Chemistry - pH Scale, Reactions and Titrations
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
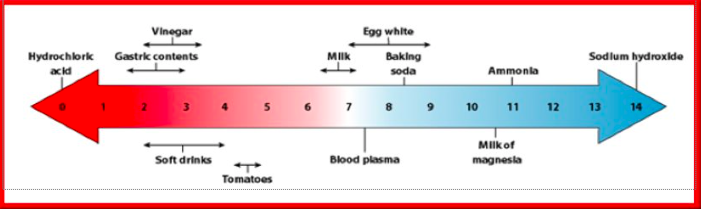
pH Scale
Measures the acidity or basicity of a substance
0-14
pH < 7: Acid
pH of 7: Neutral
pH > 7: Base

pH equation
pH is the ’negative logarithm of’ the hydrogen ion concentration
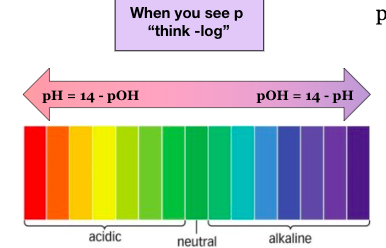
pOH
pOH is a measure of hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration (alkalinity). The pOH scale is opposite of the pH scale. (<7 is alkaline & >7 is acidic). ‘p’ in pOH also stands for negative logarithm of’.
Reactions
patterns of the reactions of acids and bases (including metals, carbonates, ammonium salts) allow products and observation to be predicted from reactants; ionic equations represent the reacting species and products in these reactions.
Types of reactions
Acid + Metal Hydroxide → Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Oxide → Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Carbonates → Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
Acid + Reactive Metals → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Strong Base + Ammonium Salts → Salt + Water + Ammonia gas
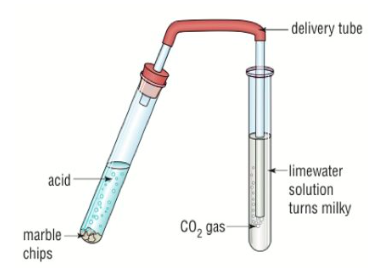
Test for CO2
CO2 turns limewater solution milky
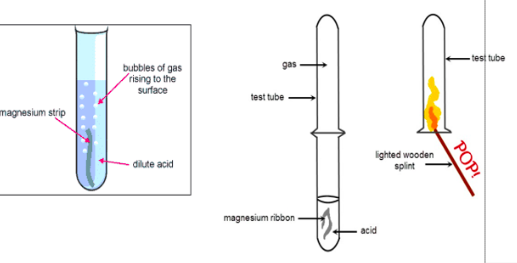
Test for H2
Pop test
Test for NH3
Use litmus paper to detect acid gas
Titration
Titration is an analytical quantitative method of determining the concentration of an unknown analyte by allowing it to gradually react with a titrant until an end point is reached
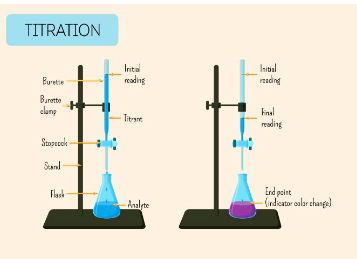
Process of titration
Get a titrant of a known concentration and an analyte of an unknown concentration, a chemical indicator that changes colour, a graduated burette with a tap, a flask and a burette holder with a stand
Drip by drip, the titrant is slowly mixed with the analyte until the colour of the indicator changes.
As the titrant is added to the analyte, neutralisation of the titrant creates H2O. The equivalence points occur when the amount of titrant exactly equals the stoichiometric equivalent amount of analyte.
Titrant
a solution of known concentration that is added (titrated) to another solution to determine the concentration of a second chemical species.
Analyte
a chemical substance that is being found and measured
How do we know the equivalence point is reached?
pH Indicator
pH probe/sensor
pH Indicator
pH indicator such as phenolpthalein indicates when the solution is acidic (clear) and when the solution is basic (pink). The point at which the indicator changes colour is called the end point. (A suitable indicator should be chosen, preferably one that will experience a change in colour close to the equivalence point of the reaction)
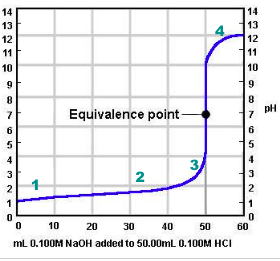
pH probe/sensor
e.g. HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) -> H2O(l) + NaCl(aq)
For this neutralisation reaction, at the equivalence point, the number of moles of acid will equal the number of moles of base: nH+ = nOH-