aggregate demand
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
aggregate demand
The total demand for the goods and services of a nation at a given price level and time period.
aggregate demand is equal to consumption + investment + government spending + net exports, which is equal to GDP using the expenditure method
= C+I+G+(X-M)
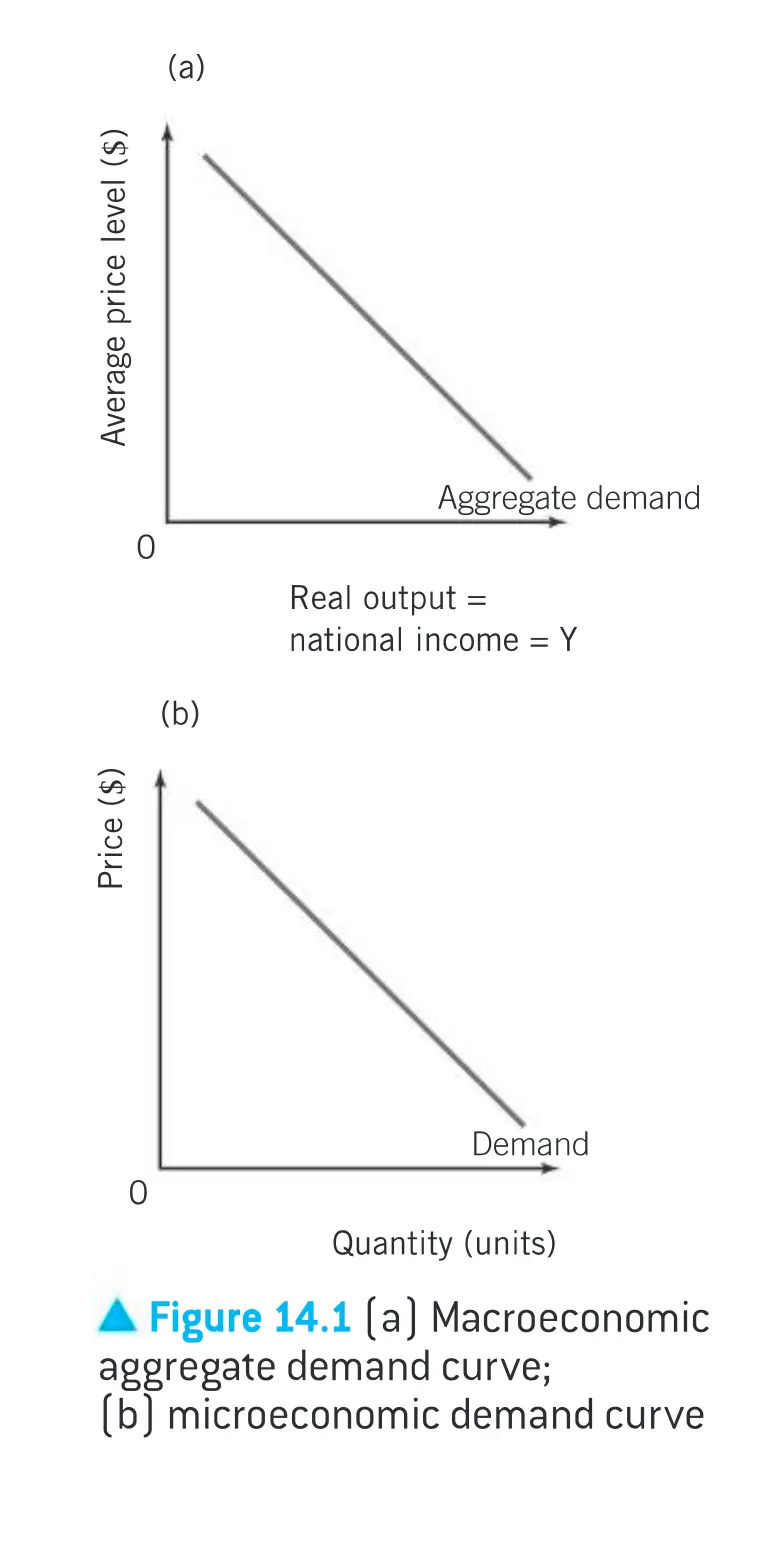
AD curve
AD curve shows the inverse relationship between the average price level and the total real output demanded → at a lower average price level, a higher quantity is demanded (Law of Demand on an aggregate level)
aggregate means total
when constructing an aggregate demand curve, we look at the demand from all possible sectors within the economy
consumption
the total spending by consumers on domestic goods and services → durable goods and non durable goods
durable goods are goods such as cars and phones that are used by consumers over a period of time (usually more than one year)
non-durable goods are goods such as rice and toilet paper that are used up immediately or over a relatively short period of time
investment
defined as the addition of capital stock to the economy
carried out by firms → two main types
replacement investment → occurs when firms spend on capital in order to maintain the productivity of their existing capital
induced investment → occurs when firms spend on capital to increase their output to respond to higher demand in the economy
the economy’s capital stock includes all goods that are made by people and are used to produce other goods or services, such as factories, machines, offices or computers
government spending
governments at a variety of levels spend on a wide variety of goods and services such as health, education, law and order, transport, social security, housing and defence
the amount of government spending depends on the policies and objectives of the government
exports
domestic goods and services that are bought by foreigners. When the firms in a country sell exports to foreigners, it results in an inflow of export revenues to the country
imports
goods and services that are bought from foreign producers. When imports are bought it results in an outflow of import expenditure.
net exports
the net trade component of AD is actually export revenues minus import expenditure
positive: whereby export revenues exceed import expenditure
negative: whereby import expenditure exceeds export revenues
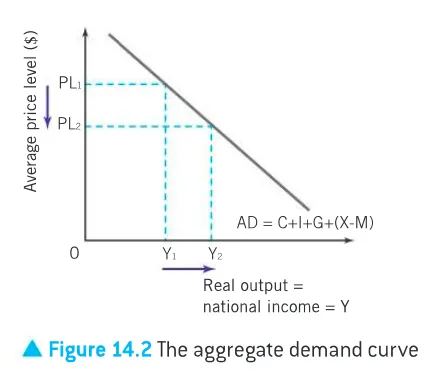
shift along AD curve
when the average price level in the economy falls from PL1 to PL2, the level of output demanded by consumers (C) plus firms (I) plus governments (G) and the net foreign sector (X-M) increases from Y1 to Y2
income effect allows consumers to spend more
factors of consumption
change in income taxes
change in interest rates
change in consumer expectations/ confidence
change in wealth
lack of household incomes
changes in income taxes
most significant determinant of consumption is income
as incomes rise people have more money to spend on goods and services, so consumption increases
if there is an increase in direct income taxes (the taxes paid on income by individuals), then people will have less disposable income
the income the people have remaining for spending and saving after income taxes have been paid
change in interest rates
spending on non-durable goods is carried out with the day-to-day money that people earn (their income)
but some of that money that is used to buy durable goods comes from money which people borrow from the bank
when people borrow money they must pay interest to the bank
if there is an increase in interest rates (price of borrowed money) then there is likely to be less borrowing (as it is more expensive). Therefore consumption will fall, resulting in a fall in AD
a rise in interest rates makes saving more attractive → people would prefer to put their extra income in the bank to earn money rather than spend it on goods and services
wealth
defined as the net worth of an individual or a household including the value of all its assets minus all its liabilities.
household assets include
financial assets: value of money in savings or retirement
real assets: value of a house or stock in companies
change in house prices: when house prices increase across the economy, consumers feel more wealthy and are likely to feel confident enough to increase their consumption by saving less or borrowing more
change in the value of stocks and shares: many consumers hold shares in companies. If the value of those shares increases then people feel wealthier. This might encourage them to spend more. Or they might sell those shares and then use the earnings to increase consumption
change in consumer confidence/ expectations
if consumers are optimistic about their economic future, then they are likely to spend more now
likely to get a promotion due to a booming economy and strong sales
economists regularly measure consumer confidence and put the information together in the form of a consumer confidence index
consumer expectations regarding the future price level will also affect consumption
If consumers expect the price level to increase in the future, ie inflation, then they will increase consumption now, especially on durable consumer goods.
household debt
Household debt is the amount of money owed by a household to lenders, including consumer debt accrued through the use of credit cards or by borrowing from a bank to finance consumption of durable goods.
In the short run, an increase in consumer debt allows households to increase consumption at each level of household income.
But in the long run, debts must be paid back, which is only achieved through reductions in future consumption as household income must go towards repaying past debts.
changes in investment
changes in interest rates
changes in business taxes
technological change
changes in business confidence/ expectations
levels of corporate indebtedness
changes in interest rates
in order to invest, firms need money. The money that firms use for investment comes from several sources.
ex: retained profits or borrowing money
If the money is to be borrowed, then an increase in the cost of borrowing may lead to a fall in investment. If interest rates are high, then firms may prefer to put their retained profits in the bank to earn higher returns as savings, rather than use
them to invest.
changes in business taxes
If the government increases taxes on business profits, then it will reduce post-tax profits, which will mean that firms have less money to invest and so we would expect to see a fall in AD.
In the same way, if the government was to lower taxes on business profits, then more investment could take place and there would be an increase in AD,
ie a shift of the AD curve to the right.
technological change
In order to keep up with advances in technology and to remain competitive firms will need to invest. This will increase AD.
changes in business confidence/expectations
If businesses are very confident about the future of the economy and expect consumer demand to rise then they will want to be ready to meet the increases in consumer demand by investing to increase potential output and productivity.
Levels of corporate indebtedness
The extent to which businesses are willing and able to borrow money affects investment. If it is easy to borrow money (easy credit) and interest rates are low then it is likely that businesses will take on more debt and investment will rise.
government spending
depends on the political and economic priorities of the government
rises: when the gov has made a commitment to financially support a given industry, when gov is obliged to correct the market failure, a new education/health policy
rises → AD shift right
falls → AD shift left
trade surplus
a positive (X-M), a trade surplus, will lead to AD shifting right
trade deficit
a negative (X-M), a trade deficit, will shift AD left
changes in level of exports
changes in foreign countries income → If foreign incomes rise, then their consumption of imported goods will rise.
changes in the value of a country’s currency (its exchange rate) → if a country’s exchange rate becomes stronger, then this makes the country’s exports relatively more expensive to foreigners. According to the Law of Demand, this will cause the quantity of exports to fall → affects export revenues
changes in countries’ trade policies → if a country decides to adopt a policy of more liberalised (free) trade, then it may reduce the tariffs that it charges on imports (goods coming in) and allow countries to export more to that country
changes in level of imports
as people consume more goods, some of these goods will be imported
as national income rises, so does spending on imports + if national income falls, there will be reduced spending on imports