LBYZOOL Activity 01-04 (Lab Exam 1)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Microscope, Animal Cell Structure, Membrane Transport, & Cell Division - Mitosis
Last updated 5:09 AM on 11/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
1
New cards
Microscopy
term for any technique for producing visible images of structures or details too small to otherwise be seen by the human eye
2
New cards
Microscope
instrument used to magnify objects that can't be seen by the naked/unaided eye
3
New cards
Ocular / Eyepiece
the lens through which the object or the specimen is viewed
10x magnification
for Magnification
10x magnification
for Magnification
4
New cards
Revolving Nosepiece
holds and shifts the 4 objectives
feel the distinctive "click" as each objective is in proper position for viewing
for Support
feel the distinctive "click" as each objective is in proper position for viewing
for Support
5
New cards
Objective Lens
gives initial magnification
6
New cards
Scanning Lens / Scanner
4x magnification, red
7
New cards
Low Power Objective (LPO)
10x magnification, yellow
8
New cards
High Power Objective (HPO)
40x magnification, blue
9
New cards
Oil Immersion Objective (OIO)
100x magnification, white
10
New cards
Stage
flat surface where the slide/specimen is positioned
for Support
for Support
11
New cards
Aperture
round opening in the center of the stage
the slide/specimen is positioned over it
the slide/specimen is positioned over it
12
New cards
Stage Clips
holds the slide in place on the stage
13
New cards
Mechanical Stage
a type of stage that allows the slide to be manipulated by means of the 2 knobs located underneath it
14
New cards
Substage Condenser
condenses the light and focuses it on the specimen
lens under stage & specimen
for Illumination
lens under stage & specimen
for Illumination
15
New cards
Iris Diaphragm
controls the amount of light passing through the specimen
beneath the condenser
for Illumination
beneath the condenser
for Illumination
16
New cards
Substage Illuminator
source of light which illuminates the object being viewed
may be replaced by a mirror
for Illumination
may be replaced by a mirror
for Illumination
17
New cards
Illuminator Control Knob
knob located on the side of the base below the mechanical stage adjustment knobs
controls the light output of the illuminator
controls the light output of the illuminator
18
New cards
Coarse Adjustment Knob
knob for focusing the Scanner and LPO
bigger movements
for Support
bigger movements
for Support
19
New cards
Fine Adjustment Knob
knob for focusing the HPO and OIO
smaller movements
for Support
smaller movements
for Support
20
New cards
Resolving Power
measure of lens quality
ability to deliver a clear image in fine detail
ability to deliver a clear image in fine detail
21
New cards
Field of View
size of the area that the lens views
higher magnification, smaller the area
higher magnification, smaller the area
22
New cards
Total Magnification
product of magnifications of eyepiece and objective lens
23
New cards
Parfocal Capability
ability of a microscope to stay relatively in focus as the user switches among objectives
24
New cards
Working distance
distance between the front of the microscope objective lens and the surface of the specimen
25
New cards
Image and Direction of movement under a Compound Microscope
Image:
appears upside-down & backward
Direction of Movement:
appears to be in opposite direction than actual movement
appears upside-down & backward
Direction of Movement:
appears to be in opposite direction than actual movement
26
New cards
Stage Micrometer
glass slide etched with a scale of known units, usually divided into 0.01mm graduations
27
New cards
Ocular / Eyepiece Micrometer
circle of glass/plastic etched with non-unit scale ranging from 0 to 100
placed in ocular lens
placed in ocular lens
28
New cards
Formula for Calibration Constant (mm)
( stage micrometer spaces / ocular micrometer spaces ) * 0.01mm
^multiply answer to 1000 when using micrometer (μm)
^multiply answer to 1000 when using micrometer (μm)
29
New cards
Dissecting microscope
a type of microscope used when magnifications between 5x and 50x are desired
used for small animals or body parts of larger animals
gives a 3D view of object
used for small animals or body parts of larger animals
gives a 3D view of object
30
New cards
Cell
basic structure and functional unit of all organisms
basic unit of life
basic unit of life
31
New cards
Cytology
study of cells
32
New cards
Prokaryotic Cell
type of cell:
small & simple
unicellular organisms
NO nucleus
LACK of membrane-bound organelles
small & simple
unicellular organisms
NO nucleus
LACK of membrane-bound organelles
33
New cards
Eukaryotic Cell
type of cell:
large & complex
unicellular or multicellular organisms
presence of nucleus
has membrane-bound organelles
large & complex
unicellular or multicellular organisms
presence of nucleus
has membrane-bound organelles
34
New cards
Methylene Blue
dye used to stain nucleus, organelles, DNA, and RNA
35
New cards
Fusiform or Spindle-shaped Cell
an animal cell shape:
long, cylindrical, and tapered on both ends
seen in smooth muscle cells of a frog's stomach
long, cylindrical, and tapered on both ends
seen in smooth muscle cells of a frog's stomach
36
New cards
Spherical-shaped Cell
an animal cell shape:
seen in the egg cells in a frog's ovary
seen in the egg cells in a frog's ovary
37
New cards
Oval Shape
an animal cell shape:
seen in the red blood cells of a frog's blood smear
seen in the red blood cells of a frog's blood smear
38
New cards
Amorphous Shape
an animal cell shape:
seen in the white blood cells of a frog's blood smear
seen in the white blood cells of a frog's blood smear
39
New cards
Whip-like Flagella
an animal cell shape
threadlike appearance
seen in the sperm cells in the frog's testis
threadlike appearance
seen in the sperm cells in the frog's testis
40
New cards
Homeostasis
constant internal environment
necessitates a constant entrance of materials into the cell and the passage of other substances out of it
necessitates a constant entrance of materials into the cell and the passage of other substances out of it
41
New cards
Diffusion
type of membrane transport:
spontaneous movement of molecules of different substances
results from kinetic energy of the molecules
from higher concentration to lower concentration of the solute
until substance is equally distributed
spontaneous movement of molecules of different substances
results from kinetic energy of the molecules
from higher concentration to lower concentration of the solute
until substance is equally distributed
42
New cards
Rate of Diffusion
increases with HIGH temperature and LOW molecular weight and size
43
New cards
Diffusion Rate (Gas) Experiment
glass tube with HCl and NH4OH at both ends, forming a white ring made of H2O and NH4Cl
44
New cards
Diffusion Rate (Liquid) Experiment
Congo Red, Methylene Blue, and Potassium Permanganate in solidified agar media
45
New cards
Diffusion and Temperature Experiment
Potassium Permanganate in beakers with hot and cold water
46
New cards
Diffusion and Molecular Size Experiment
Cellulose sac with starch solution placed in beaker with iodine solution, producing a blue-black color in the sac
47
New cards
Osmosis
diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane
high to low concentration of WATER
from a dilute solution to a concentrated one
high to low concentration of WATER
from a dilute solution to a concentrated one
48
New cards
Dialysis
process of diffusion of crystalloid solute through a semi-permeable membrane
49
New cards
Rate of Osmosis Experiment
5 sacs and 4 beakers with water and 1 beaker with sucrose
NEGATIVE % change in weight for sac E
NEGATIVE % change in weight for sac E
50
New cards
Graph of % change in weight vs sucrose concentration
concave-like downwards
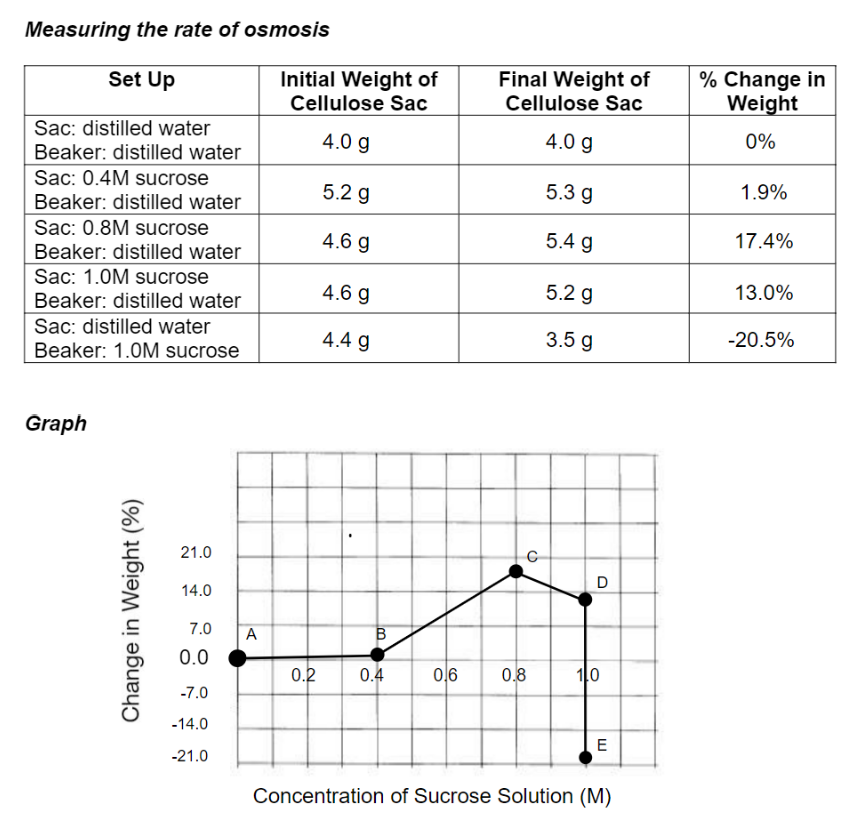
51
New cards
Facilitated Diffusion
type of passive transport:
movement of specific molecules across the cell membrane with the help of a transport proteins
movement of specific molecules across the cell membrane with the help of a transport proteins
52
New cards
Active Transport
type of membrane transport:
moves substances AGAINST their concentration gradients
requires energy (ATP)
moves substances AGAINST their concentration gradients
requires energy (ATP)
53
New cards
Sodium Potassium pump
Example of Active Transport
54
New cards
Isosmotic
equal concentrations of solute in & out of cell
55
New cards
Hypoosmotic
less concentration of solute outside of the cell
water will enter cell
cell will swell & burst
water will enter cell
cell will swell & burst
56
New cards
Hyperosmotic
greater concentration of solute outside
water will leave the cell
cell will shrivel
water will leave the cell
cell will shrivel
57
New cards
2 Main stages of the Cell Cycle
Interphase and Mitosis
58
New cards
Interphase
longest phase of the cell cycle (90%)
composed of G1, S, and G2 phases
composed of G1, S, and G2 phases
59
New cards
Chromatin
thread-like genetic materials inside the nucleus
60
New cards
Nucleoli
1-2 in nucleus
dense, darkly stained bodies formed by several chromosomal materials that code for certain RNAs
dense, darkly stained bodies formed by several chromosomal materials that code for certain RNAs
61
New cards
G0 phase
phase when cells become non-dividing
62
New cards
Centrosome
organelle near the nucleus that contains centrioles
63
New cards
Prophase
mitotic phase wherein:
chromatin condenses into chromosomes
centrioles with asters in opposite poles of the cell
mitotic spindles form between centrioles
nuclear membrane & nucleoli disappear
chromatin condenses into chromosomes
centrioles with asters in opposite poles of the cell
mitotic spindles form between centrioles
nuclear membrane & nucleoli disappear
64
New cards
Asters
ray-like microtubule bodies around centriole
65
New cards
Metaphase
mitotic phase wherein:
chromosomes line up in the _______ Plate / Equatorial Region
spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each chromosome
chromosomes line up in the _______ Plate / Equatorial Region
spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each chromosome
66
New cards
Kinetochore
protein complex around the centromere of a chromosome
67
New cards
Centromere
region of each chromosome where the chromatids are held together to form an X shape
68
New cards
Kinetochore microtubules
mitotic spindles that get longer & attach to the chromosomes' kinetochores
69
New cards
Nonkinetochore microtubules
spindles NOT attached to chromosome
elongate the cell
elongate the cell
70
New cards
Anaphase
mitotic phase wherein:
sister chromatids are pulled toward the opposite poles and will be considered as daughter chromosomes
sister chromatids are pulled toward the opposite poles and will be considered as daughter chromosomes
71
New cards
Telophase
mitotic phase wherein:
the cell has a cleavage furrow
nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear
chromosomes uncoil
the cell has a cleavage furrow
nuclear membrane and nucleolus reappear
chromosomes uncoil
72
New cards
Cleavage furrow
constriction of plasma membrane at the equatorial plate
73
New cards
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
74
New cards
Karyokinesis
division of nucleus
formation of 2 nuclei for the 2 daughter cells
formation of 2 nuclei for the 2 daughter cells
75
New cards
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes
2 daughter cells with 46 chromosomes each
2 daughter cells with 46 chromosomes each
76
New cards
Meiosis
division of sex cells (sperm and egg cells)
contains the formation of chiasma
result in 4 daughter cells
haploid (23 chromosomes each)
contains the formation of chiasma
result in 4 daughter cells
haploid (23 chromosomes each)
77
New cards
Haploid
1 set of chromosomes
23 chromosomes per cell
23 chromosomes per cell
78
New cards
Chiasma
site of crossing over of 2 chromatids from homologous chromosomes
79
New cards
Whitefish Blastula
this animal's embryo is constantly dividing its cells so each stage of the cell cycle is easily observed