3 Normal UE Vascular System
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
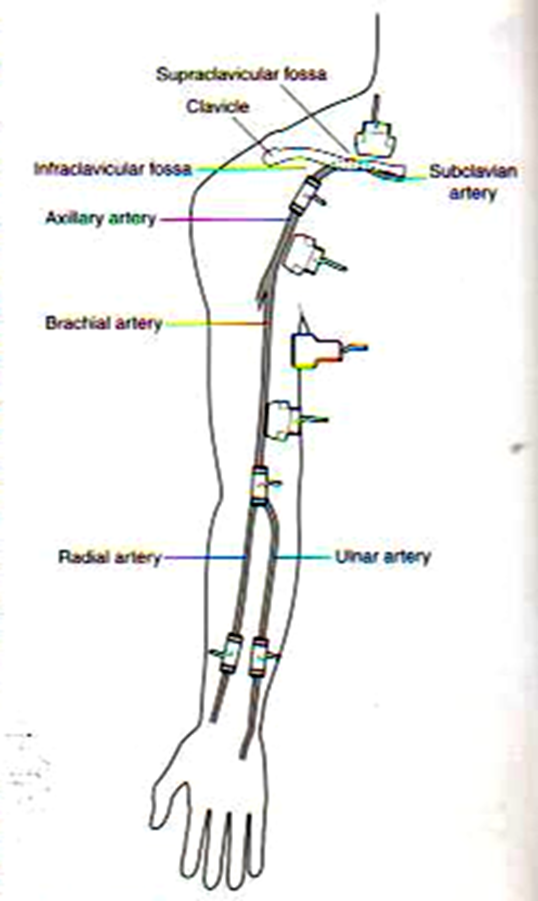
label the arteries from the arm down to the hand
subclavian
axillary
brachial
radial/ulna
palmar arches (superficial and deep)
digital arteries of fingers
what is the origin of the right subclavian art? left?
right SCA : brachiocephalic artery bifurc
left SCA : aorta
how does the subclavian artery course?
passess laterally between scalene muscles
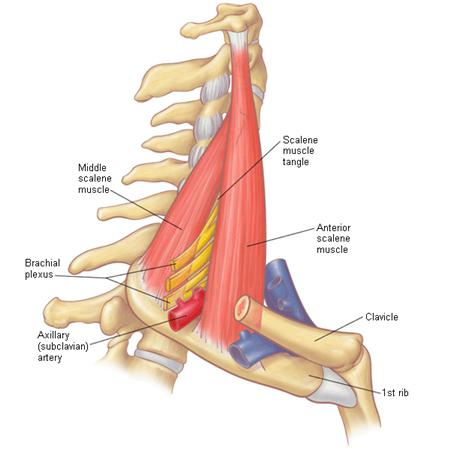
when does the SCA terminate? what does it terminate into?
terminates into axillary artery after it crosses the border of the first rib
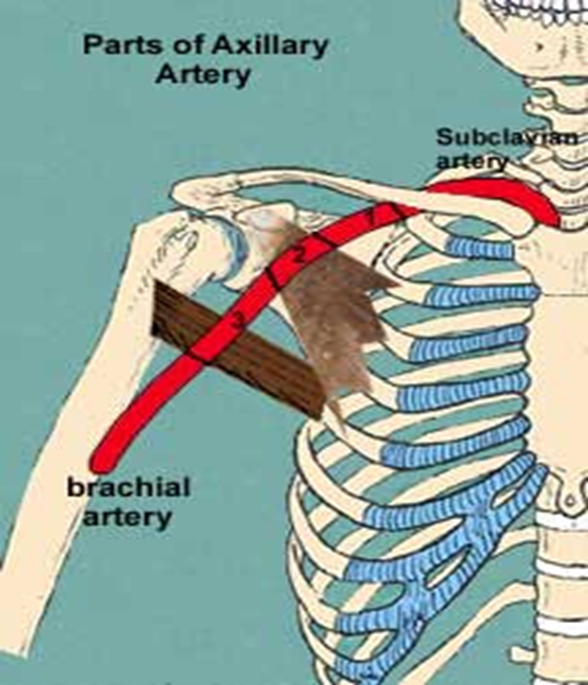
what is the diameter of the SCA
.6 - 1.1cm
where does the axillary artery begin?
lateral border of 1st rib
how does the axillary artery course?
continuation of SCA towards arm
where does the axillary artery terminate and what does it become
terminates at inferior border of teres major muscle and becomes the brachial artery
what is the diameter of the axillary artery?
.6 - .8cm
how does the brachial artery course?
runs from medial to lateral over inner elbow
where does the brachial artery end?
bifurcates 1-2cm below elbow
brachial artery becomes
ulnar and radial artery
where does the ulnar artery course?
runs deep along MEDIAL side of forearm (pinky)
where does the radial artery course?
runs along LATERAL side of forearm (thumb side)
what is the common interosseus artery? where is it in relation to ulnar and radial art
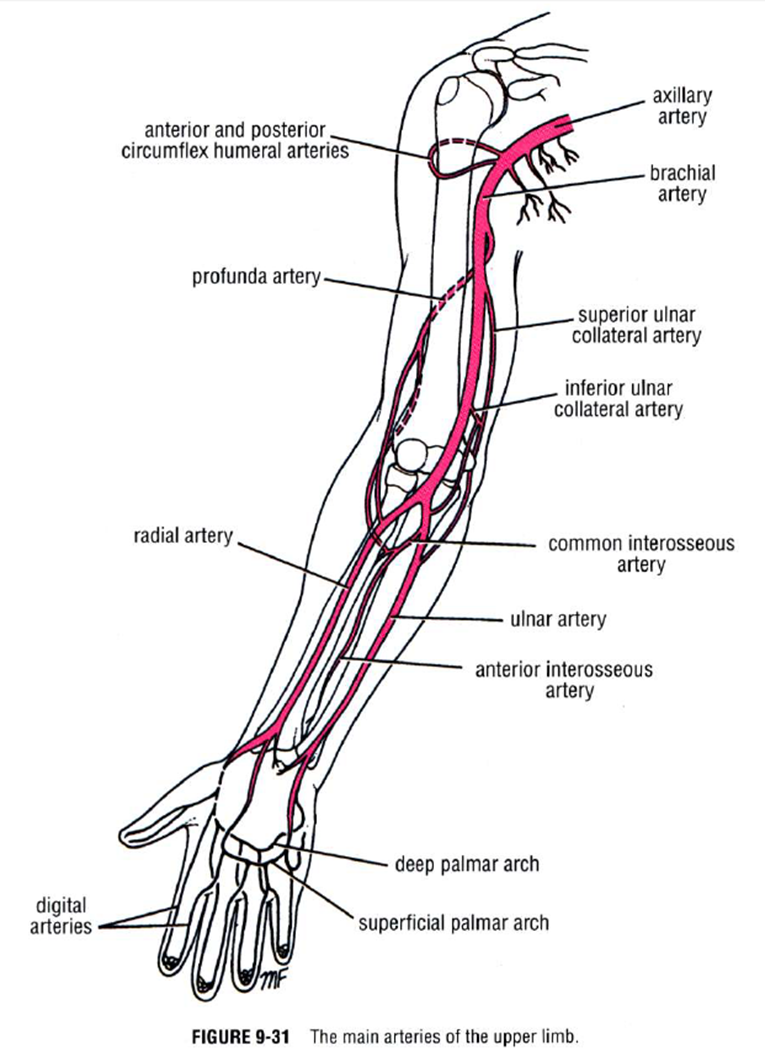
branch of ulnar art; runs medial to radial and ulnar
what happens if the radial and ulnar arteries are occluded?
interosseus artery can act as a collateral pathway
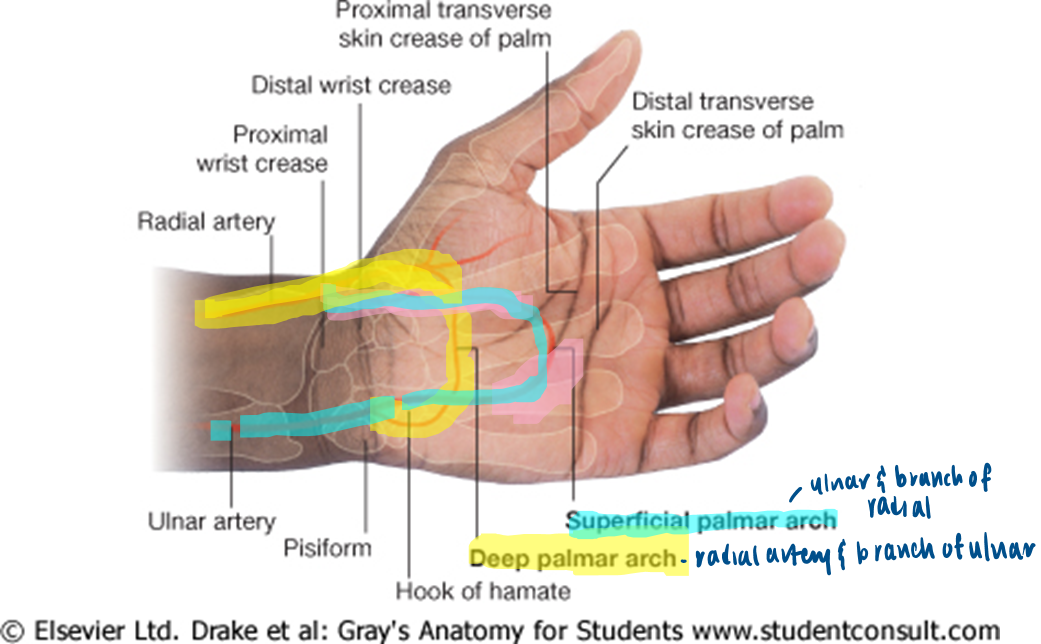
what supplies the palmar arch superficial?
ulnar
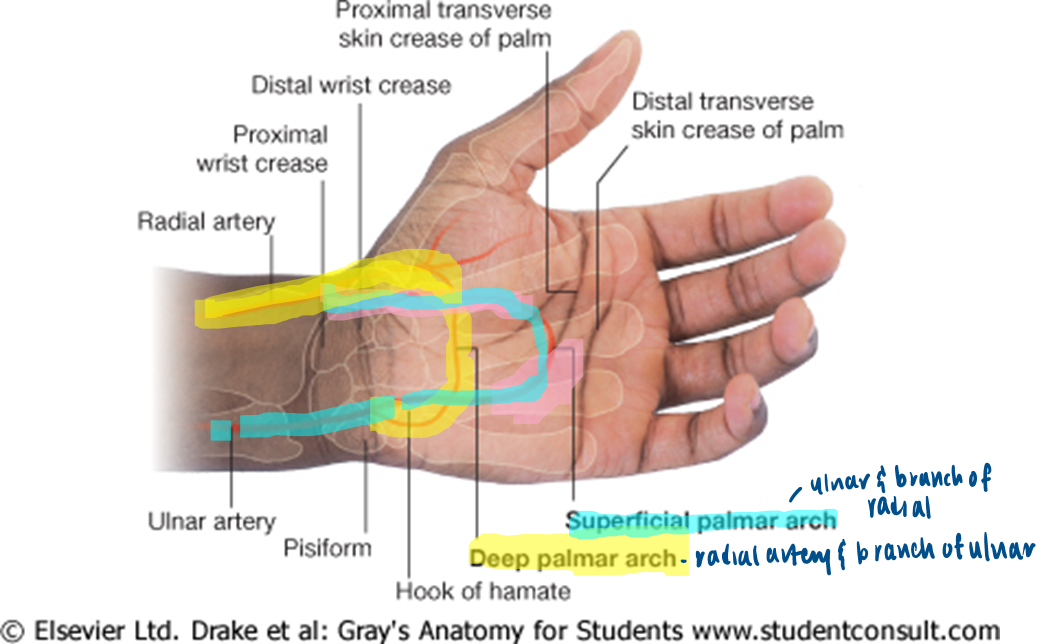
what supplies the palmar arches deep?
radial artery
what are deep veins?
have corresponding arteries
what are the deep veins of UE?
subclavian (neck)
axillary (axilla)
brachial (arm/elbow)
ulnar & radial (forearm)
deep palmar venous arches
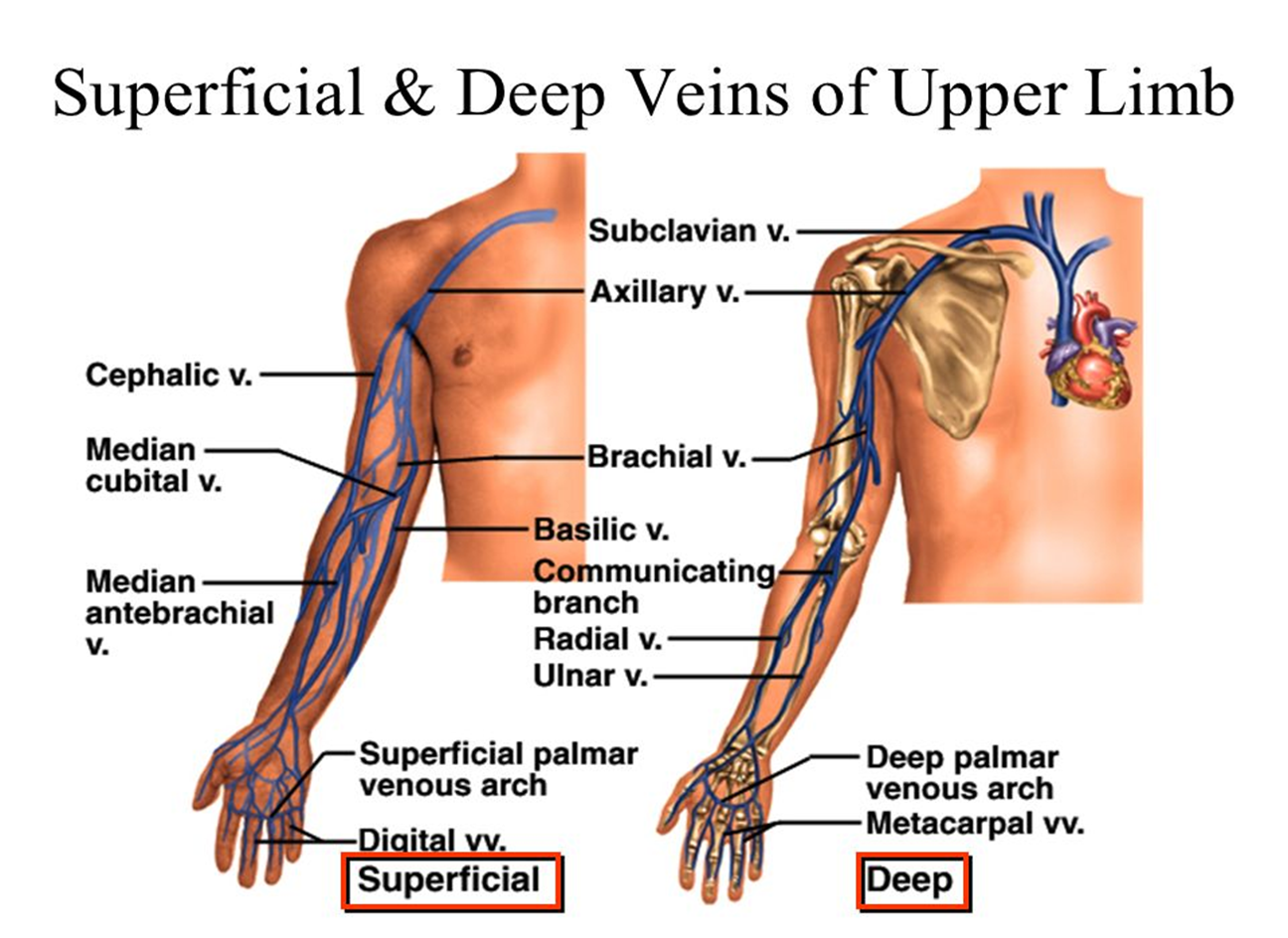
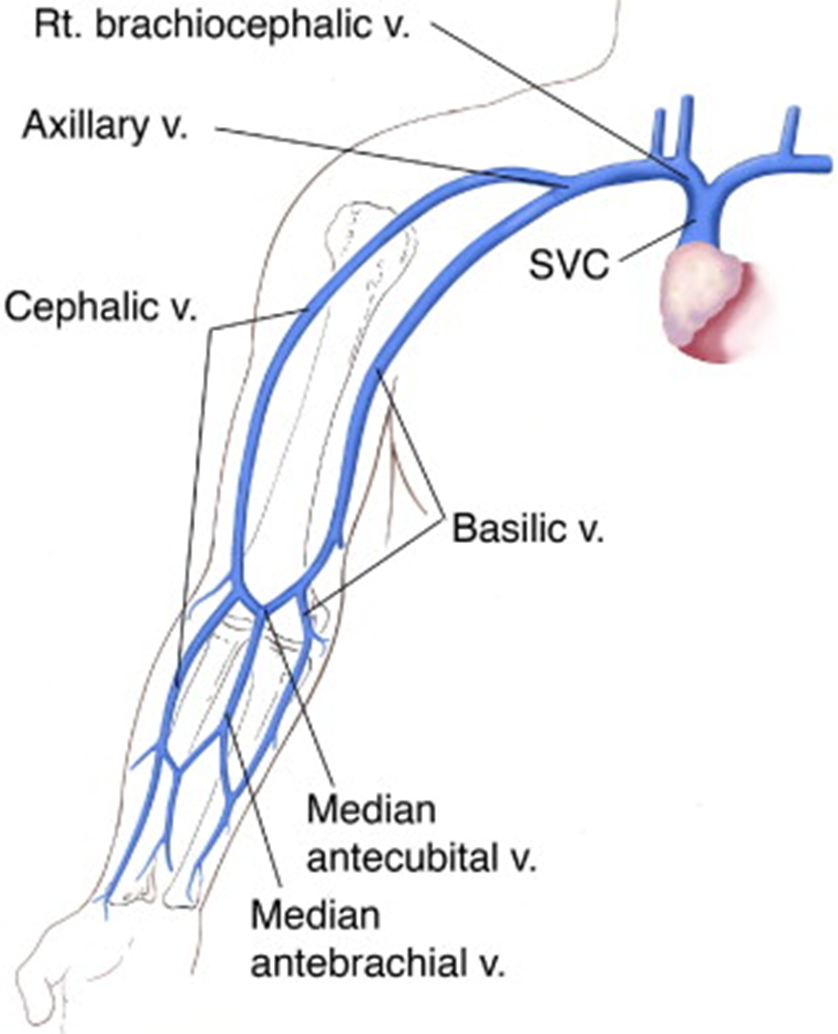
what are the superficial veins of UE?
cephalic (arm/forearm)
basilic (arm/forearm)
median cubital (elbow)
superficial palmar venous arches
digital
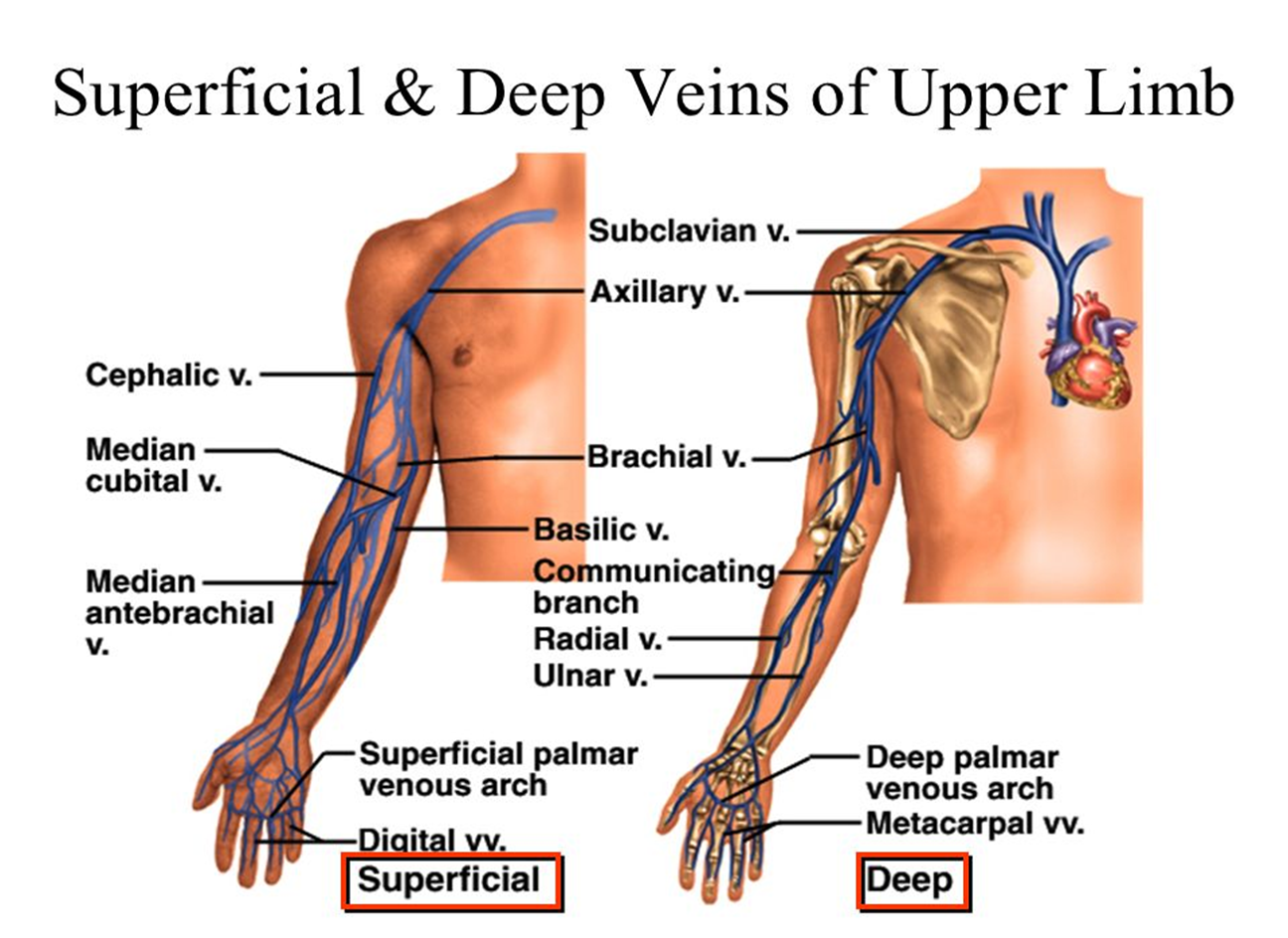
the cephalic vein courses on which side
radial side
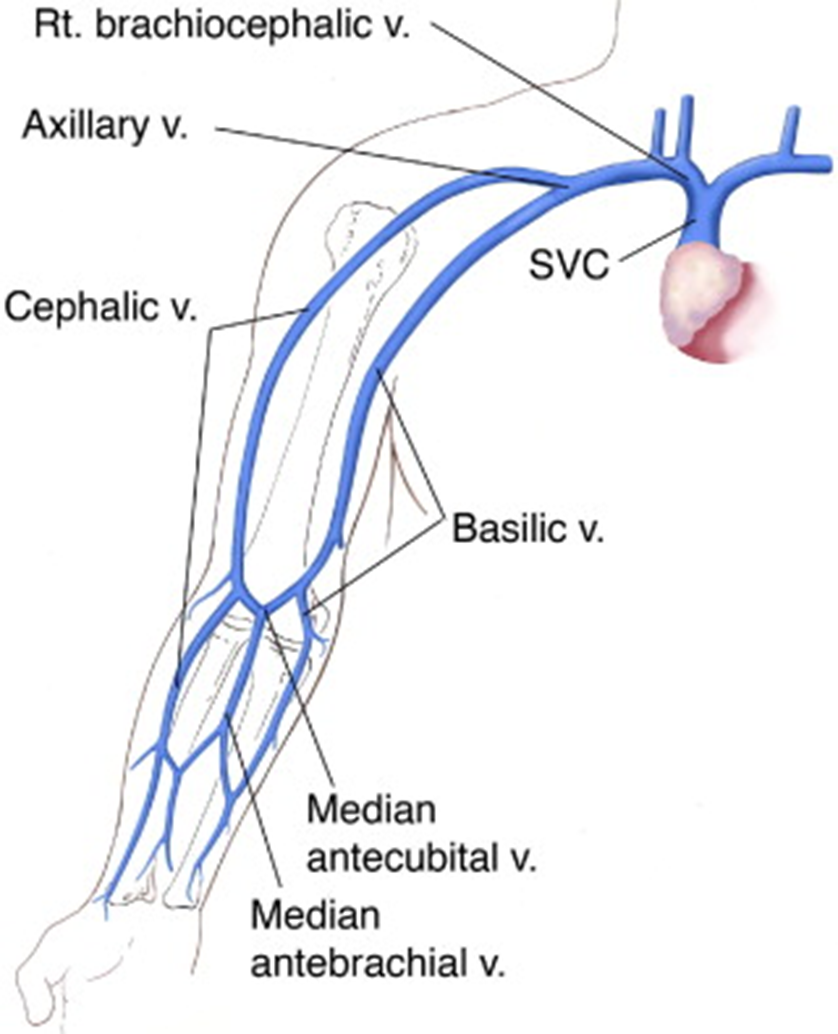
the cephalic vein joins
the subclavian
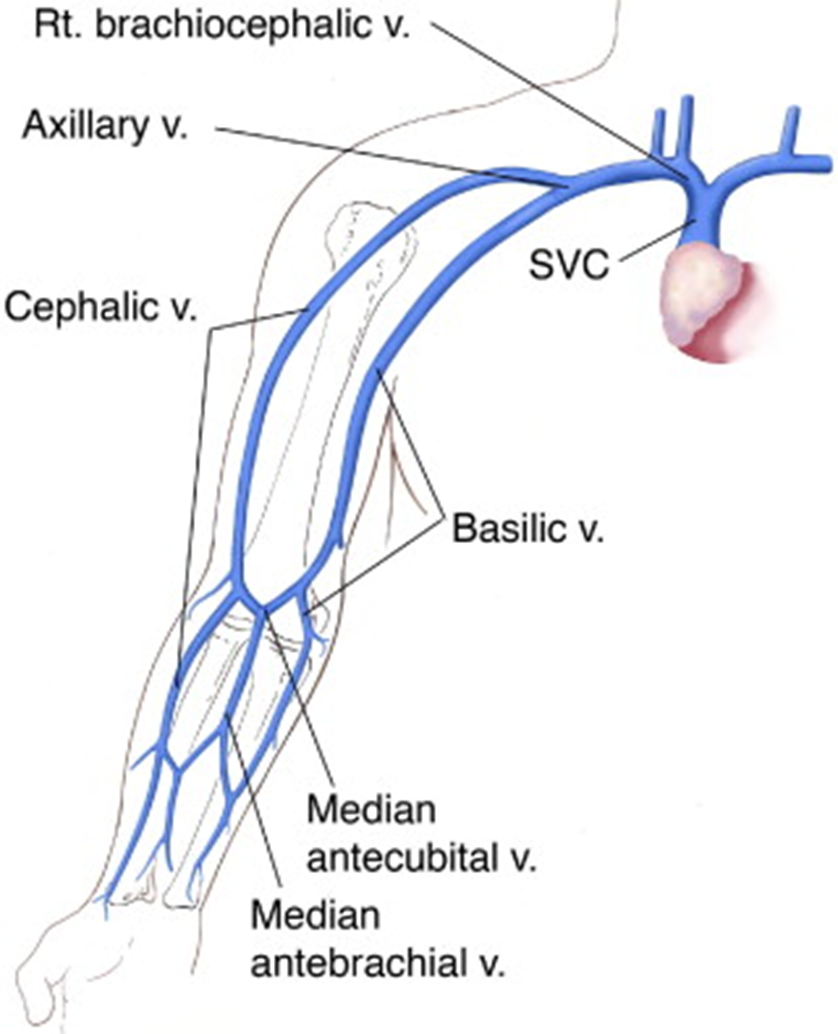
the median cubital joins
cephalic and basilic in forearm
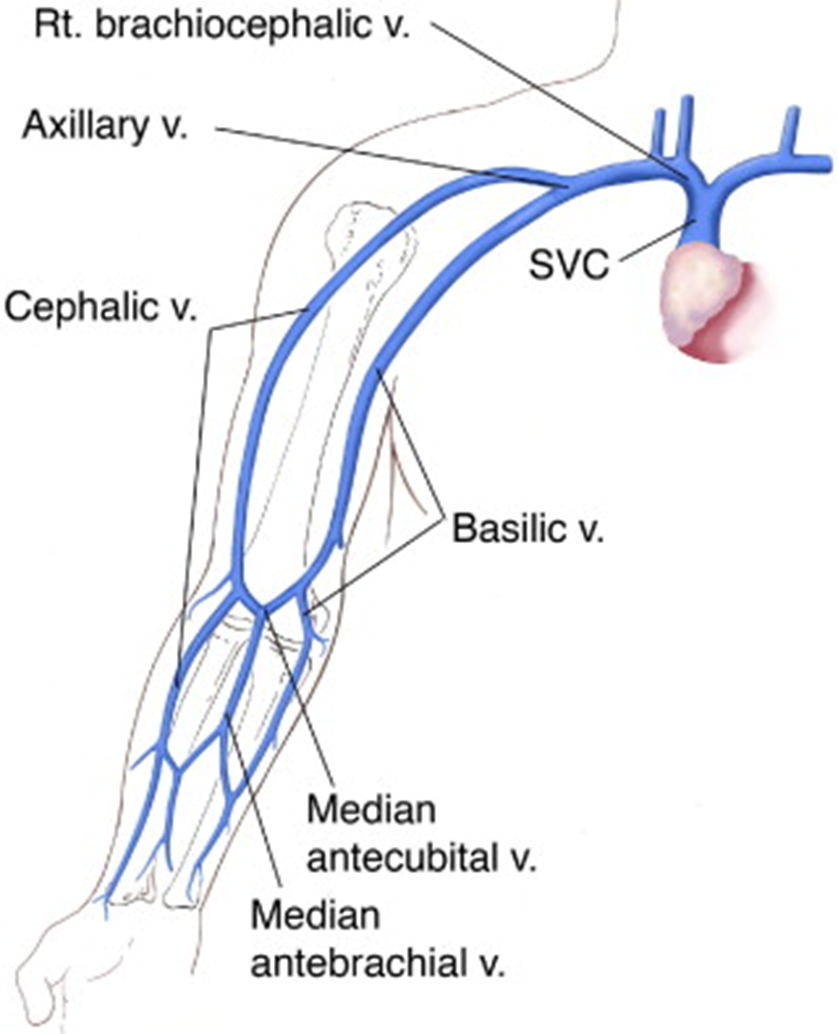
the basilic vein courses on which side?
ulnar side
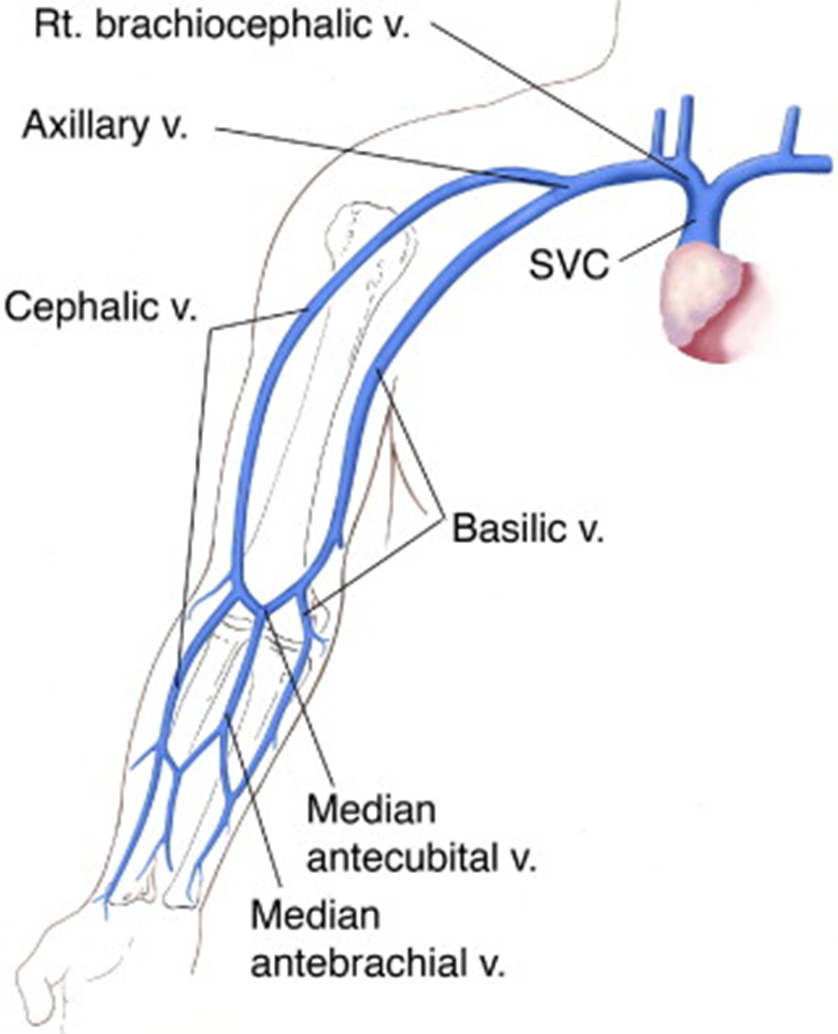
the basilic vein courses
medially to join axillary
what are venae commitantes
paired veins
what are examples of venae commitantes?
brachial
ulnar
radial
what are the veins of the antecubital fossa?
cephalic vein
basilic vein
median basilic vein
median cephalic vein
median antebrachial
what are the main causes of upper limb arterial disorders
occlusion of aubclavian access lines
acute obstruction due to embolization from heart or SA aneurysm
atherosclerotic disease (RARE) 5%
what are the most commonly affected sites of arterial disorders
subclavian artery and axillary artery
what is thoracic outlet syndrome
compression of the SCA, SC vein, or brachial plexus between clavicle and first rib in region of neck ; vessels are partially or completed compressed with arm in certain positions
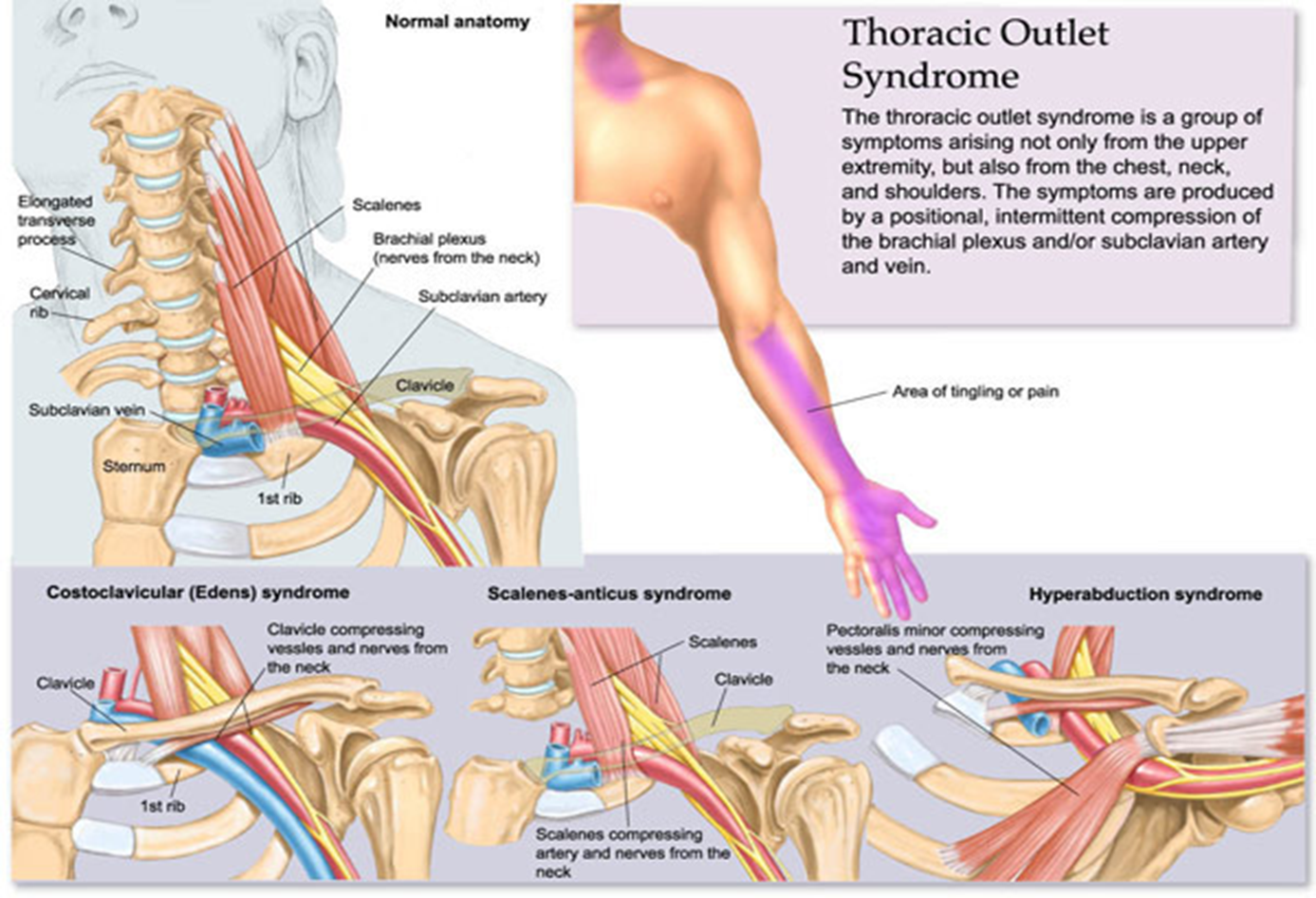
what can thoracic outlet syndrome cause?
intimal damage. thrombus formation, numbness
why do patients with chronic upper limb arterial diseases have few symptoms
arms develop good collateral circulation around diseased segments
what are the common indications for UE arterial duplex
assess patients with documented arterial disease
pre procedure assessment for planning of intervention
post angioplasty / stent placement
post op evaluation of arterial bypass grafts
eval aneurysm, pseudoaneurysm and arterial venous fistula
evaluation of arterial trauma
evaluation of pts with exercise related pain
what transducer is used to scan UE vessels?
5-10 MHz linear transducer
what freq transducer is best for scanning left SCA and brachiocephalic?
2-2.5 MHz
visuals

what are normal extremity arterial waveforms?
at rest : triphasic high resistance
after exercise : low resistance waveform
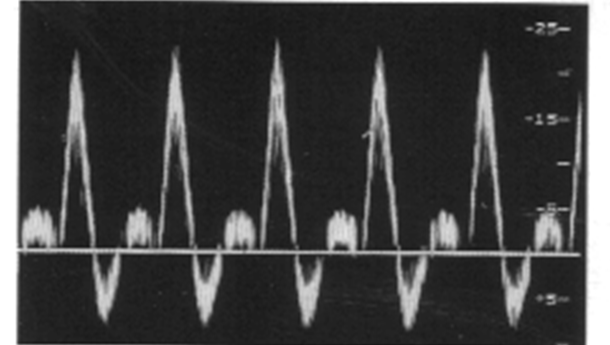
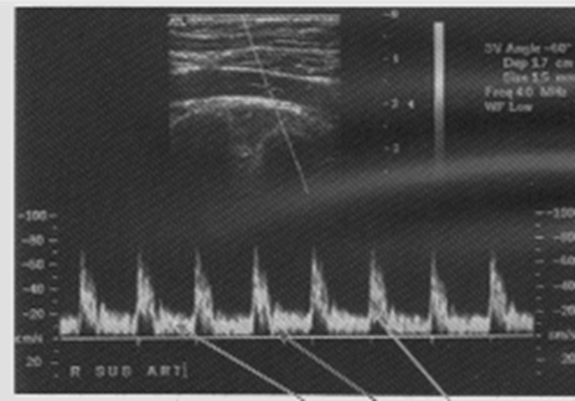
what are the three phases in triphasic waveform?
sharp systolic peak
short phase of flow reversal due to elastic recoil
short phase of antegrade flow
what is the purpose of duplex UE venous imaging
assess deep and superficial venous system for the presence or absence of pathology; facilitate clinical management decisions
larger proximal veins have what type of flow pattern
spontaneous phasic flow
what is the flow pattern in veins farther from heart
fewer cardiac pulsations ; demonstrate gentile phasicity due to resp variation
what are common indications for UE venous US?
swelling, pain, tenderness, palpable (arm) cord, pre placement of a central line, indwelling catheter
DVT in axillary, subclavian and braciocephalic/innominate veins
why is venous pathology important?
very noticable and clinically important for thrombosis of major draining vessels
contraindications and limitations to UE scanning
obesity, casts/bandages/sutures, trauma or open wounds, severe edema, central venous line/dialysis catheter, clavicle hampers visualization of entire length of subclavian vein
what transducer is used in scanning UE veins?
5-18 MHz
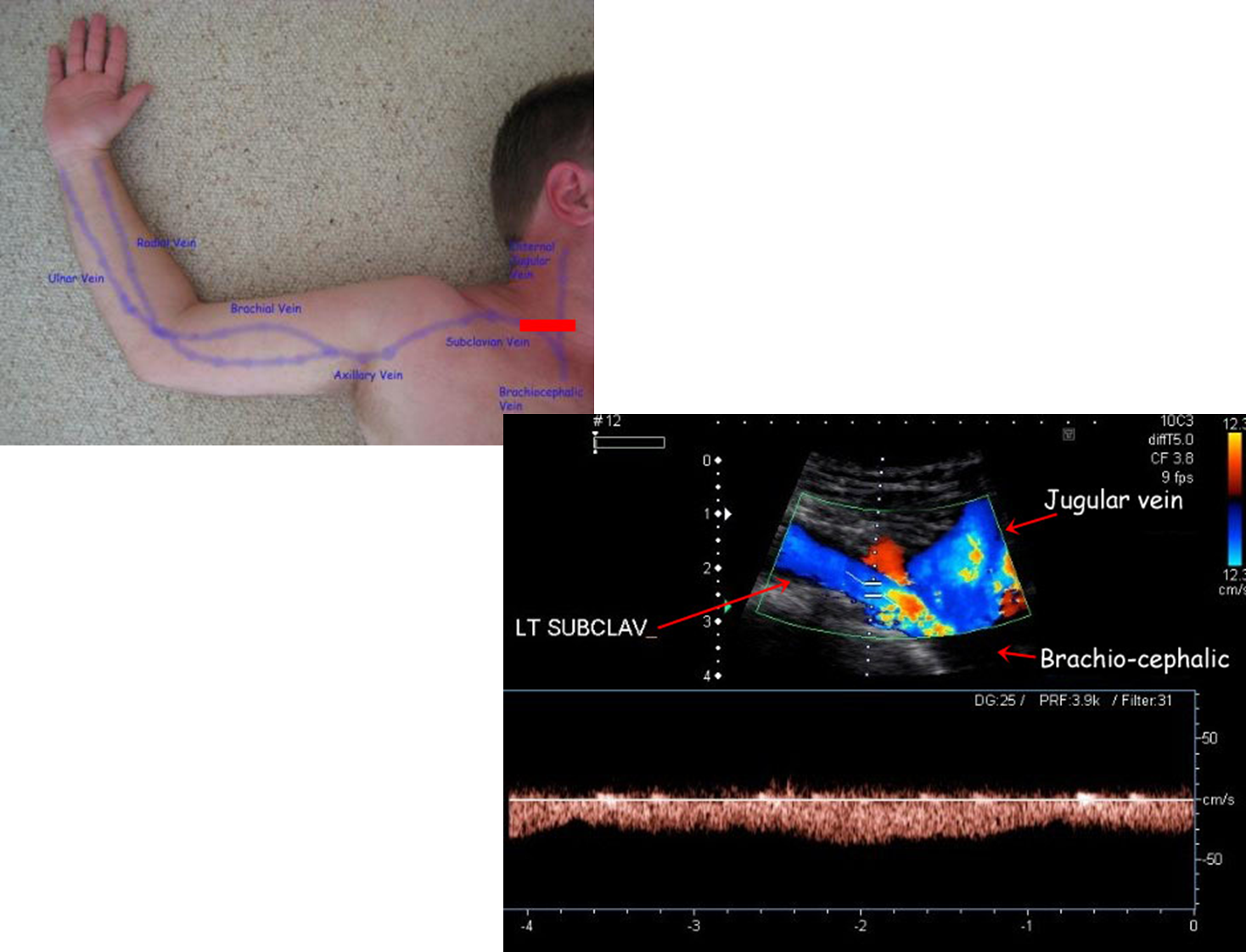
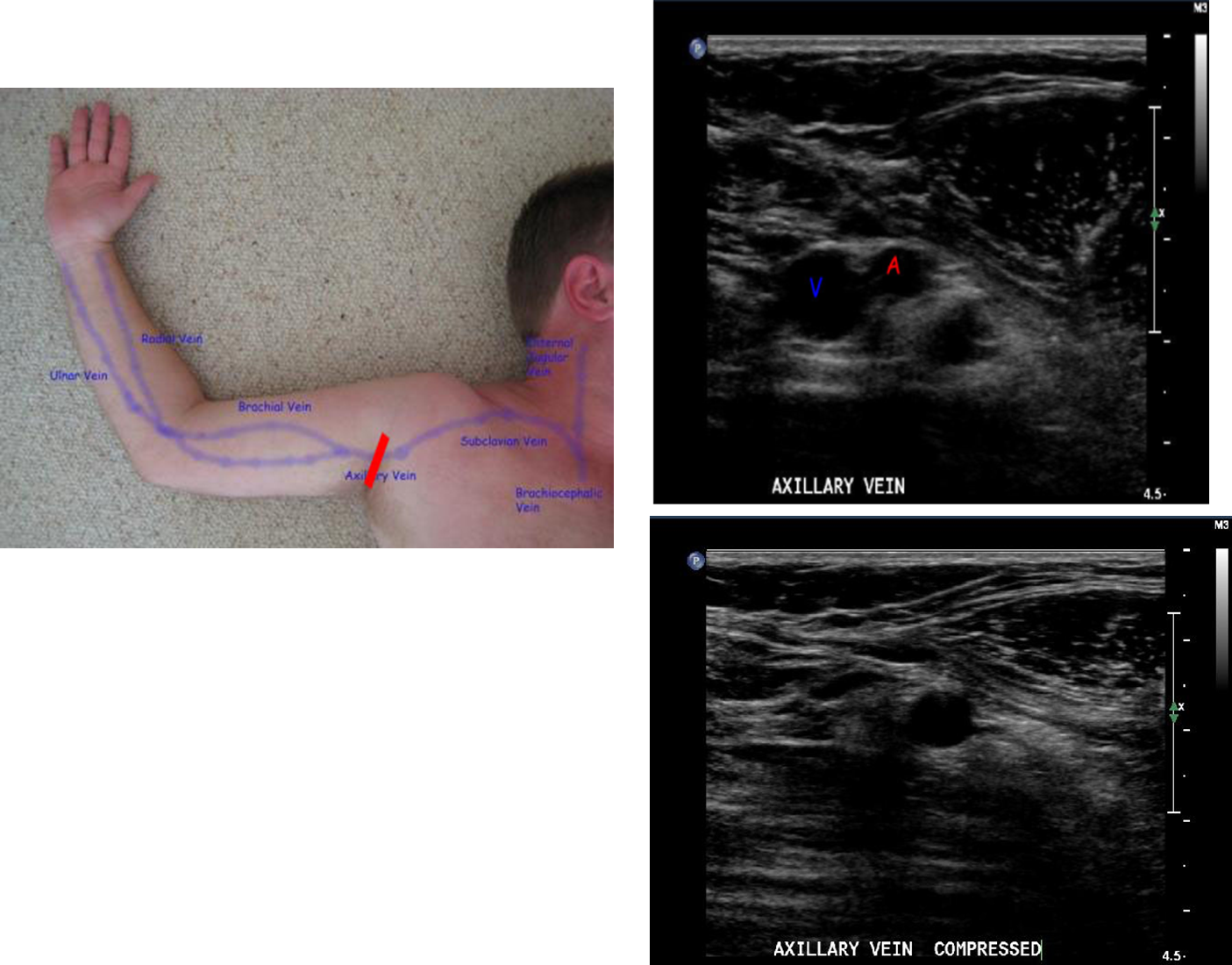
what vessels are documented in UE venous exam
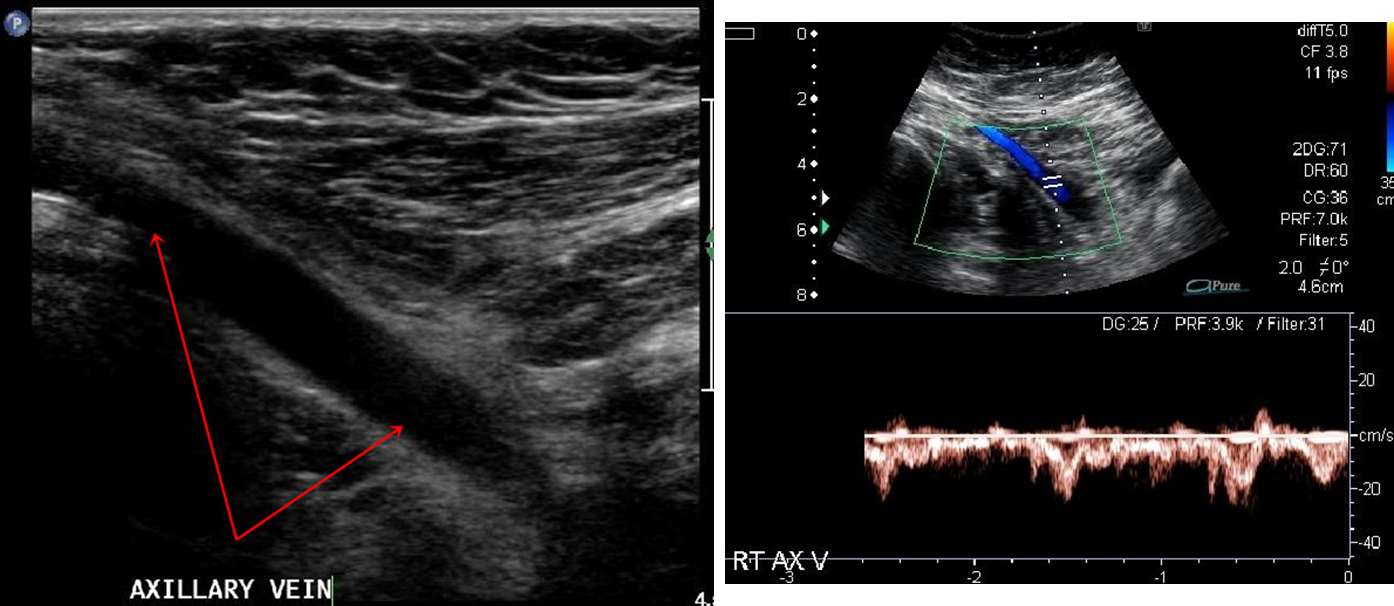
IJV, brachiocephalic veins, subclavian vein, axillary vein, brachial veins, basilic vein, cephalic vein
do you angle correct in UE venous exam?
no unless measuring velocities
what is the sniff technique
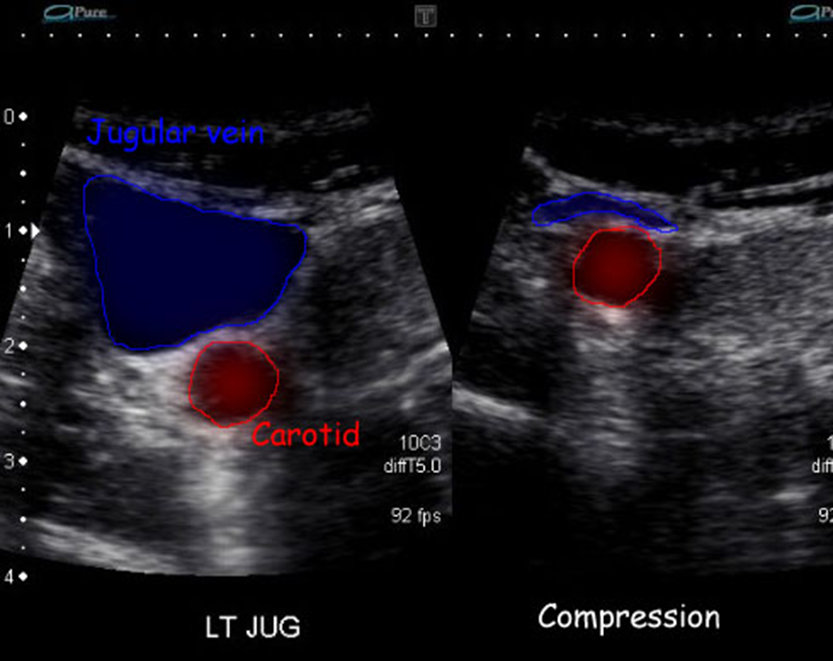
good way to check for wall coaptation (joining of two parts) where clavicle obstructs compression
know
know
know
know