Primary Structure of Proteins & Acid/Base Chemistry
1/16
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
proteins
polymers of amino acids
protein functions
catalysis (enzymes)
transport and storage (haemoglobin)
movement/motion (action/myosin)
mechanical support (collagen)
immunity (antibodies)
signal and nerve transmission (G-coupled receptors)
growth, differentiation, biological control (gene expression and programming)
amino acid stereochemistry
all L (levorotatory)
all S (sinister) EXCEPT cysteine (R (rectus) because of sulfur…)
amino acid functional groups
alkane (CnH2n+2)
alcohol (-OH)
phenol (-ArOH)
carboxylic acid (-COOH)
amine (-NH2)
amide (-CONH2)
thioether (-SR)
imidazole ((CH)3(NH)N)
indole (C6H4CCNH3)
guanidinium (HNC(NH2)2)
phenyl (-Ar)
thiol (-SH)
Fischer Projection of amino acids
most oxidised (COOH) on top; what side is the amino acid on?
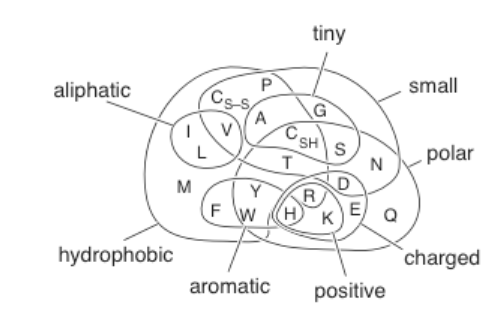
Side chain chemical properties
overlapping, but even similar residues can’t be swapped without changing structure and function of a protein
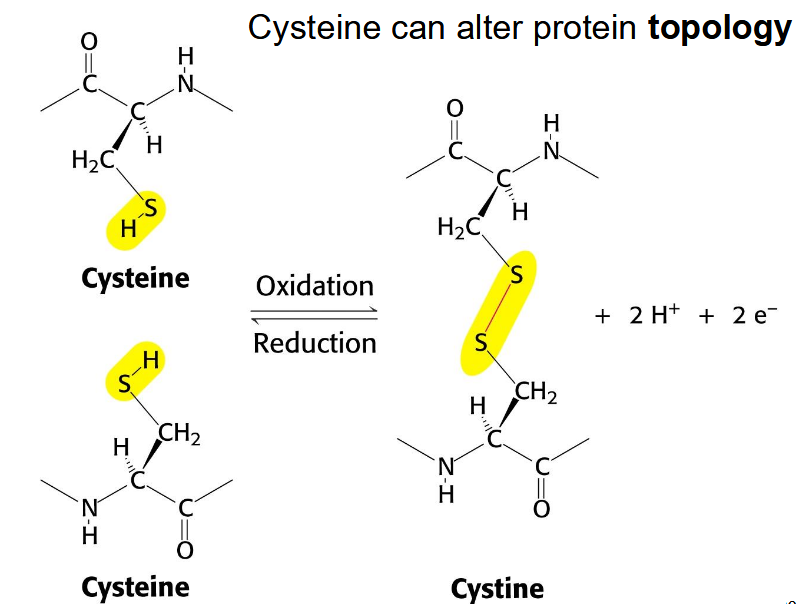
cysteine disulfide bridges
trigger massive conformational change; redox; weaker than oxygen bonds; reversible locks on structure
Tryptophan and Tyrosine chromophores
UV absorbance ~280nm can determine protein concentration; fluorescence can be used to study protein structure
Determining protein concentration
Beer’s Law (A=εcl)
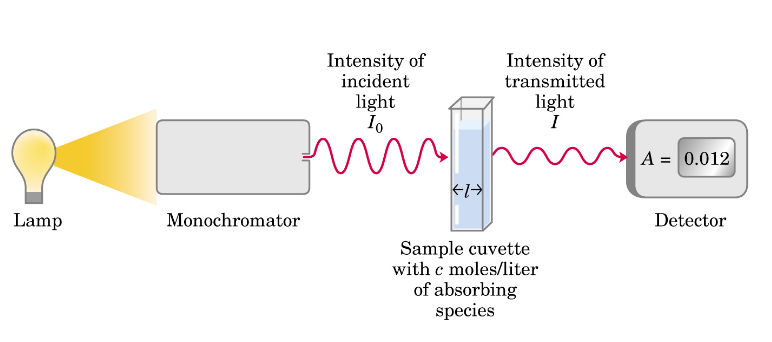
acid-base properties of amino acids
Free amino acids are acids and bases in aqueous medium
amine pKa = 10
carboxylic acid pKa = 4
form amide bonds in chains
Henderson–Hasselbalch equation
describes the change in pH during titration of a weak acid or a weak base
pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]
![<p>describes the change in pH during titration of a weak acid or a weak base</p><p>pH = pKa + log [A-]/[HA]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bc918859-da97-4d64-b9ff-c6652773ff5d.png)
Leveling Effect
An acid/base stronger than the conjugate acid/base of the solvent cannot exist in any appreciable concentration in that solvent.
Ex. in water, no acid stronger than H3O+ or base stronger than OH- can exist (pKa ~1.74 to 14)
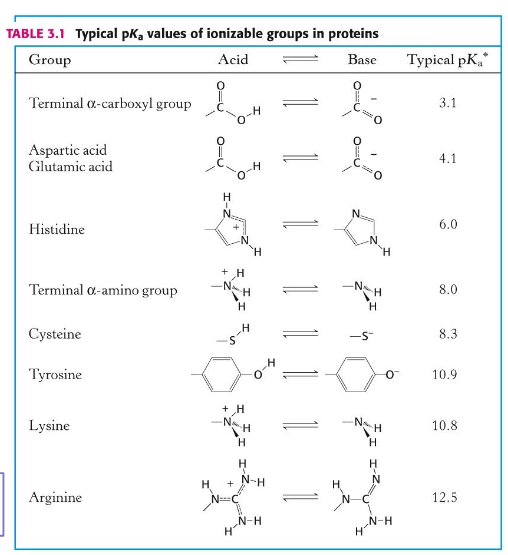
R groups @ pH 7
pKa values of ionizable groups in proteins
carboxylic acid
amine
cysteine (thiol)
histidine (pKa ~7)
arginine
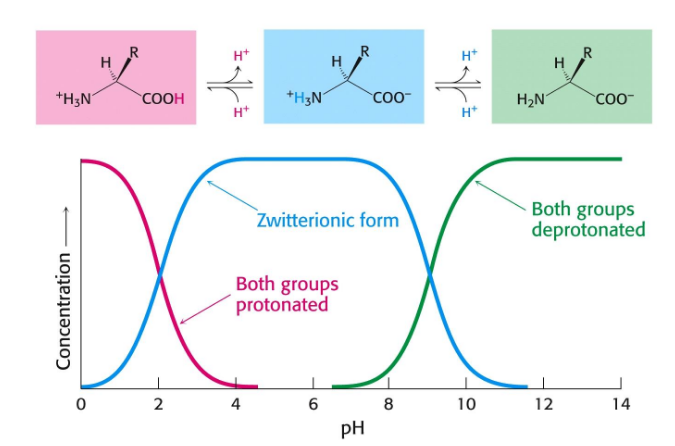
Isoelectric point (pI)
pH at which the overall charge of an amino acid/polypeptide is neutral; considers pKa and charge state of each ionization group; intermediate value theorem
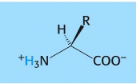
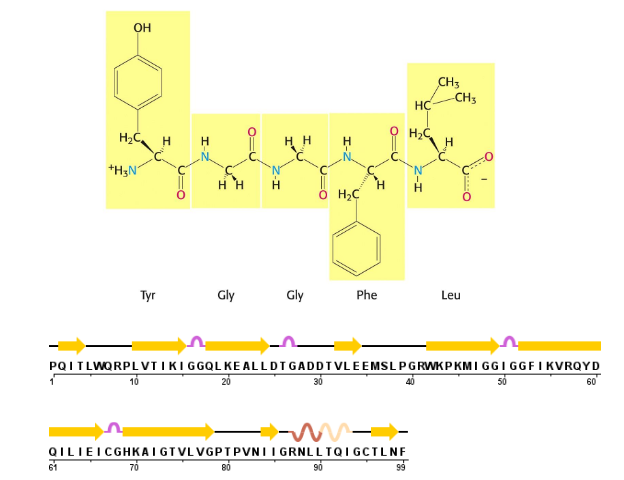
Peptide bond formation/condensation reaction
Thermodynamically, peptide bond hydrolysis is more favorable than peptide bond formation. The rate at which this hydrolysis occurs, however, is extremely slow.
Note cancellation of amino and carboxy charges when the groups join to become amides
primary structure
the amino acid structure alone