Chapter 6 - Anxiety Disorders
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Anxiety
fear, worry, nervousness, stress
mood state with marked negative affect and bodily symptoms of tension
subjective sense of unease, apprehension of future danger
future oriented mood state
Fear
emotion of immediate alarm as reaction to potential danger
sympathetic nervous system
immediate reaction to current danger
Worry
specific and rational state
Anxiety Disorders
characterized by excessive levels of fear or anxiety
avoidance
distress/impairement
Prevalence of anxiety disorders
31.1% lifetime prevalence
more common in women
genetic
varying onset age
culturally specific anxiety
Comorbidity
having more than 1 diagnosis at once
common in anxiety disorders
major depression - most common secondary diagnosis
Anxiety can be useful
motivation
react to bad situations
increased physiological response
Types of anxiety disorders
specific phobia
panic disorder
agoraphobia
social anxiety
selective mutism
separation anxiety
substance induced anxiety
anxiety related to a medical condition
Characteristics of anxiety disorders
affect: anxious, fearful
cognitive: inability to concentrate
behavioral: avoidance
psychophysiological: sweating, shaking, heart racing
Specific Phobia
unreasonable fear of specific object or situation that interferes with daily life functioning
9%/yr
onset in early childhood
treatment: exposure therapy
Specific phobia symptoms
A. Marked fear or anxiety about a specific object or situation typically lasting for 6
months or more.
B. The phobic object or situation almost always provokes immediate fear or
anxiety
C. The phobic object is avoided or endured with intense fear or anxiety.
D. The fear or anxiety is out of proportion to the actual danger posed by the
specific object or situation, and to the sociocultural context.
E. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more.
F. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or
impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
G. Rule Out: The disturbance is not better explained by the symptoms of
another mental disorder.
Panic Attack
abrupt experience of intense fear or discomfort with physical symptoms
can be expected or unexpected
Panic attack symptoms
sweating, shaking, shortness of breath, high heart rate, nausea, numbness, dizziness, fear of death
Panic Disorder
severe, unexpected panic attacks sometimes accompanied by agoraphobia
5% lifetime prevalence
more common in females
onset: early adulthood
treatments: SSRIs, benzodiazapines, psychosocial treatment
Panic control treatments
exposure to panic attack symptoms, reducing worry cognitions
Panic disorder symptoms
A. Recurrent unexpected panic attacks are present. Four (or more) of the
following symptoms (look at symptoms on last slide) occur
B. At least one of the attacks has been followed by 1 month of more of one
or both of the following: a) persistent concern or worry about
additional panic attacks or their consequences or b) A significant
maladaptive change in behavior related to the attacks.
C. The disturbance is not attributable to the physiological effects of a
substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication)
D. The disturbance is not attributable to another medical condition and is not
better explained by another mental disorder.
Agoraphobia
fear/avoidance of situations viewed as unsafe
often occurs with panic disorder
avoidance used to cope with panic attacks
dread about feared situations
Agoraphobia Symptoms
A. Marked fear or anxiety about two (or more) of the following five situations:
1. Using public transportation (e.g., automobiles, buses, trains, ships, planes).
2. Being in open spaces (e.g., parking lots, marketplaces, bridges).
3. Being in enclosed places (e.g., shops, theaters, cinemas).
4. Standing in line or being in a crowd.
5. Being outside of the home alone.
B. The individual fears or avoids these situations because of thoughts that escape might be difficult or
help might not be available in the event of developing panic-like symptoms or other incapacitating
or embarrassing symptoms (e.g., fear of falling in the elderly; fear of incontinence).
C. The agoraphobic situations almost always provoke fear or anxiety.
D. The agoraphobic situations are actively avoided, require the presence of a companion, or are
endured with intense fear or anxiety.
E. The fear or anxiety is out of proportion to the actual danger posed by the agoraphobic situations
and to the sociocultural context.
F. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more.
G. The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social,
occupational, or other important areas of functioning. (Will always be
considered)
Rule Outs
H. If another medical condition (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease, Parkinson’s
disease) is present, the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is clearly excessive.
I. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not better explained by the symptoms of another
mental disorder
Panic disorder and agoraphobia statistics
2.7% per year
more common in women
onset: early adulthood
nocturnal panic attacks common
Social Anxiety
extreme enduring fear and avoidance of social or performance situations
fear of being negatively evaluated
2nd most common anxiety disorder
equal between genders
onset: adolescence/early adulthood
precedes depression and other disorders
on a spectrum
Social anxiety symptoms
A. Marked fear or anxiety about one or more social situations in which the
person is exposed to possible scrutiny by others, with the fear that one will
act in a way, or show anxiety symptoms, that will be negatively evaluated.
B. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way or show anxiety
symptoms that will be negatively evaluated (i.e., will be humiliating or
embarrassing; will lead to rejection or offend others).
C. The social situations almost always provoke fear or anxiety
D. The social situations are avoided or endured with intense fear or anxiety.
E. The fear or anxiety is out of proportion to the actual threat posed by the social
situation and to the sociocultural context.
F. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or
more
G. The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in
social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. (Will
always be considered)
Rule Outs
H. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not attributable to the physiological
effects of a substance
I. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not better explained by the
symptoms of another mental disorder
J. If another medical condition (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease,
Parkinson’s disease) is present, the fear, anxiety, or avoidance is
clearly excessive.
Social anxiety treatment
CBT - incorporates feared situations to disprove automatic perceptions of danger
SSRIs
Generalized anxiety disorder
characterized by intense, uncontrollable, unfocused, chronic, continuous worry that is distressing and unproductive about multiple areas of life
physical symptoms: tenseness, irritability, restlessness
6% lifetime prevalence
onset: adolescence
more common in females
less physiological stress response than other anxiety disorders
Generalized anxiety disorder symptoms
A. Excessive anxiety and worry (apprehensive expectation), occurring more
days than not for at least six months about a number of events or
activities (such as work or school performance).
B. The individual finds it difficult to control the worry.
C. The anxiety and worry are associated with at least three (or more) of the
following symptoms (with at least some symptoms present for more days
than not for the past 6 months):
1. restlessness or feeling keyed up or on edge,
2. being easily fatigued,
3. difficulty concentrating or mind going blank,
4. irritability,
5. muscle tension
6. sleep disturbance.
D. The anxiety, worry, or physical symptoms cause clinically significant
distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of
functioning.
Rule Out
E. The disturbance is not due to the direct physiological effects of a
substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication)
F. The disturbance is not due to a general medical condition and is not better
explained by another mental disorder.
Influences on anxiety disorders
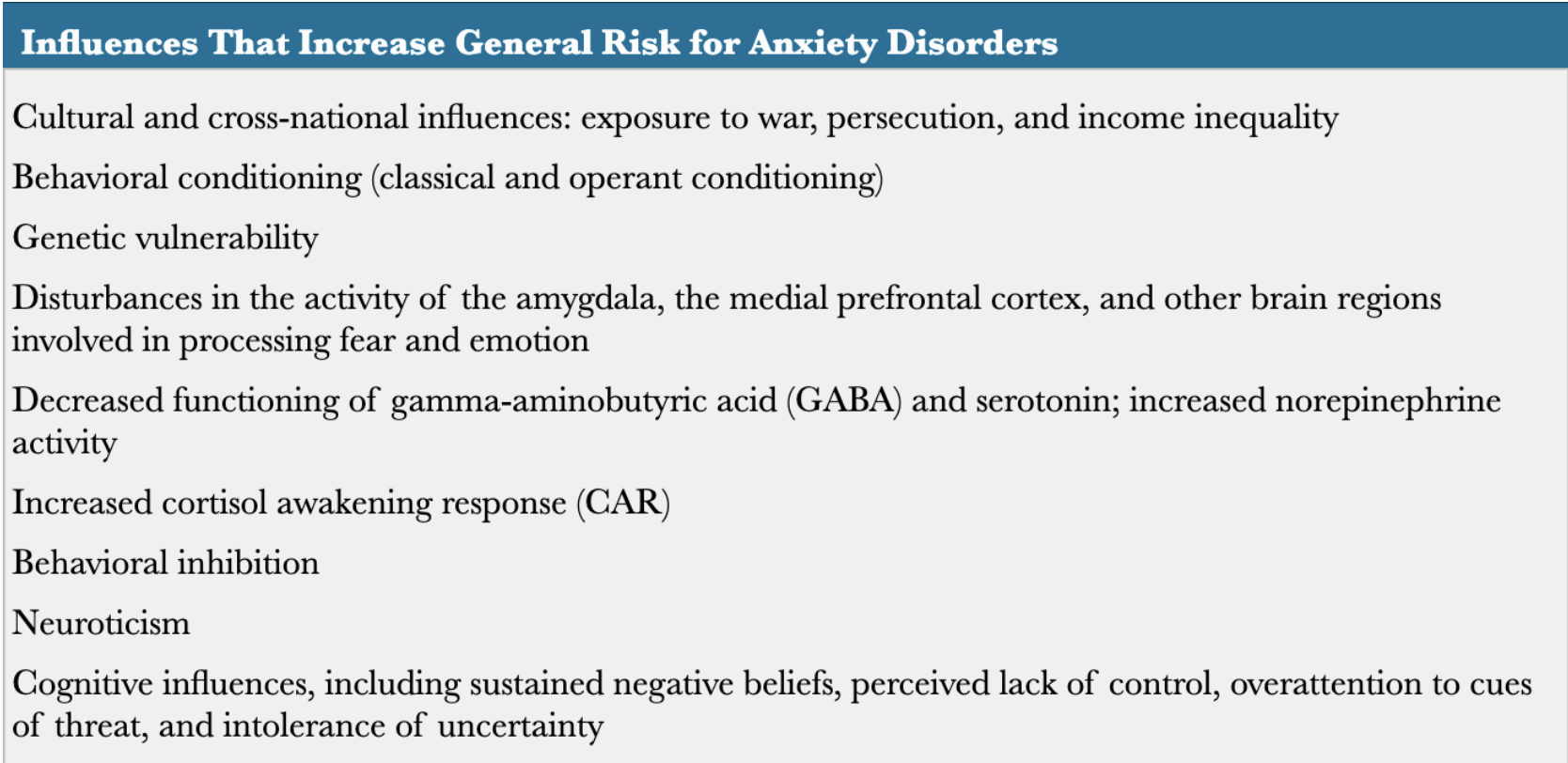
Mower’s 2 factor model - fear conditioning
behavioral influences on anxiety disorders
classical conditioning
- learns to fear neutral stimulus when paired with intrinsically aversive stimuli
operant conditioning
- gain relief by avoiding conditioned stimulus
limitations:
people with anxiety disorders often cannot remember what triggered symptoms
many who experience significant threats do not develop anxiety disorders - could be based in underlying vulnerability
People with anxiety disorders
more easily conditioned to fear stimuli
sustain conditioned fears longer
respond more strongly to unpredictable threats
Genetic influences on anxiety disorders
heritability ~0.5-0.6
genetic vulnerability to anxiety disorders and major depressive disorder
Brain region and neurotransmitter influences on anxiety disorders
activation of amygdala when anxious/fearful
medial prefrontal cortex: reduced activity when someone with anxiety disorder views threatening stimulus
disruption of serotonin levels
higher norepinephrine levels
Personality influences on anxiety disorders
neuroticism and behavioral inhibition are predictors
Behavioral Inhibition
tendency to become agitated toward certain stimuli
strong predictor of social anxiety disorder
Cognitive influences on anxiety disorders
sustained negative beliefs about future
safety behaviors: behaviors used to avoid feeling anxious
perceived lack of control
early life experiences show life is not controllable
intolerance of uncertainty
more susceptible to anxiety disorders, MDD, OCD
attention to threat
pay more attention to negative cues in environment
Integrative model - triple vulnerability threat
biological vulnerability: heritable contribution to negative affect
specific psychological vulnerability
generalized psychological vulnerability: sense that events are unpredictable/uncontrollable
Etiology of panic disorder and agoraphobia
genetic contributions to anxiety
psychological vulnerability to developing anxiety, experiencing negative emotional states, lack of sense of control
associations of bodily sensations with danger
anxiety sensitivity: fear of fear (panic disorder)
Etiology of social anxiety
evolutionary: avoid threatening people
biological vulnerability: to anxiety, shyness
psychological vulnerability: think stressful events are uncontrollable
stress → anxiety → self focus → worse performance
stress → unexpected panic attack → conditioning to social cues
social trauma → conditioned to social cues
Etiology of generalized anxiety disorder
higher psychophysiological arousal because of worry
contrast avoidance model
people with GAD highly aversive to rapid emotion shifts
to stop shifts - think it is better to have chronic state of worry and distress
Treatment for anxiety disorders
common theme: stopping avoidance, learning to respond to fear in different ways
ACT
CBT
breathing skills
medication
systematic desensitization
ACT (acceptance and commitment therapy)
comfortability with uncontrollability of life
Exposure Therapy
exposure to feared stimuli to reduce associated anxiety response
can be imaginal or direct
often used for specific phobia
Treatments for panic disorders and agoraphobia
SSRIs, benzodiazapines
panic control treatment
relaxation techniques
Panic control treatment
therapy for panic attacks that gradually exposes clients to somatic sensations associated with panic attacks, modification of attitudes about them
Treatment for social anxiety
CBT for social anxiety/phobia
track avoidance, worry about panic, anxiety, stress, depressive feelings
Cognitive behavioral framework
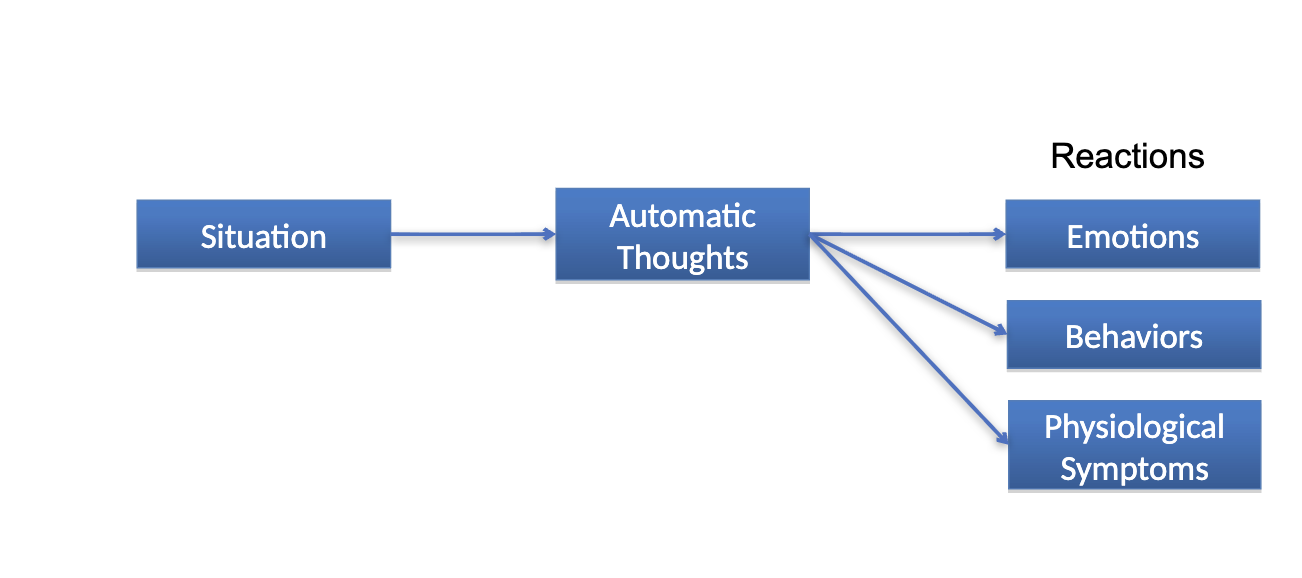
Treatment for GAD
exposure therapy (CBT)
behavioral: worry breaks, relaxation exercises
cognitive: challenge thoughts, face source of worry