Biochemistry Chapter 18: Oxidative Decarboxylation of Pyruvate
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the fates of pyruvate?
anaerobic conditions- lactic acid/ethanol through fermentation; active muscle
aerobic conditions- acetyl coenzyme A through the citric acid cycle; resting muscle
How is pyruvate linked to the citric acid cycle?
Pyruvate is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl CoA, then transported from the cytoplasm into the mitochondrial matrix.
E1 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
pyruvate dehydrogenase, TPP prosthetic group, catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate
E2 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
dihydrolipoyl transacetylase, lipoamide prosthetic group, transfers the acetyl group to CoA
E3 of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, FAD prosthetic group, reoxidizes lipoamide and produces NADH
What is the structure of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
E2 core, E1 and E3 outer shell
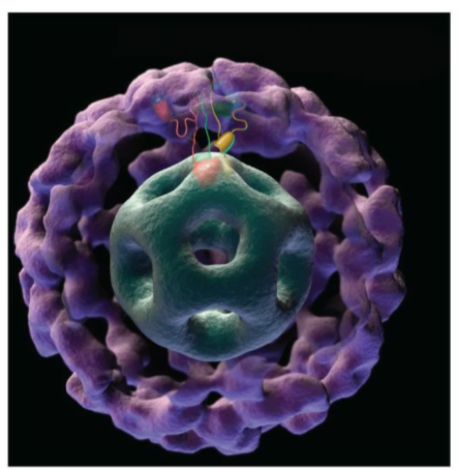
coenzymes required for synthesis of acetyl CoA
catalytic coenzymes- TPP, lipoamide, FAD
stoichiometric coenzymes- CoA, NAD+
Step 1- decarboxylation of pyruvate
E1 pyruvate dehydrogenase
Step 2- oxidation of hydroxyxethyl group to acetyl group
E1 pyruvate dehydrogenase
Step 3- transfer of acetyl group from lipoamide to CoA
E2 dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
Regeneration Step- oxidation of dihydrolipoamide, formation of NADH
E3 dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
structure of E2 transacetylase
hollow cube of 20 catalytic trimers, each with three major domains
amino terminus (lipoamide arm), small domain, large transacetylase domain
lipoamide arm
long, flexible arm which carries substrates from one active site to the next
E3 binding protein
essential protein contained in the core which facilitates interaction between E2 and E3, activity is greatly reduced without it
What are the benefits of a integrated enzyme complex?
increases reaction rate, minimizes side reactions, intermediates remain bound to complex and are readily transferred
What is the significance of turning pyruvate into acetyl CoA?
The irreversible reaction commits the carbons of glucose to either oxidation to CO2 (CAC) or incorporation into fatty acids (fatty acid synthesis).
inhibitors of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
high concentrations of reaction products, acetyl CoA and NADH
high ATP signals high energy charge
How is the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex regulated?
reversible phosphorylation
pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase- terminates activity by phosphorylating E1
pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase- stimulates activity by reversing phosphorylation
stimulators of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
high ADP and pyruvate indicate low energy charge
high Ca2+ to stimulate muscle contraction
epinephrine (liver), insulin (liver, adipose tissue) indicate high energy demand