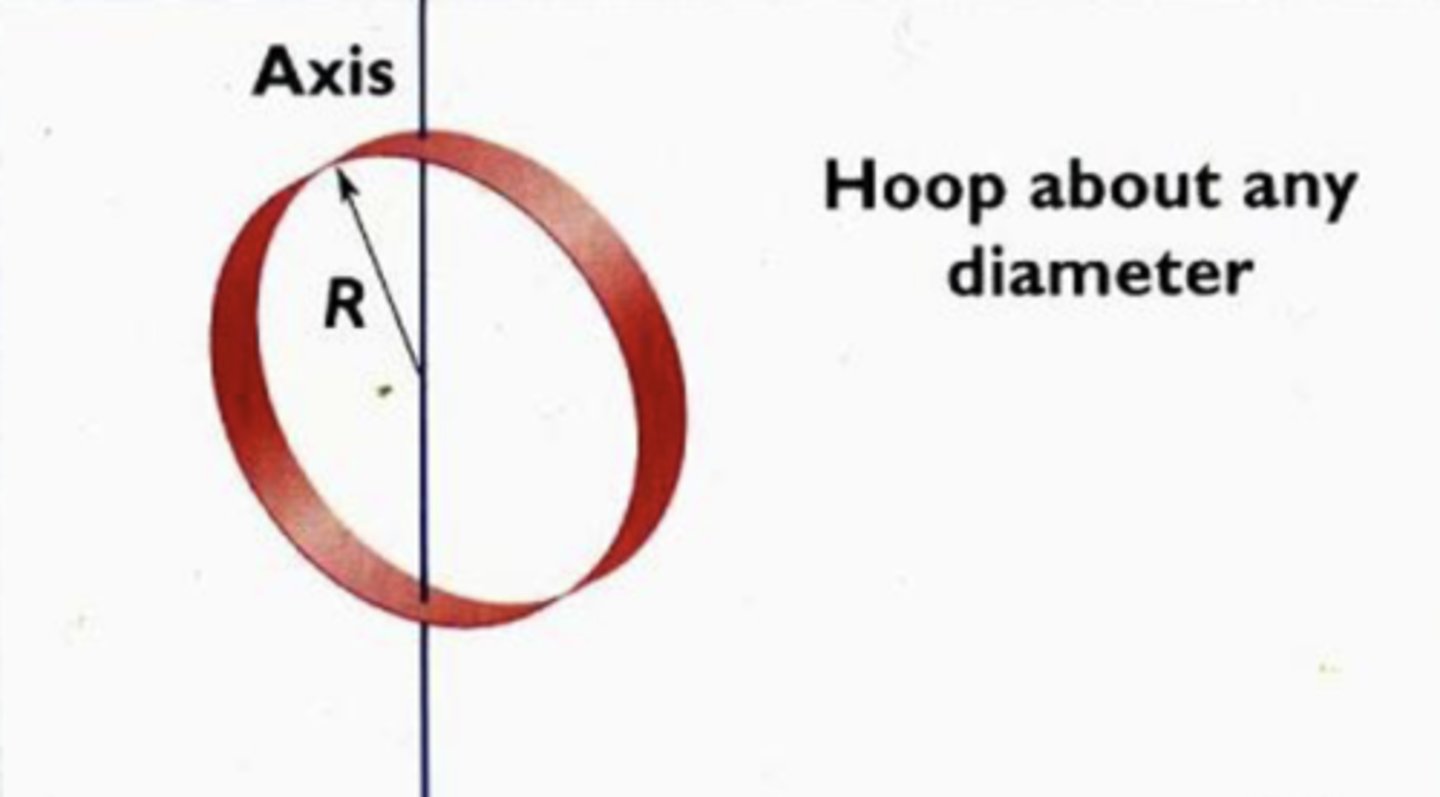
9
New cards
I = 1/12M(a^2+b^2)
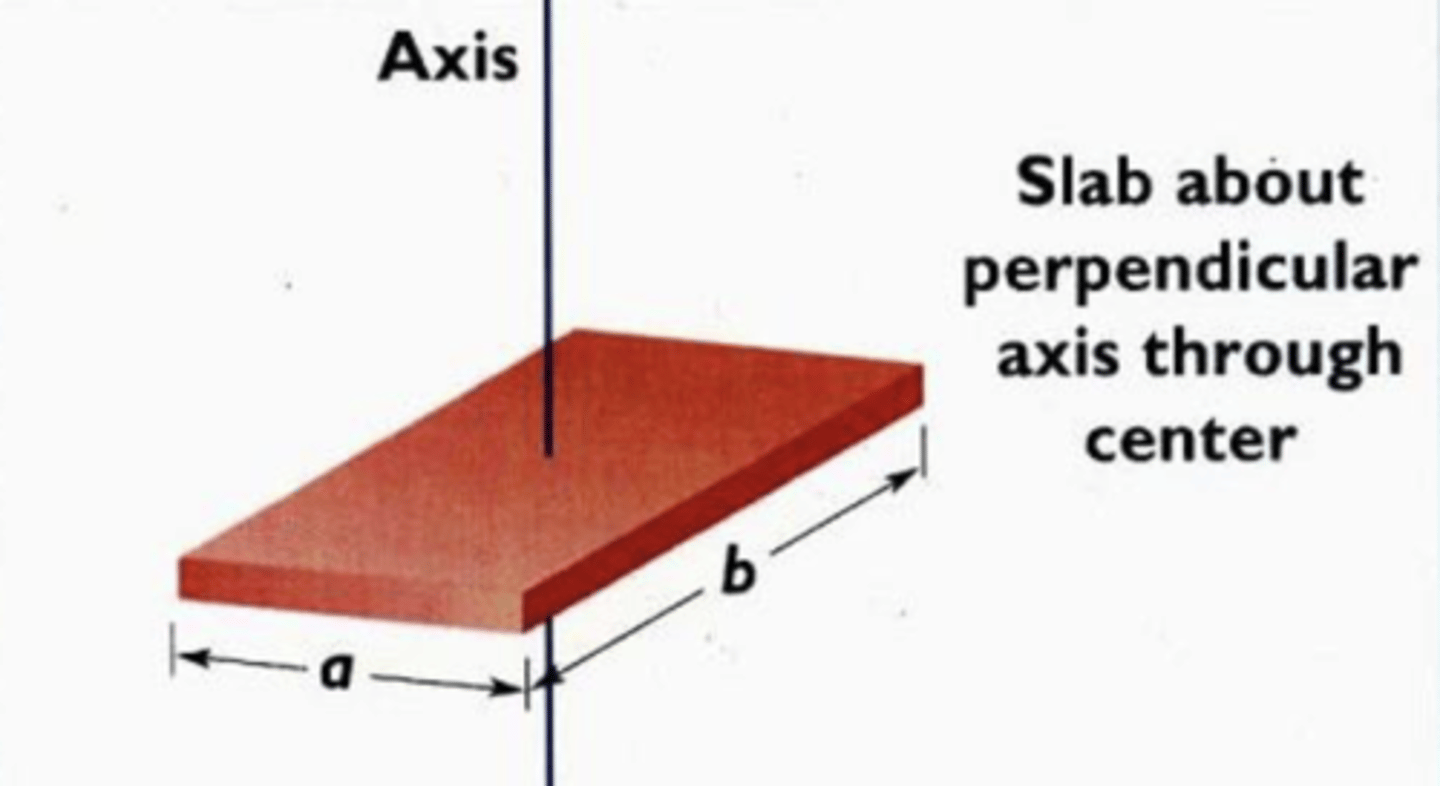
10
New cards
I=∫𝑟^2𝑑𝑚
When the object is not of uniform mass
11
New cards
𝐼=𝐼𝑐𝑚+𝑚H^2
Parallel Axis Theorem - Use when the axis of rotation is not in the center