Exam 2 - II: Seedless Plants
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Plant
Multicellular photosynthetic eukaryote
Advantages of land
Plentiful light for photosynthesis
CO2 present in higher concentrations
Disadvantages of land
Threat of drying out (desiccation)
Gravity
Need for body support
Less water than water environments
Adaptations of plants to life on land
Alternation of generations
Apical growth
Protection of embryo from drying out
Waxy cuticle on leaves prevents drying out
Internal skeleton to oppose gravity
Vascular system to move water internally
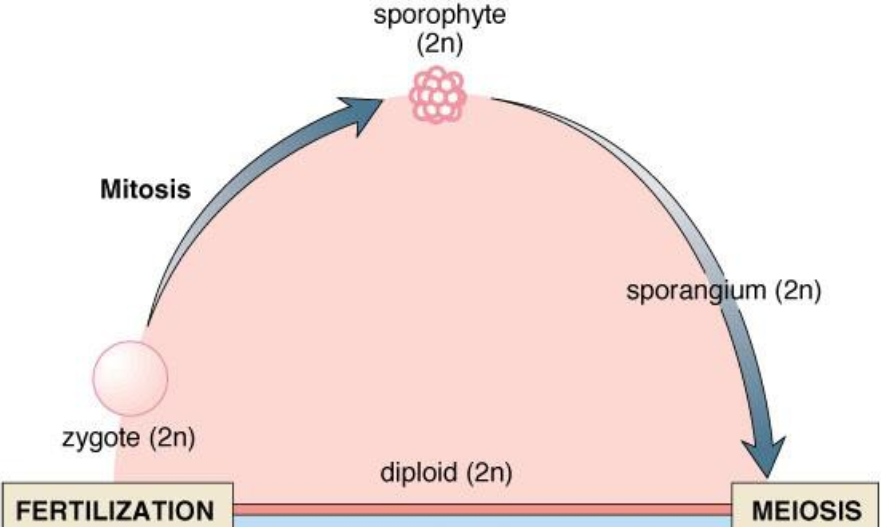
Sporophyte
Produces spores through meiosis and represents diploid generation (2n)
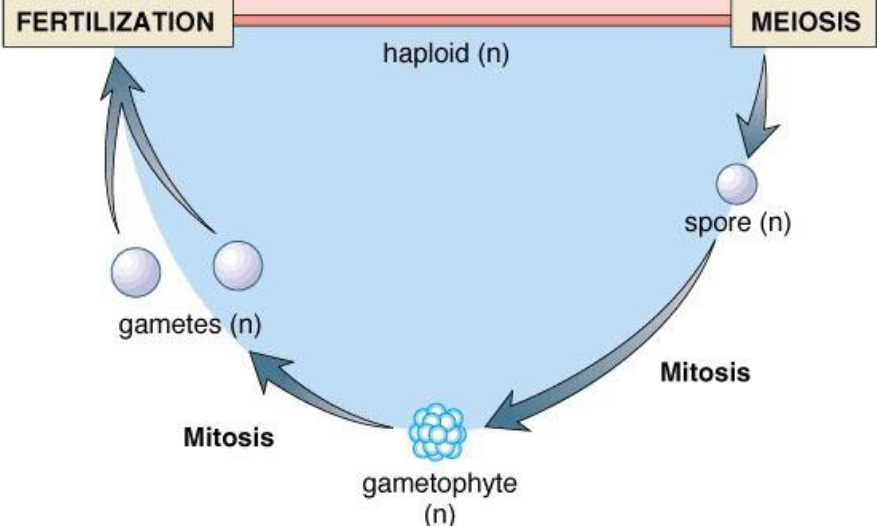
Gametophyte
produces gametes and represents haploid generation (n)
What does it mean when a plant alternates generations?
The plant is going through two stages that alternate, haploid and diploid
Alternation of generations process
gametophyte produces gametes (n) through mitosis
fertilization- zygote is formed (2n)
zygote grows into a sporophyte (2n)
sporophyte produces haploid spores (n) through meiosis
spores grow into gametophytes
What is a dominant generation?
The stage in a plant’s life cycle that is larger, longer-lived, and more visible, the generation that the plant is recognized as