Chapter 9 Study Guide
1/91
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbial Nutrition and Growth Lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What is Nutrition?
It’s the process by which chemical substances called nutrients are acquired from the environment and used in cell metabolism and growth
What is Essential Nutrient?
a nutrient that must be provided to an organism through food or enviornment
What are the nutrients for microbes?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
What are MACRO nutrients?
they are required in large quantities, play principal roles in cell structure and
metabolism.
What are MICRO nutrients?
they are trace elements, needed in small amounts, help with enzyme and protein structure
What are 3 Sources that nutrients can come from?
organic sources, inorganic sources, or a combination
Parasites get nutrition from???
a host
Cell Composition: Water
70% of cell weight, most abundant of all components
Cell composition: Proteins
next most prevalent compound
96% of dry cell weight is composed of what?
CHONPS elements (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur)
2 carbon sources?
heterotrophs, autotrophs
Heterotrophs
organism that gets its carbon in an organic form.
· Pseudomonas spp. can metabolize more than 100 different substrates
· Heterotrophs can be highly variable.
Autotrophs
organisms that uses inorganic CO2 as its carbon source
· "self-feeder"
· Algae, many archaea are autotrophs
Most nitrogen on earth is in the atmosphere as N2, but this is inaccessible to
most organisms and must be transformed.
Some bacteria and algae can utilize inorganic nitrogen such as
NO3- NO2- NH3
What is nitrogen fixation
bacteria converts N2 into compounds that can be used by other organisms
components of organic compounds
major role in structural and enzymatic functions of the cell
Oxygen and Hydrogen
Hydrogen helps/serves
Serve as a source of free energy in oxidation- reduction reactions (involved in cellular respiration)
. Maintain pH, Form hydrogen bonds
Main inorganic source of phosphorus is
phosphate- found in phosphoric acid,
phosphate is a major component of many rocks and mineral deposits
Phosphate is a key component of nucleic acids.
Corynebacterium can store phosphate in
metachromatic granules
Sulfur is widely distributed in minerals, often in the form of
sulfate (SO42-)and sulfides (FeS, H2S),
Potassium
essential to protein synthesis and membrane function
used in cell transport
sodium
Calcium- What it’s for
stabilizes cell wall and endospores in bacteria
Magnesium- what it’s for
component of chlorophyll and stabilizes membranes and ribosomes.
Iron- what it’s for
used in cytochrome proteins used in cellular respiration
Zinc- what it’s for
necessary for eukaryotic gene regulation
What are the 3 nutritional types?
Photoautotrophs
Chemoautotrophs
Chemoheterotrophs
Photoautotrophs
- organisms that photosynthesize
· Algae, cyanobacteria
Chemoautotrophs
organisms that gain energy from chemical reactions involving simple chemicals in the environment.
inorganic chemicals———> energy
· Methanogens
Chemoheterotrophs
- derive carbon and energy from organic compounds.
· Some use aerobic respiration- using oxygen to break down organic compounds.
Extremophiles live in
"extreme" environments- cold, hot, salty, full of generally toxic environments
Hyperthermophiles
live in high-heat environments
This is used in PCR reactions
Thermophile DNA polymerase
Cell membrane
allows nutrients and waste to move across it selectively.
Diffusion
the natural tendency of molecules to move across a gradient.
Diffusion across the membrane is determined by the
concentration gradient and permeability of the substance.
Osmosis
the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane.
Hypotonic Solution
ex: salt concentration INSIDE the cell is HIGHER than the salt concentration OUTSIDE the cell (water will diffuse into the cell due to higher concentration, causing CELL LYSIS)
Isotonic solution
same amount of salute inside and outside the cell
(salt example: same salt concentration in and out)
Hypertonic solution
salt example: too much salt outside, not enough water inside (causing a shriveled cell)
Facilitated diffusion
- transport that utilizes a carrier proteins that binds to a specific substance.
Carrier proteins
they only bind to one or a few molecule types.
The transport of a substance is limited by the number of binding sites on the cell membrane is called
saturation
when two molecules can bind the same carrier protein, they compete- molecules
with the greater affinity to the carrier or molecules with greater concentration gradient will be transported for quickly into the cell. what is the term for this?
Competition
Active Transport-What is it?
Transport nutrients across the diffusion gradient or faster than diffusion allows
What requires presence of specific membrane proteins?
Active Transport
Active Transport requires…
the expenditure of energy
This process couples the transport of a nutrient with its conversion to a substance that is immediately useful inside the cell.
Group Translocation
Endocytosis
A form of active transport to bring in large molecules, particles, or liquids.
Phagocytosis
when cells ingest other cells or large solid matter
Pinocytosis
the endocytosis of liquids such as oils or solutions
Do you think medical grade saline is an isotonic, hypertonic or hypotonic solution?
Isotonic-Isotonic solutions have the same concentration of solutes as body fluids, meaning they don't cause cells to swell or shrink when introduced into the body
Microbes are unable to control their internal temperature so they must to able to
live within a range of different temps.
LOWEST temperature that permits microbial growth
Minimum temperature
HIGHEST temperature that permits growth.
Temperatures above that can cause permanent enzyme and nucleic acid breakdown
maximum growth
small range of temperatures that maximizes growth and metabolism
Optimum temperature
Psychrophile temp
optimum temperatures below 15 degrees celcius
Mesophiles temp
optimum temperatures between 20 and 40 degrees Celsius
Thermophiles
optimum temp. greater than 45 degrees
Most ______ cannot survive above 60 degrees.
eukaryotes
Microbes are one of three forms:
. Those that use oxygen and can detoxify it
. Those that neither use oxygen nor detoxify it
. Those that do not use oxygen but can detoxify it
can use gaseous oxygen and poses enzymes to neutralize toxic oxygen
Aerobes
This aerobe must have oxygen in their environment.
obligate aerobe
This aerobe does not require oxygen and is capable of growth without it.
Facultative aerobe
need small amounts of oxygen, but cannot grow with normal atmospheric oxygen
Microaerophile
lacks enzymes for using oxygen in respiration
Anaerobe
·Obligate anaerobes
cannot tolerate free oxygen in environment
Many _________ _______ are anaerobic.
gut/ oral bacteria
can tolerate oxygen but can break down toxic forms of oxygen.
. Aerotolerant anaerobes
Acidophiles
grow at extremely low pH
. Euglena mutabilis-alga that grows in low pH pools, first found near acidic waste pits from mining
Alkalinophiles
grow at extremely high pH
Halophiles
tolerate or require high salt concentrations
Facultative halophiles
- can live in high salt concentrations
· Staphylococcus aureus
Mutualism
when organisms live in a mutually beneficial relationship
· Usually obligatory
Commensalism
one organism benefits but the other is not affected.
Parasitism
- one organism benefits but the other is harmed.
Antagonism
- when species not in a symbiotic relationship compete.
. Microbes can excrete chemical substances that inhibit or destroy microbes into the same habitat
Synergism
- an interrelationship between two or more free-living organisms that benefits them but isn't necessary for their survival.
80% of chronic infections are caused by
biofilms
What are Biofilms
- communities of different kinds of bacteria and other microbes that are attached
to surfaces
Biofilms can sense and monitor their population by means of
quorum sensing.
They are also prevalent
the process of one cell becoming two
Binary fission
the time required for cells to double
Generation time
Some microbes reproduce extremely fast- E. coli.
exponential growth
Growth that doubles repeated
Populations typically demonstrate a
growth curve.
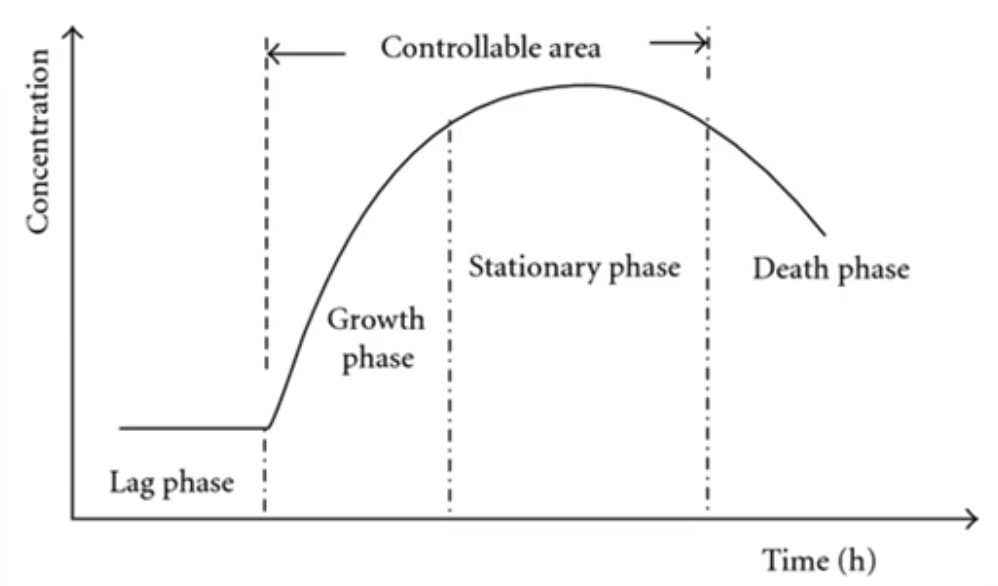
Look at this chart
Look at this chart
Chemostat
a device that allows for continuous culturing.
· Adds a steady stream of nutrients to prevent dying, siphons off old media and dead bacterial cells.
Turbidometry
measuring the turbidity of a solution of bacteria to estimate population size.
Direct cell count
- counting cells microscopically
can be counted or counted by a computer
special slide calibrated to accept a tiny sample spread over a grid
cytometer
Flow cytometer
measures cell sizes, cell count, and can tell the difference between live and dead cells