Alkyl Halides and Substitution – Part 1 (Lecture Notes)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards summarizing key terms and definitions from the lecture on alkyl halides, their classification, physical properties, and SN2 substitution chemistry.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
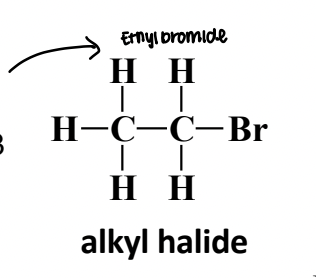
Alkyl Halide
An organic compound in which a halogen atom (F, Cl, Br, I) is directly bonded to an sp3-hybridized carbon.
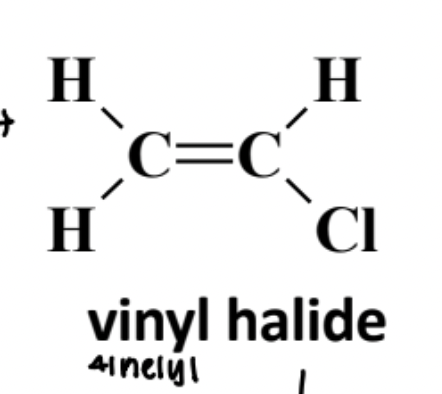
Vinyl Halide
A halogen-substituted alkene in which the halogen is bonded to an sp2 carbon of a C=C double bond; generally unreactive toward SN1/SN2 substitution.
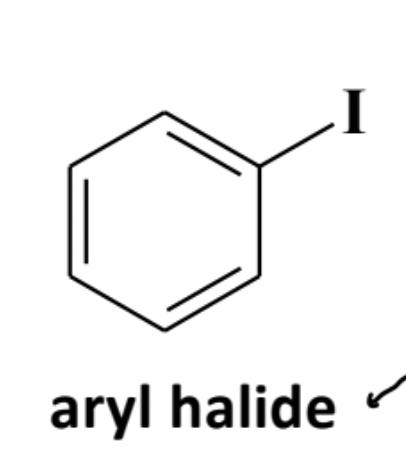
Aryl Halide
A compound where a halogen is attached to an sp2 carbon on an aromatic ring (e.g., chlorobenzene); also resistant to ordinary nucleophilic substitution.
Methyl Halide
An alkyl halide in which the halogen is attached to a CH3 group (e.g., CH3Cl).
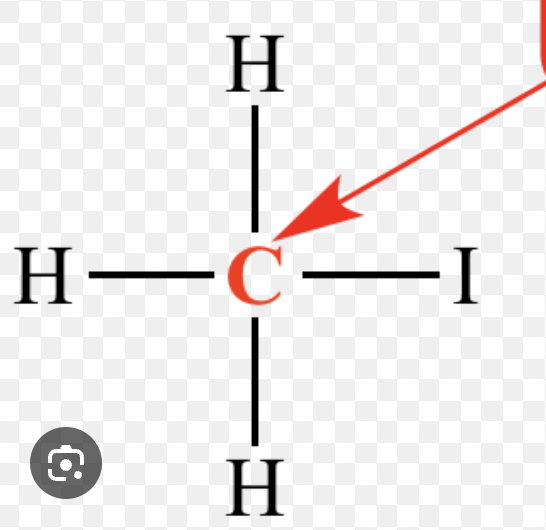
Primary Alkyl Halide (1°)
An alkyl halide whose carbon–halogen bearing carbon is attached to only one other carbon atom.
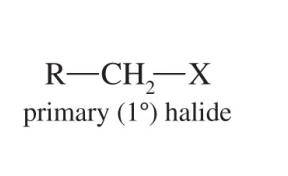
Secondary Alkyl Halide (2°)
An alkyl halide whose halogen-bearing carbon is attached to two other carbons.
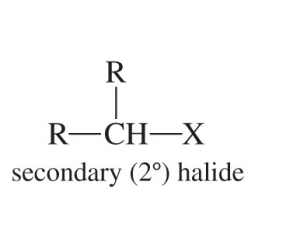
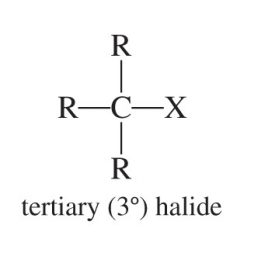
Tertiary Alkyl Halide (3°)
An alkyl halide whose halogen-bearing carbon is attached to three other carbons.
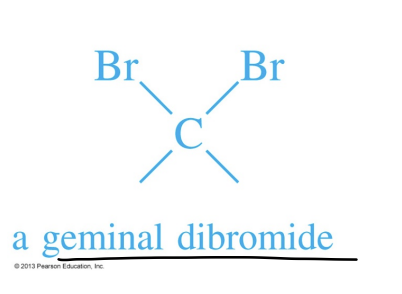
Geminal Dihalide
A molecule containing two halogens on the same carbon atom.
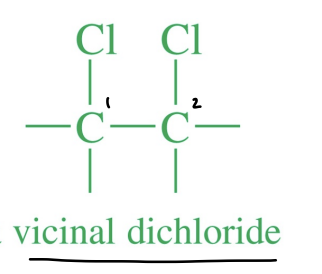
Vicinal Dihalide
A molecule containing halogens on two adjacent carbons.
Leaving Group
An atom or group that departs with an electron pair in a substitution or elimination; good leaving groups stabilize the negative charge (e.g., I⁻, Br⁻, Cl⁻).
Nucleophile
An electron-rich species that donates a pair of electrons to an electrophile; strength depends on charge, basicity, polarizability, and solvent.
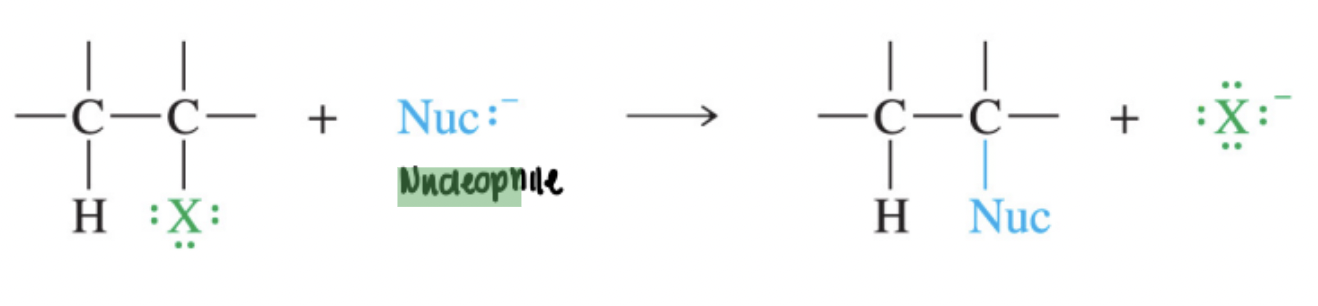
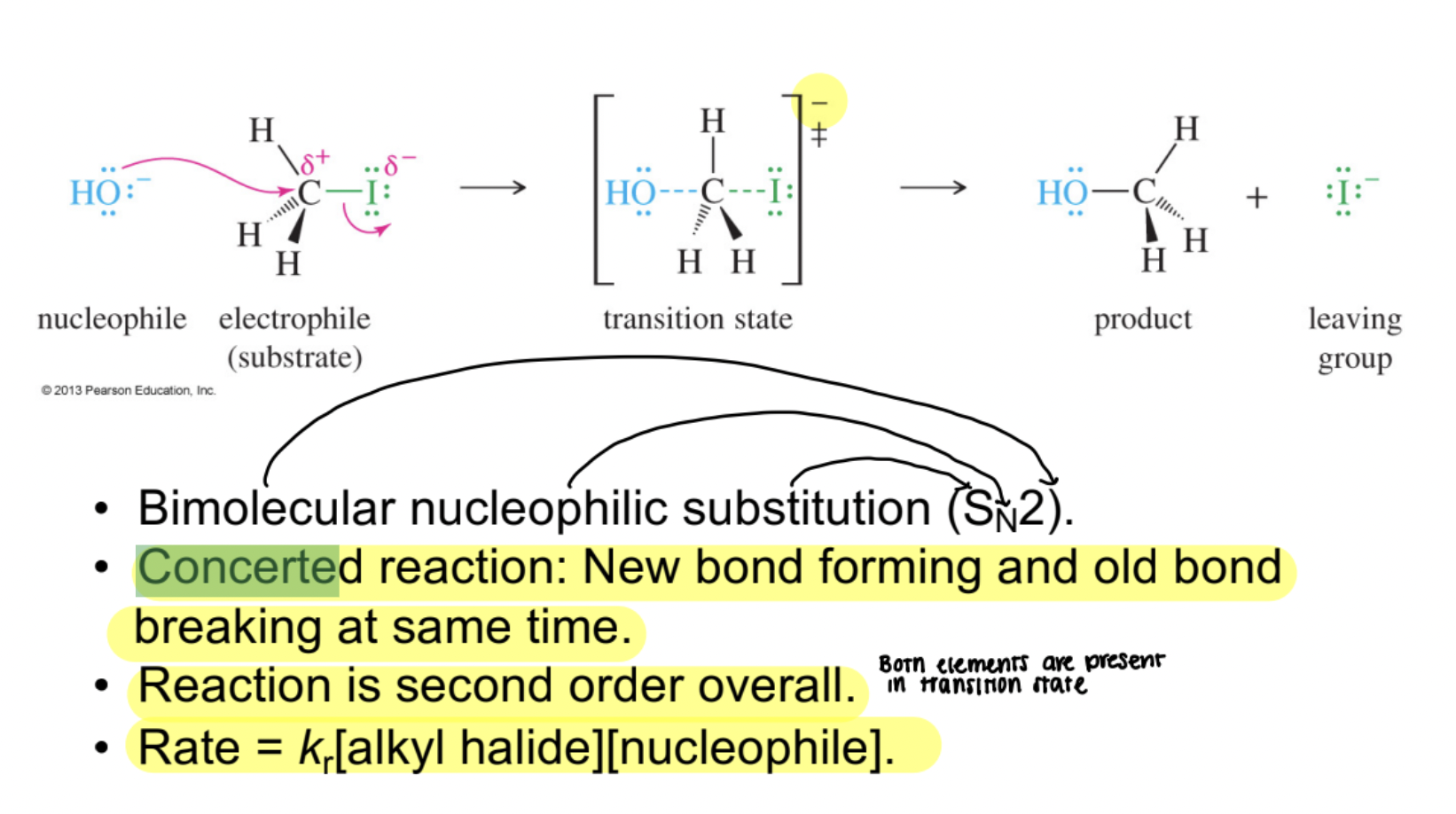
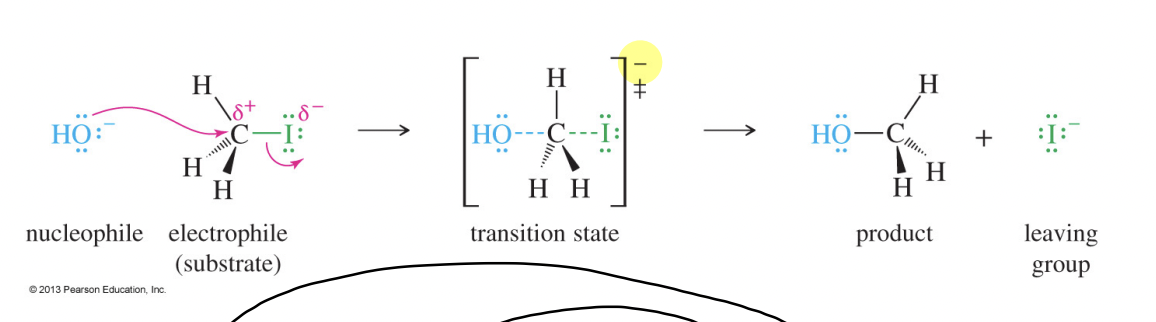
SN2 Reaction
A bimolecular nucleophilic substitution that occurs in a single concerted step with backside attack, second-order kinetics, and inversion of configuration.
SN2 Rate Law
Rate = k [alkyl halide] [nucleophile]; reaction speed depends on concentrations of both reactants.
Walden Inversion
The stereochemical outcome of an SN2 reaction in which the configuration at the stereocenter is inverted (R ↔ S).
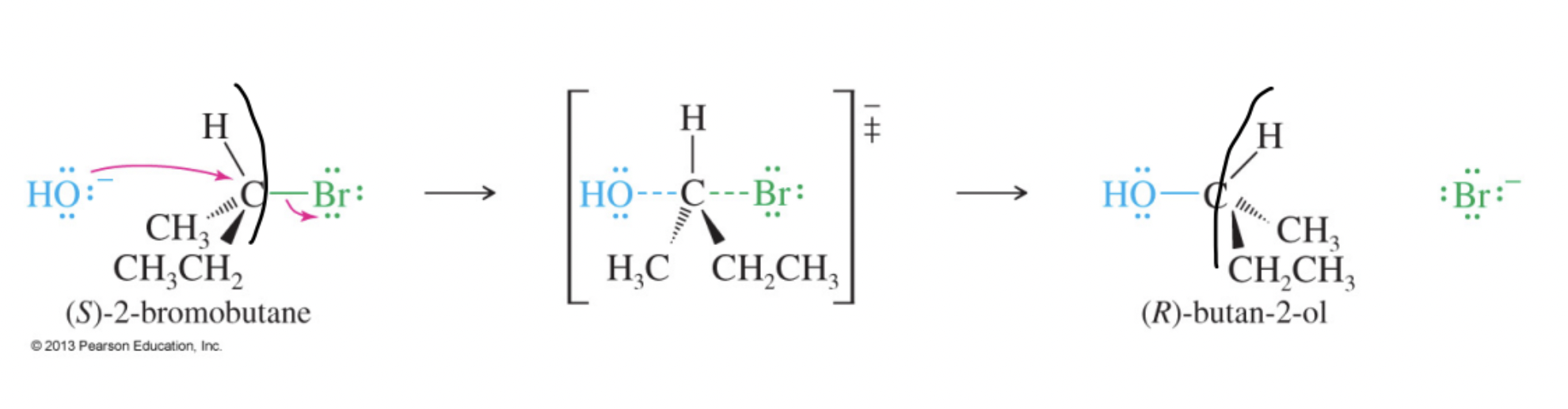
Back-Side Attack
Approach of the nucleophile opposite the leaving group in an SN2 reaction, directed toward the σ*-antibonding orbital of C–X.
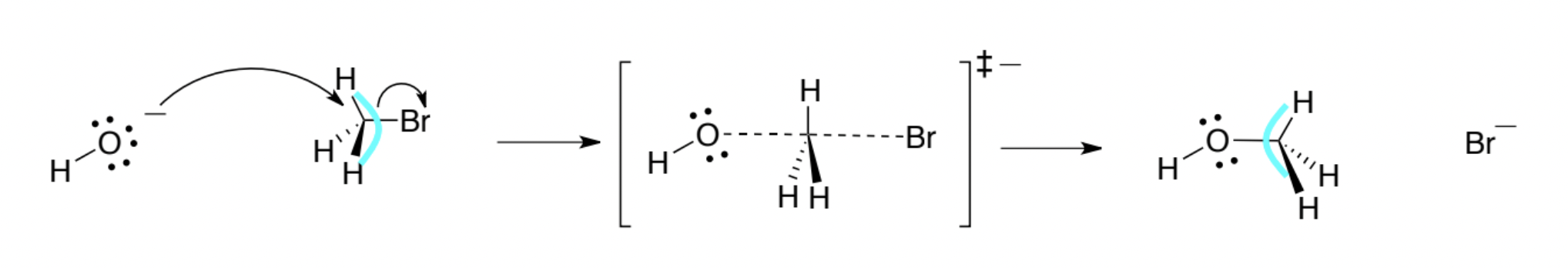
SN1 Reaction
A unimolecular nucleophilic substitution proceeding through a carbocation intermediate; rate depends only on alkyl halide concentration.
Reaction Coordinate Diagram
A plot of energy vs. reaction progress depicting reactants, transition state(s), intermediates, and products for SN1/SN2 mechanisms.
Free-Radical Halogenation
Chain reaction (initiation, propagation, termination) that installs a halogen on alkanes; Cl₂ is unselective, Br₂ is highly selective for tertiary > secondary > primary C–H bonds.
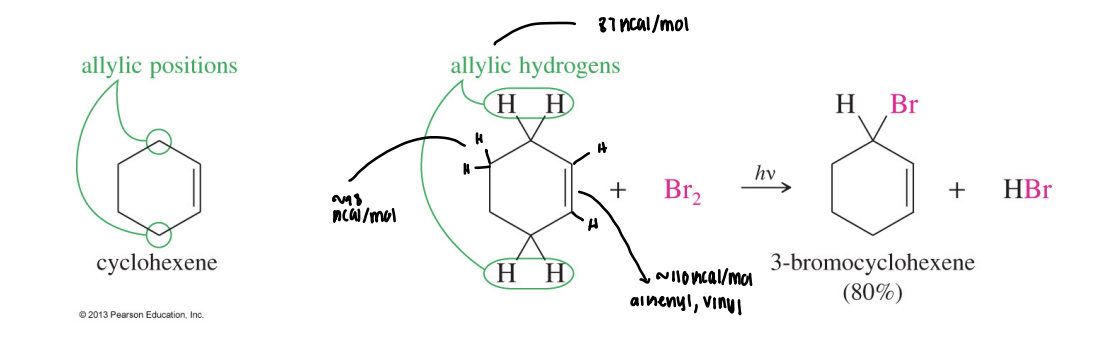
Allylic Bromination
Selective radical substitution at the carbon adjacent to a C=C bond, favored because the allylic radical is resonance-stabilized.
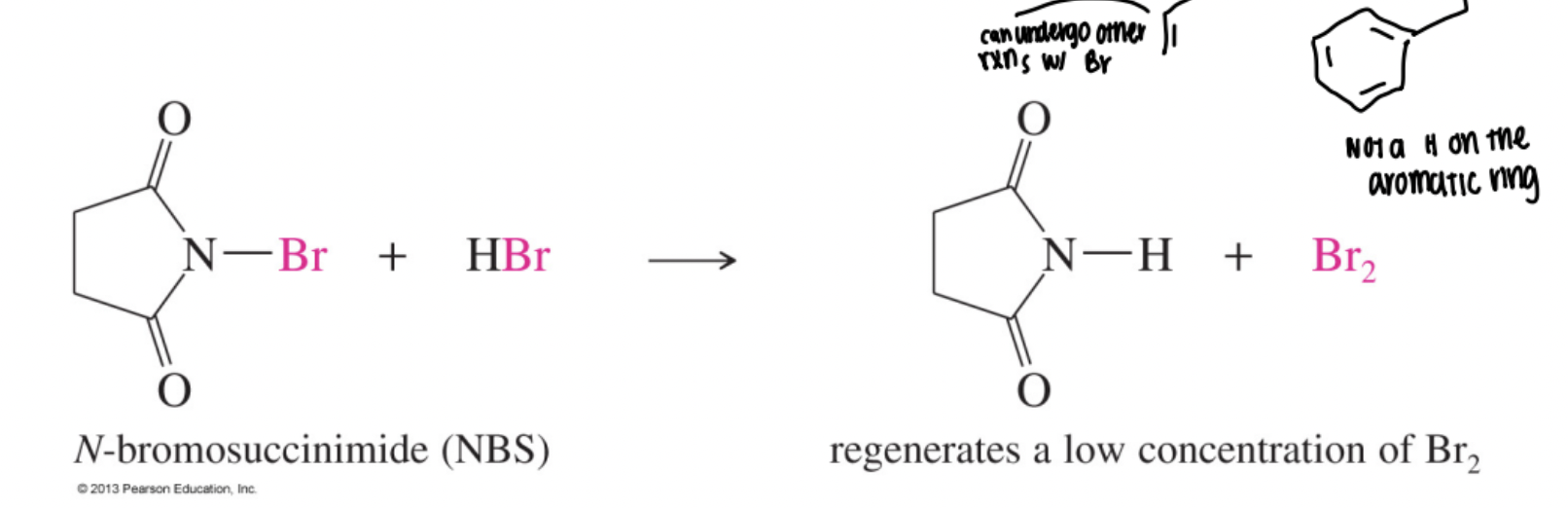
N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS)
A solid reagent that generates low, steady concentrations of Br₂ to achieve selective allylic (or benzylic) bromination without competing alkene addition.
Polarizability
The ease with which an electron cloud is distorted; larger, more polarizable atoms (I⁻, Br⁻) are typically better nucleophiles in protic solvents.
Dipole Moment (μ)
A measure of bond polarity; for C–X bonds, magnitude follows C–Cl > C–F > C–Br > C–I, though molecular dipole depends on geometry.
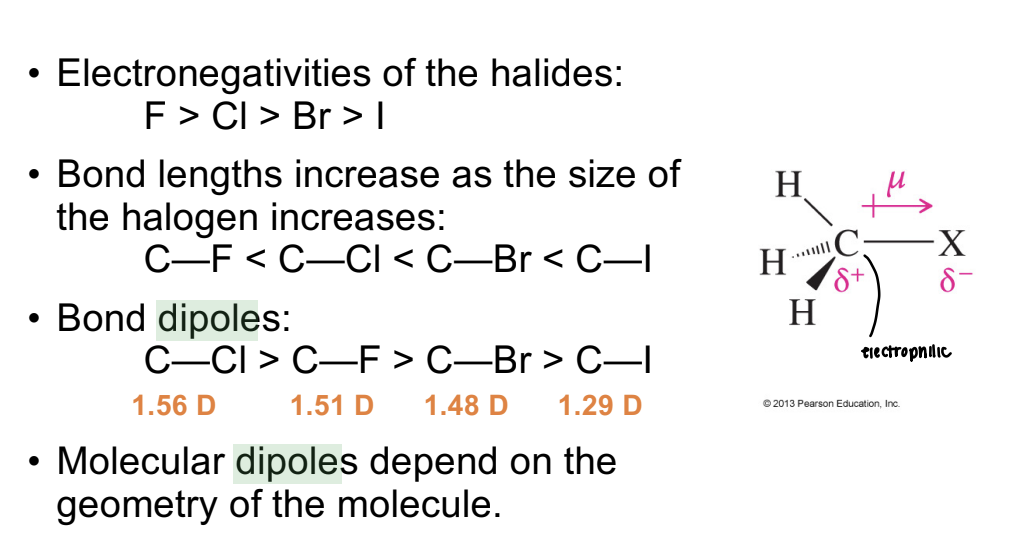
London Dispersion Forces
Weak intermolecular attractions that increase with molecular surface area and atomic size, raising boiling points of heavier alkyl halides.
Freons
Chlorofluorocarbons once used as refrigerants and foaming agents; environmentally harmful because they deplete stratospheric ozone.
Concerted Reaction
A process in which bond breaking and bond forming occur in the same elementary step, as in the SN2 mechanism.