Antibody Structure & Function: Key Terms for Biology Study
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Draw an Ig molecule. Include V region, C region, hypervariable region, L chain, H chain, F(ab)'2, Fc, and antigen binding site.
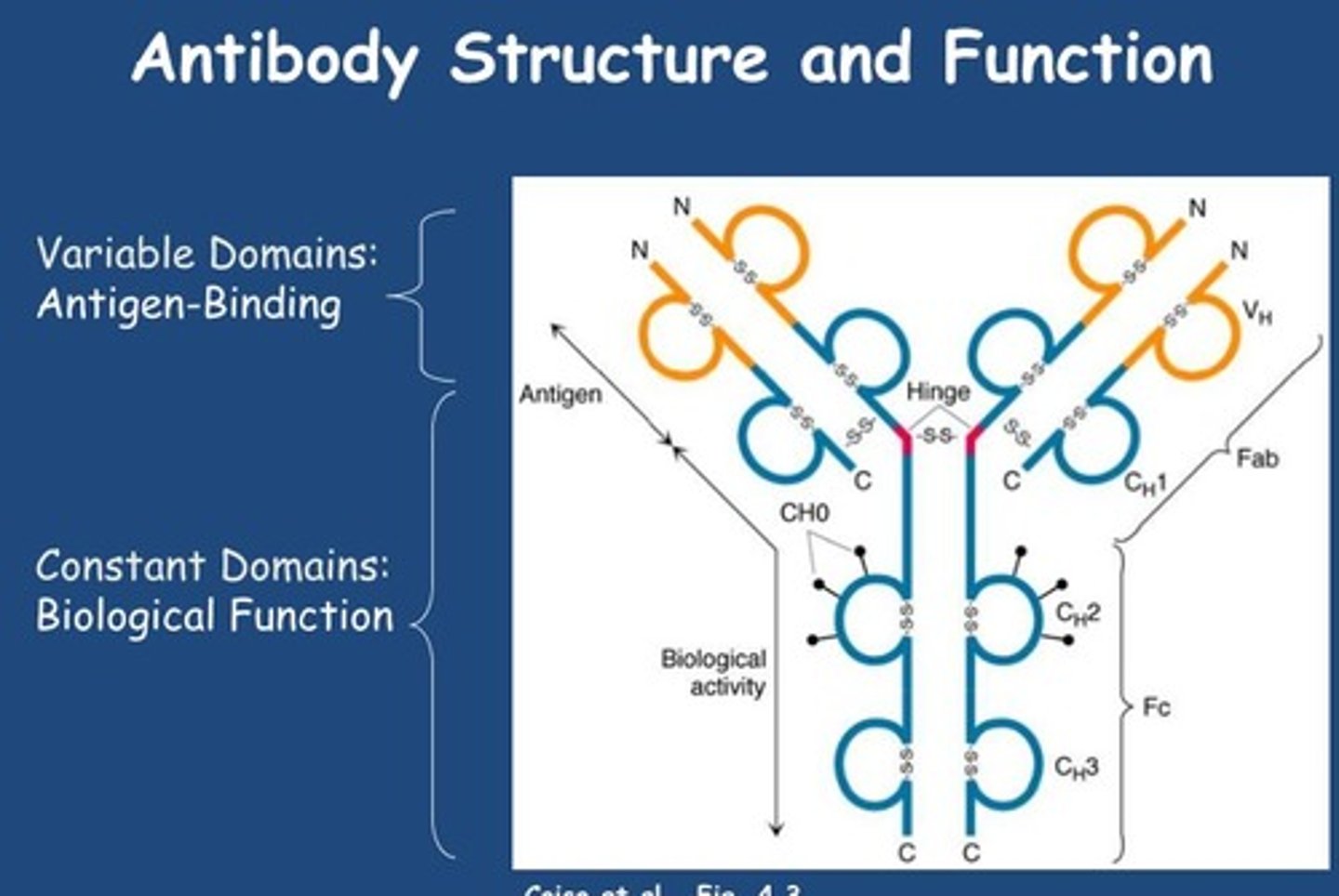
What three genes code for the variable region of the H chain?
VDJ
The ______ gene codes for the constant region of the H chain.
C
VDJ genes are joined together through ______.
V(D)J recombinase
The heavy chain genes are rearranged ______ light chain genes.
before
What is the order of heavy chain gene rearrangement?
D-J first, then add V, then add C
What is the order of light chain gene rearrangement?
V-J, then add C
Because of alternative splicing, both ______ and ______ can be expressed on a mature B cell.
VDJ-µ (IgM), VDJ-δ (IgD)
Either ______ or ______ light chain isotype can be chosen for each antibody, not both.
kappa, lambda
Isotype switching is unique to the ______ region locus.
H chain C
Isotype switching occurs with ______.
antigen stimulation
______ and ______ are both requires for isotype switching.
cytokines (IFN-y, IL-4). activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)
Mature B cells express both ______ and ______.
IgM, IgD
After ______ exposure, enzymes cut segments of the gene sequence.
antigen
Whichever ______ chain gene segment is left (and first) is expressed.
heavy
Antibodies are essential in ______ immune response.
humoral immunity is
Abs can be ______ or ______.
membrane bound (BCR), secreted (plasma cells)
There are 2 ______ and 2 ______ chains of an Ab.
heavy, light
There are ______ bonds within an Ab.
disulfide
Papain cleaves Abs just above the hinge region to create what segments?
2(Fab) + Fc
Pepsin cleaves Abs to create what segments?
1 F(ab')2, 2 identical L chains, 2 identical H chains
What region distinguishes the 5 Ab isotypes?
The constant region
The nature of the ______ chain dictates properties of that Ab.
heavy
What are the two isotypes of light chains?
kappa and lambda
Isotype means Ab ______.
class
Allotype is the ______ Ab difference between 2 people.
whole
Idiotype is the Ab ______ difference between 2 people.
binding site
What is the most abundant Ig?
IgG
IgG is important in ______ immune response.
secondary
IgG has subclasses ______, in order of abundance in serum.
IgG1-4
IgG can cross the ______ and ______.
placenta (not IgG2), tissues
IgG causes ______ and ______ of antigen.
agglutination, precipitates
What are the biological functions of IgG?
- Opsonization
- Neutralization of toxins and viruses
- Activation of complement
- Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
When the first protein in complement cascade (C1q) encounters IgG, the ______ complement pathway is initiated.
classical
IgM is the first class produced by the ______.
fetus
IgM is ______ in shape. How many antigen binding sites does it have?
pentameric
10
IgM functions in the ______ immune response.
primary
IgM can also be ______ on B cell surfaces.
monoemric
What is the first Ig present during primary immune response?
IgM
When IgM dies down, ______ increases.
IgG
Eventually, IgG ______.
dies down
During secondary response, ______ shows up first, in the same amount as in the primary response.
IgM
When IgM dies out during secondary response, ______ comes in very high amounts and stays high.
IgG
This allows for...
Lessened symptoms, quicker alleviation of disease
At birth, ______ levels decrease and ______ levels increase.
Maternal IgG
IgM/G/A
IgM is the first line of defense for ______ immunity.
neonatal
IgM has the best ______.
complement fixation
IgM is the best isotype at ______.
agglutinating
Why is IgM the best at all these?
Because of its increased number of binding sites due to its pentameric shape
IgA is found in ______.
secretions
IgA protects against ______ and ______ infections.
respiratory, GI
IgA is a monomer in ______, but has no function.
serum
IgA is a ______ in secretions.
dimer
IgA has ______ and ______ component when dimerized in secretions.
J chain, secretory
IgA is the most common Ab ______.
deficiency
IgE is important in ______.
type I hypersensitivity (allergy)
IgE binds to Fc receptors on what cells?
Mast cells, basophils
IgE increases during ______ infection.
parasitic
IgE can be responsible for the transfer of ______ between individuals.
allergy
The role of IgD is unknown, but it may play a role in ______ activation.
B cell
IgD is a receptor on naive ______.
B cells
Which Igs activate classical complement?
IgG (1,2,3), IgM
Which Igs can cross the placenta?
IgG
Which Igs are present on the membrane of mature B cells?
IgM, IgD
Which Igs are important in mucosal transport?
IgA, IgM
What Igs induce mast cell degranulation?
IgE
What contributes to the diversity and large number of Abs?
- Germline diversity (inherited genes)
- Combinational diversity (VDJ recombination)
- Junctional diversity (imprecise VDJ joining)
- Somatic hypermutation
- Class switching
Somatic hypermutation is a mutation that occurs in the V region that results in the creation of ______ Abs
variant
Some of these variant Abs have a higher affinity for their ______.
antigen
Monoclonal antibodies are a collection of ______ that interact with a single antigen site.
identical antibodies
mAbs are created through the combination of what three things? What does this create?
B cells, myeloma cells
Hybridoma
The hybridomas then undergo ______, individual screening, then mAbs are produced by hybridoma clones.
ELISE screening
mAbs are essential for what things within the clinical lab?
In vitro diagnostics, pregnancy, rapid tests, ELISA, flow cytometry, autoimmune disease treatment
RA and Crohn's disease can be treated with a mAb towards the cytokine ______.
TNFa
IgM heavy chain gene
μ
IgG heavy chain gene
γ
IgD heavy chain gene
δ
IgA heavy chain gene
α
IgE heavy chain gene
ε
Which immunoglobulins have a J chain?
IgM and IgA
Through allelic exclusion, only one ______ is kept for each Ab.
light chain (kappa or lambda)
If kappa rearrangement is successful, then ______ is not rearranged.
lambda
If kappa rearrangement fails, ______ rearrangement occurs.
lambda