Human gas exchange system - Lungs and Alveoli
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
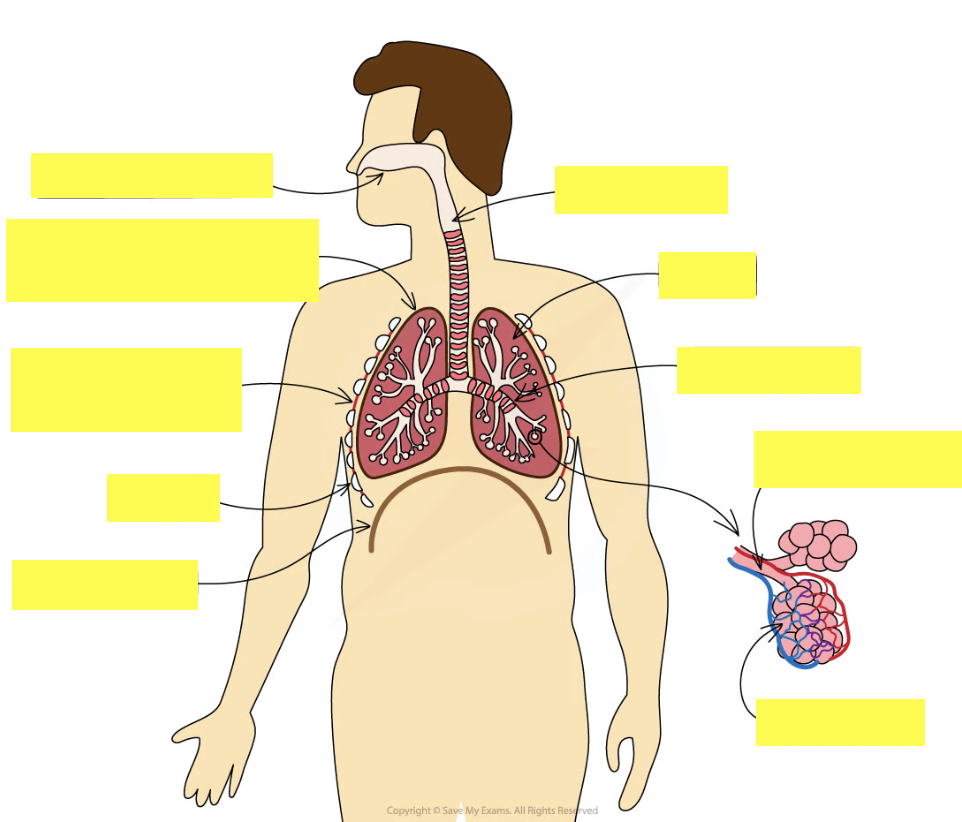
Label the diagram
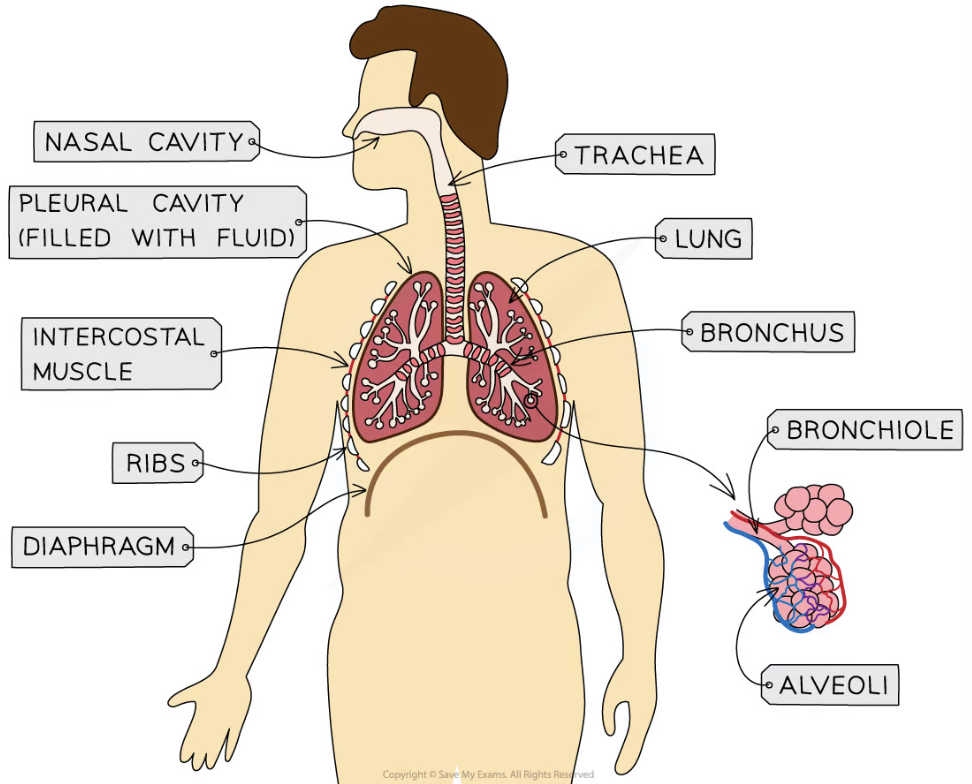
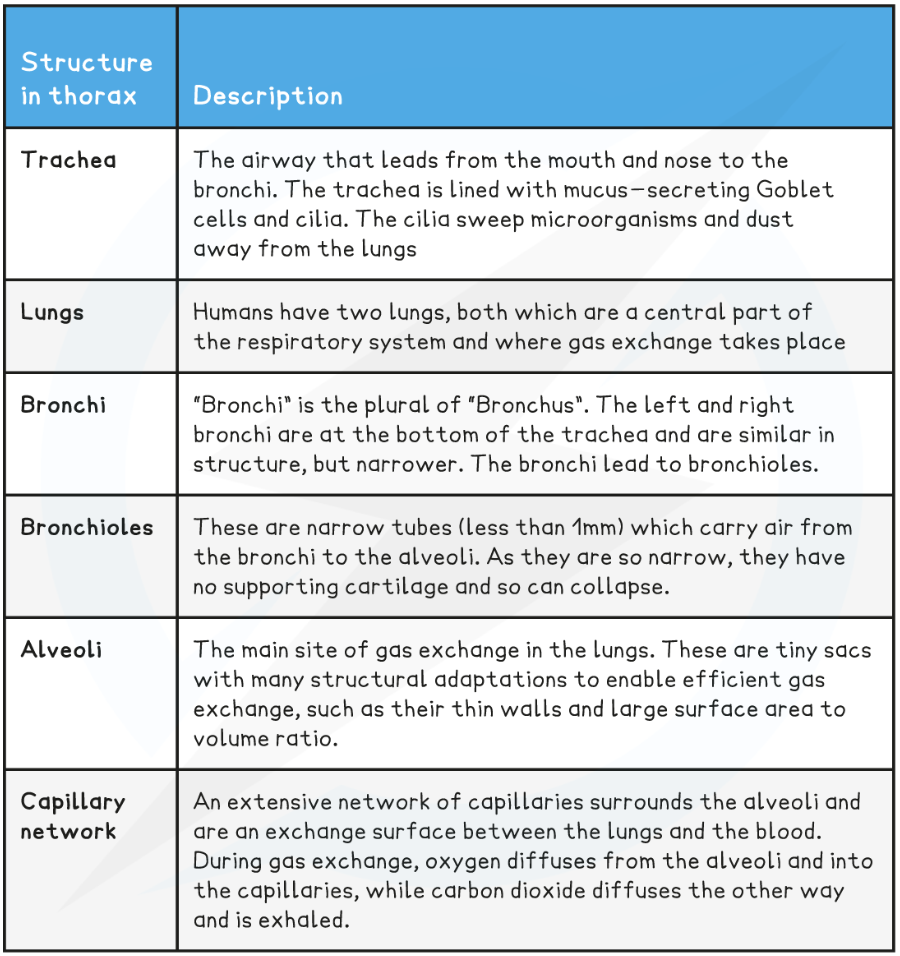
Describe the main structures of the human gas exchange
Name the 2 gas exchange tissues and their functions
Cartilage is a strong and flexible tissue found along the trachea to help support and and ensure it stays open, while allowing it to move and flex while we breathe
Ciliated epithelium is a specialised tissue found along the trachea down to the bronchi. Each cell has small projections of cilia which sweep mucus, dust and bacteria upwards and away from the lungs and the epithelium itself
Goblet cells and Mucus
They’re found scattered throughout the ciliated epithelium in the trachea
They’re mucus-producing cells that secrete viscous mucus which traps dust, bacteria and other microorganisms and prevents them from reaching the lungs
The mucus is then swept along by the cilia of the ciliated epithelium upwards and is swallowed
The mucus and any microorganisms will then be destroyed by the acid in the stomach
Why is ventilation so important
Ventilation ensures that the concentrations gradients of CO2 and O2 are maintained
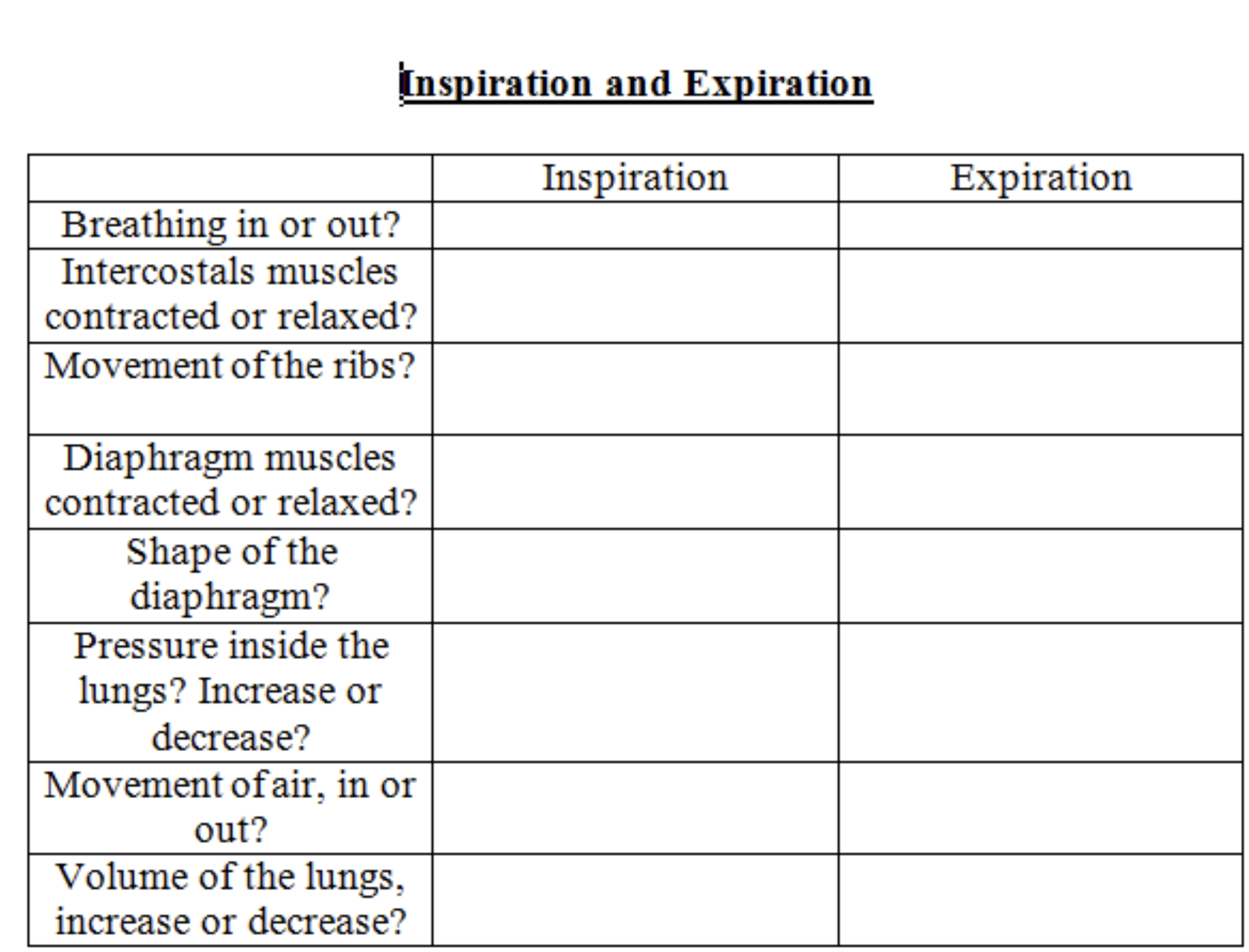
Air moves down a pressure gradient in and out of the lungs
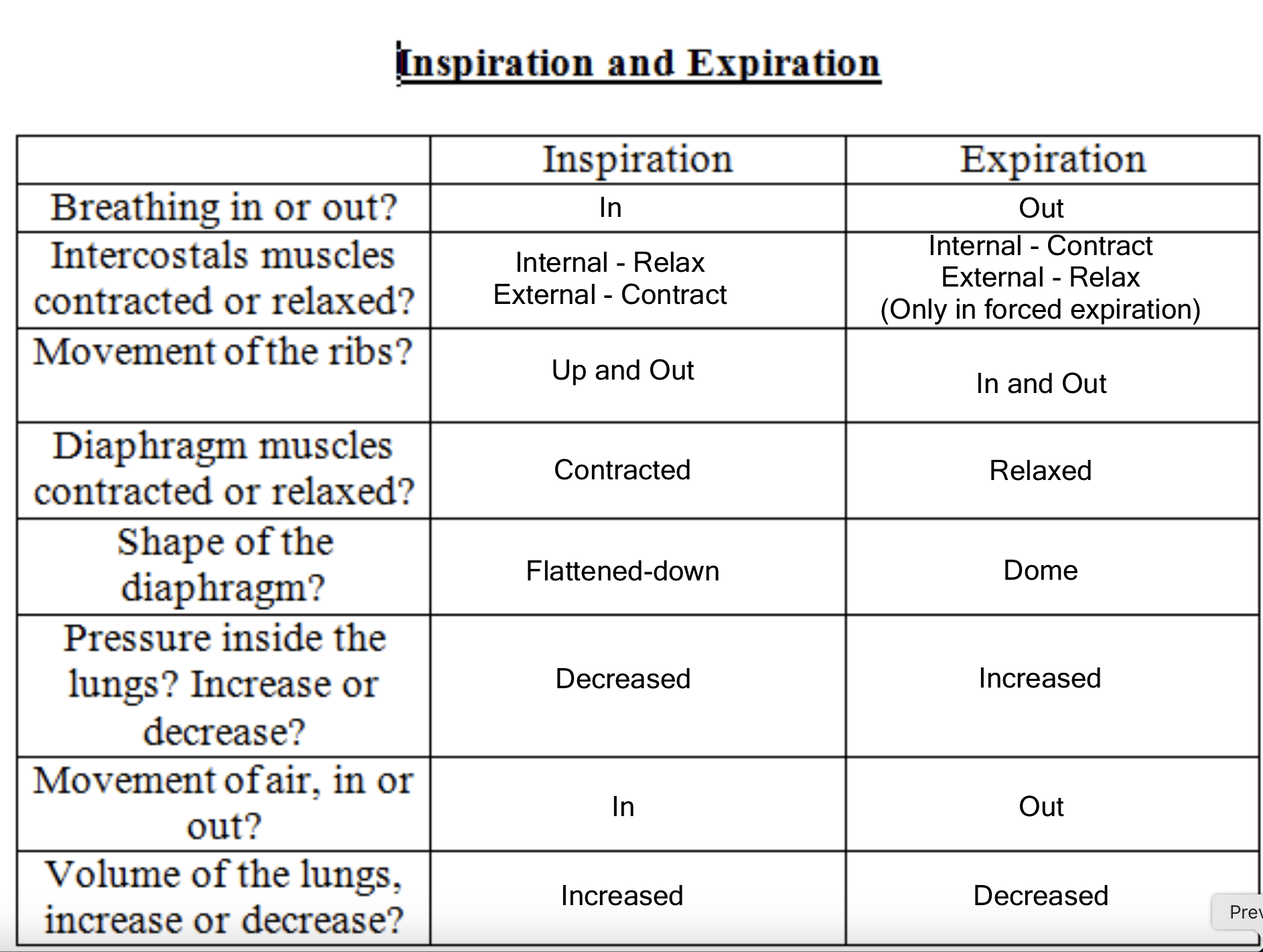
Tidal volume and ventilation rate
Pulmonary ventilation rate: the total volume of air moved in and out of the lungs during 1 minute
Tidal volume: the volume of air normally inspired at rest (0.5dm3)
Ventilation rate: number of breaths in one minute (12-20)
Pulmonary Ventilation (dm3min-1) = tidal volume (dm3) x ventilation rate (breaths per min)
What type of epithelium cells do the alveoli have
Simple squamous
Alveolar structure
Tiny air sacks
Around 100-300μm in diameter
Walls of the alveoli are mainly epithelial cells, contain collagen fibres and elastic fibres
Elastic fibres allow walls to stretch when the alveoli are filled with air during inspiration and then to recoil and help force air out of the lungs during expiration
Capillary endothelium
The wall of the capillary wrapped around the alveoli is also only 1 cell thick
The lumen of the capillaries are very small
RBCs pass through in single file, slowing them down long enough for diffusion of gases to take place
Adaptations of the alveoli and capillary
Thin epithelium/ endothelium short diffusion pathway
Inhale/ exhale air so air in alveoli is replenished to maintain steep concentration gradients
Continuous blood flow to maintain a steep concentration gradient
Large SA (highly folded membrane)
Single file RBCs to allow time to exchange gases
Layer of moisture called the surfactant prevents the walls of the alveoli from sticking to each other - reduces surface tension, prevents collapse of alveoli during exhalation
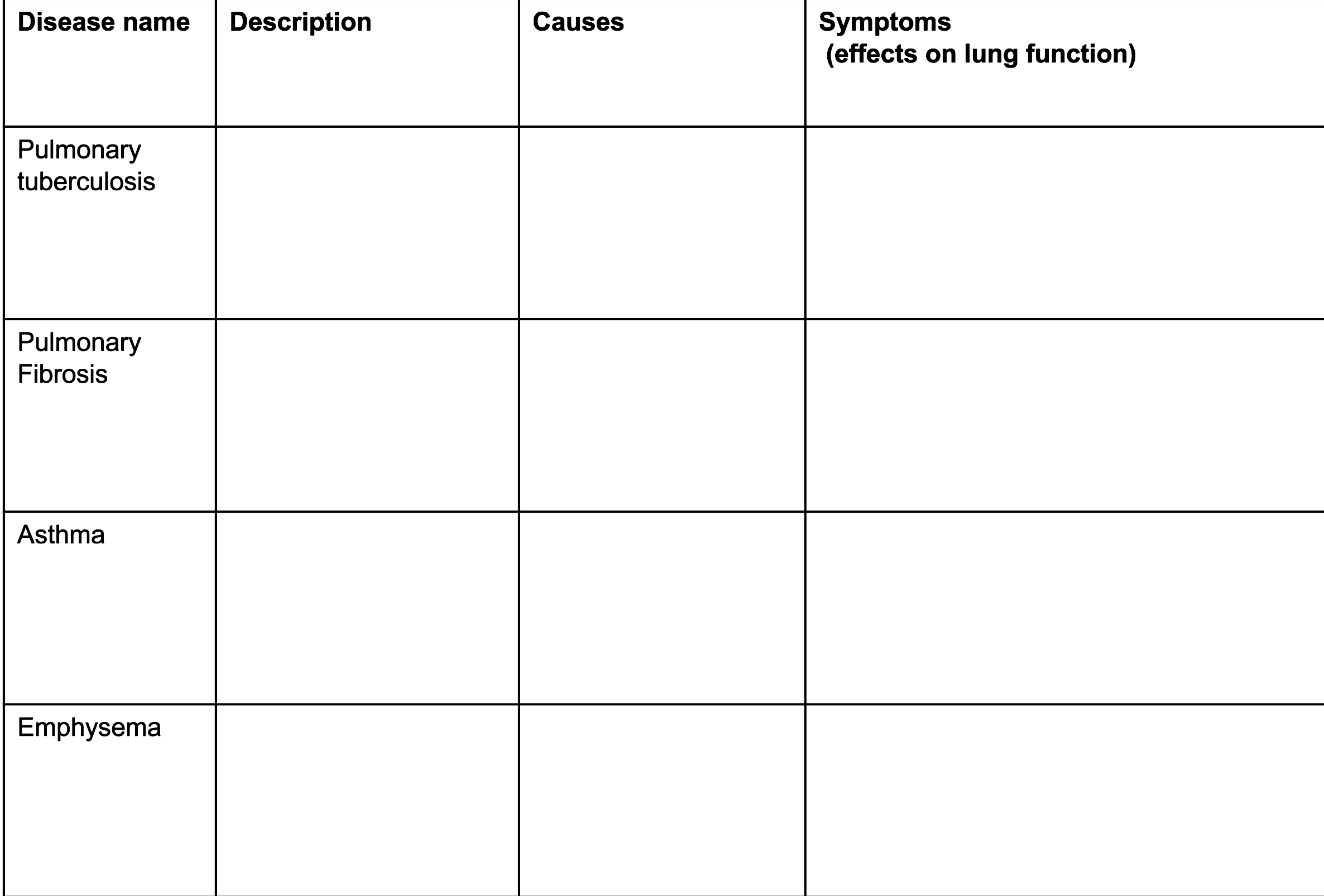
Suggest and explain 3 ways how different lung diseases reduce the rate of gas exchange
Thickened alveolar tissue (e.g. fibrosis) → increases diffusion distance
Alveolar wall breakdown → reduces SA
Reduce lung elasticity → lungs expand/ recoil less → reduces conc. gradients of O2 / CO2
Suggest and explain 3 ways how different lung diseases affect ventilation
Reduce lung elasticity (e.g. fibrosis-build-up of scar tissue) → lungs expand/ recoil less
Reducing tidal volume
Reducing max volume of air breathed out in 1 breath
Narrow airways/ reduce airflow in and out lungs (eg. asthma- inflamed bronchi)
Reducing max vol of air breathed out in 1 second
Reduced rate of gas exchange → increased ventilation rate to compensate for reduced O2 in blood
Suggest why people with lung disease experience fatigue
Cells receive less O2 → rate of aerobic respiration reduced → less ATP made