Chapter 2, Lesson 2: Water and Mixtures
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 2, Lesson 2 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Mixtures
Substances that are physically blended but not chemically combined; most are body fluids with water
Properties of water
Solvency, cohesion, adhesion, reactivity, thermal stability
Solvency
The ability to dissolve other chemicals; water is the universal this
Hydrophilic substances
Substances that dissolve in water; molecules that are this are polarized or charged (like sugar)
Hydrophobic
Substances that do not dissolve in water; molecules that are this are nonpolar or neutral (like fats)
Hydration spheres
Ionic bonds being overpowered by hydrogen bonds from water
Adhesion
The tendency of one substance to cling to another; water does this in membranes
Cohesion
The tendency of like molecules to cling to each other; water does this due to its hydrogen bonds and makes surface tension
Chemical reactivity
The ability to participate in chemical reactions; water does this into H+ and OH-
Heat capacity
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree C
Calorie
The base unit of heat that raises the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree C
Thermal stability
The ability to stabilize the temperature of its surroundings; water can absorb high levels of heat and remove calories

Solution
Consists of the solute particles mixed with a more abundant substance called the solvent; particles are under 1 nm, do not scatter light, will pass through membranes, and won’t separate on standing

Colloid
Consists of mixtures of protein and water; particles are 1-100 nm, scatter light, do not pass through membranes, and remain permanently mixed
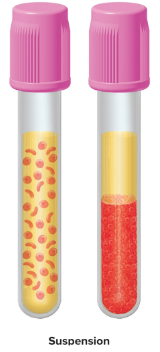
Suspension
A mixture of particles that are bigger than 100 nm, too large to pass through membranes, cloudy or opaque, and will separate on standing
Acid
A liquid that donates protons through releasing H+ ions; the pH is less than 7 and H+ > OH-
Base
A liquid that accepts protons by accepting H+ ions or donating OH- ions; the pH is greater than 7 and H+ < OH-
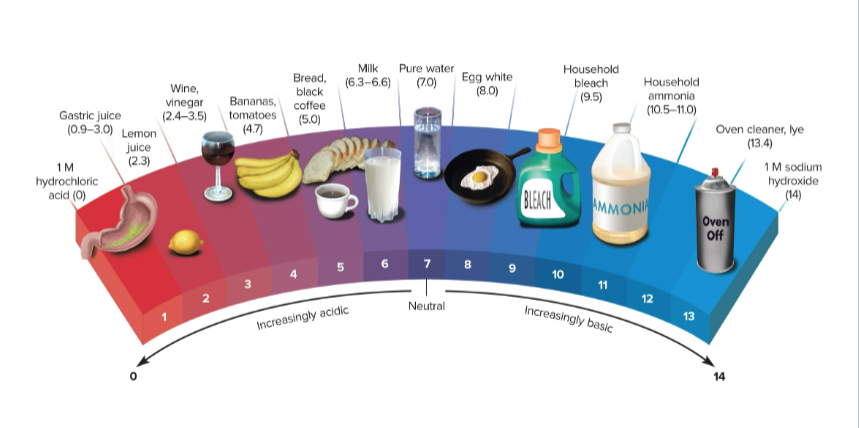
pH
The measure of acidity derived from the molarity of H+, 7 is neutral when H+ = OH-
Weight per volume
Weight of solute in a given volume of solution; milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) is common in biology
Percentages in solutions
May be weight (solid) or volume (liquid) per volume of solution
Electrolyte measurement
Measured in equivalents (Eq); 1 Eq = amount needed to neutralize 1 mole of H+ or OH- ions