Chapter 16: Aldehydes and Ketones
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ochem
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
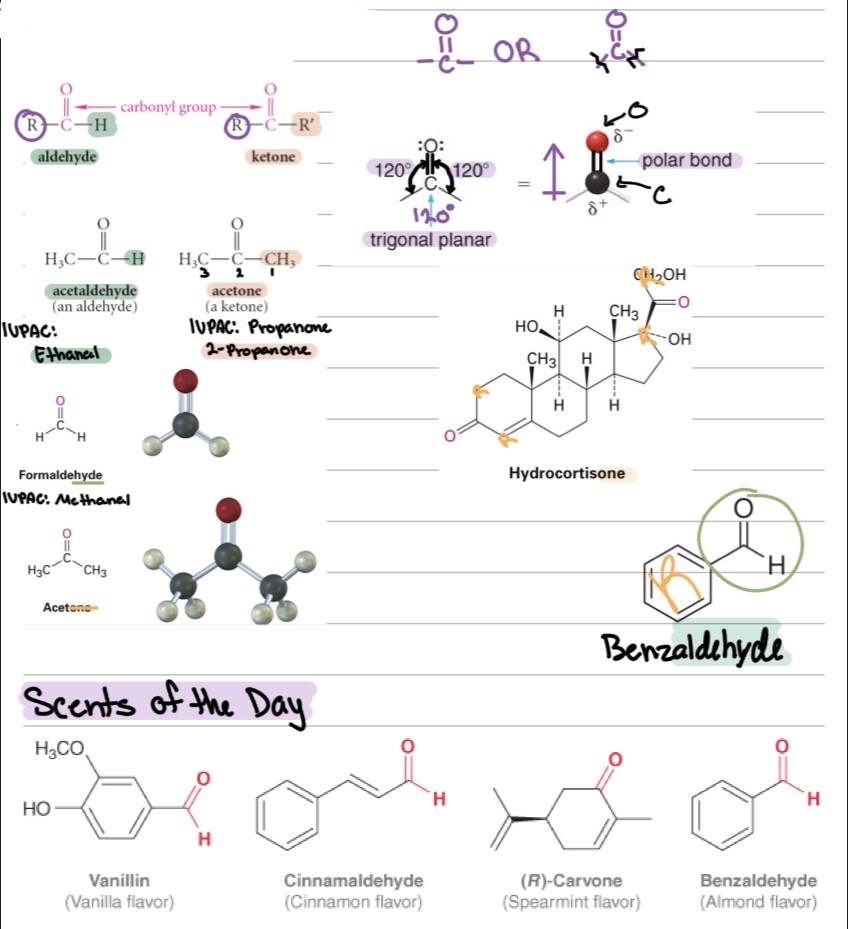
Functional group:
Aldehyde: C=O at the end of the chain →
Ketone: C=O in the middle of the chain →
Many have distinct smells (fruity, floral, etc.).
Most simple aldehydes and ketones are liquids.
Carbonyl (C=O)
R–CHO
R–CO–R′
Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones
What physical state are most simple aldehydes and ketones at room temperature?
What causes aldehydes and ketones to have relatively high boiling points compared to alkanes?
Why do aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than alcohols?
They are liquids
The polar carbonyl group (C=O) creates dipole–dipole interactions between molecules
They cannot form hydrogen bonds with each other (no –OH group)
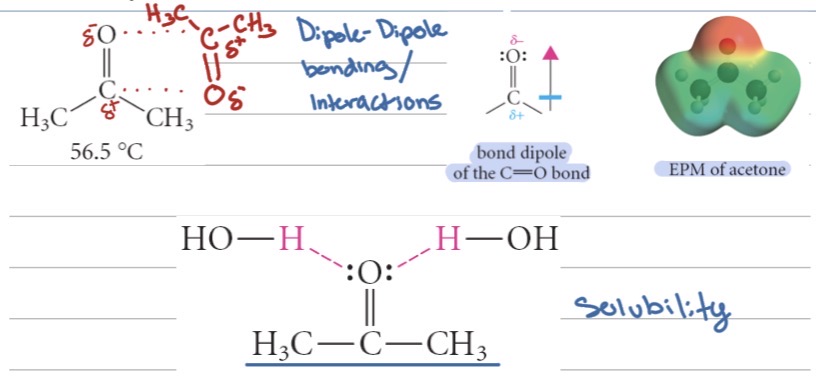
Physical properties of aldehydes and ketones
Are small aldehydes and ketones soluble in water?
What happens to water solubility as the carbon chain length increases?
Do aldehydes and ketones have distinct smells?
weak or strong acids?
Yes, because they can hydrogen bond with water molecules.
Solubility decreases because the nonpolar chain gets larger
Yes — many have pleasant or noticeable odors, like fruity or floral scents
weak
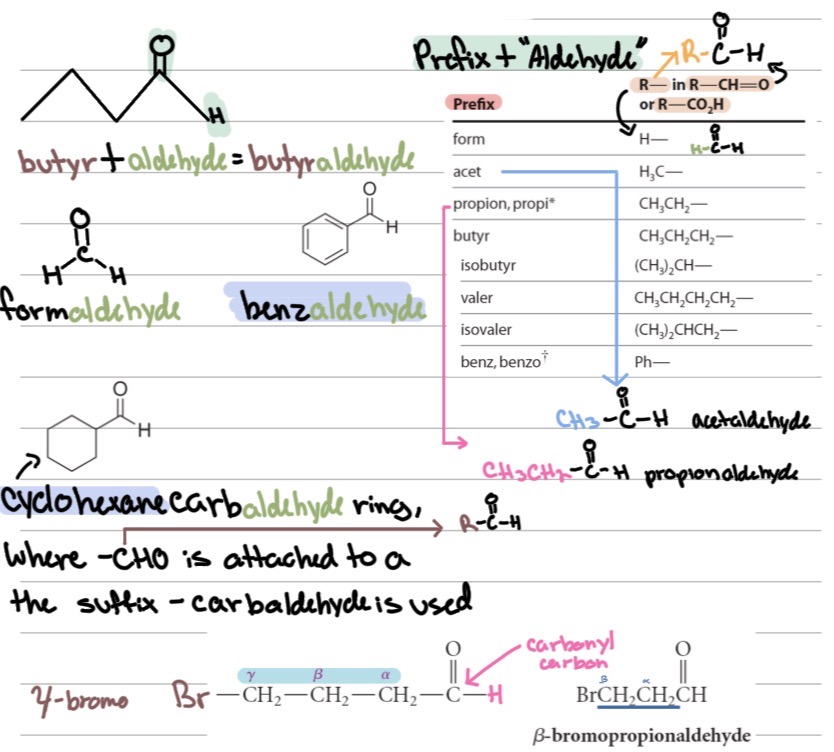
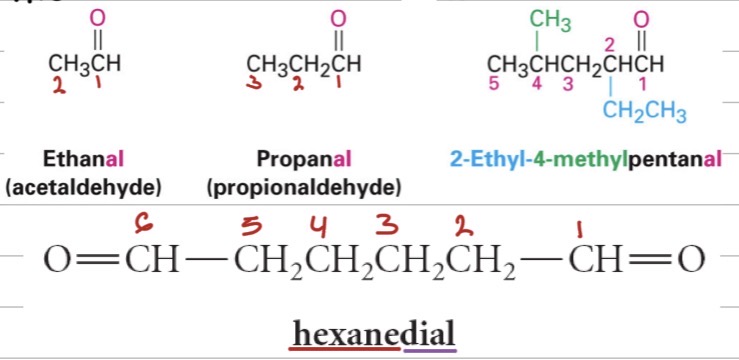
Aldehydes IUPAC:
Find the longest chain including the ?
Carbonyl carbon is ?.
Replace -e with ? → e.g., ethane → ?.
If attached to a ring, use ?.
If there’s more than one –CHO, use ?
Common names: Use acid name + ?
–CHO group
C1
-al, ethanal
–carbaldehyde
Greek prefixes (di-, tri-) and keep the “-e.”
“aldehyde” (e.g., formaldehyde, acetaldehyde).
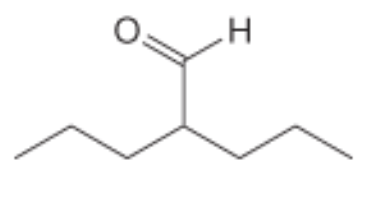
Problems
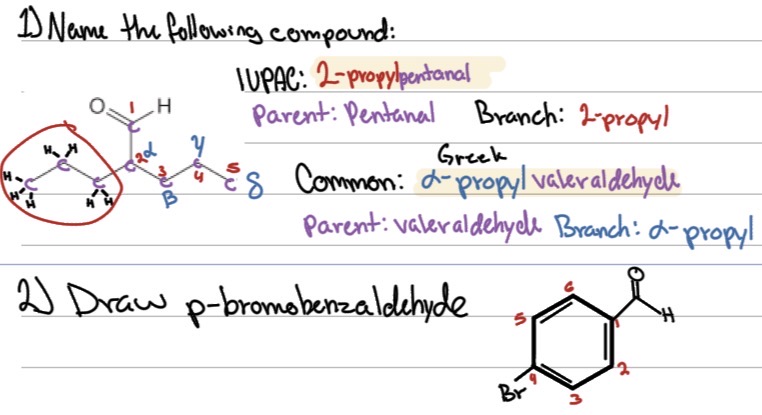
Name the following compound:
Draw p-bromobenzaldehyde:
practice
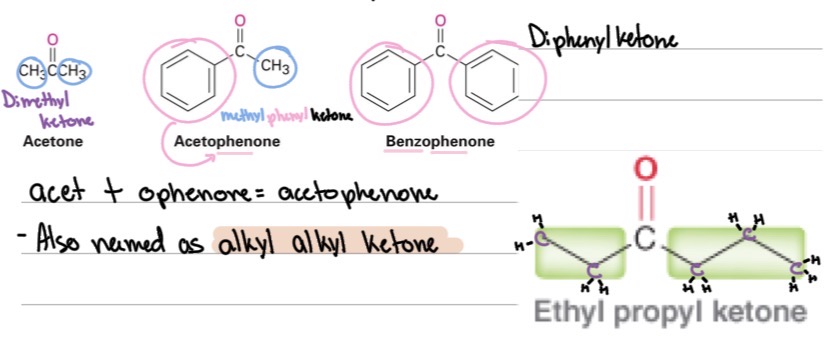
Ketones IUPAC:
Find the longest chain with the ?.
Replace -e with ?→ e.g., propane → ?.
Number so the carbonyl gets the lowest number.
Common names: Name the two alkyl groups alphabetically + ? (e.g., methyl ethyl ketone).
carbonyl
-one, propan-2-one
“ketone”
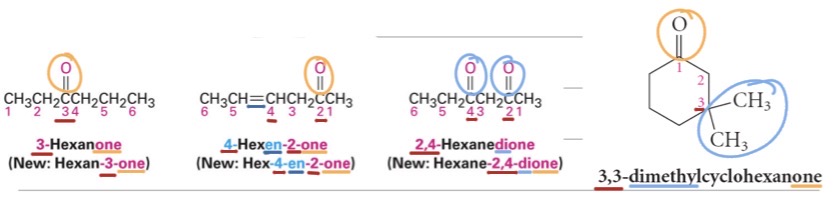
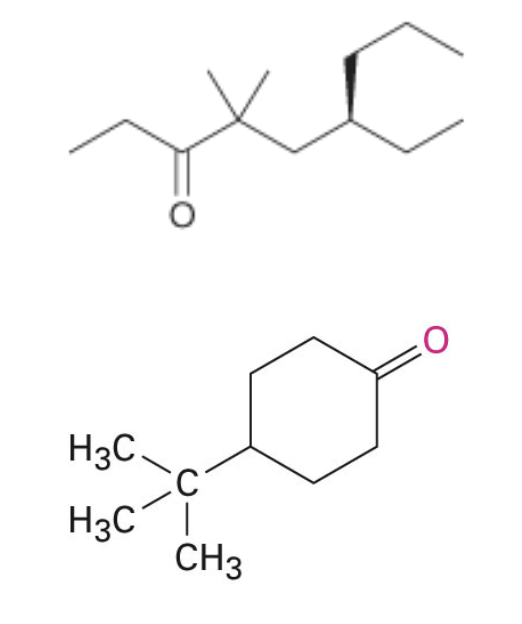
Problems
Name the following compounds:
Draw 2, 3-butanedione.
practice

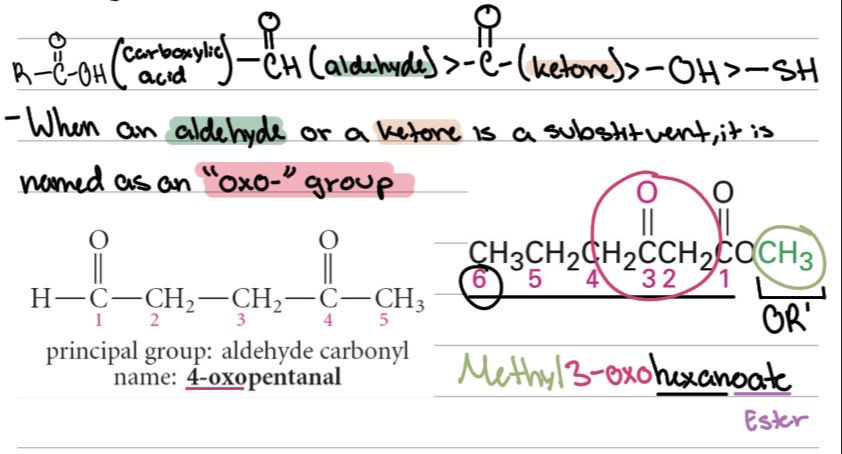
More than a Ketone?
When an aldehyde or a ketone is a substituent, it is named as ?
an “oxo-” group
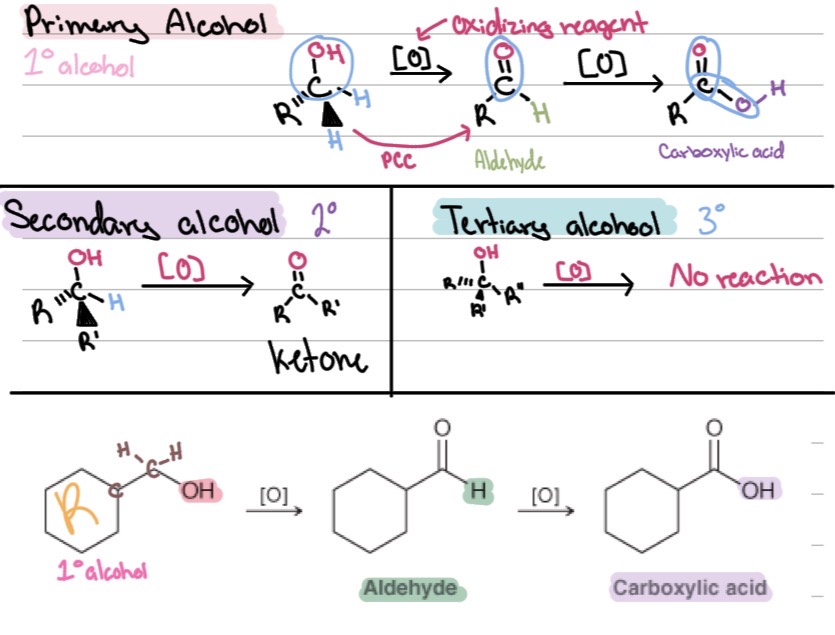
Preparation
Aldehydes:
Ketones:
Oxidation of primary alcohols
Oxidation of secondary alcohols
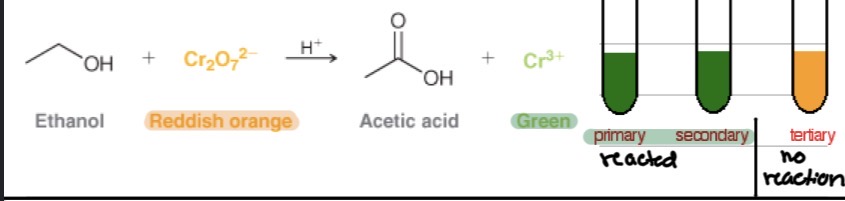
Tests
Dichromate Test: ?
Tollens’ Test:?
Aldehydes turn orange → green (positive). Ketones don’t react.
Aldehydes form a silver mirror. Ketones give no reaction.
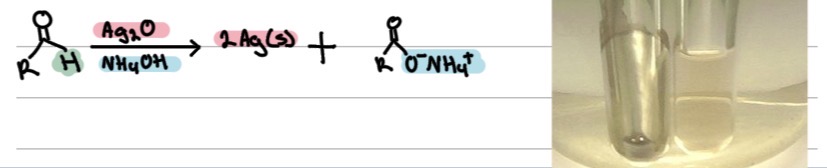
Reactions
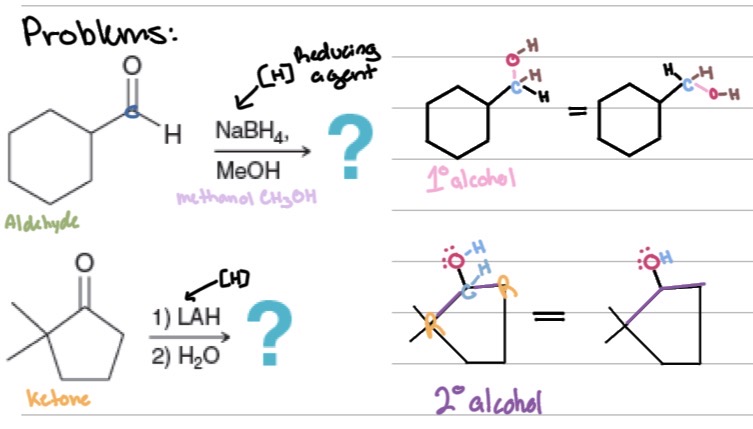
Reduction:
Aldehydes → ?
Ketones → ?
Reagents: ?
1° alcohols
2° alcohols
H₂/Pd, NaBH₄, LAH

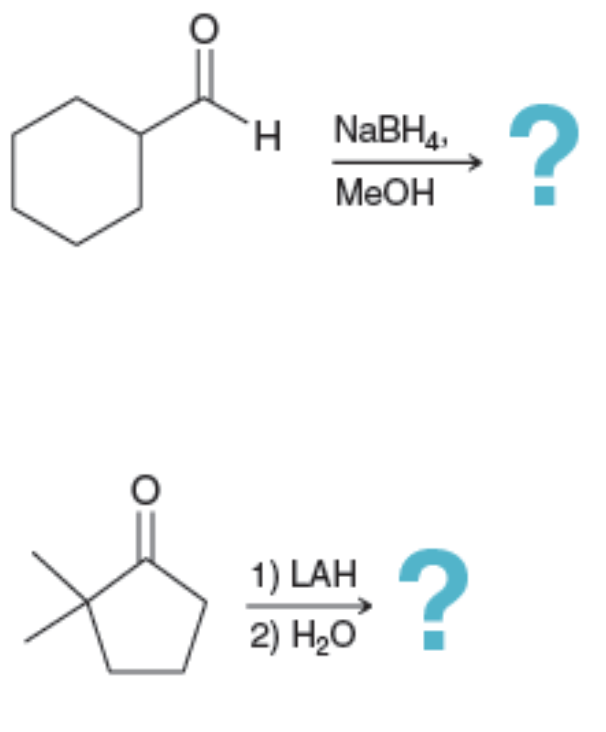
Problems
practice
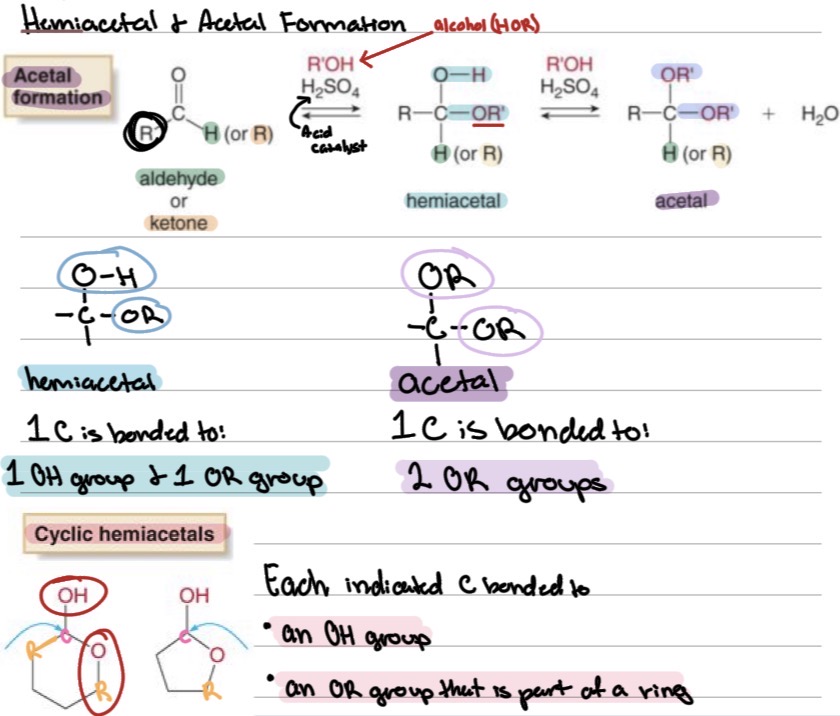
Reactions
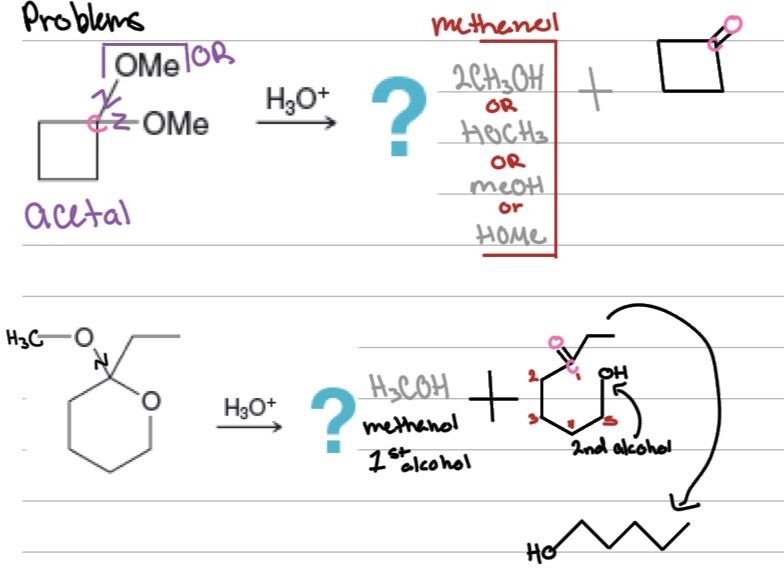
Hemiacetal and Acetal Formation:
Aldehyde + alcohol → hemiacetal → acetal (with excess alcohol)
hemiacetal: 1C is bonded to ?
acetal: 1C is bonded to ?
1 OH group & 1 OR group
2 OR groups
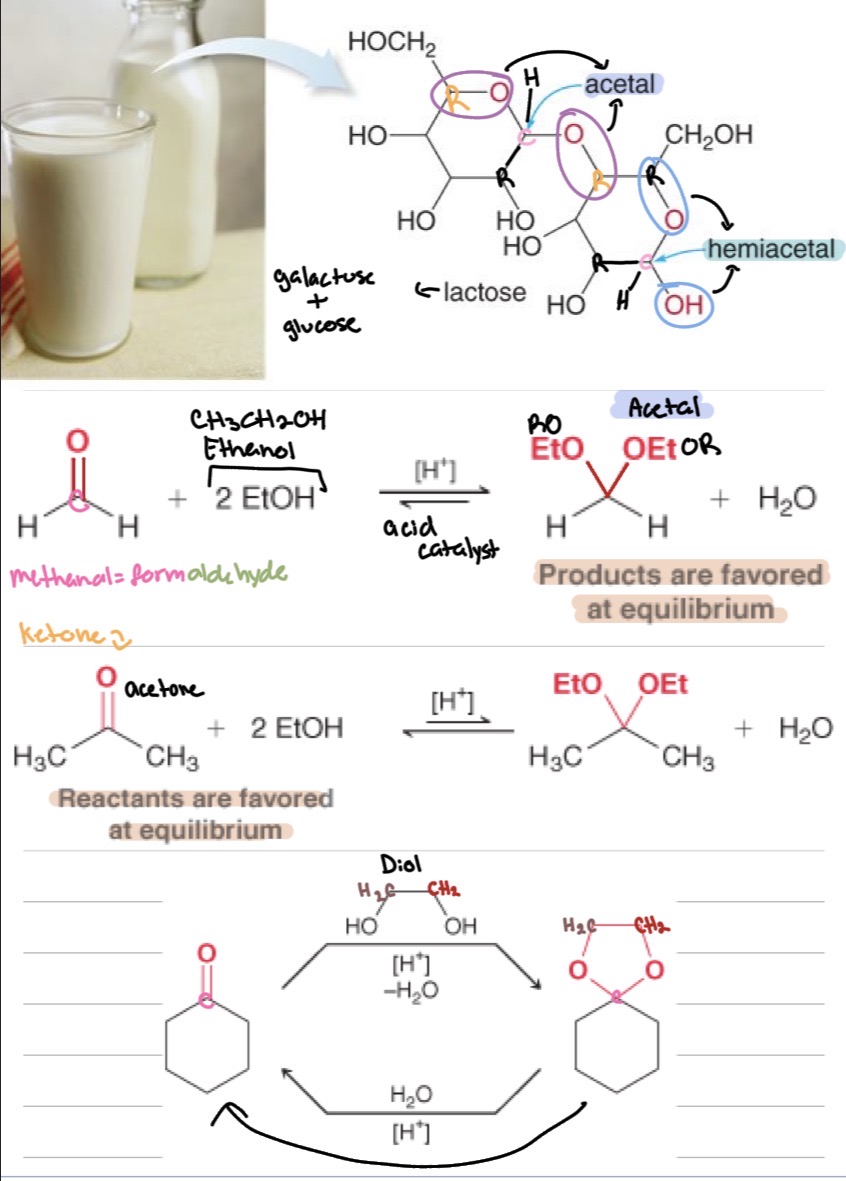
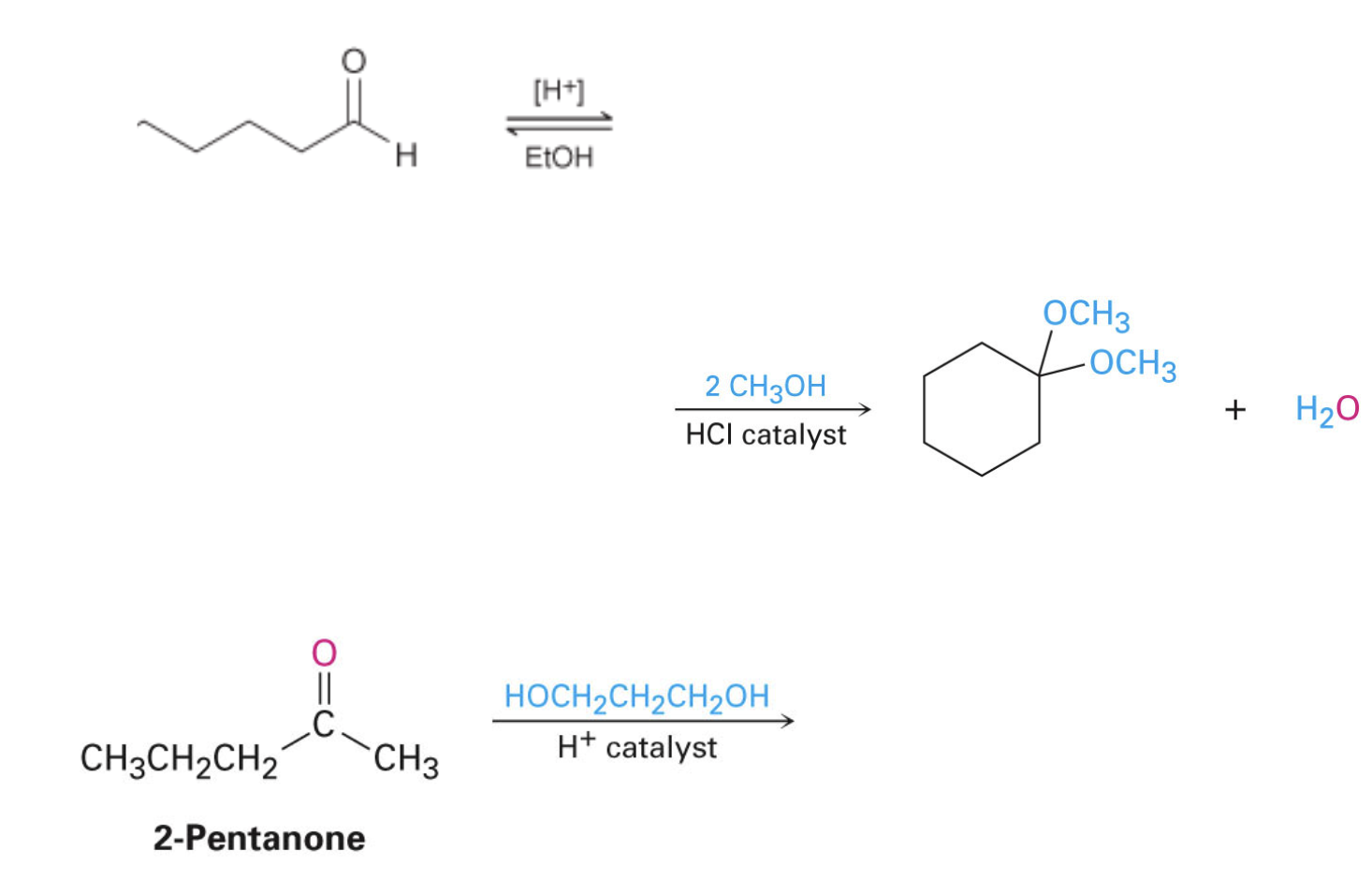
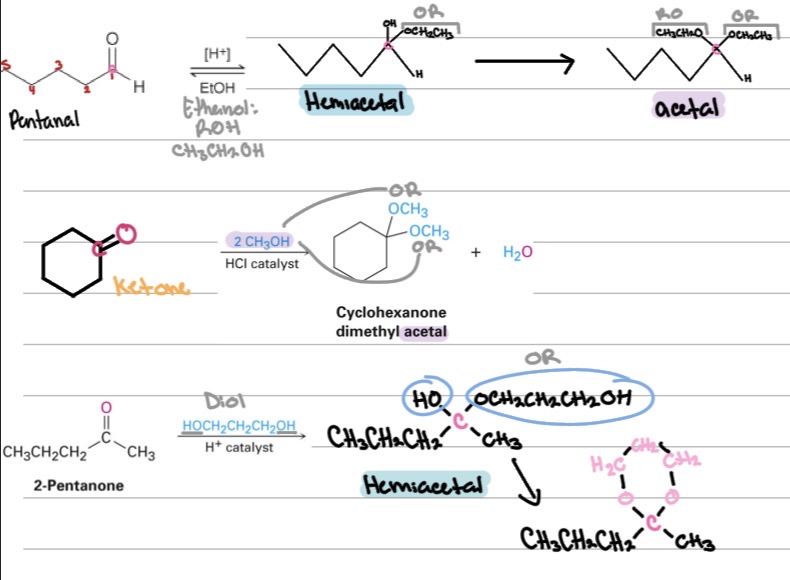
Problems
Draw the missing reactant or product for the following reactions:
practice
Reactions
Acetal Hydrolysis: Reverse reaction —?
acetal → aldehyde or ketone + alcohol
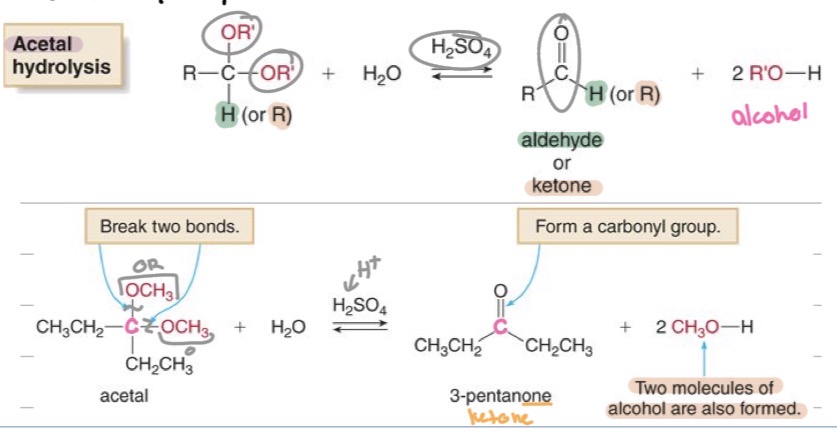
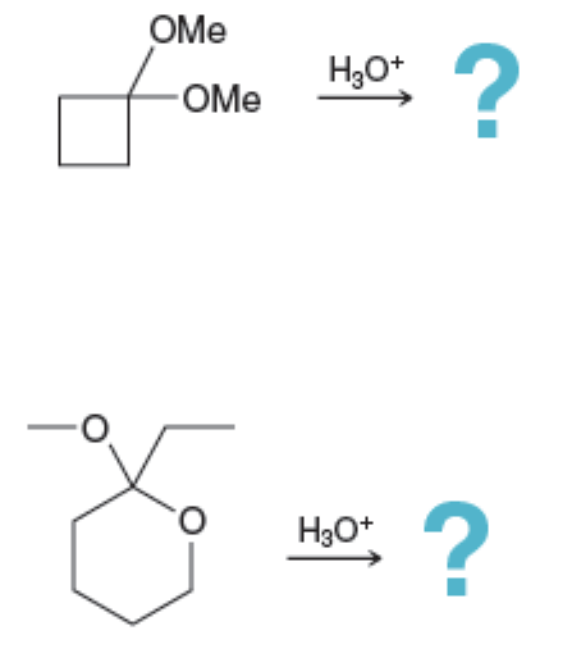
Problems
practice