Psychoactive Substances CH 3
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Neuraxis
an imaginary line draw through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom of the spinal cord to the front of the forebrain
Anterior
Near/towards the head
Posterior
Near/towards the tail/feet
Rostral
another word for anterior
toward the front of the face
“toward the beak”
Caudal
another word for posterior
away from the front of the face
“toward the tail”
Dorsal
toward the back or top of the head
Ventral
toward the belly
toward the bottom of the skull of the front surface of the body
lateral
away from the middle
toward the side of the body
medial
closer to the middle
toward the middle of the body
ipsilateral
refers to structures on the same side of the body
contralateral
refers to structures on opposite sides of the body
Cross section
with respect to the CNS, a slice taken at right angles to the neuraxis
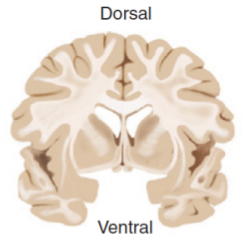
Frontal/coronal section
a slice through the brain parallel to the forehead
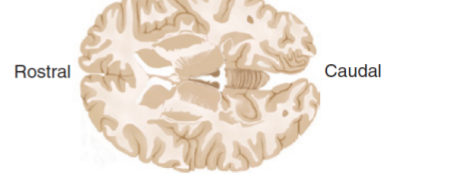
Horizontal/transverse section
a slice through the brain parallel to the ground
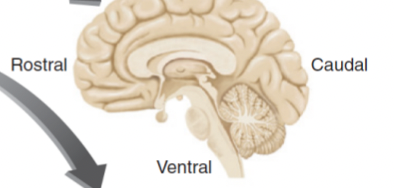
sagittal section
a slice through the brain parallel to the neuraxis and perpendicular to the ground
divides the brain into left and right sections
midsagittal plane
the plane through the neuraxis perpendicular to the ground
divides the brain into 2 symmetrical halves
Describe the essential blood supply in the brain
brain gets 20% of blood flow
brain cannot store energy
needs oxygen to extract energy
disruption of blood flow results in unconsciousness in 6 seconds
What makes up the central nervous system (CNS)?
Brain and spinal cord
What makes up the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Nerves and peripheral ganglia
describe the meninges in the PNS
dura mater and pia mater fuse
no arachnoid membrane space
meninges
the 3 layers of tissue that encase the CNS:
dura mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
dura mater
outermost layer of meninges
tough and flexible
arachnoid membrane
the middle layer of the meninges
located between the dura mater and pia mater
pia mater
the inner most later of meninges that clings to the surface of the brain
thin and delicate
subarachnoid space
the fluid-filled space that cushions the brain
located between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
a clear fluid, similar to blood plasma
fills the ventricular system of the brain and the subarachnoid space surrounding the brain and spinal cord
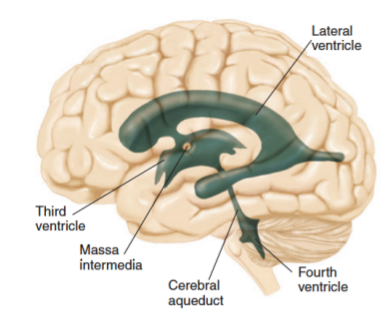
ventricle
one of the hollow spaces within the brain
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
lateral ventricle
one of the 2 ventricles located in the center of the telencephalon
third ventricle
the ventricle located in the center of the diencephalon
massa intermedia
bridge of neural tissue through the 3rd ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
a narrow tube interconnecting the third and fourth ventricles of the brain
located in the center of the mesencephalon
fourth ventricle
the ventricle within the center of the metencephalon (between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons)
choroid plexus
the highly vascular tissue that protrudes into the ventricles
produces cerebrospinal fluid
about 125 mL with a ½ life of 3 hours
reabsorbes CSF into the blood stream
What ventricle(s) make up the forebrain?
lateral and third ventricles
What makes up the telencephalon subdivision of the lateral ventricle?
cerebral cortex
basal ganglia
limbic system
What makes up the diencephalon subdivision of the third ventricle?
thalamus and hypothalamus
What ventricle(s) make up the midbrain?
cerebral aqueduct
What makes up the mesencephalon subdivision of the cerebral aqueduct?
tectum and tegmentum
What ventricle(s) make up the hindbrain?
fourth ventricle
What makes up the metencephalon subdivision of the fourth ventricle?
cerebellum and pons
What makes up the myelenceohalon subdivision of the hindbrain?
medulla oblongata
cerebral cortex
the outermost layer of gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres
3 mm thick
corrected for body size
it is largest in humans than any other species
develops from the inside out
apoptosis
death of a cell caused by a chemical signal that activates a genetic mechanism inside the cell
neurogenesis
the production of new neurons
occurs in the adult brain
demonstrated in the olfactory bulb and hippocampus
sulci
small grooves
the valley between mountains
fissure
large groove/sulci
gyri
raised ridges
the mountains between valleys
longitudinal fissure
divides the left and right hemispheres
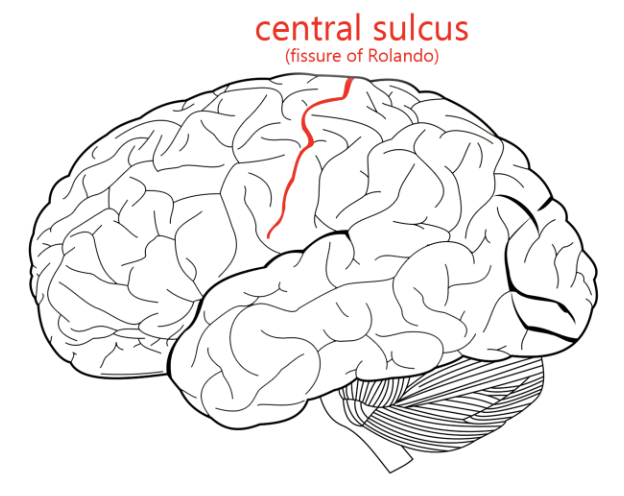
central sulcus
separates the frontal and parietal lobes
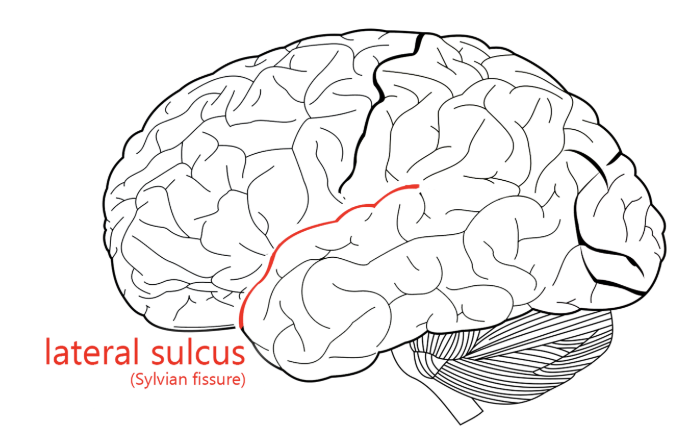
lateral sulcus/fissure (AKA Sylvian fissure)
divides the frontal and parietal lobes superiorly from the temporal lobe inferiorly
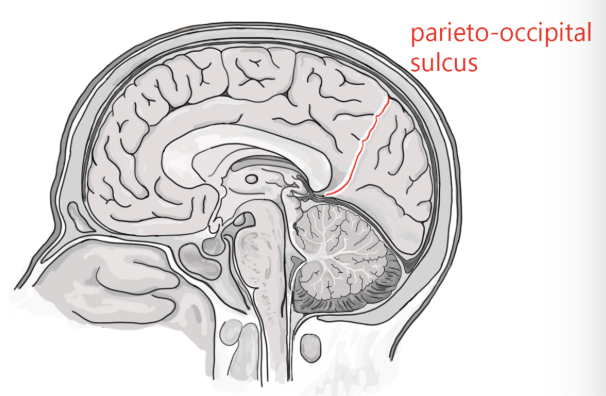
parieto-occupital sulcus
separates the parietal and occipital lobe
Describe the geography of the frontal lobe
largest of all lobes
ends at the coronal sulcus
What is within the frontal lobe?
motor cortex (most posterior part) → controls voluntary movement
anterior cingulate cortex - default mode network (DMN) - posterior cingulate cortex
What are the functions of the frontal lobe?
decision making
future-planning
personality
judgement
motor movement
impulse control
Describe the default mode network (DMN)
where your personality is stored
this area lights up when you describe yourself as an addict
when you are hallucinating, you imagine who you are and start to build new connections (neural plasticity)
when you exit this state, you are a new person
What are the functions of the parietal lobe?
Spacial awareness, etc.
What are the functions of the temporal lobe?
auditory processing, memory formation, etc.
What are the functions of the occipital lobe?
visual processing
What are the structures of the limbic system?
limbic cortex
hippocampus
amygdala
fornix
mammillary bodies
What is the function of the limbic system?
Emotion processing
Describe the Basal Ganglia
subcortical nuclei involved in movement
responsible for involuntary movements/reflexes
develop reflexes from habitual voluntary movement to free up space in the motor cortex
compulsive behaviors live here
Define compulsive
consistent habitual habits without control
Describe the thalamus
relays all senses EXCEPT olfactory
psychedelics can disrupt this, causing hallucinations
What are the functions of the hypothalamus?
regulate autonomic nervous system
regulates endocrine system by releasing hormones
biological drive structure
feeding, fighting, fleeing, fornicating
regulates food/water intake
temperature regulation
sex drive
How does MDMA/ecstasy affect the hypothalamus?
tells the brain region that you’re super hot
makes one super horny
makes one feel super thirsty
How does THC affect the hypothalamus?
increases appetite
How does cocaine/amphetamines/methamphetamines affect the hypothalamus?
appetite suppresent
All substances that have abuse potential activates which area?
The tegmentum of the hindbrain
Describe the ventral tegmental area (VTA)
a cluster of nuclei that projects to the nucleus accumbens
this area is very active when one is abusing substances and dopamine neurons are activated
reinforces the removal of pain (negative reinforcement)
What would happen if you were to lesion/ablation the VTA in a rat study were they are addicted to some drug?
the rat would no longer eat, drink, have sex, etc. because there is no reward
no motivation without reward
Nucleus accumbens
reward center
What are the functions of the cerebellum?
standing
walking
coordinated movements
balance
refinement center
equilibrium
What is an example of a drug disrupting the neural activity of the cerebellum?
Stumbling on alcohol
How does IPSP drugs affect motor movement?
It causes a breakdown, leading to decreased motor control
How does EPSP drugs affect motor movement?
It causes an enhancement, leading to increased motor control
Describe the function of the pons
involved in alertness/enrichment
controls the circadian rhythm (sleep and arousal)
controls light sensitivity
What happens to the pons while on a psychoactive substance (specifically amphetamines for example0?
disregulates norepinephrine response
norepinephrine release in the dense nuclei increases indirectly
Describe the functions of the medulla oblongata
regulates the autonomic nervous system and skeletal muscle
controls vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, etc
where the declaration of death is determined
What happens when you take 2 drugs of the same class (ex: sleeping pills and alcohol [2 CNS depressants])?
the synergistic affects will enhance each other
shuts down the medulla oblongata
doesn’t matter if it is an EPSP drug and an IPSP drug