Skin & Soft Tissue Infections:
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What organism is suspected in purulent SSTI? Non-purulent SSTI?
Purulent: Staph aureus
Nonpurulent: Usually strep but can be staph
What patients should you consider for getting a culture in SSTI?
Necrotizing infection or patients with persistent, recurrent fever and neutropenia
In a previously healthy patient, what are the likely organisms? How is this differing among people who inject drugs? History of diabetes?
Prev healthy: CA-MRSA, MSSA, GAS
Inject: CA-MRSA, MSSA, GAS, Gram (-), Anaerobes
Diabetics: P. aeruginosa, HA-MRSA, MSSA, Gram (-)
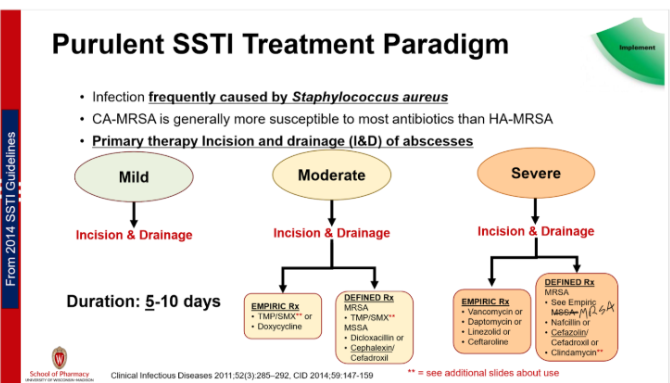
What makes mild, moderate, and severe SSTI different?
Mild: Typical infx, systemic sx absent
Moderate: Typical infx, systemic sx present
Severe: Systemic and severe sx present, failed oral therapy
Does a mild purulent SSTI require antibiotics?
No only incision and drainage
What are the empiric regimens for Moderate and Severe purulent SSTI? What patient / infection factors might be present where an option may not be ideal
Moderate: Bactrim* or Doxycycline
Severe: Vanco, Dapto, Linezolid, or Ceftaroline
**Bactrim should always be combined with incision and drainage- DO NOT USE if incision can't be drained
Should we use Clindamycin for MRSA?
Clinfamycin not recommended for MRSA, not first line for MSSA, due to inducible resistance
How long do you treat purulent SSTI?
5-10 days (shorter the better)
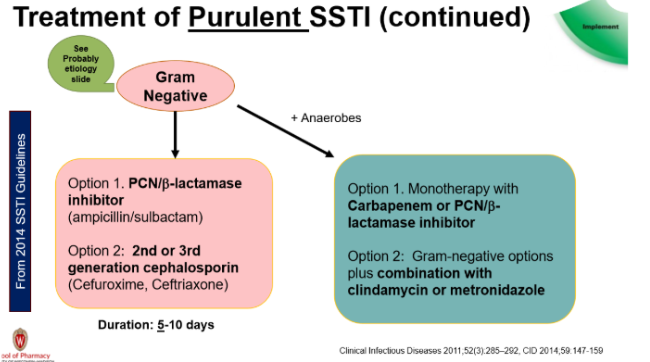
If there is a risk of Gram-negative +/- anaerobe purulent SSTI, what antibiotics should be used?
PCN/B-lactamase inhibitor (ex: Amp/Sulbactam) OR
2nd/3rd gen Cephalosporin (ex: Cefuroxime, Ceftriaxone) → only once daily dosing easier for pt
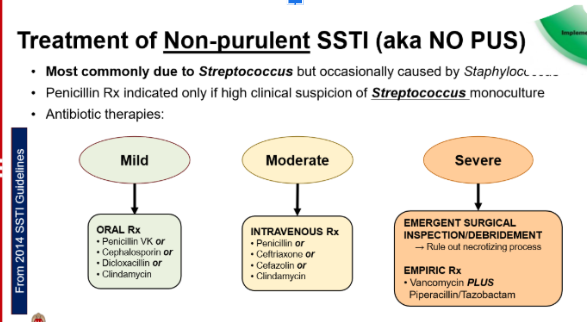
Does a mild non-purulent SSTI require antibiotics?
Yes - options are
PCN → if highly suspect strep as cause
Cephalosporin → once daily dosing easiest for pt
Dicloxacillin
Clindamycin
What are the empiric regimens for non-purulent SSTI based on severity? What patient / infection factors might be present where an option may not be ideal?
Mild: PO- Penicillin, Cephalosporin, Dicloxacillin or Clindaymycin
Moderate: IV- Penicllin, Ceftriazone, Cefazolin, Clindamycin
Severe: emergency surgery+ Vanco+ Pip/tazo
For necrotizing infections, what are the organisms involved in monomicrobial infections? What are the treatments? Why use clindamycin?
Strep pyogenes and Clostridial sp
Txt with PCN + Clinda
Clinda reduces release of toxins
For necrotizing infections, what are the organisms involved in polymicrobial infection? What is the antibiotic regimen?
Txt with Vanco + Pip/Tazo
What is the organism is most found in lymphangitis? What is the initial and step-down therapy?
S. pyogenes
Initial: IV PCN-G 1-2 million units q4-6 hrs for 2-3 days
Step-down: PO PCN-V for 10 days total
If PCN allergy use clinda
What is the causative organism in erysipelas? How are treatments for mild and severe different? B-hemolytic strep (GAS)
B-hemolytic strep (usually GAS)
Mild: PO PCN-V or Amox for 7-10 days
If PCN allergy use cephalexin, clinda, or erythro
Severe: IV PCN-G 2-8 MU daily
What are the organisms that cause impetigo? When do you consider topical vs oral therapy? What do you use for treatment?
Strep pyogenes and Staph aureus
Topical for mild → Mupirocin or Retapumulin for 5 days
Oral for more severe (multiple lesions/outbreak) → Dicloxacillin or Cephalexin for 7 days
If culture is only S. pyogenes → PCN for 7 days
If PCN allergy use cephalexin