Macroeconomics
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final Exam Prep.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What are macroeconomical frameworks?
indicators that are used by economists to determine changes.
e.g.
inflation
recession
What are Policy tools?
tols used by the federal government to influence macro economy
e.g.
new laws
permits or licenses
taxes
What is the Gross domestic product (GDP)?
value of the output of all final goods and services produced within one year in one region/country
measurement for overall economy purchases by consumers or produces
In which parts can the GDP be seperated?
consumer spendings (consumption)
business spending (investment)
govenment spending on goods and services
spending on net exports
What is the trade balance?
TB= Exports - Imports
TB>0 Trade Surplus
TB<0 Trade deficit
What can the GDP be measured as?
GDP= C+I+G+(X-M)
What is the Gross National Product (GNP) ?
Sum of production that can take place domestically or international
e.g. VW producing in China
What is the Net National Product?
GNP - Depreciation
used to determine how high the GNP is after deducting the costs that occur to maintain the output
Difference between Nominal Value and Real Value
Nominal Value: What is written on the price tag or paycheck
Real value: adjusted for inflation
What is a recession?
a significant decline in national output/ GDP
What is a Depression?
an especially lengthy and deep decline in output
the economic damage is significant larger than in a recession
What is a Trough?
The lowest point of output in a recession before recovery begins
recession lasts from peak to trough
upswing lasts from trough to peak
What is referred to as Business cycle?
economys relatively short-term movement in and out of recession
Why is the GDP not appropriate to describe the standard of living of people?
As GDP does not include:
leisure time
level of enviromental cleanliness, healt and education
inequality and security
available technology
Who does the the number of unemployed include?
People that are out of work and actively looking for a job
What is reffered to as “Out of the labor force”
People that are unemployed and not willing or able to find a job
What is reffered to as “Labor Force” ?
People that are employed and the unemployed (the ones looking for a job)
How to calculate the labor force?
Employed + unemployed
Thus, everyone that is working or wants to work
What is the base for the unemployement rate?
Total labor force
What is reffered to as “Hidden unemployment”?
people that have a job that underestimates their skills and abilities
discouraged workers that stopped looking for a job out of frustration
What is the problem with sticky wages? (wages that stay at a certain level and are not decreasing)
In a Recession the supply that would pay those wages drops and the shortage intensifies
Why are wages sticky?
Implicit contract that wages are not moving down
Efficiency wage theory - efficiency is related to pay
Adverse selection of wage - if employer cuts wages the best employees will seek work elsewhere
What is the natural rate of unemployement?
rate of unemployement that occurs eventhough the economy ist healthy
can be caused by:
frictional unemployment - unemployment that occurs as workers move between jobs
structural unemployment - as individuals lack skills valued by employers
What is Inflation
general ongoing rise in the level of prices in an entire economy
pressure for prices in most countries
What is the Substitution Bias used for?
It considers the ability of consumers to subsitute goods
What is an Indexation
Adaption to Inflation
Can be linked to mortages, prices, interests or rent
Trade balance
Gap between a region / nations exports - imports
Exports - Imports
What does Merchandise trade balance refer to?
balance of trade only looking at goods
What is the Current acoount balance
trade balance under influence of international flows of income and foreign aid
What is uniliteral transfers?
payments from governments, charities of individuals who don’t receive any exchange
What is referred to as Financial capital?
international flow of money that faciliates trade and investment
How can a government surpus or deficit be calculated?
Supply of financial capital - Demand for financial capital
Savings + (Imports - Exports) = private Investments + (Government Spending - Taxes)
If G<T than the government is a money supplier
If G>T than the the government is a money demander
How can the trade deficit be determined other than Imports-Exports
Domestic Investment -(Private domestic saving + (Taxes - Government spending)
Thus, all the investment made - all the savings results in the “leftover” investment that must be payed for abroad
How can the trade surplus be determined other than Exports - Imports
private domestic saving + (Taxes - Government spending) - total investment
Thus, all the leftover capital that is not getting domestically investment gets invested abroad
What usually happens to the trade deficit during a recession?
It gets lower
Less investments means that the savings are closer to being sufficient and that lowers the imports
What is the level of trade?
Percentage to which a country exports in relative to the GDP
How can trade deficit / surplus be used do evaluate a countrys economy?
Not at all.
Neither surplus nor deficit are an explicit good or bad sign.
It all is up to that the borrowing / lending makes overall sense in the economic conditions that the country is facing.
For what time frame is Say’s law: Supply creates its own demand a good approximation?
long run
As the cycle components recession and depressions are therefore leveled out
When is Keynes’law: Demand creates its own supply applicable?
short run
e.g. during recessions buyers are deciding how the companies are producing
What is the total aggregate supply (AS) ?
total quantity of output that firms produce and sell
What is reffered to as Potential or Full-employment GDP?
the maximum quantity an economy could reach under ideal conditions
Thus, full employment, availability of technology and sufficient capital
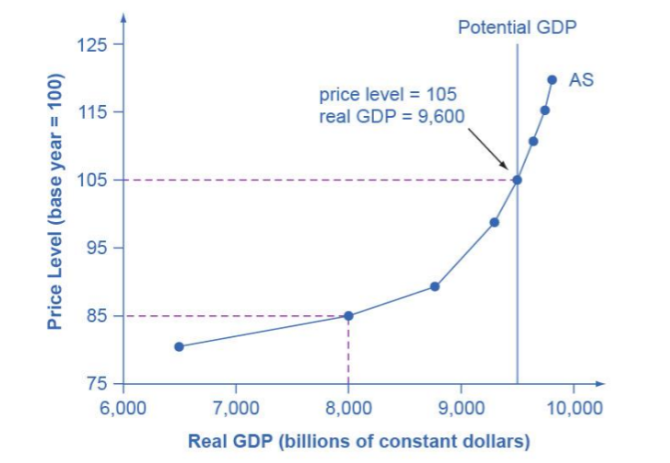
How can the Aggregate Supply Curve cross the Potential GDP?
potential GDP refers to the natural unemployment rate and the sustainable level of work.
If people work overhours, maintenance of machines is left out to keep them running the potential GDP can be exceeded to reach a higher maximum GDP
What is the Aggregated Demand (AD) ?
total amount of spending on domestic goods and services
It includes:
consumption
investment
government spending
net exports
What does the equilibrium of AD and AS show?
the real GDP
how many units are produced at which price
What is the short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) ?
It looks at the economical behaviors while contracts and wages are fixed
So saying how does the supply differs with change in price when the costs don’t change.
e.g. a coffee shop is able to sell coffee for 4$ instead of 3$ but wages increase only once a year and are therefore fixed for a period of time
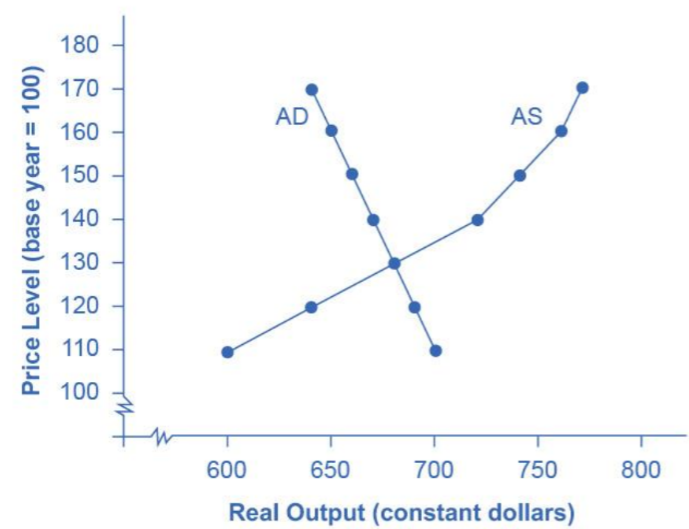
Evaluate where the economy stands
not at maximum capacity as AS is not vertical
operating at a medium price range not in a deep depression
economy is more facing unemployment than inflationary risks
Why are the LRAS curves vertical?
In the long-run price and costs level out so firms produce at their ideal capacity, no matter of price.
What shifts the SRAS curve to the right?
Increase in productivity or reduced costs
What shifts the SRAS to the left?
Higher prices for key input variables (e.g. labor)
What happens usually if companys loose trust in the market?
AD perspective
they tend to invest less which lowers the AD and shifts the curve left
How are LRAS and potential GDP related to eachother
they indicate the same
What happens when AD shifts left?
Equilibrium will have a lower output and lower price
Farther below potential GDP
What happens when AD shifts right?
New Equilibrium has a higher quantity and price
Closer to potential GDP
How can you tell whether an economy is in a recession from looking at the AD, SRAS and LRAS graphs?
How close the Equilibrium of AD and SRAS is to the LRAS
If Equilibrium is close to LRAS the economy is near full employment
How can you identify growth in the AD/AS diagram?
shift of AS to the right
shift of LRAS (potential GDP) to the right
How can you identify recessions in the AD/AS diagram?
If Equilibrium is substantially below potential GDP
Name the two ways of how inflationary pressure arises
AD continues to shift to the right finding the equilibrium on the steeper part of the AS curve
rise in input that shifts AS to the left and therefore equilibrium up
How is the Keynesian Zone in the AD AS diagram described?
high unemployment
low risk for inflationary prices
low cost increase if demand cuve shifts right
How is the Neoclassical Zone (Say’s Law) in AD-AS diagram described?
curve is vertical so no increase of real GDP possible
unemployment is low (just natural unemployment left)
only a shift of AS to the right can increase the quantity and the real GDP
shift to the right in AD causes higher prices and inflation
How is the indermediate zone in AD-AS diagram described?
economy gets closer to potential GDP
prices rise more quickly as first constraints are being encountered (shortage of workers or materials)
unemployment lowers
What does the Keynesian perspective focus on?
That firms only produce if they expect to sell it
What is a recessionary gap?
equilibrium below potential GDP
What is an inflationary gap?
equilibrium above potential GDP
What happens to the price when demand decreases (AD shifts left) to the price according to the Keynesian model?
the price is constant and the AD only afffects output, just price
What institution can move AD during a deep recession?
Government by increasing spending
What are menu costs and why do they slow down perfect price adjustments as in economical theory?
costs the firm faces when changing prices
holds the firm from lowering or increasing prices
Thus, eventhough AD fluctuates, prices don’t change accordingly
What results from sticky wages and prices?
Unemployment and recession (excess supply)
What is referred to as Expenditure mutliplier?
As ones spending becomes anothers income who than can spend again, the inital investment has a much larger impact on the GDP
What does the Phillips Curve represent?
the trade-off between unemployment and inflation
If the unemployment is low, inflation will be high and versa vice
What is reffered to as Expansionary fiscal policy?
tax cuts or increases in government spendings to stimulate aggregate demand and move out of recession
What is referred to as Contracionary fiscal policy?
tax increases or cuts in government spending to shift demand curve to the left to reduce inflationary pressure.
continue chapter 26