ADM 2315 - CHAP 9
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
THE NATURE OF SERVICES
– Any act or performance one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything
– The government sector, with its courts, employment services, hospitals, loan agencies, military services, police and fire departments, postal service, regulatory agencies, and schools, is in the service business. The private nonprofit sector—museums, charities, churches, colleges, foundations, and hospitals—is in the service business.
THE SERVICE ASPECT OF AN OFFERING
5 Categories of service product offerings:
• A pure tangible good-soap/toothpaste/milk, etc
• A tangible good with accompanying
services-car/phone/computer
• A hybrid-restaurants
• A major service with accompanying minor
goods/services-air travel
• A pure service-babysitting, massage, therapy
CHRACTERISTICS OF SERVICE
INTANGIBILITY
INSEPARABILITY
VARIABILITY
PERISHABILITY
INTANGIBILITY
• Services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled
• “Tangibilize the intangible” to reduce customer
uncertainty, customers will look for evidence of quality by
drawing inferences from
– Place
– People
– Equipment
– Communication material
– Symbols
– Price
INSEPARABILITY
• Services are typically produced and consumed
simultaneously
• Cannot separate the service from the provider of the
service
• Several strategies exist for getting around the limitations
of inseparability. The service provider can work with
larger groups. The service organization can train more
service providers and build up client confidence, as H&R
Block has done with its national network of trained tax
consultants.
VARIABILITY
• The quality of services depends on who
provides them, when and where, and to
whom
– As such, services are highly variable
Strategies for increasing quality control
– Invest in good hiring and training procedures.
– Standardize the service-performance process
throughout the organization.
– Monitor customer satisfaction.
PERISHABILITY
• Services cannot be stored
• Companies have to manage demand. He right services
have to be available to the right customers at the right
places at the right times.
– Offer differential pricing, try to increase nonpeak demand, reservation systems
OVERCOME PERISHABILITY
Demand side
• Differential pricing
• Nonpeak demand
• Complementary services
• Reservation services
Supply side
• Part-time employees: Part-time employees can serve peak demand. Colleges add part-time teachers when enrollment goes up; stores hire extra clerks during holiday periods.
• Peak-time efficiency routines: Peak-time efficiency routines can allow employees to perform only essential tasks during peak periods.
• Increased consumer participation: Increased consumer participation frees service providers’ time. Consumers fill out their own medical records or bag their own groceries.
• Shared services: Shared services can improve offerings. Several hospitals can share medical-equipment purchases.
• Facilities for future expansion: Facilities for future expansion can be a good investment. An amusement park might buy surrounding land for later development.
NEW SERVICES REALITIES
Increasing role of technology
• Fundamentally changing how value is delivered to
customers
• Power to make service workers more productive
Importance of the increasingly empowered customer
• Unbundled service choices
• Social media to spread the word
Need to engage employees as well as customers
• Allow employees to:
– Pamper customers
– Read their needs
– Develop a personal
relationship with them
– Deliver high-quality
service
ACHIEVING EXCELLENCE
• External marketing
– Preparing, pricing, distributing, and promoting the
service to customers
• Internal marketing
– Training and motivating employees to serve
customers well
• Interactive marketing
– Employees’ skill in serving the client
BEST PRACTICES OF TOP SERVICE COMPANIES
• Customer-centricity
– seeing the world in general, and a company’s
services in particular, from the customer’s point of
view
– ‘Customer obsessed’
• Service quality
• The best service providers set superior quality standard
• The best service providers set superior quality standards.
• The standards must be set appropriately high.
• Top firms audit their own service performance, as well as
that of competitors, on a regular basis.
• Cater to high-value customers
• Special discounts
• Promotional offers
• Special service
• Manage customer complaints
Companies that encourage disappointed customers to
complain—and also empower employees to remedy the
situation on the spot—have been shown to achieve higher
revenues and greater profits than companies without a
systematic approach for addressing service failures.
• Extra role behaviors
• Increasing quality of Call centers
• Customer service representatives
DIFFERENTIATING SERVICES
Main service differentiators are:
• Ease of ordering
• Speed and timing of delivery
• Installation, training, and consulting
• Maintenance and repair
• Returns
• When the physical product cannot easily be
differentiated, the key to competitive success may lie in
adding valued services and constantly improving their
quality.
MANAGING SERVICE QUALITY
Two important activities in managing service quality are:
• Managing customer expectations
• Incorporating self-service technologies
SERVICE QUALITY MODEL
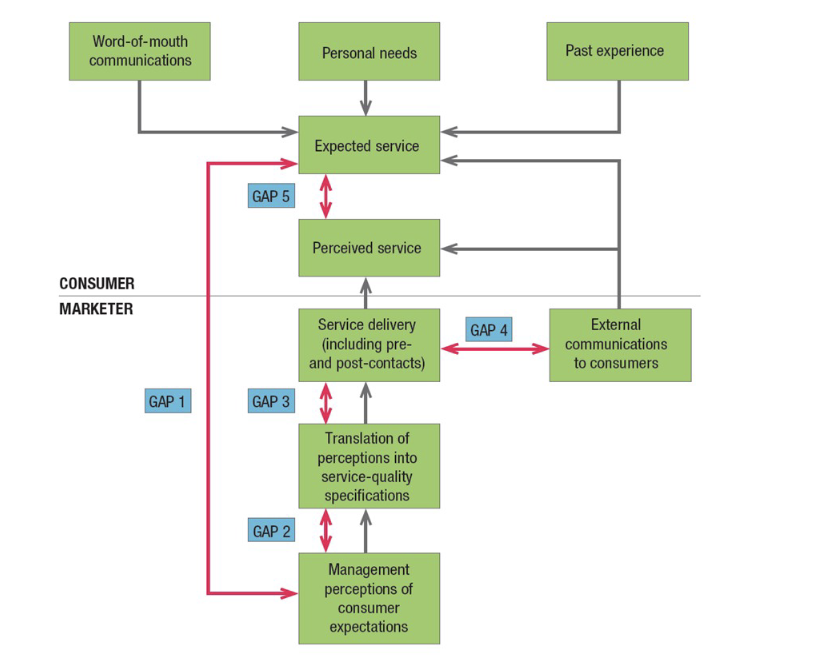
Service Quality 5 GAPS explained
Gap between consumer expectation and management perception—Management does not
always correctly perceive what customers want.
Gap between management perception and service-quality specification—Management might
correctly perceive customers’ wants but not set a performance standard.
Gap between service-quality specifications and service delivery—Employees might be poorly
trained or incapable of or unwilling to meet the standard; they may be held to conflicting standards,
such as taking time to listen to customers and serving them fast.
Gap between service delivery and external communications—Consumer expectations are
affected by statements made by company representatives and ads.
Gap between perceived and expected service—The consumer may misperceive the service
quality.