Clin Med II Exam 2 - HEME (LYMPHOMAS & MYELOMA)
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
gbalsam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
lymphoma
cancer that starts in the lymph nodes or the lymphatic system that invades other organs by unnecessary and uncontrollable growth of lymphoid tissue
myeloma
a type of cancer that occurs in blood-making cells found in the red bone marrow; abnormally dividing plasma cells
Hodgkin's lymphoma
distinguished from other lymphomas by the presence of large, cancerous lymphocytes known as Reed-Sternberg cells
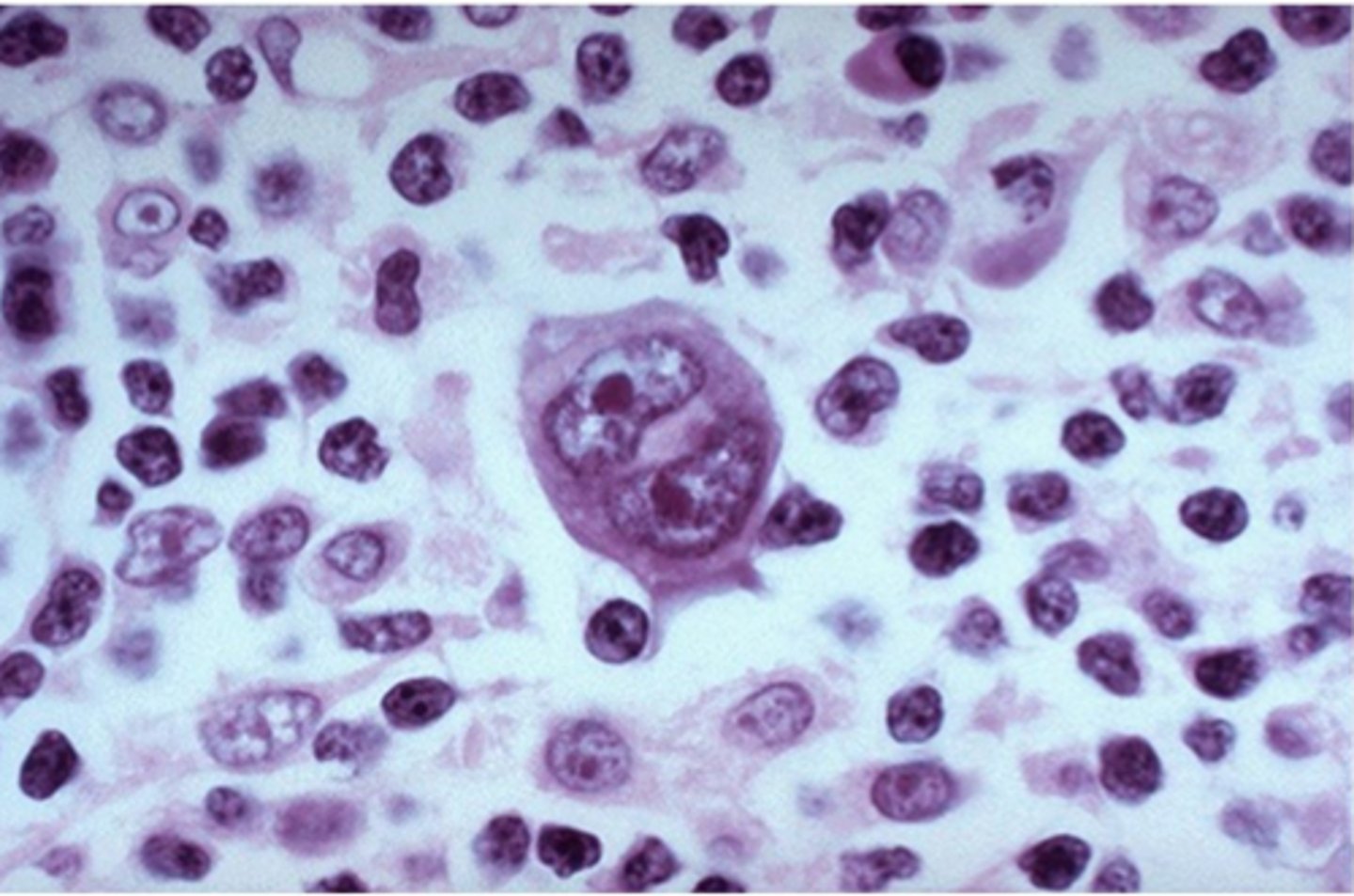
patho of Hodgkin's lymphoma
mature B cells transformed into malignant cells
classic feature of Hodgkin's lymphoma
tendency to arise within single lymph node areas and spread in an orderly fashion to contiguous lymph nodes
most common Hodgkin's lymphoma subtype
nodular sclerosis
etiology of Hodgkin's lymphoma
- unknown
- possible virus (risk linked to EBV as cells are unable to manufacture intact antibodies)
- some evidence for tumor associated antigens
classic Hodgkin's lymphoma
- nodular sclerosis
- lymphocyte rich
- mixed cellularity
- lymphocyte depleted
non-classic Hodgkin's lymphoma
nodular lymphocyte predominant
symptoms of Hodgkin's lymphoma
- often asymptomatic
- painless lymphadenopathy most commonly in the neck
- constitutional "B" symptoms (may be sign of advanced disease)
- generalized and severe pruritis
- pain associated with alcohol ingestion in specific sites or regions (often lymph nodes or bones)
- anemia symptoms
- persistent non-productive cough
- headache and facial fullness
- weakness and numbness
constitutional "B" symptoms
fever, weight loss, or drenching night sweats
pel-ebstein fever
relapsing, high-grade fever that can reach 105-106ºF with a periodicity of 7-10 days
signs of Hodgkin's lymphoma
- non-tender lymphadenopathy in the neck, supraclavicular area, and axilla
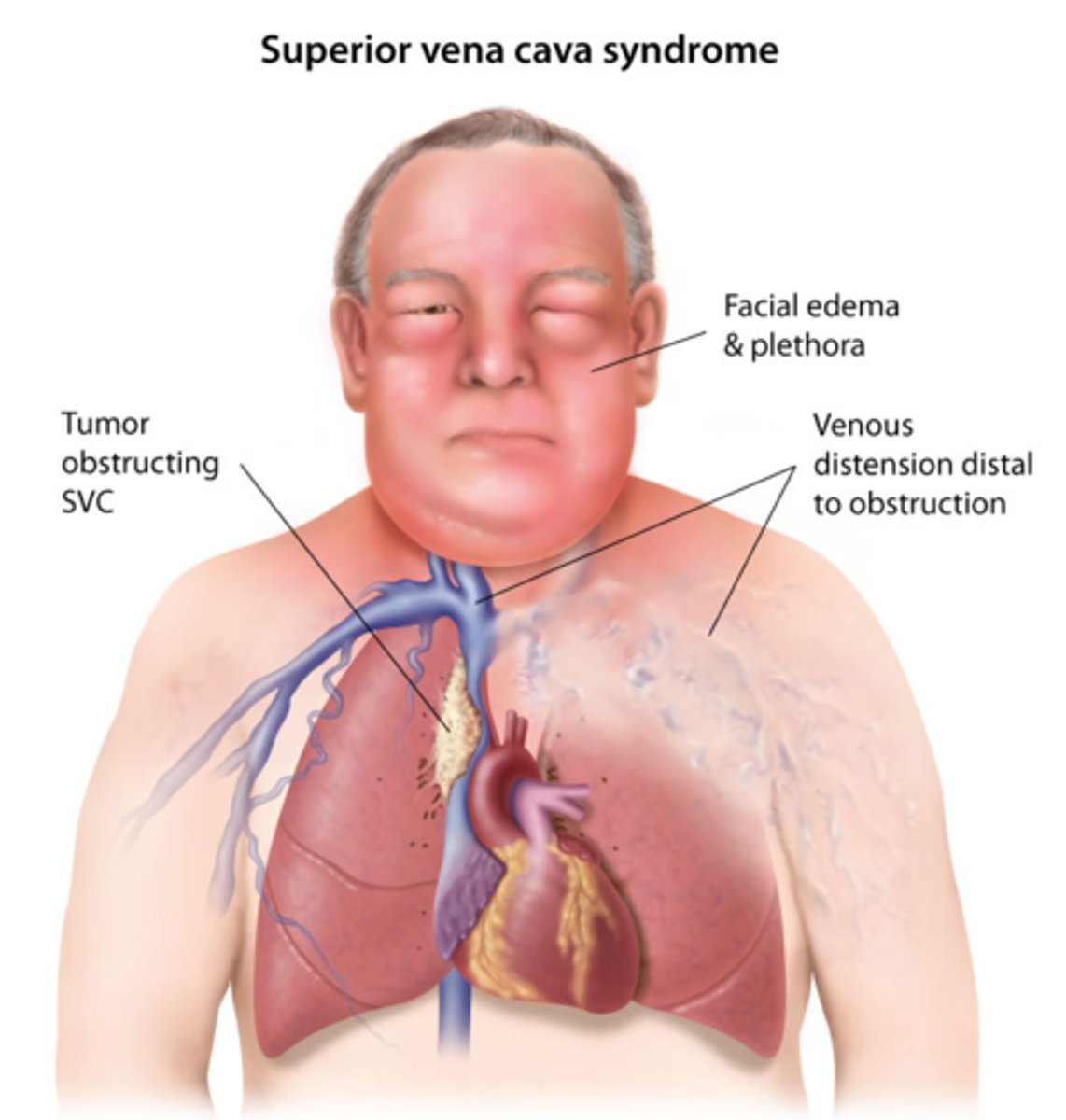
- mediastinal mass (may cause dysphagia, dyspnea, cough, stridor, or the superior vena cava syndrome)
- T-cell mediated immune deficiency leading to propensity to infections (i.e., herpes zoster, fungal or mycobacterial infections, etc.)
less common signs of Hodgkin's lymphoma
- splenomegaly and hepatomegaly
- peripheral weakness and numbness with attenuated reflexes
- plethora and distended neck and facial veins
- variety of skin lesions (i.e., ichthyosis, Bazex syndrome, urticaria, etc.)
nodular sclerosis Hodgkin's lymphoma
disease above the diaphragm and mediastinal node involvement
lymphocyte depletion Hodgkin's lymphoma
presents with abdominal nodal involvement and often has extra-nodal disease (advanced with systemic "B" symptoms)
which subtypes of Hodgkin's lymphoma often present with disease of the liver?
mixed cellularity or lymphocyte depletion
nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma
localized peripheral disease in the upper neck
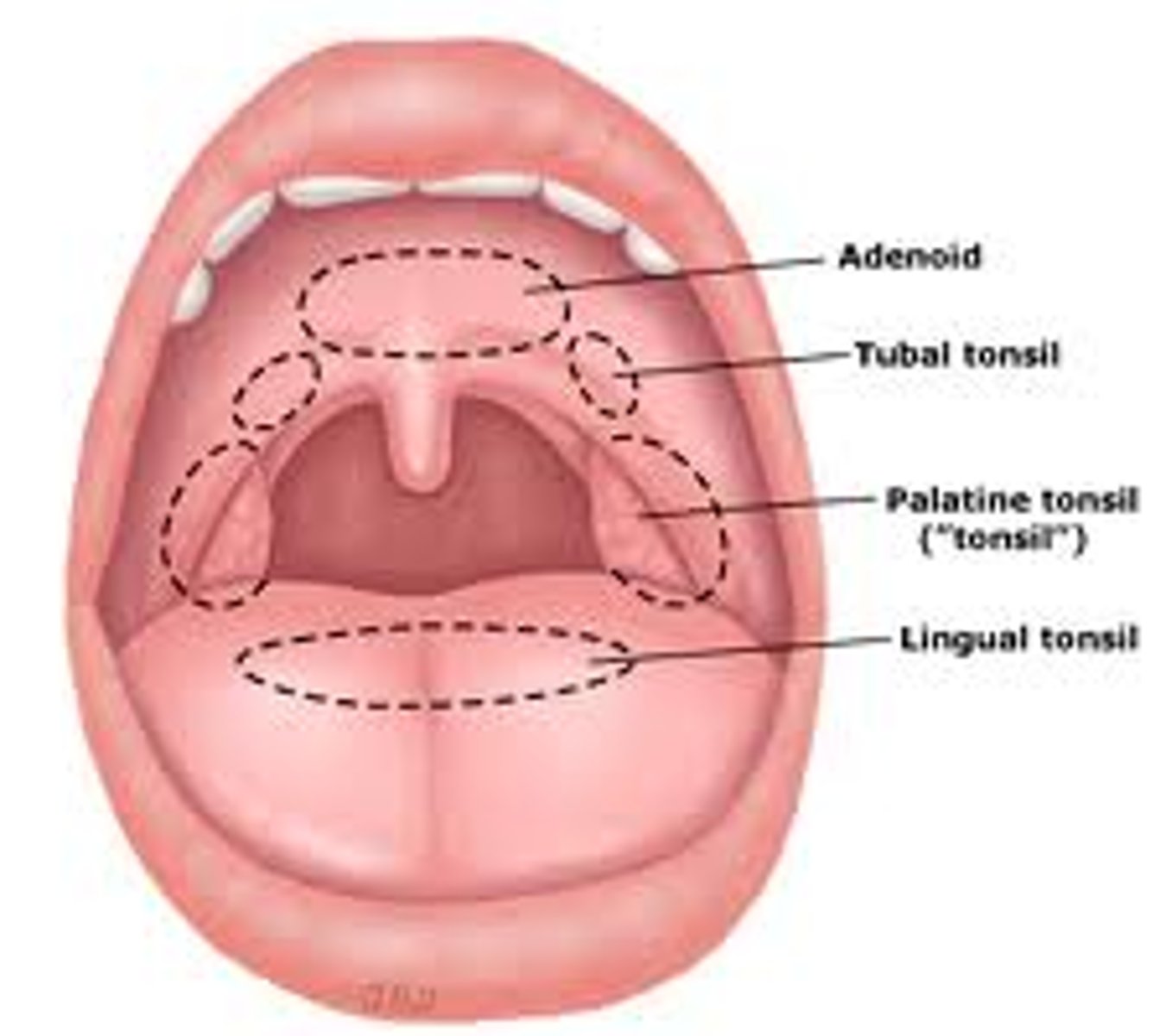
Waldeyer's ring
the ring of lymphatic tissue formed by the two palatine tonsils, the pharyngeal tonsil, the lingual tonsil, and intervening lymphoid tissue
superior vena cava syndrome
progressive occlusion of the superior vena cava that leads to venous distention of upper extremities and head
immunophenotyping of Hodgkin's lymphoma
CD30 and CD15 markers
diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma
excisional nodal biopsy required; presence of Reed-Sternberg cells in an inflammatory background containing a variable number of small lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils, histiocytes, plasma cells, fibroblasts, and collagen fibers
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage I
single lymph node region involved
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage II
involvement of two lymph node areas on one side of the diaphragm
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage III
lymph node regions involved on both sides of the diaphragm
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage IV
disseminated disease with bone marrow or liver involvement
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage A
lack of constitutional symptoms
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage B
there is a 10% weight loss over 6 months, fever, or night sweats ("B" symptoms)
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage X
bulky disease; mediastinal mass with a maximum width that is ≥1/3 of the internal transverse diameter of the thorax
Hodgkin's lymphoma stage E
(local) extra-nodal disease
standard treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma
"ABVD"
- adriamycin
- bleomycin
- vinblastine
- dacarbazine
other treatments of Hodgkin's lymphoma
- BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide, adriamycin, cyclophosphamide, oncovin, procarbazine, prednisone)
- standford V (doxorubicin, vinblastine, mechlorethamine, vincristine, bleomycin, etoposide, and prednisone)
- add radiation in stages I-II
treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma in patients with primary refractory disease
may attain double responses and remissions with second line chemotherapy that incorporates drugs not used in the initial treatment (i.e., ABVD) followed by high dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic cell rescue
treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma in patients with secondary refractory disease
these patients are high candidates for high dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation as well
complications of Hodgkin's lymphoma
- high incidence of second malignancies (leukemia first 10 years, followed by solid tumors over time)
- hypothyroidism
- constrictive pericarditis
- infertility (after the use of alkylating agents)
- heart failure after adriamycin treatment
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
a large group of more than 60 different malignant subtypes that arise from the lymphoid system
subtypes of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- B-cell origin (most common)
- T-cell origin
- natural killer cell-origin
essentials of diagnosing non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- patient presenting with painless lymphadenopathy
- no Reed-Sternberg cells or eosinophilia
- diagnosis is confirmed by excisional tissue biopsy
- nearly all respond to chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy
etiology of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- unknown
- higher risk for individuals who have been exposed to chemicals, EBV history, family history, HIV
patho of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
each type can be viewed as a lymphocyte arrested at a certain stage of development and transformed into a malignant cell
patho of Burkitt lymphoma
proto-oncogene c-myc is translocated from chromosome 8 to heavy chain locus on chromosome 14
patho of follicular lymphomas
t(14,18) translocation is characteristic resulting in an overexpression of bcl-2
prognosis of low grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
incurable
prognosis of aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
potentially curable
symptoms of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- isolated or diffuse lymphadenopathy
- constitutional symptoms (fever, night sweats, weight loss)
signs of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- lymphadenopathy that may fluctuate or spontaneously remit
- hematogenous spread of disease with no predictable pattern
- extra-nodal primary more common in high grade lymphomas
- Waldeyer's ring involvement frequent in GI lymphomas
- cytopenias
- hepatosplenomegaly
- abdominal pain or abdominal fullness (Burkitt lymphoma)
diagnosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
lymph node and tissue biopsy with paratrabecular lymphoid aggregates
patho of mantle cell lymphoma
t(11,14) translocation resulting in cyclin D1 gene
when would you get a lumbar puncture in working up non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
if you suspect
- AIDS lymphoma
- T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma
- high grade lymphoma with positive marrow
T-cell lymphomas
- anaplastic large cell lymphoma
- peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- mycosis fungoides
B-cell lymphomas
- MALT
- hairy cell leukemia
- follicular lymphoma
- mantle cell lymphoma
- diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Burkitt lymphoma
most common indolent B-cell lymphoma
follicular lymphoma (grade I and II)
one of the most indolent T-cell lymphomas
mycosis fungoides
most common aggressive B-cell lymphoma
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
highly aggressive B-cell lymphomas
- Burkitt lymphoma
- precursor B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
highly aggressive T-cell lymphomas
- adult T-cell lymphoma/leukemia
- precursor T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma
acute treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- chemotherapy with alkylating agents (i.e., chlroambucil)
- combo chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone
- rituximab as salvage therapy for relapsed low-grade B-cell lymphomas
CHOP therapy in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone plus localized radiation for localized intermediate-grade lymphomas
worse prognosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- age over 60
- elevated serum LD
- stage III or IV
- poor performance status
Burkitt lymphoma
most rapidly growing human tumor that arises from B-cells
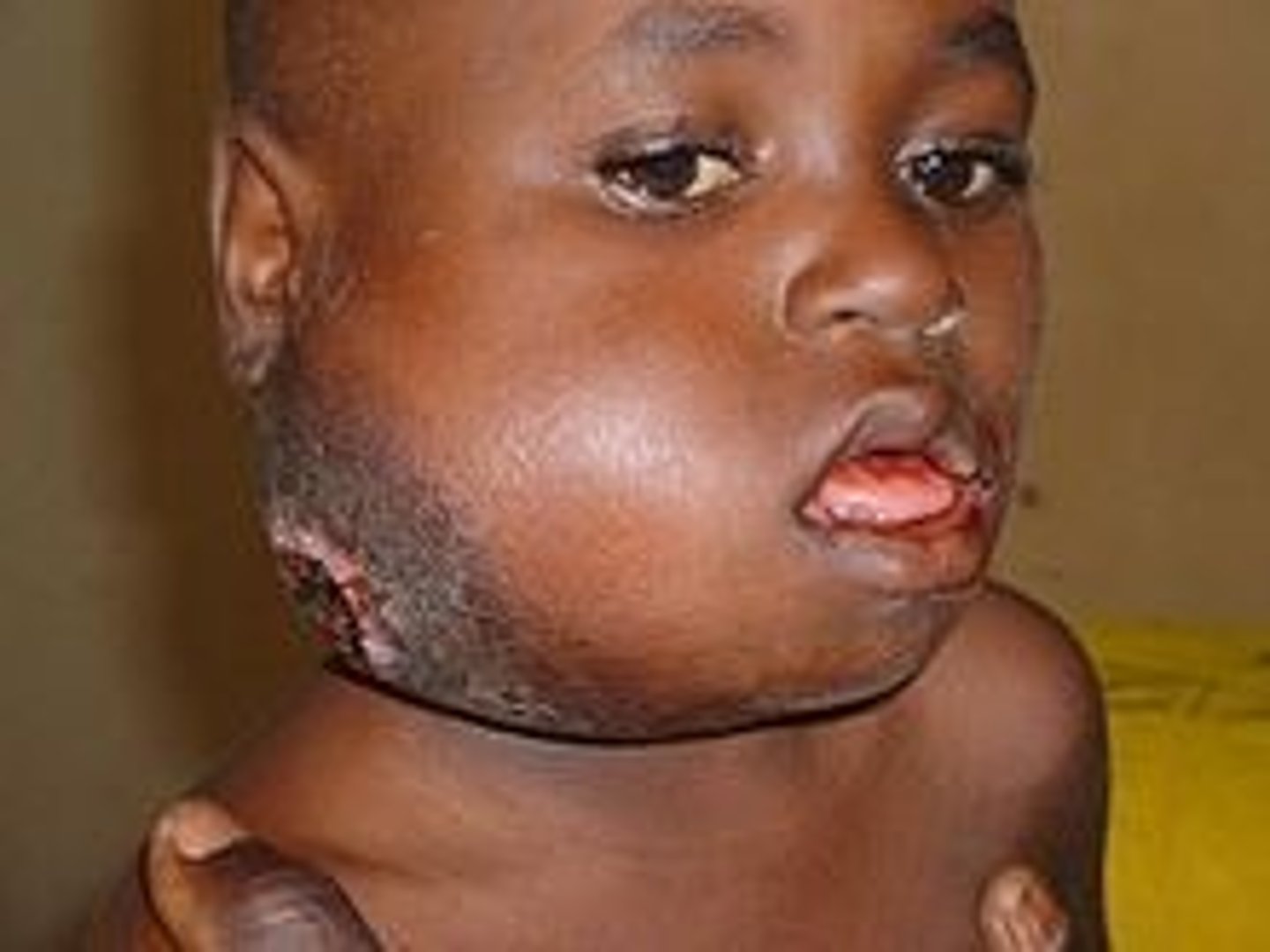
endemic (African) Burkitt lymphoma
jaw tumor that is strongly linked to the Epstein-Barr virus
non-endemic (sporadic) Burkitt lymphoma
usually has an abdominal presentation, most often with massive disease and ascites
treatment of Burkitt lymphoma
multi-drug regimen (urgent and intensive chemotherapy) similar to pediatric leukemia/lymphoma regimens
mycosis fungoides
cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (malignancy of helper T-cells)
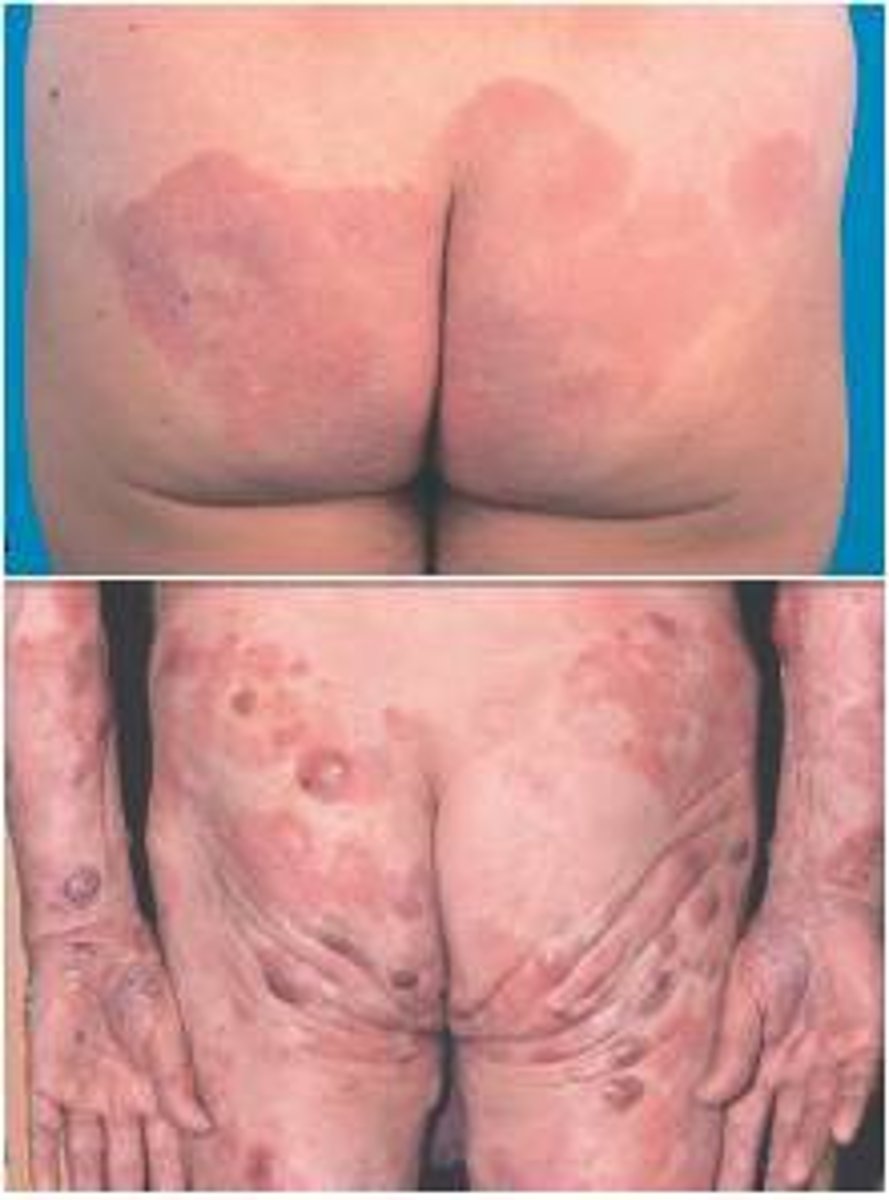
presentation of mycosis fungoides
skin lesions include patches or plaques that may be localized or widespread, tumors, and erythroderma
erythroderma
abnormal redness of the entire skin surface
treatment of mycosis fungoides
can be treated with electron beam radiation, UV light therapy, or topical alkylating agents
adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
associated with HTLV-1 infection and characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, leukocytosis, lymphadenopathy, skin involvement, lytic lesions of the bone, and hypercalcemia
treatment of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
may respond to AZT and interferon
AIDS lymphoma
aggressive lymphomas of b cell origin (Burkitt, Burkitt-like, and large cell immunoblastic)
MALT lymphoma
aka "mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue;" chronic infection of the stomach by H. pylori
treatment of MALT lymphoma
combination antibiotics with proton pump inhibitor acid blockade
ocular adnexal lymphoma (OAL)
lymphoma affecting the tissues surrounding the eye that may arise after chronic inflammation
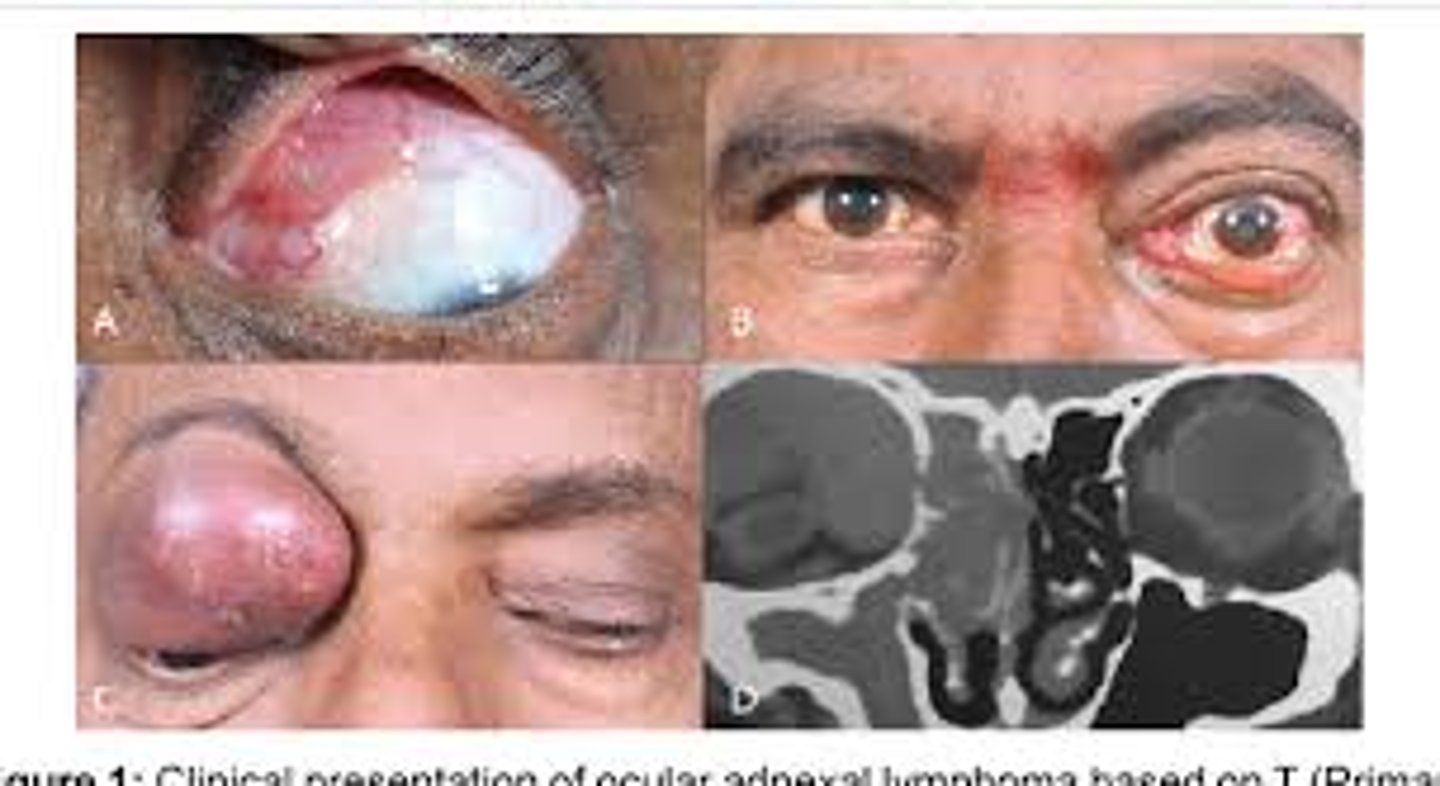
treatment of ocular adnexal lymphoma
may response to antibiotic therapy against chlamydia (i.e., doxycycline)
follicular lymphoma
neoplastic proliferation of small B cells (CD20+) that form follicle-like nodules
most common presentation of follicular lymphoma
new, painless lymphadenopathy (with multiple sites common)
diagnosis of follicular lymphoma
small cleaved and large cells in varying proportions organized in a follicular pattern of growth
treatment of follicular lymphoma
highly responsive to radiation/chemo but unlikely to be cured
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
neo-plastic proliferation of large B cells (CD20+) that grow diffusely in sheets
signs/symptoms of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- rapidly enlarging symptomatic mass, most usually nodal enlargement in the neck or abdomen
- systemic "B" symptoms in 30%
- bone marrow involvement in 30%
- extra-nodal extramedullary disease in 40%
diagnosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- large, transformed B-cells with prominent nucleoli and basophilic cytoplasm
- diffuse growth pattern
- B-cell markers CD20 and CD79a
treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
chemo (R-CHOP)
international prognostic index
used to categorize patients with intermediate-grade lymphoma into risk groups
international prognostic index (0-1 risk factor)
80% complete response rate to standard chemotherapy
international prognostic index (2 risk factors)
70% complete response rate to standard chemotherapy
international prognostic index (more than 2 risk factors)
lower response rates and poor survival with standard regimens; early treatment with high-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation
complications of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
- cytopenias secondary to bone marrow infiltration
- bleeding secondary to thrombocytopenia
- infection
- cardiac problems secondary to large pericardial effusion
- respiratory problems secondary to pleural effusion
- SVC syndrome secondary to large mediastinal mass
- spinal cord compression secondary to vertebral metastases
- neurologic problems
- GI obstruction, perforation, and bleeding
- pain secondary to tumor invasion
- leukocytosis
multiple myeloma
a collection of abnormal plasma cells that accumulate in the bone marrow where they interfere with the production of normal blood cells
overview of multiple myeloma
- disease of malignant B-lymphocytes
- plasma cell dyscrasia/cancer characterized by the presence of anemia, hypercalcemia, lytic bone lesions, and renal failure
- associated with increased levels of a monoclonal immunoglobulin detectable on SPEP or UPEP
prognosis of multiple myeloma
treatment with chemotherapy or autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation can improve renal function, decrease fracture risk, and improve cytopenias resulting in prolonged survival, but treatment is rarely curative
etiology of multiple myeloma
- unknown
- possible predisposing factor of viral infection of human herpes virus 8 (HHV 8)
- MGUS (monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance)
clinical features of multiple myeloma
- bone marrow failure: anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia
- renal failure
- bone disease with skeletal destruction (lytic lesions, generalized decrease in bone density)
- hypercalcemia
- hyperviscosity syndrome
- recurrent infections
- amyloidosis
- neurological symptoms
hyperviscosity syndrome
clinical sequelae of increased blood viscosity; increased serum viscosity results from increased circulating serum immunoglobulins
amyloidosis
rare disease that occurs when amyloid builds up in your organs
bone "break" in multiple myeloma
- bone pain
- recurrent infection
- elevated calcium
- anemia
- kidney failure
labs found in multiple myeloma
- anemia
- RBC morphology normal but rouleaux formation common
- hypercalcemia
- proteinuria (Bence-Jones proteins)
- ESR elevated
- plasma cells rarely visible on peripheral blood smear
- monoclonal spike in B- or γ-globulin region
- clonal plasma cells on bone marrow biopsy
poor survival associated with multiple myeloma
B-microglobulin level >3 mg/L
dismal outcome associated with multiple myeloma
if bone marrow cytogenetic analysis shows deletions of chromosome 13q
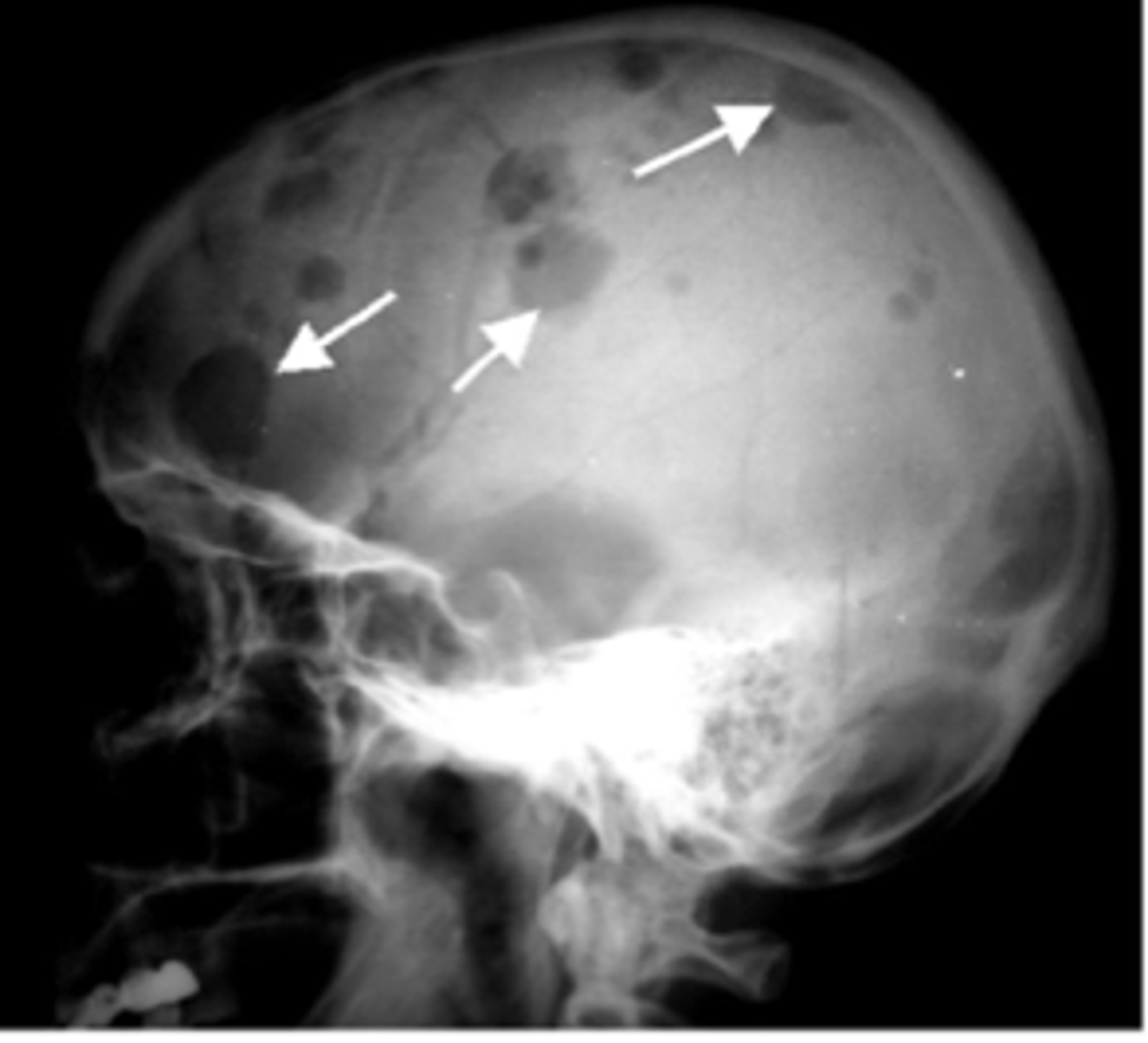
lytic bone lesions
"punched out" lesions found especially in axial skeleton (i.e., skull, spine, proximal long bones, and ribs)
diagnosis of multiple myeloma
≥10% clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow or biposy-proven bony/soft tissue plasmacytoma plus one of the following:
- presence of related organ or tissue impairment (i.e., increased calcium, renal deficiency, anemia, lytic lesions)
- presence of a biomarker associated with near inevitable progression to end-organ damage