aerobic respiration
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
name the 4 main stages in aerobic respiration and where they occur
glycolysis- cytoplasm. link reaction- mtochondrial matrix. krebs cycle- mitochondrial matric. etc- inner mitochondrial membrane on cristae
how many ATP molecules are produced in anaerobic respiration
2
how many ATP molecules are produced for aerobic respiration?
36-38
how many ATP molecules are produced for aerobic respiration of a typical lipid?
500
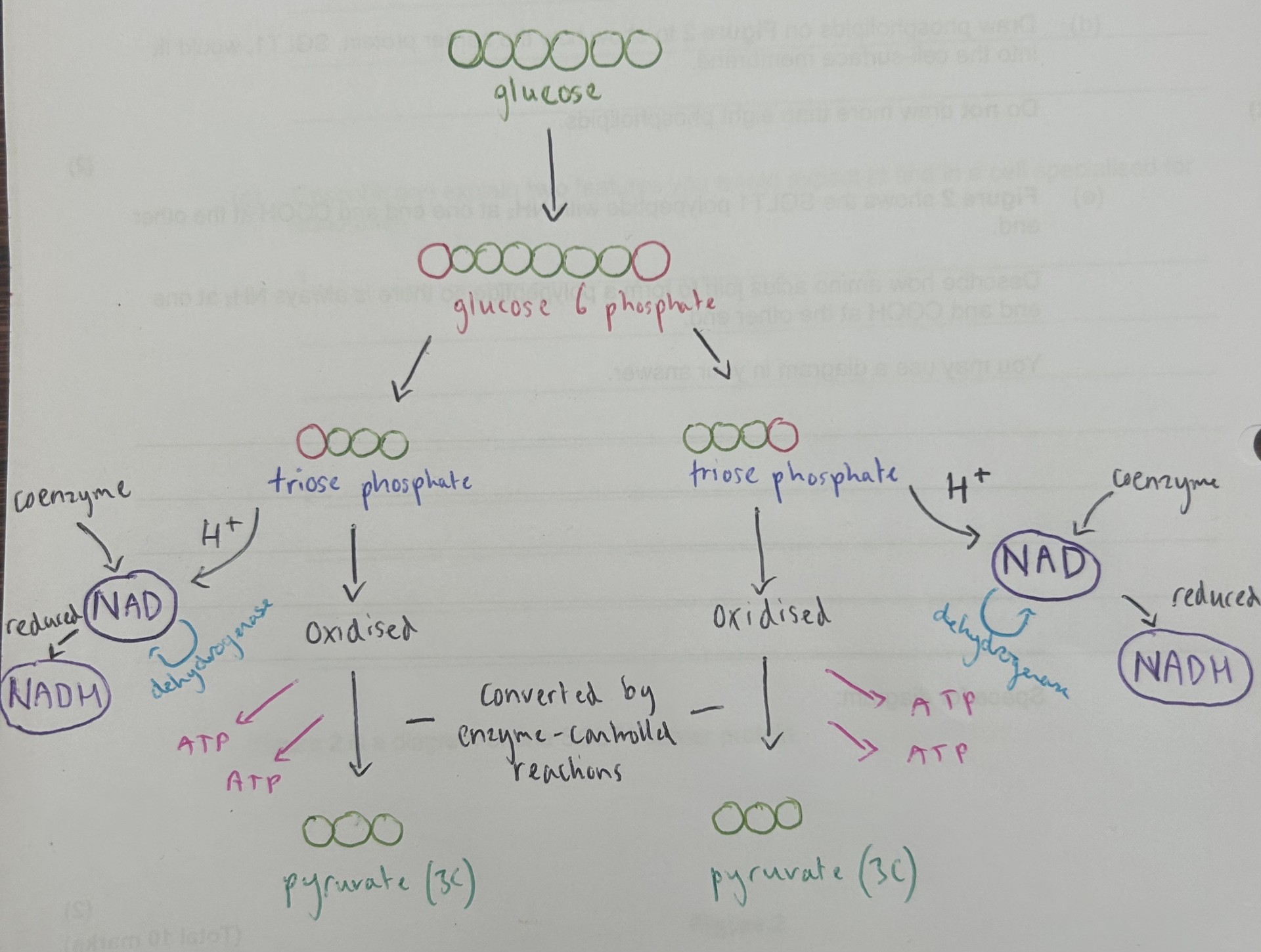
outline the stages of glycolysis
glucose molecule phosphorylation by 2 ATP molecules which are hydrolysed, 2 molecules of ADP produced. raises glucose energy level, lower activation energy for enzyme controlled reactions. lysis of glucose 6 phosphate creates 2x TP. 2x TP is oxidised and converted by enzyme controlled reactions into 2x pyruvate, releases 2x ATP per TP.
what are the products of glycolysis PER GLUCOSE?
2x ATP (2 used to phosphorylate glucose) 2x pyruvate, 2x NADH
how is NADH produced from glycolysis?
TP oxidised, releases H+ which is used to reduce NAD, a coenzyme, using dehydrogenase to create NADH
what 2 processes can pyruvate from glycolysis be used for?
aerobic or anaerobic respiration
what are the reactants and products during anaerobic respiration of animal and bacteria?
cellulose - lactic acid/lactate
what are the reactants and products during anaerobic respiration of fungi and plants
glucose - ethanol + CO2
what process is universal evidence for evolution of a common ancestor and why?
glycolysis as it is used in the cytoplasm of all living cells
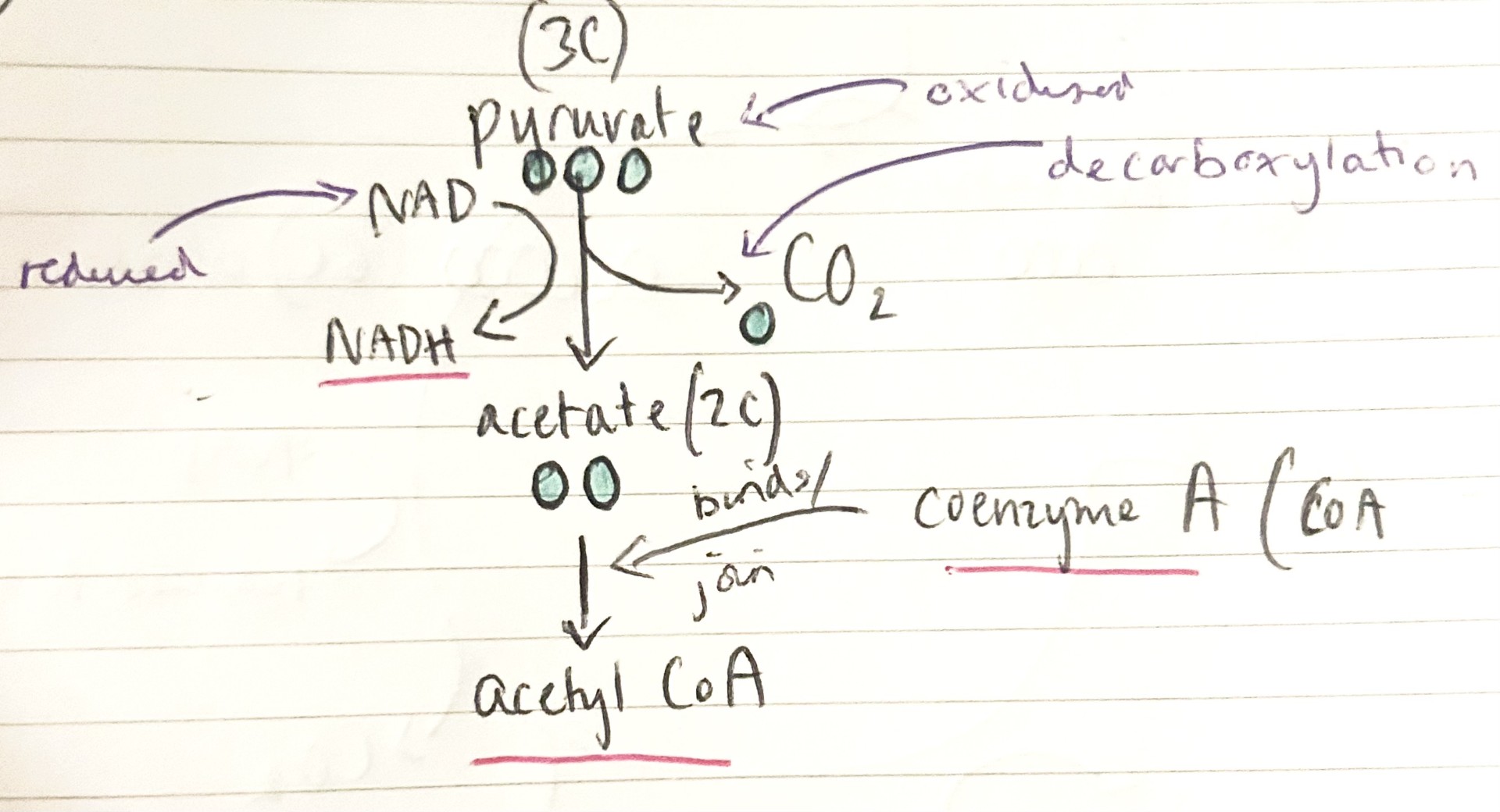
explain what occurs in the link reaction
pyruvate enters mitochondrial matrix by active transport. pyruvate is oxidised to acetate, producing reduced NAD and CO2. acetate combines with coenzyme A to produce acetyl coenzyme A. produces 2x acetyl Coa, 2x Co2 and 2x NADH- occurs twice for every glucose
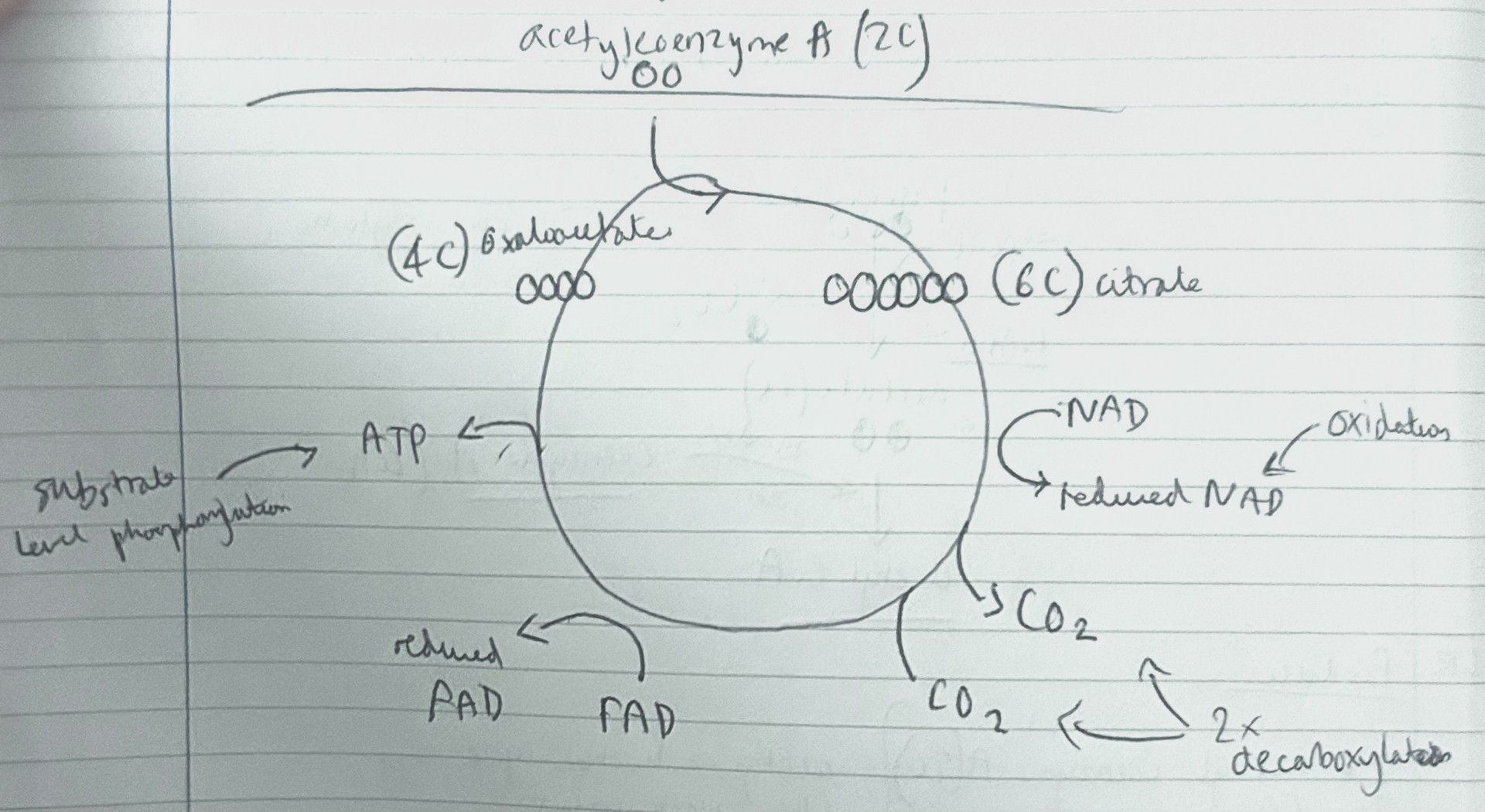
explain what happens in the krebs (citric acid) cycle?
acetylcoenzyme A reacts with oxaloacetate (4C). causes release of coenzyme A (returns to link reaction) and produces citric acid (6C). citrate enters krebs cycle. series of oxidation reduction reactions where 6c molecule returns to a 4c molecule. includes coenzymes NAD and FAD are reduced, ATP is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation, carbon dioxide is lost
what are the products of the krebs cycle?
3x NADH, 1x FADH, 1x ATP, 2x CO2, og 4C oxaloacetate per pyruvate, double produced for 1 glucose molecule
where do the 3X NADH and 1x FADH go from the krebs cycle?
cristae for etc
where do the 2x co2 from the krebs cycle go?
blood
what are FADH and NADH
dinucleotides