How the macroeconomy works?
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Define national income
The flow of new output produced by the economy in a particular period using stock of physical/capital
What is national capital stock
Stock of capital goods that has accumulated over time
National wealth?
The total value of all assets owned by the residents of a country at a given point in time
What happens if replacement investment does not occur?
Capital stock shrinks
Negative growth occurs
PPF shifts inwards
What is net investment?
Investment needed to enlarge the capital stock
Define consumption
Total spending by households on goods and services within the economy in a period of time
What is national expenditure
Spending on goods and services
A measurement of economic output
What does the circular flow model show?
How money, goods and resources move around in the economy
Highlighting the interdependence between different economic agents
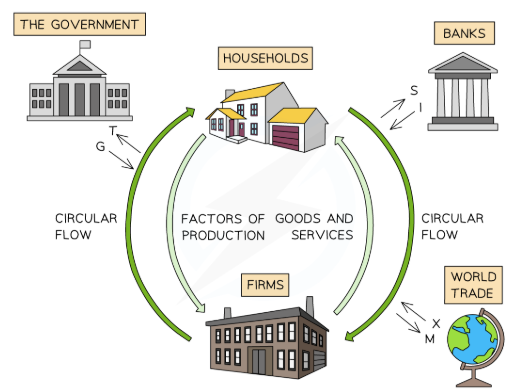
Define leakage/withdrawal and give examples
Any withdrawal of expenditure from the circular flow of income, decreasing overall economic activity
Savings
Taxes
Imports
Define injection and give examples
Expenditure in the circular flow of income, boosting economic activity
Exports
Government spending
Investment
Macroeconomic equilibrium
Leakages=injections
What is a closed economy?
Economy with no international trade
Define reflationary policies
Polices that increase AD
With the intention of increasing output and employment
Define AS
Level of real national output that producers are willing to supply at different average price levels
Define AD
Total planned spending on real output
What is an economic shock?
An unexpected event hitting the economy
Can be demand side- shock that effects aggregate demand
Supply side-shock that effects aggregate supply
What does saving instigate?
Can lead to deficient aggregate demand
Meaning there is too little demand to buy the output the economy is capable of producing
National income falls
What refutes the idea that savings lower national income
If savings are lent to other consumers via banks for the purpose of consumption
Savings end up as consumption
National income remains in equilibrium
What do free market economists say about deficient aggregate demand
They believe its a self correcting phenomenon
And interest rates fall rather than output
Why is the simple circular flow model unrealistic?
Forsakes international trade and domestic government
Explain the effect of leakages>injection
Net withdrawal of demand out of the circular flow of income causes national income to fall
Explain the effect of injections> leakages
Net injection of demand into the circular flow of income causes national income to rise
What are the components of AD?
Consumption
Investment
Government spending
Net exports
AD= C + I + G + (X-M)
What factors effect consumption?
Interest rates
Level of income
Expected future income
Wealth- Stock of personal wealth(assets)
Consumer confidence
Availability of credit
Distribution of income
What is the life cycle theory of consumption?
Explains consumption and savings in terms of how people expect their incomes to change over the future
How does availability of credit effect consumption?
Refers to the ease with which individuals can obtain loans
If credit is available easily and cheaply consumption increases
How does a distribution of income effect consumption?
Rich people save a higher proportion of their income as they earn more
Therefore a redistribution of income reduces savings and increases consumption
Define realised personal savings
The actual amount of income that individuals save after meeting their consumption and tax obligations
How do you calculate personal saving ratio and what does it show
Used as an indicator of how people spend their money
Realised personal saving/disposable income
2 types of investment
Investment in fixed capital- factories, roads
Inventory investment - raw materials
What is saving
income not spent on consumption
Factors influencing investment
expected sales revenue
expected costs of production
Future profit
Prices of capital and labour
Nature of technical progress
Impact of government policies- increased gov spending promotes investment but higer taxation reduces investment
What is the accelerator effect
Changes in investment can be directly linked to changes in the rate of GDP growth
If the rate of GDP growth increases so does investment (that firms make to keep up with growing demand)
Define economic activity
Production and consumption of goods and services in the economy together with the employment of labour and inputs that produce outputs
What is the expansionary effect
When AD increases so does real output
What is the contractionary effect
AD decreases so does real output
Define multiplier effect
Process by which any changes in the components of aggregate demand will lead to an even greater change in national output
Because an increase in spending will create income for someone else facilitating further consumption
Initial injection into the economy leads to a more than proportionate increase in national income
Multiplier equation
K= 1 / 1-MPC
Where K is the multiplier
What is MPC -
The marginal propensity to consume is the fraction of an increase in disposable income that people plan to spend
If MPC is 1 that means 100% of that increase in income is to being spent
Another equation to calculate the multiplier
Change in national income/initial change in government spending
Define nominal national income
Total value of goods and services produced in an economy measured at current market prices
Reflects changes in output and price
Define real national income
Total value of goods and services adjusted for inflation
Reflects actual change in output without effects in price
Define SRAS
Aggregate supply when the level of capital is fixed but other factors of production can be altered
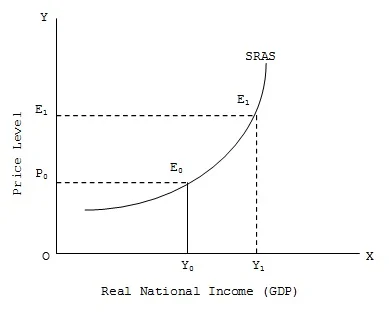
What does the slope of the SRAS indicate
In the short run the cost of producing extra units of of output increases as firms produce more output
Define the inflationary effect
A sustained increase in general price level
What does the notation of Yfe mean and tell you
Full employment level
Any increase in demand beyond this point only causes price to rise and inflation
Factors that cause a rightward shift of SRAS
Fall in production costs
Increase in labour productivity
Reduction in tax
Increase in subsidies
Technical progress
Define LRAS
Aggregate supply when the economy is producing at its productive potential
If more factors of production become available
LRAS shifts to the right
What is the normal capacity level of output
Where the LRAS is located
Maximum sustainable level of output an economy can produce when all factors of production are employed
Why is LRAS vertical
Independent of price level
Does not matter whether prices increase or decrease the economy can only produce as much as its productive resources allow
What determines the position of the LRAS
Technical progress
Productivity of labour
Quantities of factors of production
Personal enterprise
How can long run economic growth be depicted by diagrams
Outward movement of the ppf
Rightward shift of the LRAS
Define long run economic growth
Is the sustained increase in the productive capacity of an economy over time
Meaning the economy can produce more goods over time.
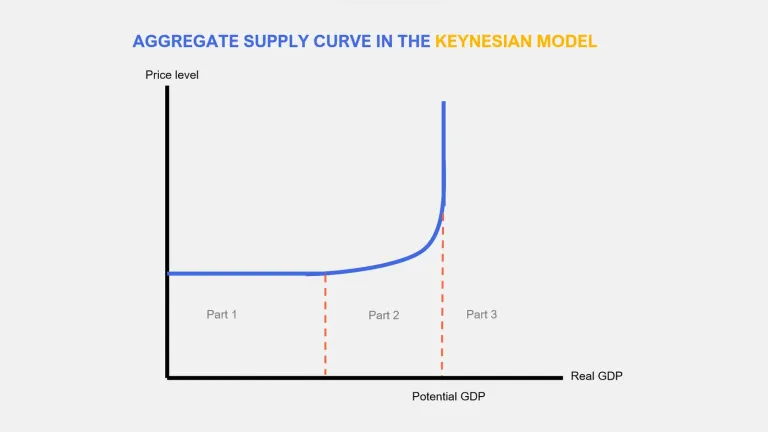
Explain the Keynesian aggregate supply curve
In the horizontal proportion the economy is operating below full capacity
At this point output can increase without changes in price level. Firms can produce more by employing idle resources
Once economy approaches full capacity curve slopes upwards
As demand rises and resources are already fully employed- price level starts to increase
Curve becomes vertical when it reaches normal capacity level of output