Module 4: Section 4 - Skeletal Muscle metabolism
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what are the two major classifications of fatigue
central and muscle
what is central fatigue
a slowing down and cessation of activity even though the muscle fibres themselves are not fatigued due to the central nervous system decreasing its activation of motor neurons
why does central fatigue happen
can be because the person is bored with the activity, they are tired, or just lack motivation to continue to exercise
what is muscle fatigue
reduced contractile activity before the ATP supply runs out
how does muscle fatigue happen
accumulation of ADP and phosphate groups
accumulation of lactic acid
accumulation of extracellular potassium
depletion of glycogen
how does an accumulation of ADP and phosphate groups cause muscle fatigue
an excess of ATP metabolite concentrations can interfere with cross-bridge cycling
how does an accumulation of lactic acid cause muscle fatigue
by inhibiting the enzymes of glycolysis which reduces ATP production and interfering with excitation-contraction coupling
how does an accumulation of extracellular potassium cause muscle fatigue
since there is no ATP, the sodium-potassium pump cannot function correctly making concentration gradients form and with extra potassium, the muscle fibres are less excitable
how does a depletion of glycogen cause muscle fatigue
there is nothing to make glucose from so no ATP is being made, no energy source present
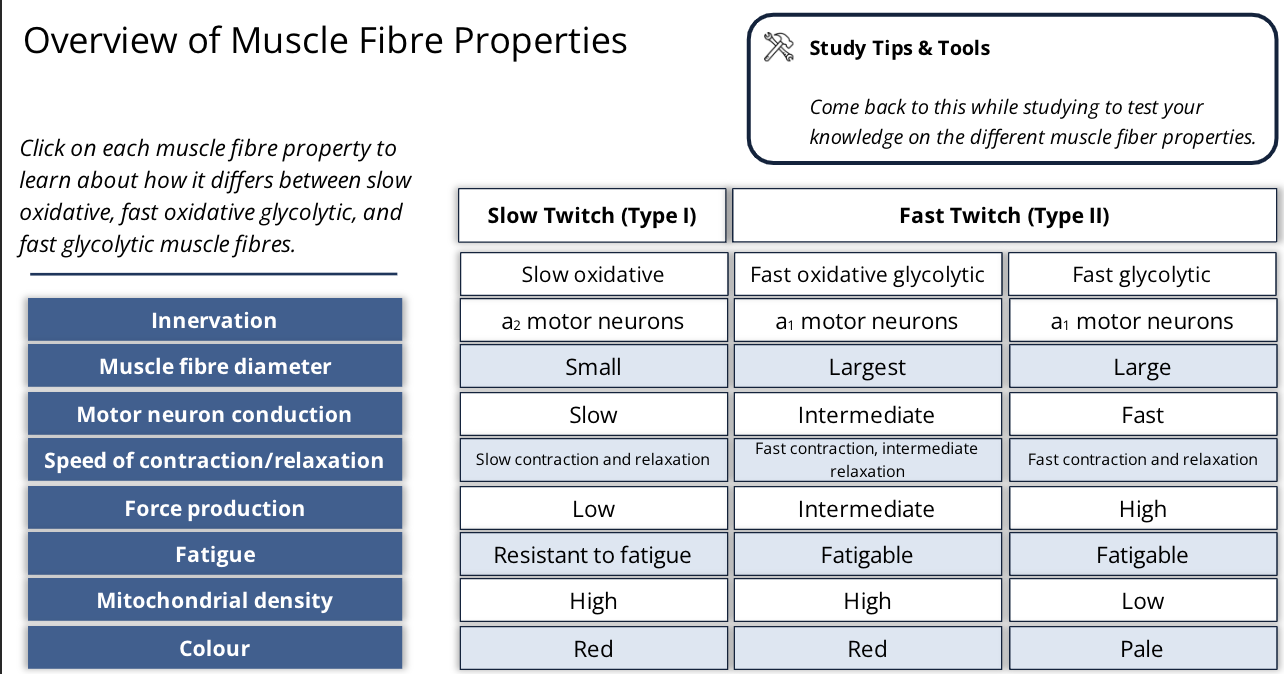
types of muscle fibres
slow twitch (type I)
fast twitch (type II)
what are the properties of slow and fast twitch muscle fibres
speed of contraction
innervation
metabolic properties
what does speed of contraction mean regarding slow twitch fibres
they contract and relax at slower rates than the other type of twitch fibres
what does innervation mean in regards to slow twitch fibres
what type of motor neuron supplies them, these types of fibres are supplied by alpha 2 motor neurons meaning they have a lower activation threshold and slower conduction speeds
what does metabolic properties mean regarding slow twitch fibres
they produce their ATP via aerobic processess (oxidative)
what does speed of contraction mean regarding fast twitch fibres
they contract and relax at a quicker rate
what does innervation mean in regards to fast twitch fibres
are supplied by alpha 1 motor neurons and since they are the larger type, they have a higher activation threshold and faster conduction speed
what does metabolic properties mean regarding fast twitch fibres
split into two types, fast oxidative glycolytic fibres and fast glycolytic fibres
how do fast oxidative glycolytic fibres work
they make ATP by both aerobic and anaerobic metabolism
how do fast glycolytic fibres work
makes ATP by anaerobic means
how does the colour of muscle fibres change
by how they produce their energy
what are red fibres
slow oxidative and fast oxidative glycolytic fibres, they have numerous mitochondria and are highly vascularized (lots of blood vessels), have lots of myoglobin to support the high use of oxygen
what does the myoglobin do in highly vascularized red fibres
gives the red fibres their red look
what are white firbes
fibres that mostly use anaerobic metabolism and have few mitochondria, no myoglobin; fast glycolytic fibres
so what are the types of muscle fibres?
slow oxidative
fast oxidative glycolytic
fast glycolytic
overview