Anesthetics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
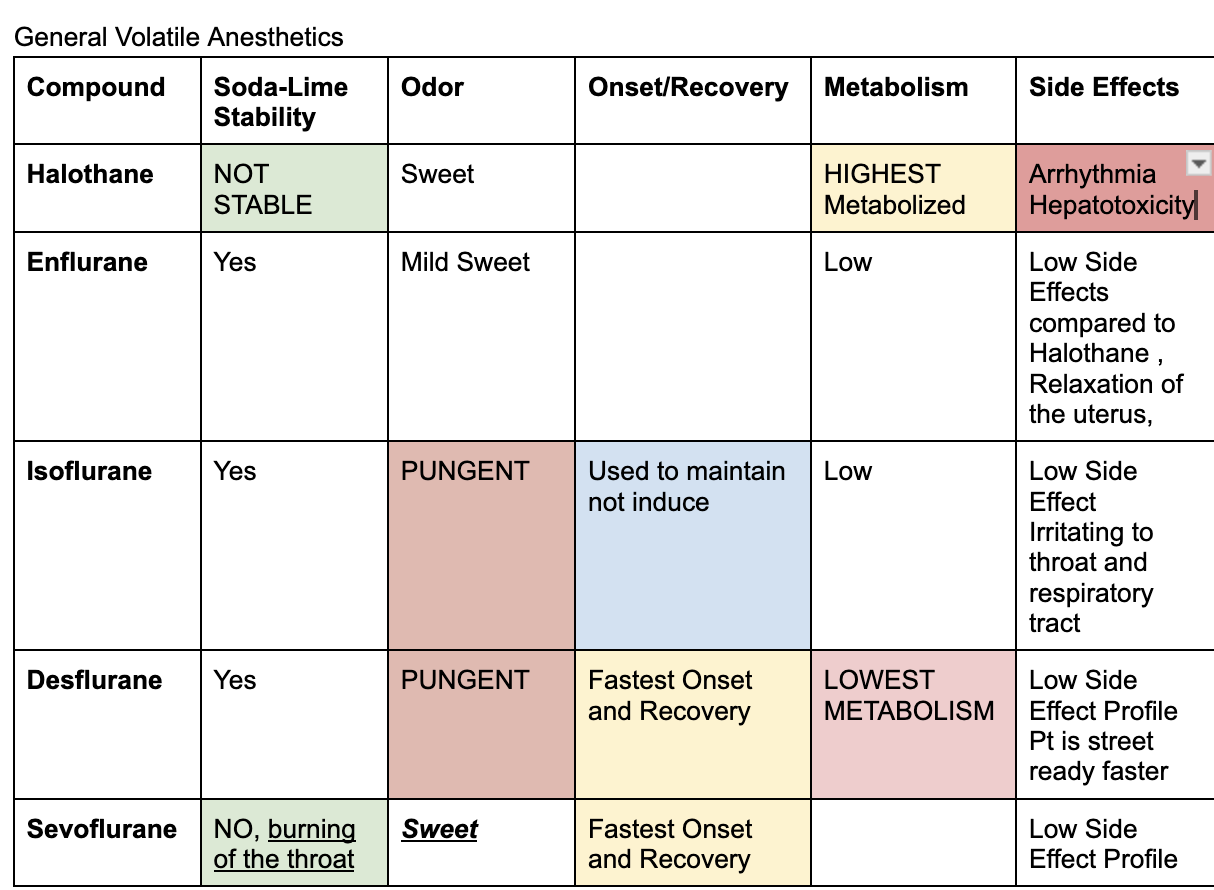
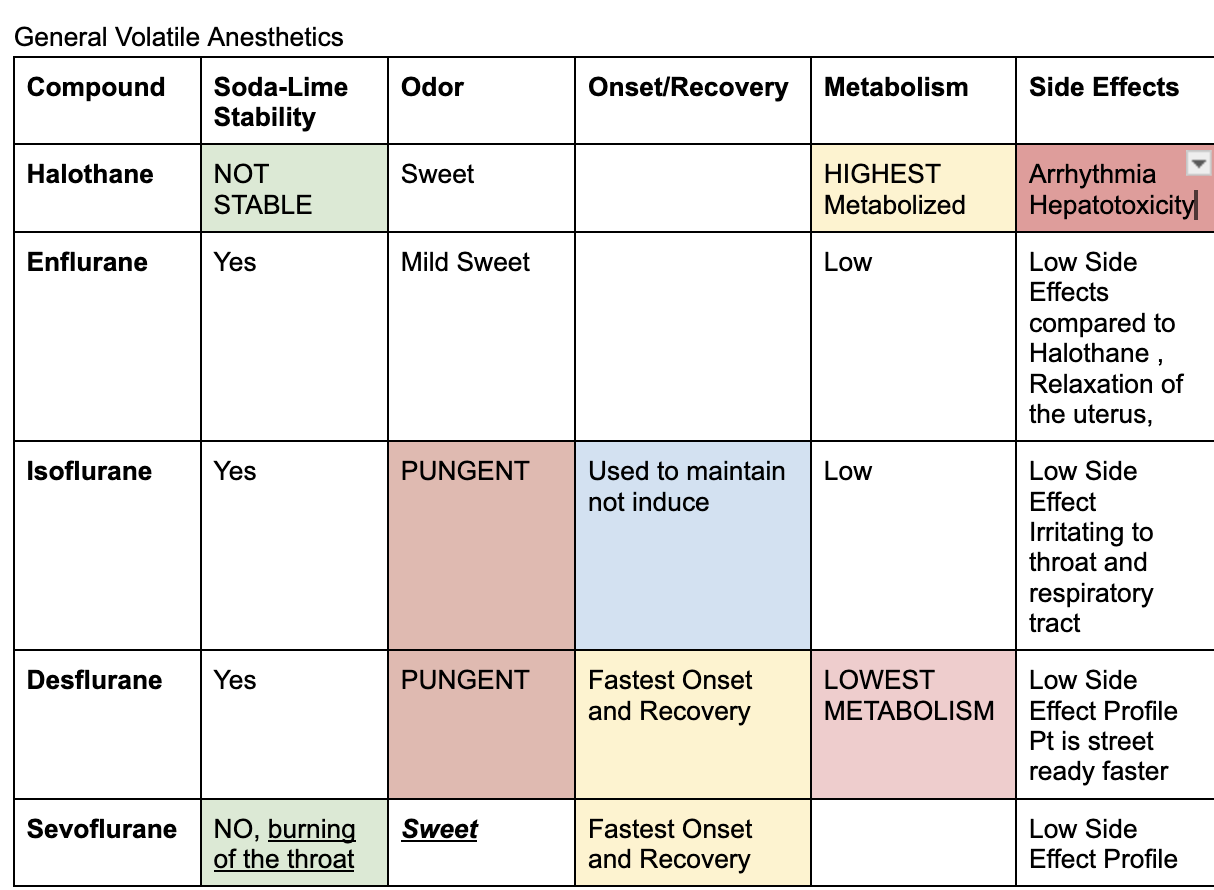
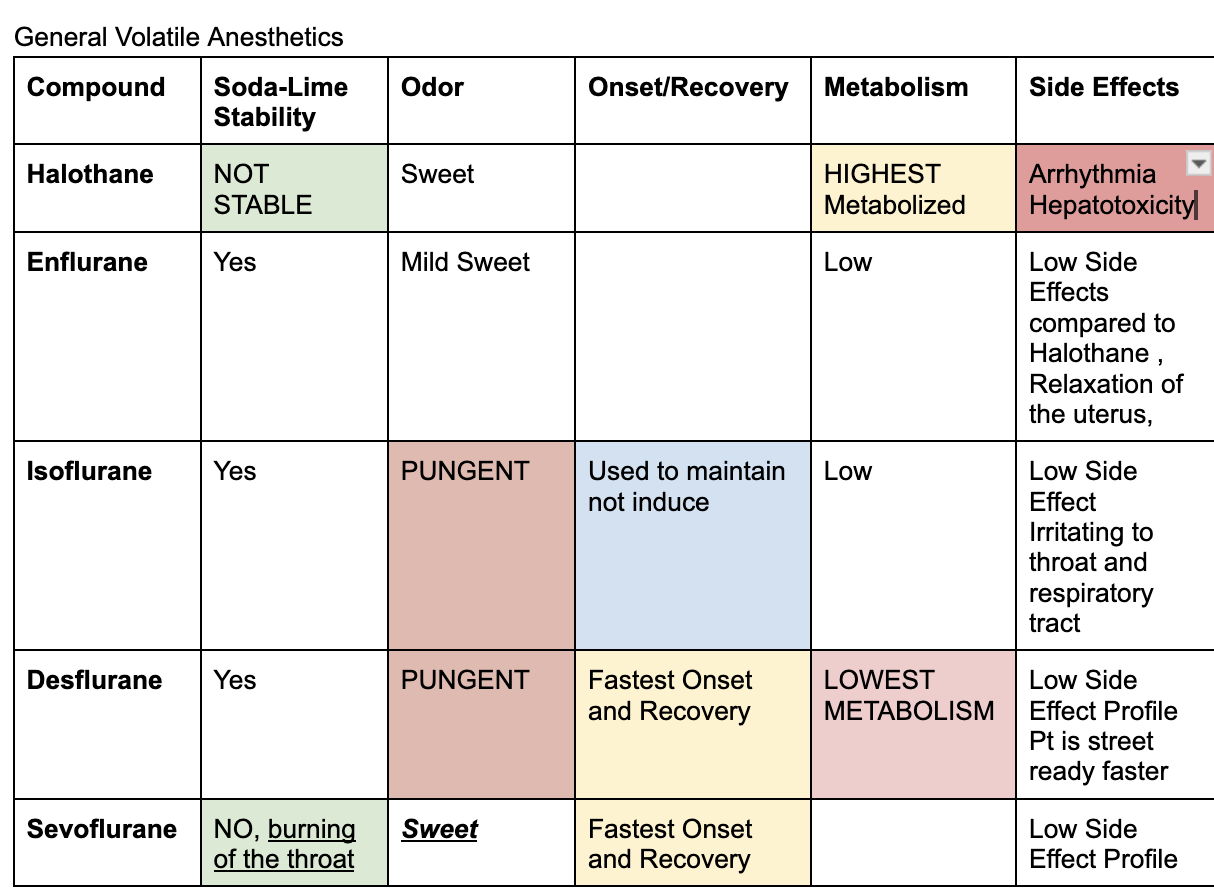
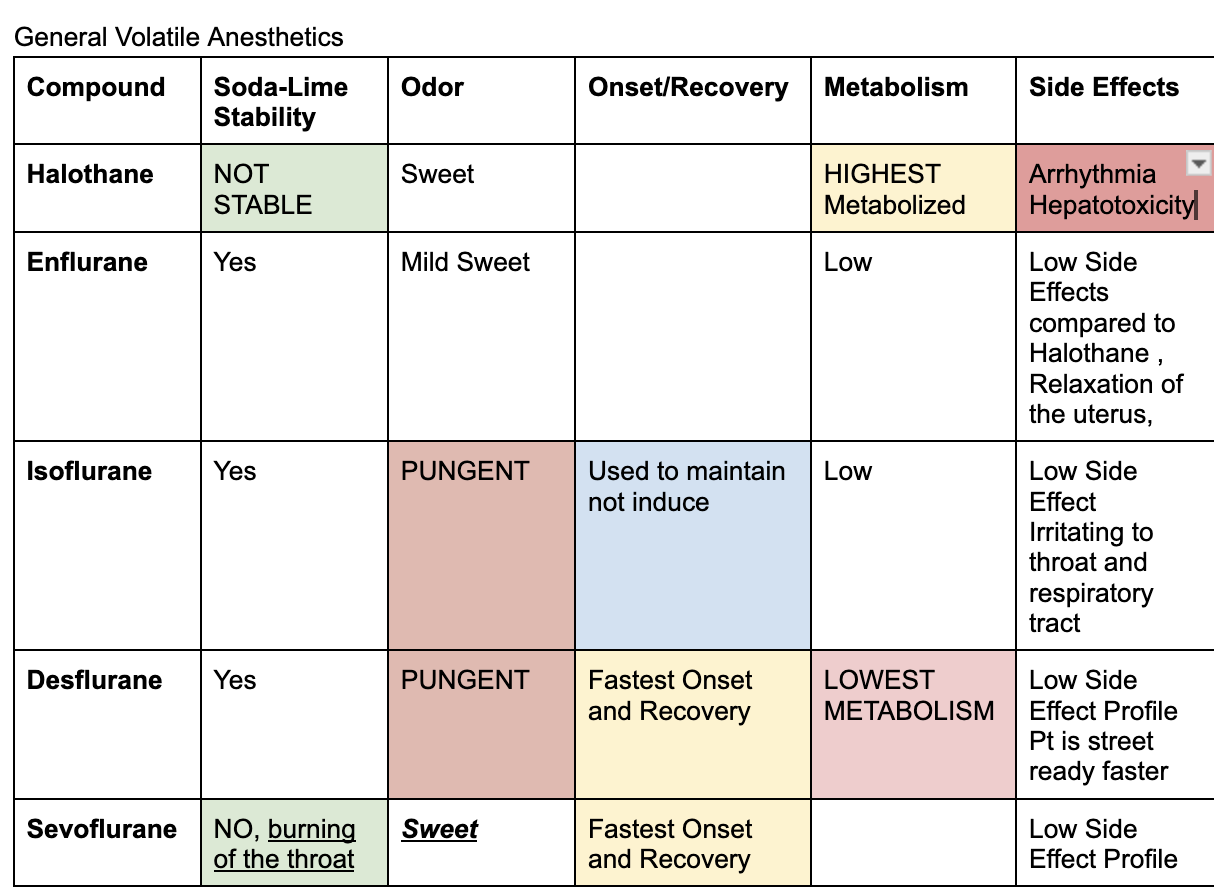
Inhaled general anesthetics
end in THANE
Halothane, Enflurane, Isoflurane, Desflurane, Sevoflurane
Sweet inhaled general anesthetics
Halothane and Sevoflurane; enflurane is mild
He aint stable but hes sweet “esh”
Pungent general anesthetics
DI
Desflurane and Isoflurane
Not Stable to soda lime
Halothane and Sevoflurane
He aint stable but he’s super sweet esh
Stable to soda lime
DEI
Desflurane, Enflurane, Isoflurane
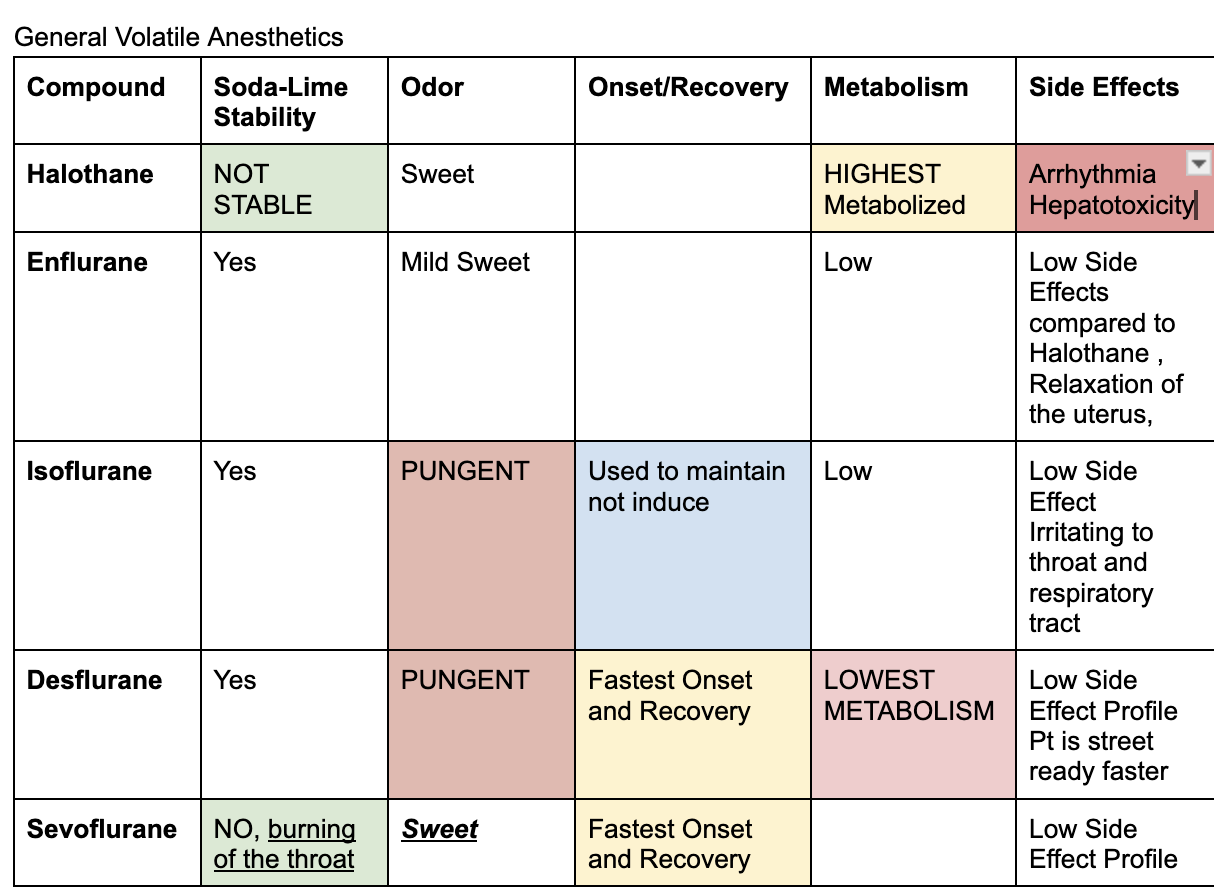
Highest metabolism
Halothane is high metabolized
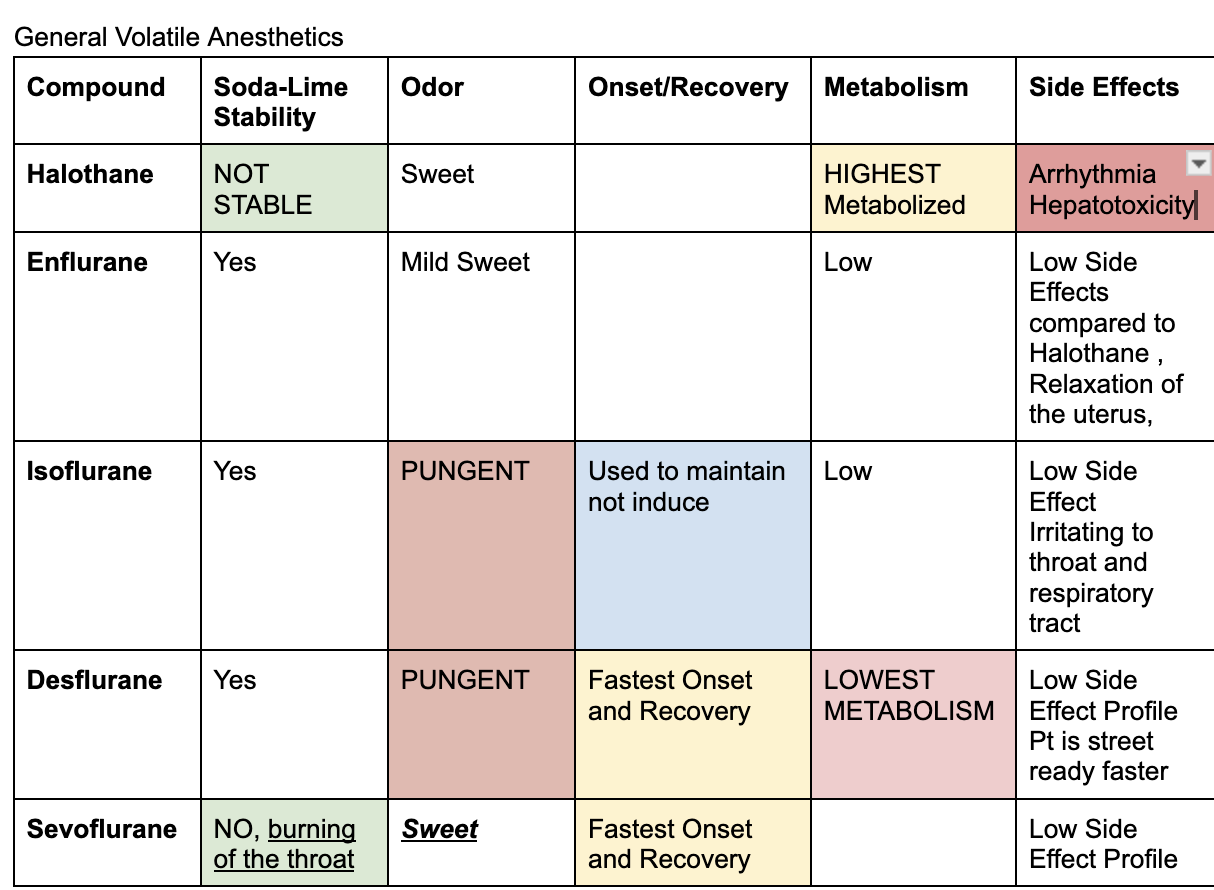
Lowest metabolism
Desflurane
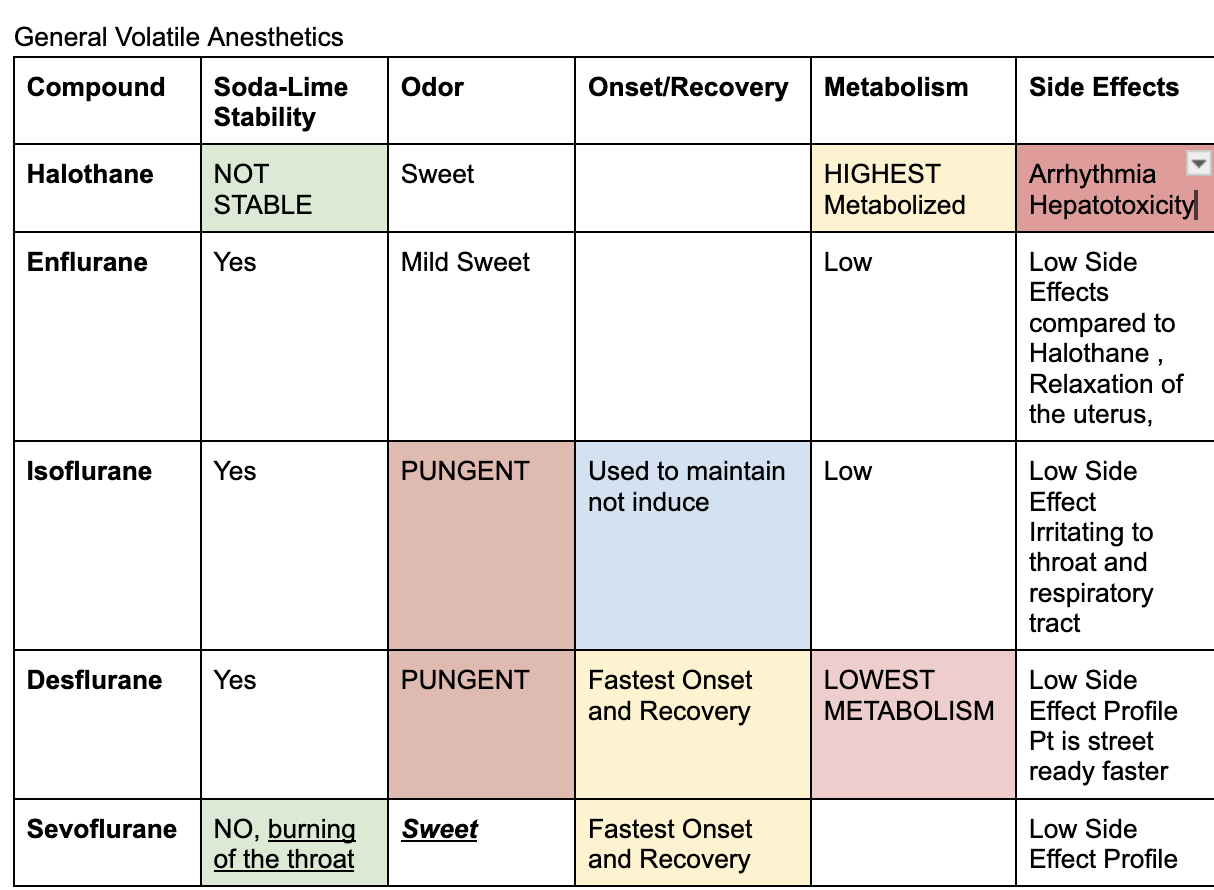
Fastest onset and recovery
between sevoflurane and desflurane (won’t give both as an answer choice)
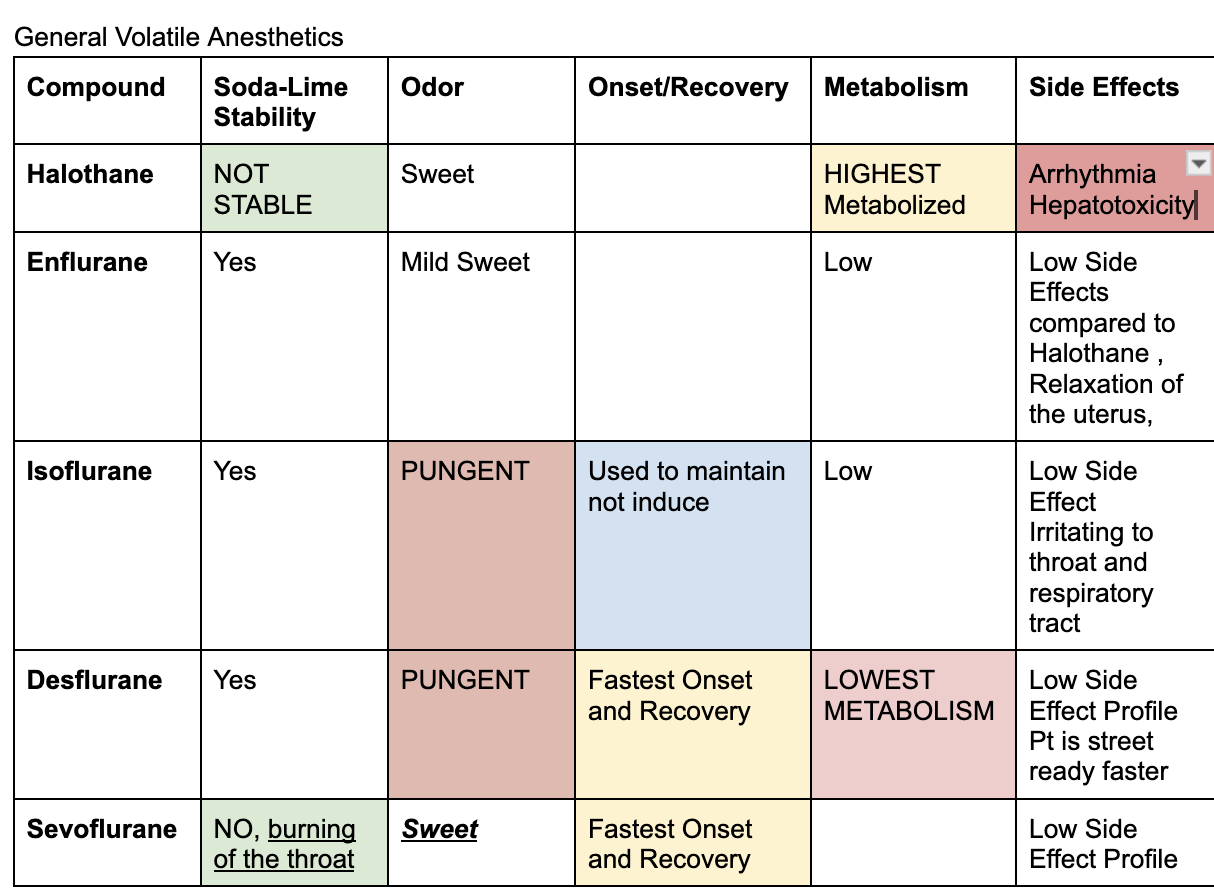
injectable general inhaled anesthetic
Etomidate, Procaine, Tetracaine, Dibucaine, Lidocaine, Mepivacaine, Prilocaine
mechanism for barbiturates
modulation of GABA receptor
bind to beta subunit to make GABA work better
propofol mechanism
interaction with GABA receptors increase GABA sensitivity
Cocaine
a2 blockage → CNS stimulation and increase of NE → vasoconstriction
ketamine
inhibits the NMDA receptor by binding to PCP binding site
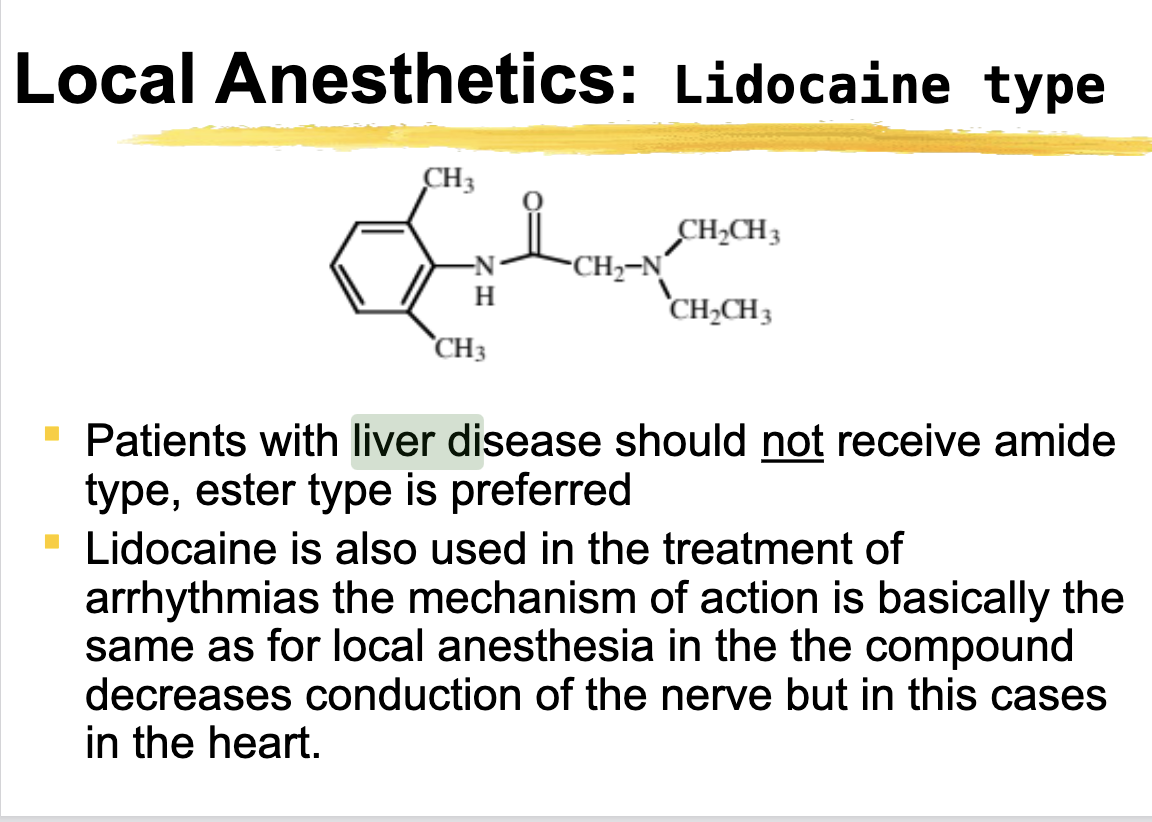
consideration for pts with liver disease
Should not receive Lidocaine (lidocaine = liver)
If Lidocaine is metabolized by the liver then WHY would you give it to someone with liver disease. Use a ester Benzoic acid or PABA type instead
Benzoic Acid types of local anesthesia
These are ester benzoic acid types
Cocaine
Hexylcaine
PABA ester type
benzocaine, procain, chloroprocaine, tetracaine
Lidocaine types
amide
Lidocaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine, bupivacaine
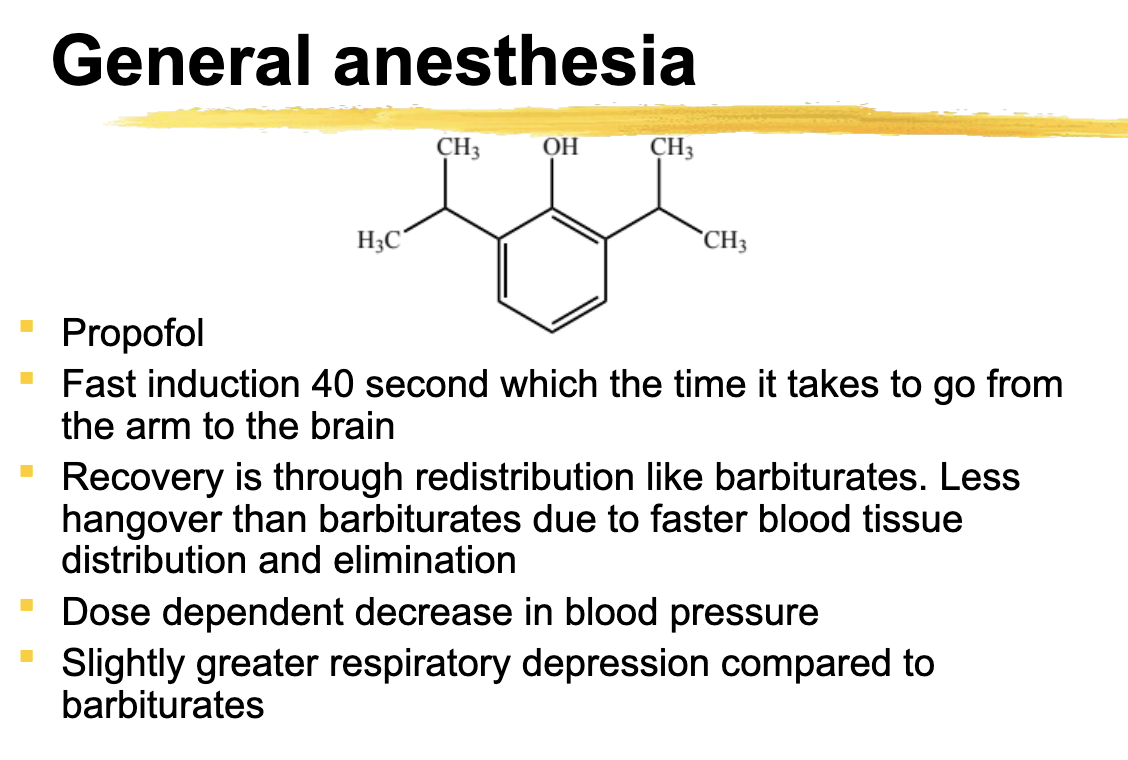
Propofol ADR
decrease BP, Greater respiratory depression compared to barbiturates
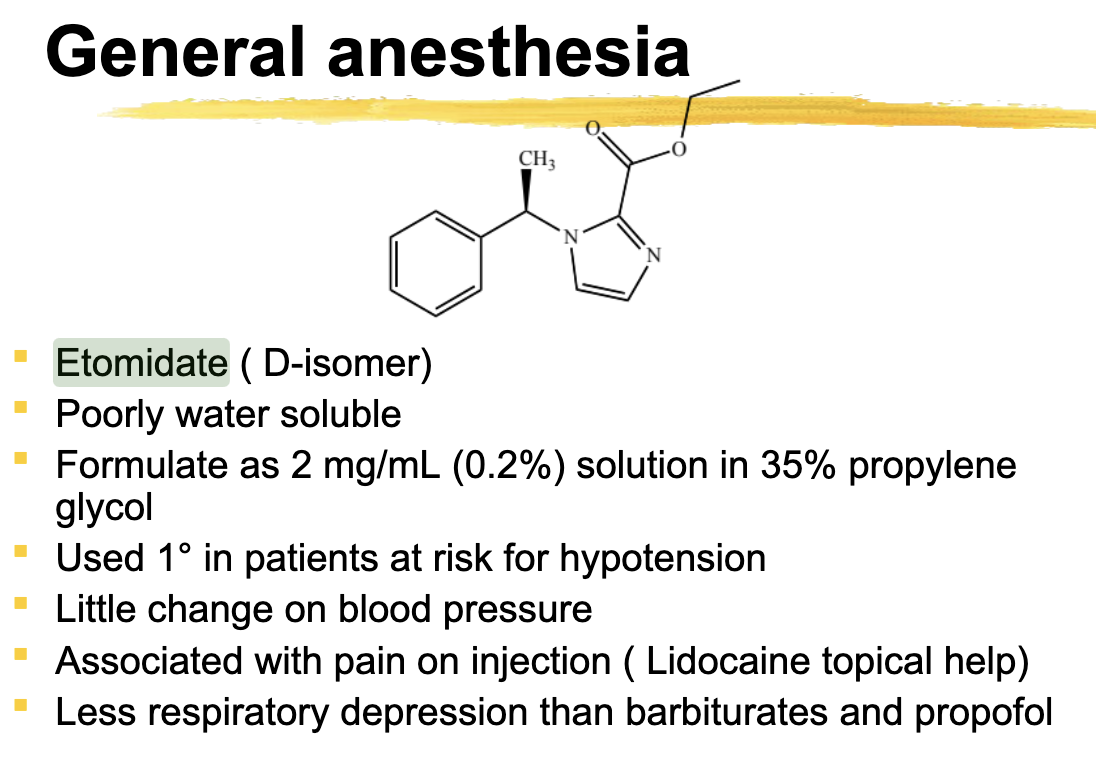
Etomidate ADR
Little change in blood pressure, less respiratory depression than barbiturates
Inhibits adrenal cortical stress response
Ketamine ADR
dissociative amnesia
Increase cerebral blood flow, increase IOP and intracranial pressure, increase BP and HR, potent bronchodilator (oddly less respiratory depression)
PABA type metabolism and inactivation
These are esters
Benzoic acid and PABA type decomposition takes place in esterases in the tissues
Lidocaine type metabolism and inactivation
Amides so
Metabolism takes place in the liver
if you have AchE deficiency…
Do not use Benzoic or PABA types (these are esters)
Use lidocaine instead
barbiturates examples
thiopental, thiamylal, methohexital
etomidate is good for pts with
at risk for hypotension
ketamine is good for
pts at risk for bronchospasms
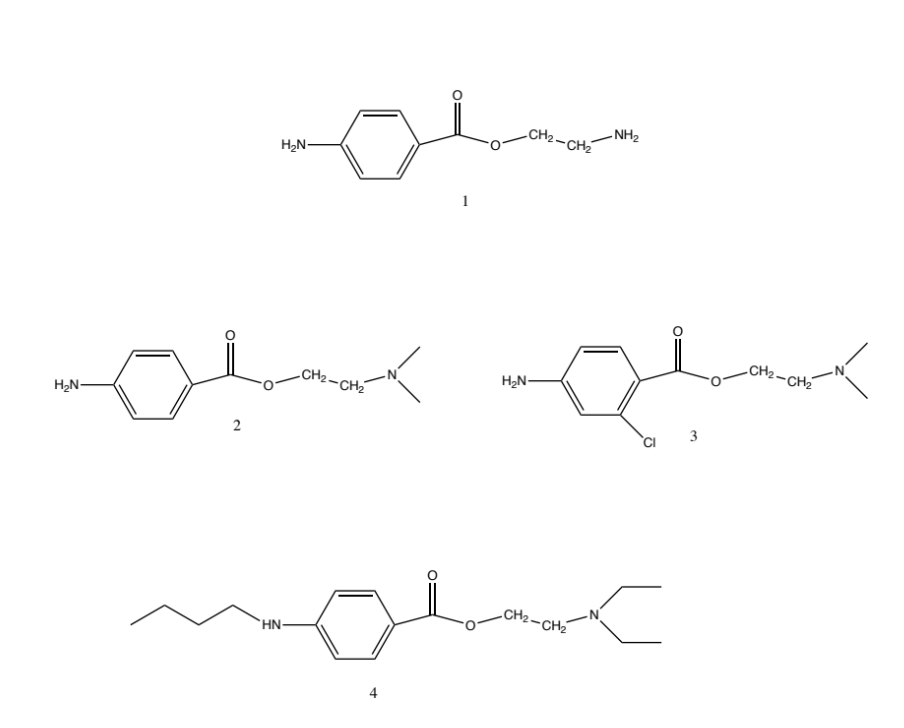
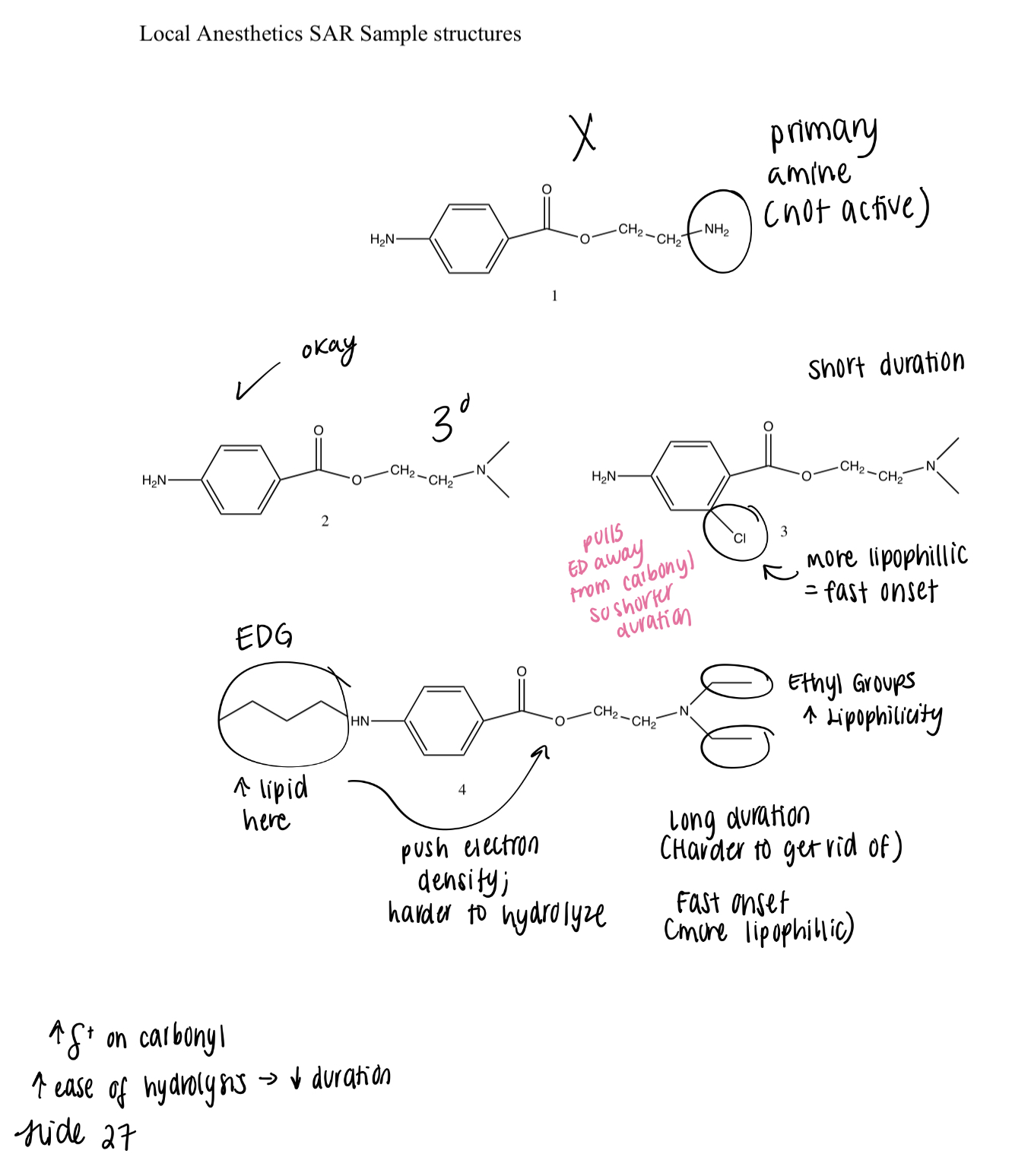
Is a primary amine -> NOT ACTIVE
Tertiary amine PABA type -> ACTIVE (just okay)
Has Chlorine -> Shorter duration due to C=O being more positive (more attractive to H2O and hydrolysis) but also MORE lipophilic -> fast onset
More Lipid due to ethyl groups and tail (Lipophilic -> fast onset) ; presence of EDG carbons on the left increases negative charge -> longer duration due to resistance to hydrolysis
general anesthesia includes
inhaled anesthetics (thanes) and propofol, etomidate, and ketamine
local anesthetics include
Benzoic Acid types, PABA, Lidocaine
adr of enflurane
relaxation of the uterus
adr of halothane
arrhythmia and hepatotoxicity