125 cardio and peripheral vascular
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
heart location
base of hear is broad and at top -apex is bottom at 5 ICS -heart sits mostly left and is measured from 2nd to 5th ICS
external and internal
jugar vein, for jugular and venous pressure
tricuspid valve
RA to RV
pulmonary valve
RV to pulmonary arteries
mitral valve
LA to LV -aka biscupid
aortic valve
LV to aorta
supply brain
carotid arteries and jugular veins
upper limbs
subclavian arteries and superior vena cava
lower limbs
thoracic aorta and inferior vena cava
systole
contraction of ventricles
diastole
ventricles relax
perfusion
The process of delivering blood from capillaries to tissues
cardiac output
amount of blood ejected from the LV each minute (CO= Stroke Volume x HR)
sinoatrial node
natural pacemaker. Sends an impulse to atrial muscles to contract and begin the cardiac cycle
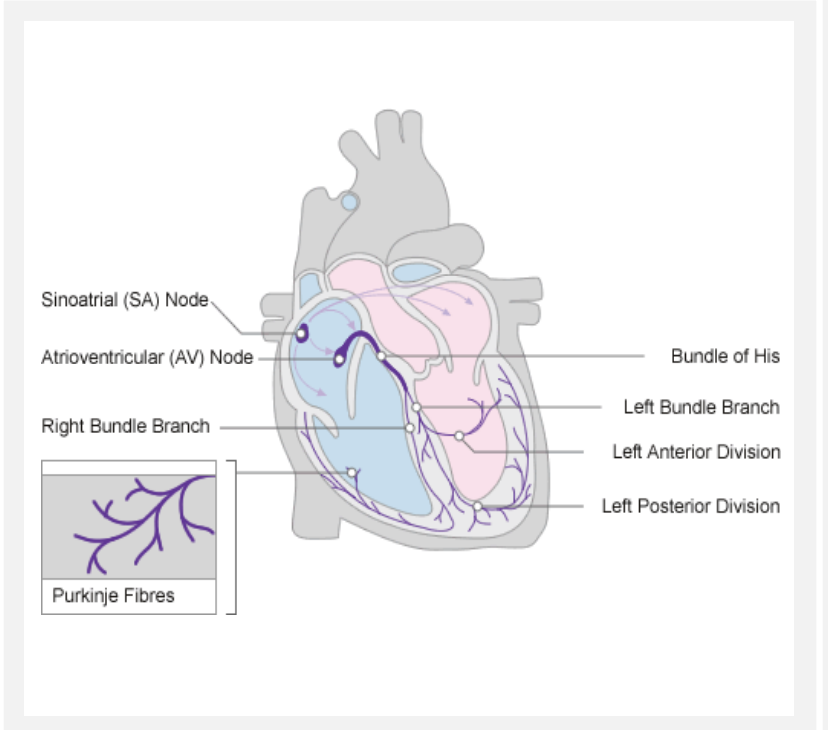
atrioventricular node
transmits the SA impulse to activate Bundle of HIS & Purkinje Fibres AND Synchronize/Mediate impulses
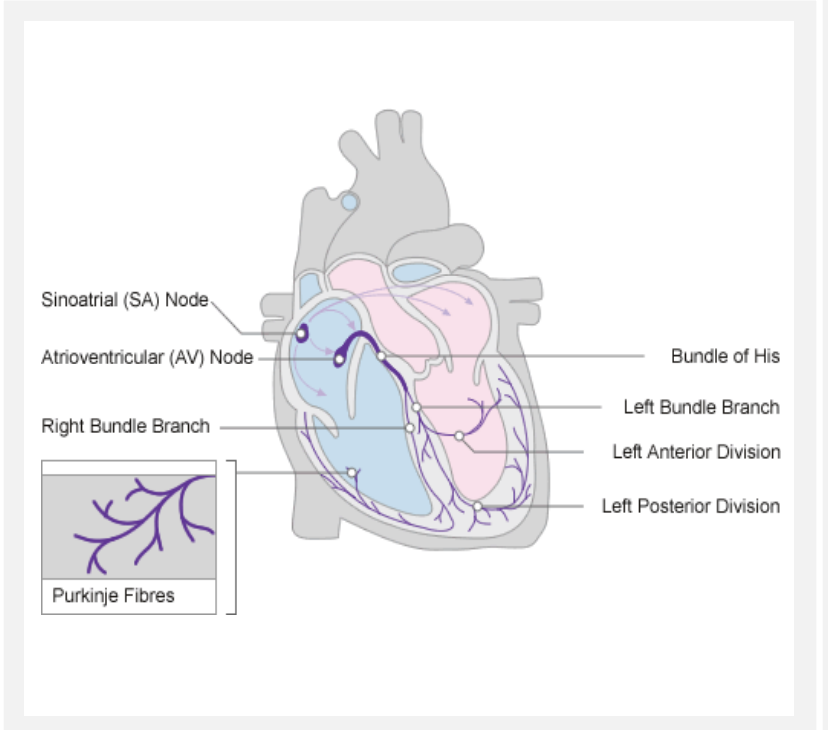
bundle of his and bundle branches
conduct impulses through ventricular wall
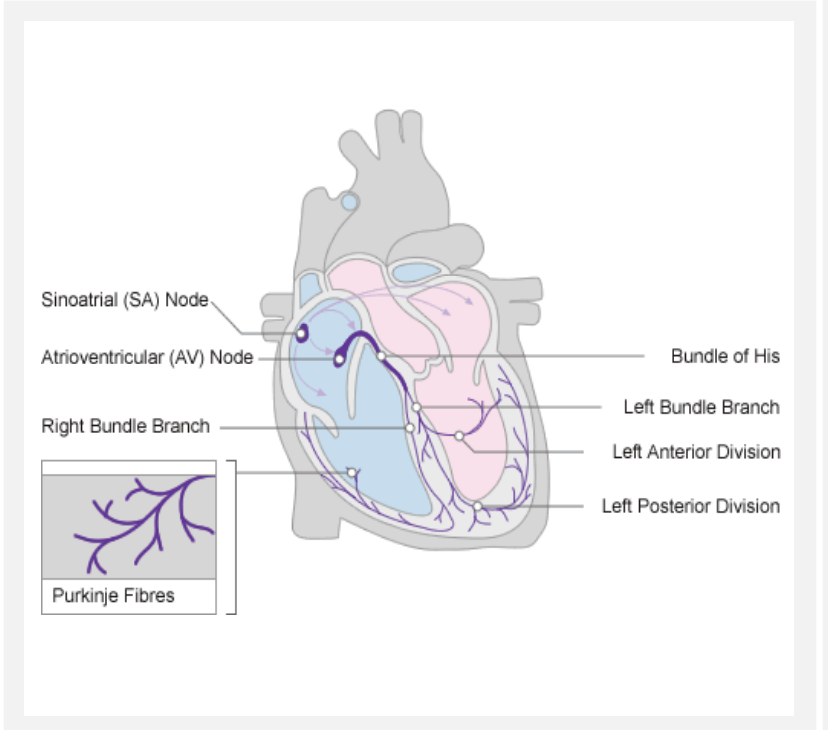
purkinje fibres
conduct impulses to ventricular walls
para and symp
control heart rate and can be impacted by stress
sounds
start of systole and start of diastole
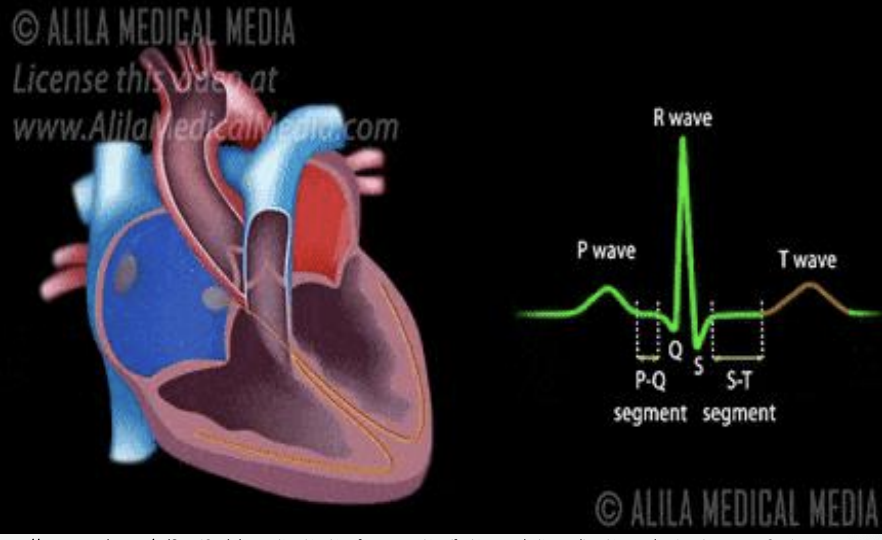
P wave
atrial depolarization (atrial contraction)
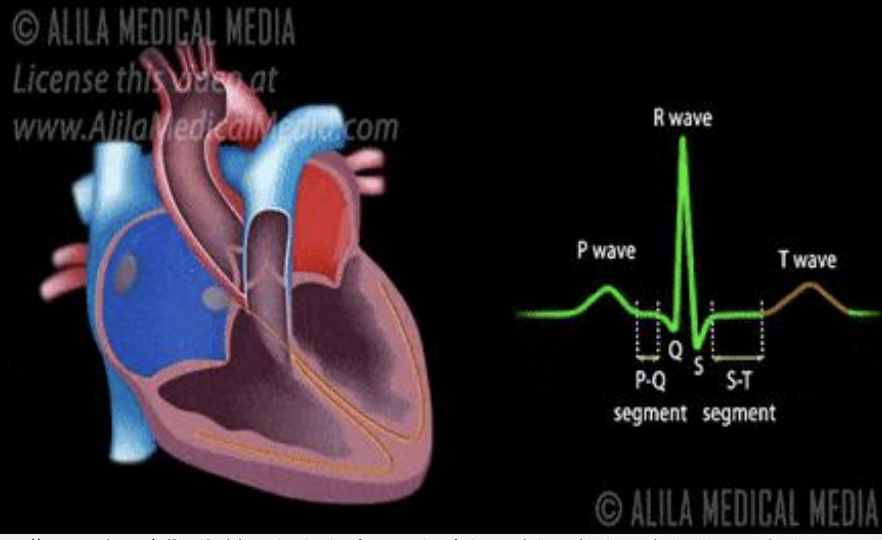
PR interval
SA-BB conduction
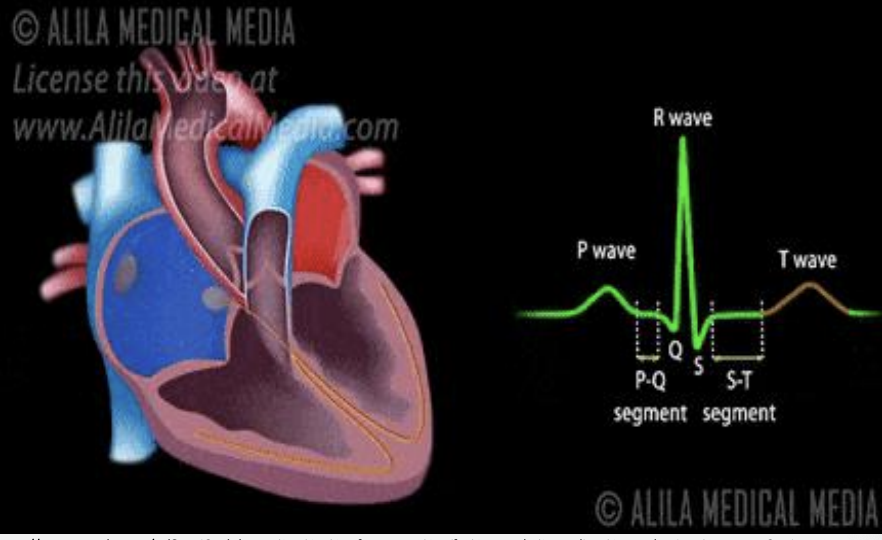
QRS
ventricular systole/contraction (hidden is atrial diastole)
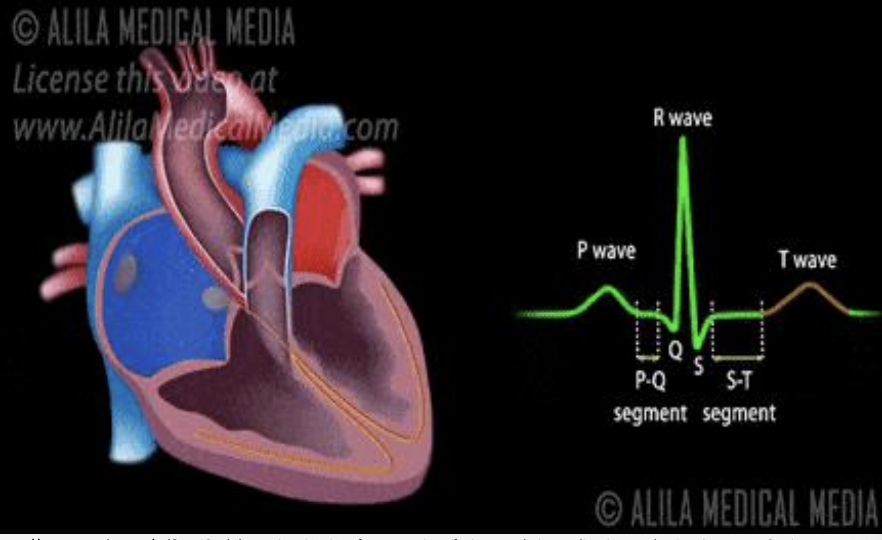
T wave
ventricular diasotle (fillling)
general survey
temp, bp, MAP, pulse
unexpected findings in gen survey
cyanosis, scar (chest area), sweating, peripheral vascular changes
risk factors
smoking, diet, active, stress, family hx, personal hx, bp and cholesterol levels, cardiac meds?
assessment
chest pain/issues, radiating pain, breathing troubles, papitations, diaphoresis, sleep changes, activity changes, edema, nocturia, cough
radiating pain
neck, jaw, shoulder, arm, back
orthopnea
SOB when lying on your back
JVP
jugular venous pulsations, reflects pressure in RA, measure should be less than 3cm
IAP (intra abdominal pressure)
listen w/ bell of stethoscope for bruits -palpate one side at a time -compare bilaterally -normal rate, rhythm, quality w/ no extra sounds
cardiac inspection
thorax and precordium for scars, pulsations, deformities, lesions, masses, heaves -30 degree angle
palpation
apical pulse at 5th ICS at MCL -hands and arms for abnormal findings -thorax and precordium with palm
s1
lubb -closure of atrioventricular valves -contraction -systole start
s2
dubb -closure of semilunar valves -relax -diastole start
all people enjoy time magazine
-aortic -pulmonic -earbs -tricuspid -mitral
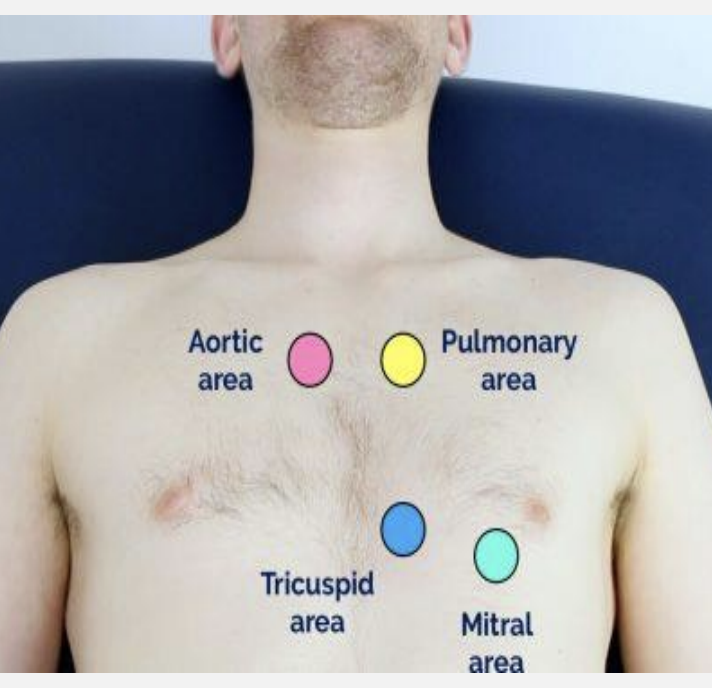
aortic
R 2nd ICS
pulmonic
L 2nd ICS
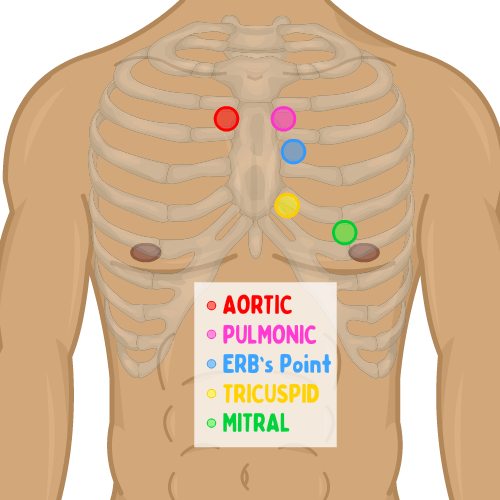
earbs
S1 and S2 best L 3rd ICS
tricuspid
4th ICS on L -lower left sternal border
mitral
L 5th ICS -medial to MCL
S2 physiological split
when valves close at slightly different times due to changes in intrathoracic pressure (especially during inspiration)
S3 and S4. sounds
(extra heart sounds) - S3 : “Lub du bub” (may be expected in people less than 40 or in CHF) - S4: “Be Lub Dub” (Pathological origin)
murmurs
(whooshing) - Caused by disrupted blood flow due to septal defects, valve abnormalities, Patent ductus arteriosus, or stenotic vessels
systolic murmurs
Aortic or pulmonic stenosis, AV valve regurgitation, VSD
diastolic murmurs
AV valve stenosis, Aortic or pulmonic regurgitation
innocent murmur
result of turbulent blood flow -during systole
red flags
LOC Changes Chest Pain Shortness of breath (!!!) Lightheadedness Fluid Volume Overload ECG changes
peripheral vascular ax
(including Fascial Compartments) ➔ Pulses ➔ Edema ➔ Compartment syndrome? ➔ Deep venous thrombosis?
lymphatics assessment check
-check for -Lymphedema -Lymph nodes -Chylothorax (fluid leaks into space between lung and chest wall)
arteries
Thick walled, elastic, high pressure - Largest is the Aorta
veins
- Thinner and less elastic, low pressure - Valves to prevent back-flow - Superior vena cava
capillaries
Location of exchange of gases, nutrients, metabolites
lymphatic system
- Lymph nodes & vessels - Valves for flow - Maintains fluid balance & immune function - Run parallel to arteries & veins - Lymph drains into Thoracic duct & Right Lymphatic duct to subclavian veins to superior vena cava to right atrium
fascial compartments
- Fascia are sheets of connective tissue that enclose the blood vessels, nerves and muscles which make up compartments. - Limited stretch in the fascia can cause problems when there is inflammation to any of the enclosed components.
DVT
pain/edema/warmth -weak pulses -delayed cap refill -risk of pulmonary embolism (blood can’t drain properly)
health hx peripheral
- Pain - Numbness/tingling (sensation) - Cramping - Changes in Skin Colour - Edema - Function - Personal History - Medications - Family History (Hx of stroke, clots etc.) *Keeping in mind CVS questions!
PVS and lymph inspection
- All extremities, comparing colour, size, and quality. - Hint: bring back Skin/Hair/Nails -raynauds, cyanosis, mottling
lymphedema
one or both limbs that lymphatic system struggles and lymph collects in parts of body -usually legs, arms more risky -
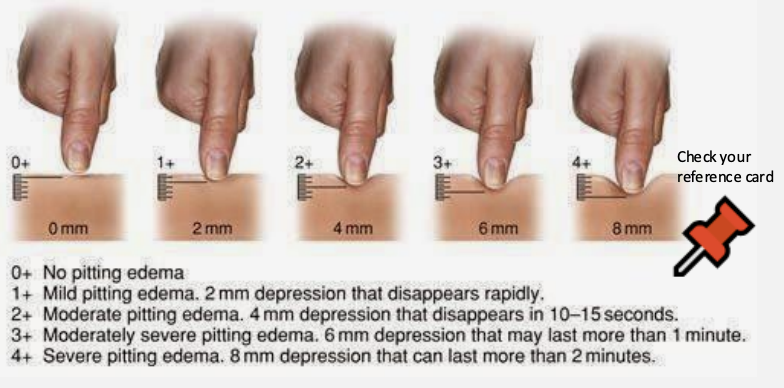
edema
fluid -depress area for cap refill to asess -pitting or non pitting
epitrochelear nodes
support forearm with elbow flexed -finger pads between bisceps and triceps (3cm above medial epicondyle) -usually not palpable: note size, consistency, mobility and tenderness
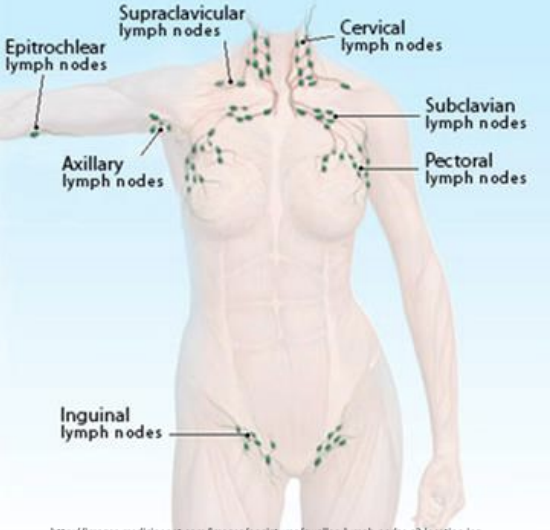
inguinal nodes
horizontal: medial (symphsis pubis) to lateral -vertical: proximal upper/medial thigh -may be palpable: <2cm, mobile and non tender
palpation for PVS
distal to proximal -TEXTURE/MOISTURE ◆ TEMPERATURE ● Warm and Dry or Trunk Warm-Extremities Cool ◆ TURGOR ◆ CAPILLARY REFILL ● Less than or equal to 2sec/Between 2-3sec/Greater than or equal to 4sec ◆ EDEMA ● Determine if pitting or non pitting ● If pitting: grade it ◆ PULSES ● Documenting strength grade and comparing for symmetry
pulses
carotid, apical, brachial, radial, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial, pedal
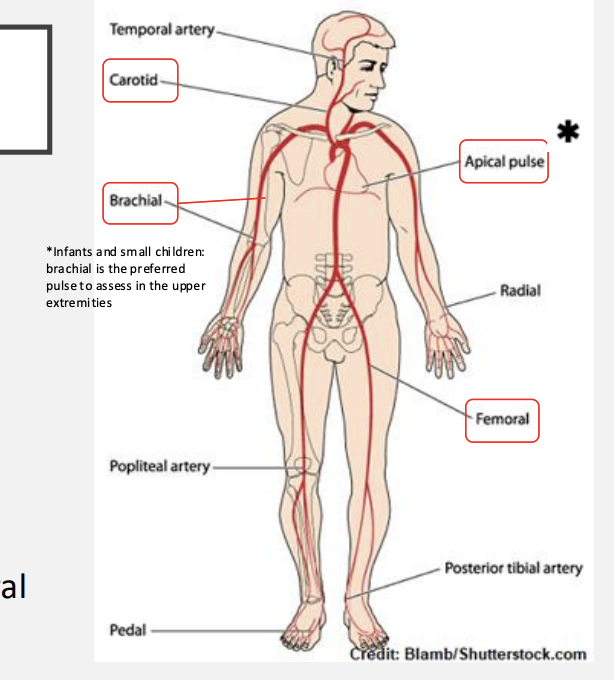
central pulses
carotid, apical, brachial, femoral
newborn pulses
check pulses on both side and all of them
pulse scale

doppler
when pulses are difficult to find -If pulse is then unable to be heard on the doppler, that is an emergent situation
compartment syndrome
usually caused by bleeding or swelling after injury into closed compartment or untreated DVT -pain and paresthesia - >6hr = permanent damage -under fascia but outside of vessels
limb ischemia
-death to limb from lack of blood flow -pain and quality -pallor (chronic pink due to compensatory vasodilation) -buergers test (pallor on elevation and erythema on dependency -pulselessness -polar sensations/poikilothermia ( cold compared to other limb) -paresthesia (burning, tingling, numbness -paralysis