Innate Immunity and Pathogen Defense Mechanisms
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Innate Immunity
Immediate immune response without memory or adaptation.
Adaptive Immunity
Immune response that adapts and remembers pathogens.
Pathogens
Microorganisms that cause disease, including viruses and bacteria.
Viruses
Intracellular pathogens that replicate inside host cells.
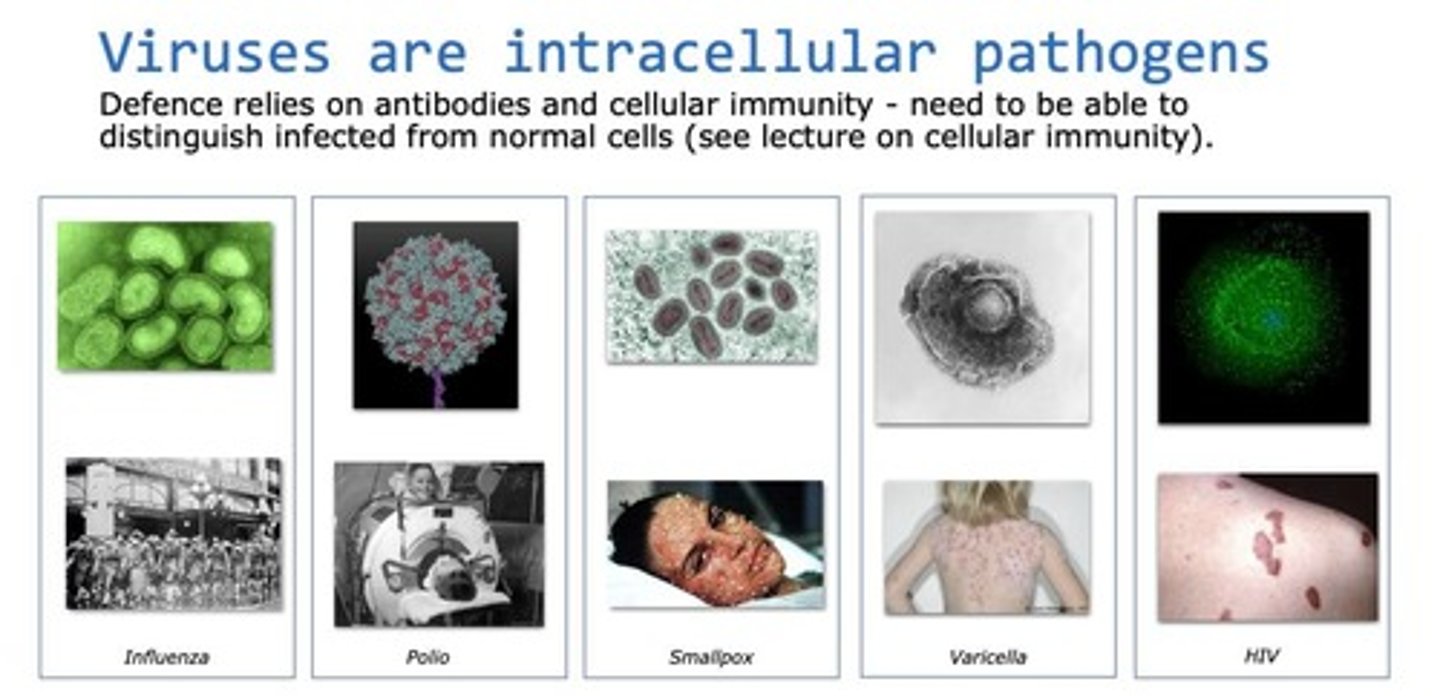
Bacteria
Extracellular pathogens that can be gram positive or negative.
Parasites
Larger pathogens requiring different immune strategies.
Gram Positive Bacteria
Thick peptidoglycan wall, resistant to MAC complement.
Gram Negative Bacteria
Thin peptidoglycan layer with tough outer membrane.
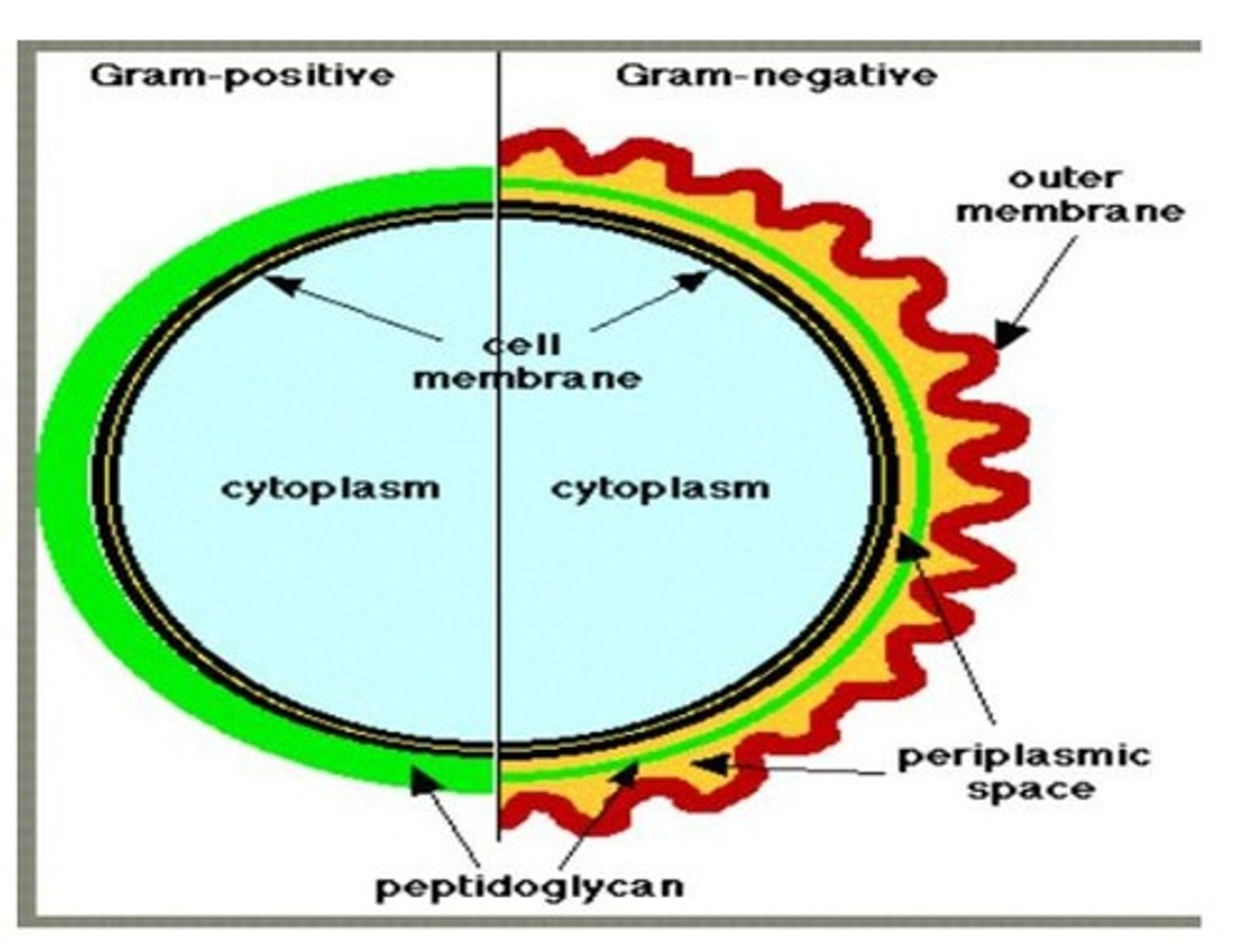
Penicillin
β-lactam antibiotic inhibiting peptidoglycan synthesis.
Neutrophil Extravasation
Process of neutrophils moving from blood to tissue.
Chemokines
Signaling molecules that attract immune cells to infection.
Tethering
Neutrophil attachment to endothelial cells via selectins.
Adhesion
Strong binding of neutrophils to ICAM-1 on endothelium.
Diapedesis
Neutrophils squeezing through endothelial cells into tissue.
Chemotaxis
Neutrophil movement along a chemokine gradient.
Opsonization
Coating pathogens with molecules to enhance phagocytosis.
Complement System
Proteins that enhance immune response and opsonization.
Phagocytosis
Process by which cells engulf and digest pathogens.
Fc Receptors (FcR)
Receptors on phagocytes that bind antibodies.
Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR)
Receptors that recognize unique microbial molecules.
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)
Unique molecules recognized by PRRs on pathogens.
Toll-Like Receptors (TLR)
PRRs that trigger innate immune responses.
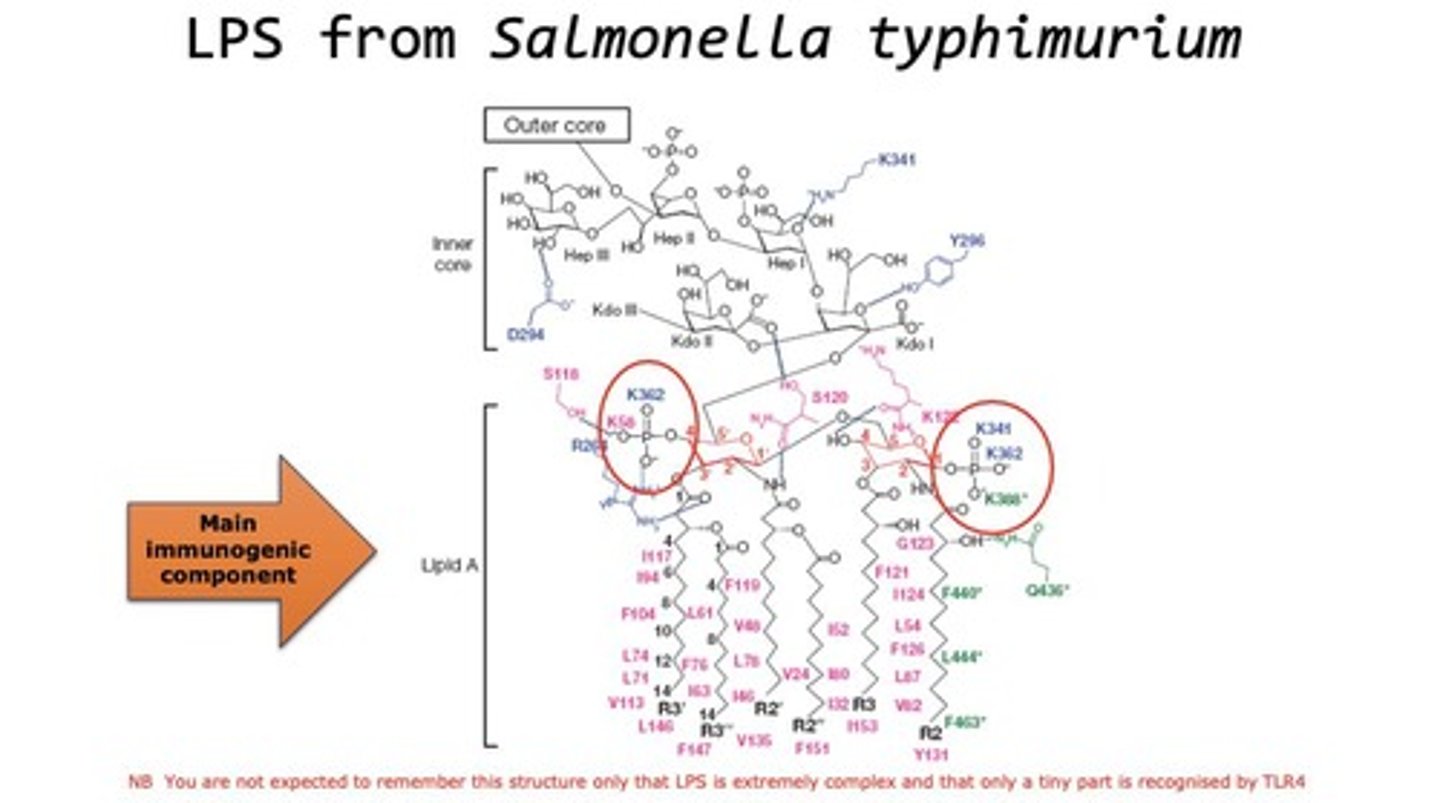
TLR4
Binds lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from gram-negative bacteria.
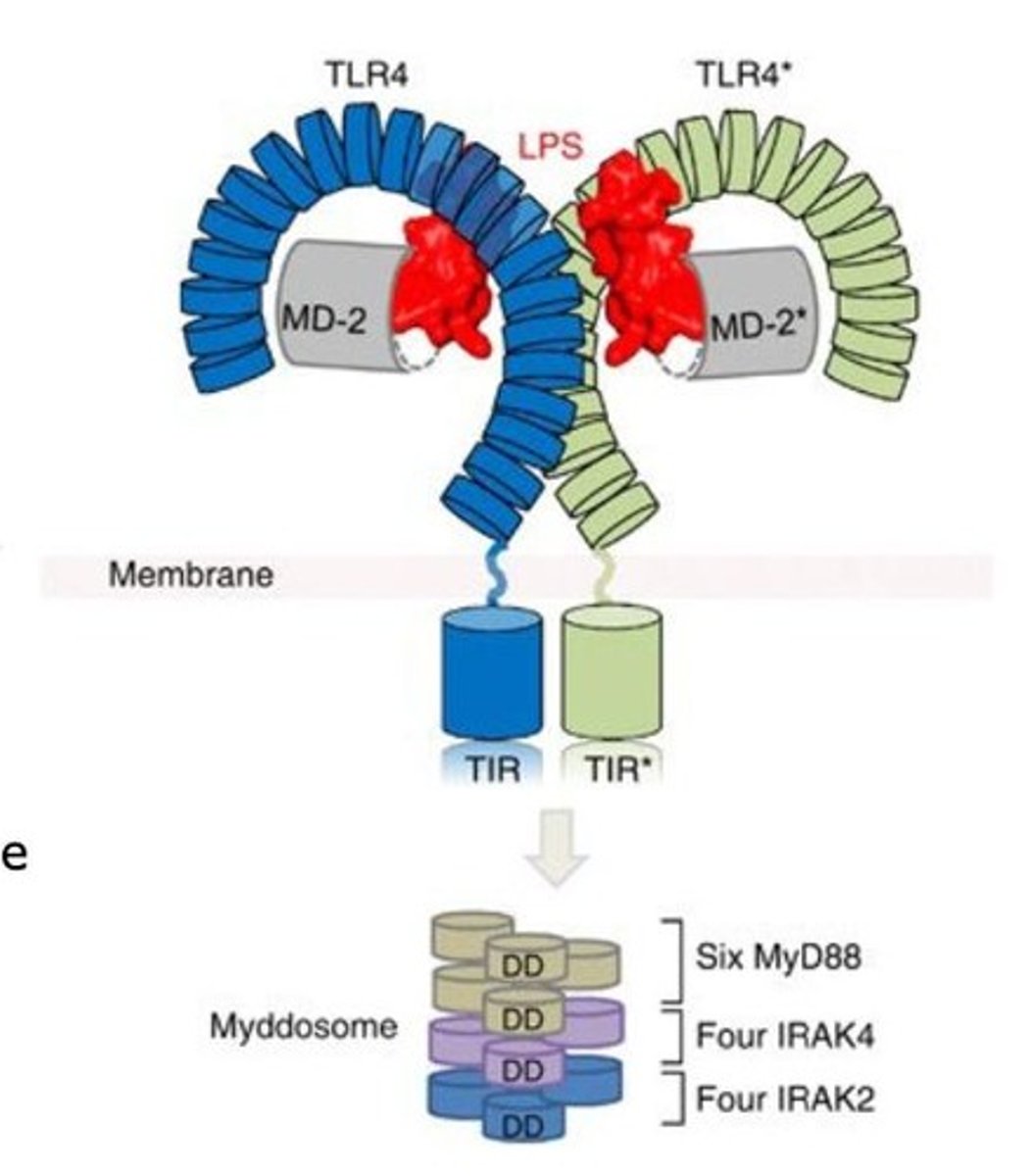
LPS
Bacterial component causing strong immune response and fever.
Neutrophil Phagocytosis
Neutrophils engulf opsonized bacteria like S. aureus.
C5a
Chemoattractant that directs neutrophil migration.
Myeloid Cells
Immune cells involved in phagocytosis and inflammation.
Degranulation
Release of cytotoxic chemicals from immune cells.
NFκB
Nuclear factor activated by TLR signaling pathways.
Immunological Memory
Ability of adaptive immunity to remember past infections.