lecture 5
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lipids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
functions
stored energy
components in plasma membrane of all cells
carrier for vitamin A,D,E,K
insulation and lubrication
definition
plants (forage, cereals) and animals
physical
group of compounds soluble in organic solvents (ether, benzene, chloroform); insoluble in water
chemical
esters of FAs and glycerol or some other alcohol
classifications
glycerol based vs non-glycerol based
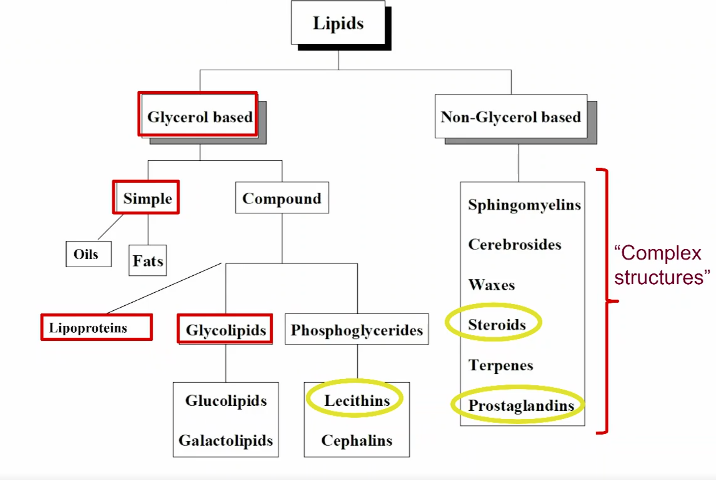
simple lipids
triacylglycerols
sterols and sterol esters
triacylglycerols (aka triglycerides)
tri-acyl esters of glycerol
most nutritionally significant of lipids group
esters of FAs w/ alcohol (glycerol)
form bulk of animal and grain/oilseed lipid
sterols and sterol esters
basic unit for all sterols including cholesterol bile acids (salts), adrenal and sex hormones (steroids)
sterols in nature
phytosterols - plant
mycosterols - fungal
zoosterols - animal (ex. cholesterol)
compound lipids
glycolipids
lipoproteins
phospholipids
lecithin
glycolipids
CHO (carbohydrate) + fat —- lipid in plants
lipoproteins
lipid + protein —- transports lipid in body
phospholipids
PO4 + lipid —- component in cell membranes
lecithin
white waxy solid
phospholipid
must abundant
secreted in bile
body store of choline, methyl donor
fatty acids
determine properties of fats and oils
natural FAs
even number of C atoms (2-24_
straight chain
carboxyl group (-COOH) at end
odd chain but only due to absorption of microbial derived FA (milk, beef)
saturated FAs
no double bonds
acetic (acetyl)
propionic (propionyl-)
butyric (butyryl-)
stearic (stearyl-)
arachidic (arachidyl-)
unsaturated FAs
double bonds (18 C)
mononenes, dienes, trienes
oilseed
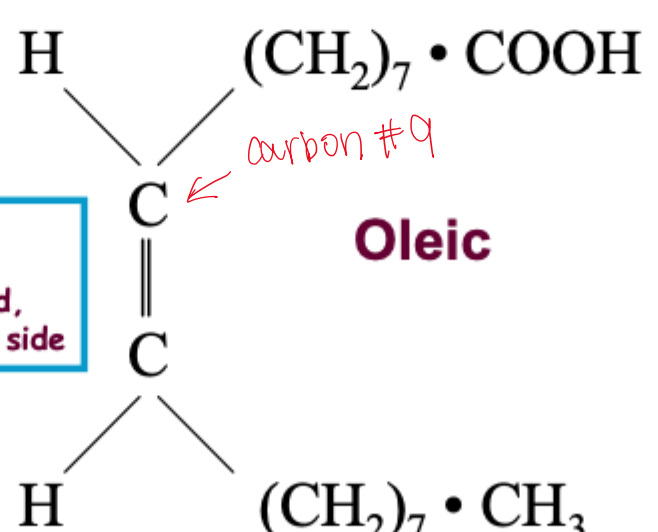
mononenes
1 double bound
ex. oleic acid, elaidic acid
dienes
>1 double bond
poly-unsaturated FA
ex. linoleic acid
trienes
3 double bonds
omega-3
cis config
most FA
orientation around C—C double bond
cis=same side
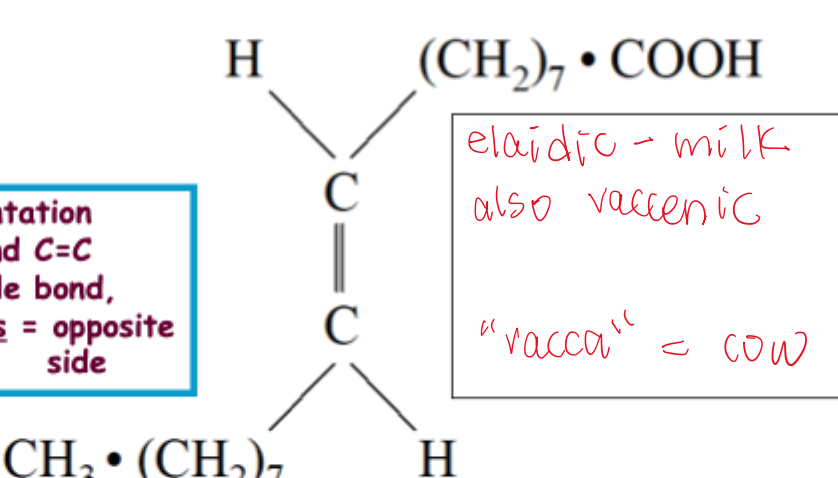
trans config
formed in rumen and during processing vegetable oils
opposite side
MP of FAs
length of carbon chain (<12 C are liquid - oils, >12 C are solid - fats)
inc in double bonds, dec MP
polyunsaturated FA
3 classes
linoleic family (w-6), linolenic family (w-3), oleic family (w-9)
phospholipids
lipid transport
precursor of eicosanoids
linoleic family (w-6)
growth, fertility, maintaining skin, RBC structure
linolenic family (w-3)
strucutre and function of eye and CNS
oleic family (w-9)
not abundant but can be made in body under conditions of essential fatty acid deficiency
fatty liver disease
common in overweight non-ruminant animals
hepatocyte filled with triacylglycerol
essential FAs
can’t synthesize sufficient quantities supplied in diet
corn oil + linseed oil, large effect
linoleic (dogs + cats)
FA defficiency
hair loss
scaly dermatitis
skin necrosis
unthrifty appearance
absorbed FA in body
organs remove and use rapidly
muscle, heart, liver
adipose tissue
mammary gland