Diagram of iGCSE Geography: Hot Deserts and Desertification | Quizlet
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Why does a desert has low rainfall?
It is caused by the GLOBAL CIRCULATION PATTERNS:
- warm air moves away from the equator loses most of its moisture towards the tropics
- the air COOLS and SINKS and creates HIGH PRESSURE
- this SUPPRESSES CONDENSATION thus suppresses cloud formation
- absence of cloud leads to low rainfall
Why does a desert has a high daytime temperature?
Its proximity to the equator causes the SUN'S RAYS to be FOCUSED over a SMALLER SURFACE AREA due to the natural CURVATURE of the earth, and the lack of CLOUDS allows radiation to heats up the ground directly.
Why does a desert has a high evapotranspiration rate?
- it has strong winds due to barren landscape
- this increases water loss by increasing the rate of transpiration and evapouration
Why does a desert has a large diurnal range?
- lack of cloud cover (due to the high pressure created by cooling, sinking air that suppresses cloud formation)
- intense radiation heats ground in daytime
- radiation escapes rapidly at night when no cloud traps heat
Soil in hot deserts
It is infertile and shallow:
- caused by soil erosion due to the lack of vegetation and exposure to wind
- caused by salinisation
Salinisation of Soil
After rainfall, rates of evaporation and transpiration increases rapidly leaving salts on the surface which forms an infertile surface.
Plants in hot deserts
Vegetation is sparse and short due to lack of rainfall. Plant growth is very slow.
- thick and waxy leaves/needles to reduce water loss by transpiration
- store water in roots/leaves/stems(succulent plants)
- wide shallow roots/deep roots
- rapid life cycles triggered by occasional rainfall
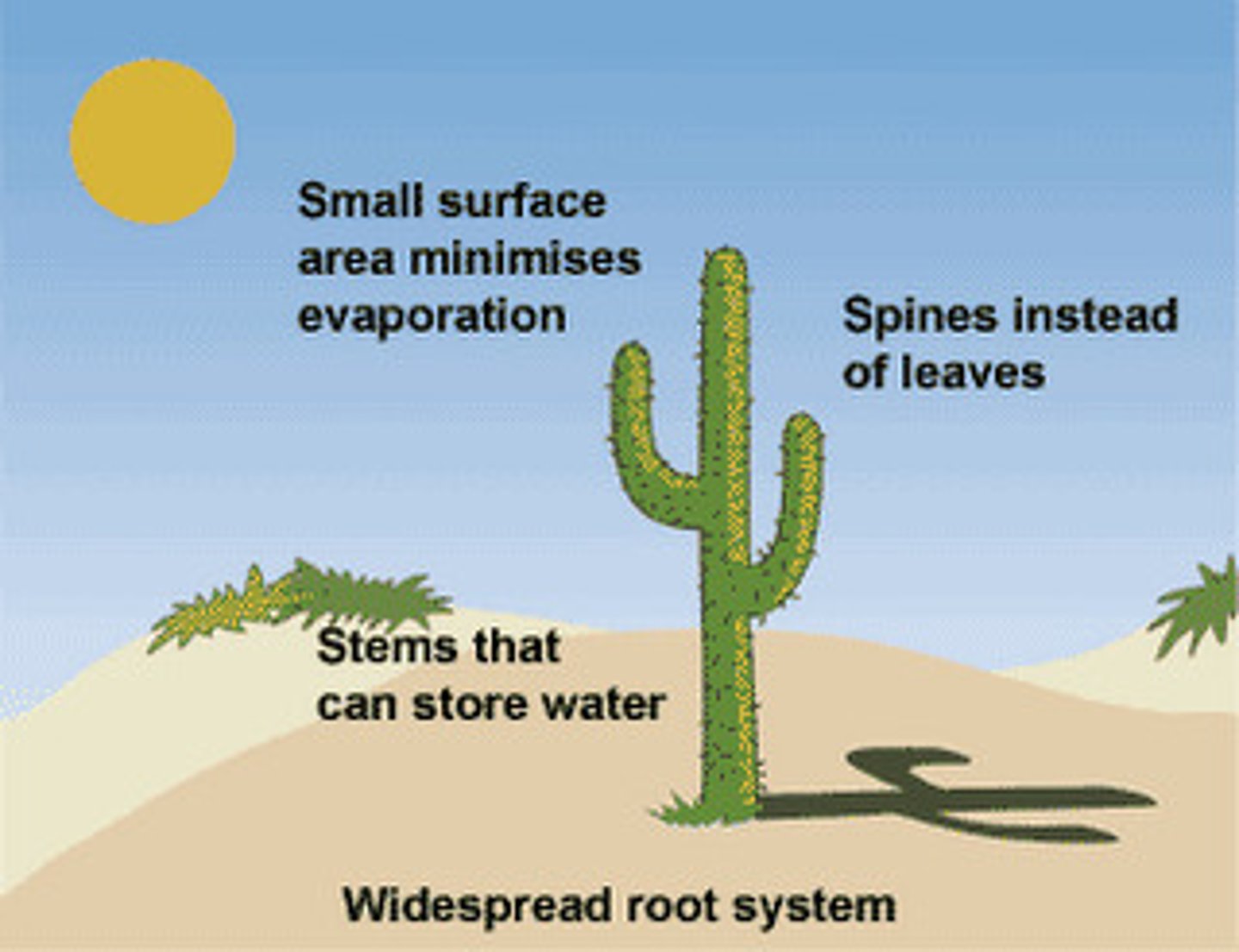
Adaptations of a cacti
- needles instead of leaves reduces transpiration
- stem has large capacity for water storage
- wide and shallow roots to absorb water after rainfall
Aniamals in hot deserts
- nocturnal animals with large eyes adapted to predate in low light condition
- often live in burrows to stay cool in daytime
- many are omnivores
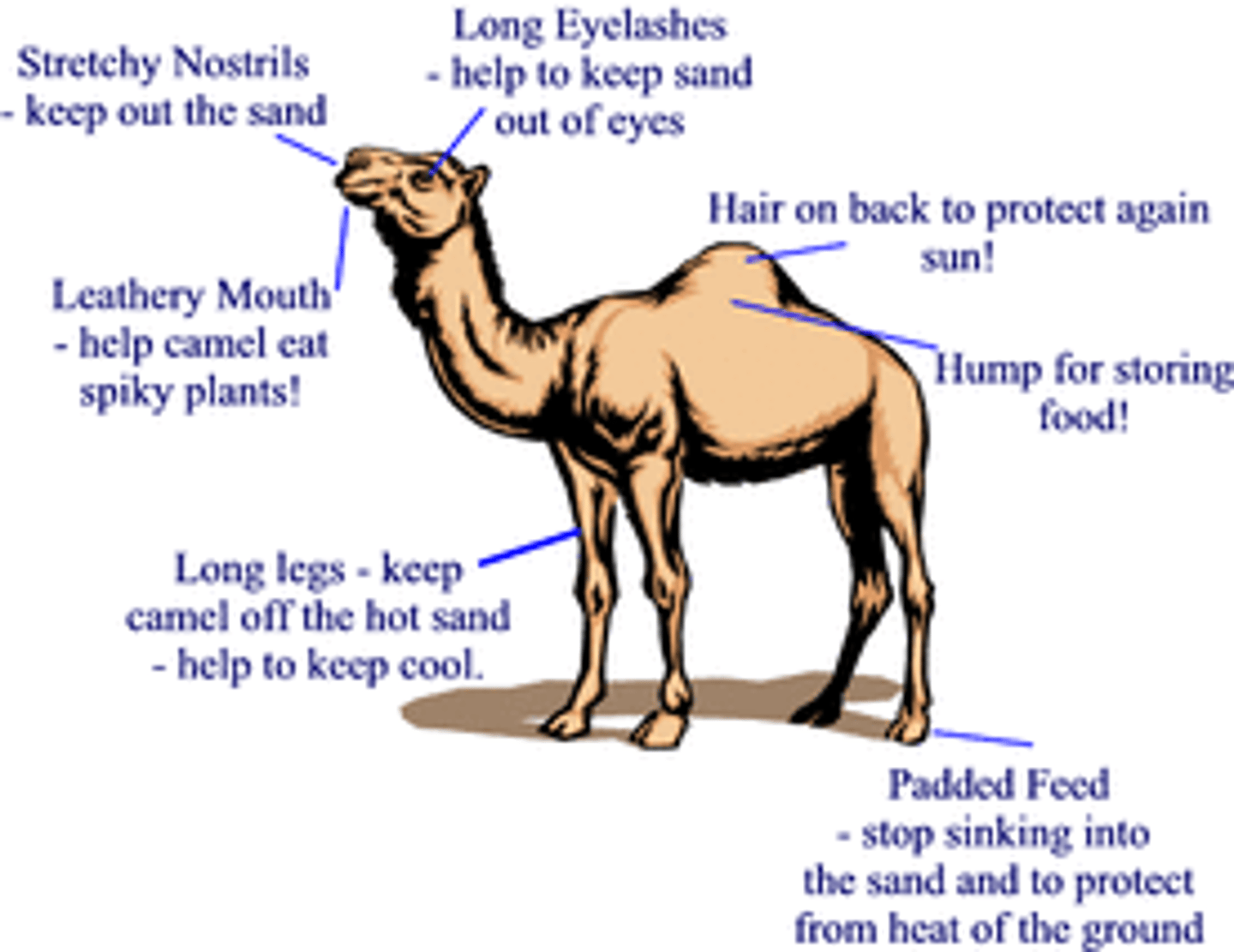
Adaptations of a camel
- long eyelashes protect vision from blowing sand
- long, muscular legs and wide feet for walking
- hump for storing fat
- long intestines for absorbing all the water from the food
interdependance of organisms
The close relationship between biotic and abiotic elements in an ecosystem.
- links between different parts of the food chain
- role of vegetation stabilising soil
- people's reliance on the physical environment
What is desertification?
The process by which fertile land becomes an infertile desert.
Causes of desertification
- Climate change is making deserts and fertile land around them hotter and drier
- Population growth increases the demand for food and accommodation which leads to deforestation
- Deforestation increases the likelihood of erosion
- Over-grazing/cultivation causes the soil to become infertile by soil erosion
- Soil erosion by rainfall or wind causes the land to be infertile
Water and soil management(Diguettes)
- stones lined along the countour of the landscape
- this slows the surface runoff of water when raining
- allowing water and eroded nutrients to infiltrate back into the soil
- farmers can collect the soil near the lines to replace infertile, eroded soil
- which reduces soil erosion and is cheap to assemble which means it is more sustainable
Tree planting(growing fruit trees)
- fruit trees bind soil together to prevent soil erosion
- fruit can be used as a supply of food or income
- local people can make money
- this reduces over cultivation of farmland so is more sustainable
Use of intermediate technology(cook-it)
- local people are taught to use the cook-it which is cheap to use and assemble
- light from the sun is concentrated into the pot and thermal radiation collected heats up food
- no need for using gas stoves
- no need to cut down trees for fuels and socioeconomically reduces stress for local people