microbio- mycotoxins
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
no
do all fungi produce mycotoxins?
crops or stored feed
mycotoxins are produced by some fungi in ______
yes
are mycotoxins heat stable?
immunosuppression, carcinogenesis, teratogenesis
what are the main effects produced by all mycotoxins?
no
are diseases caused by mycotoxins contagious?
FALSE- mycotoxic diseases are not contagious, and can only be transmitted by ingestion of mycotoxins
true or false: mycotoxic diseases are highly contagious and can be transmitted via direct contact or inhalation of spores
aflatoxins (main aflatoxin is Aflatoxin B1)
aflatoxicosis is the disease produced by ingestion of what mycotoxin?
Aspergillus flavus
aflatoxins come from what fungal species?
mammals, birds, and aquatic species. but it is more severe in birds
aflatoxicosis is a disease that affects what animals?
rice, corn, wheat, oats, barley, nuts
where do toxic strains of Aspergillus flavus with aflatoxins grow?
they are absorbed in the digestive system and metabolized by the liver
when an animal ingests aflatoxins, where do they go in the body?
hepatocellular necrosis and impaired liver function
because aflatoxins are absorbed by the liver upon ingestion, what effects does it mainly have?
causes aplasia of the thymic cortex
what is the immunosuppressive affect that aflatoxins have on the animal?
the duck has acute aflatoxicosis from ingesting the fungi Aspergillus flavus that contained aflatoxins
a farmer brings in a duckling on his farm that he noticed was experiencing ataxia, opisthotonos (muscle spasms), and then suddenly died. the vet does a necropsy and observes aplasia of the thymic cortex and necrosis of the liver. the farmer says that the corn that the animals have been eating does look a little moldy, so he brings in one for examination. the vet isolates some cells from the corn on SDA at 37 degrees and observes the colony and the phialoconidia that has grown. what is the diagnosis (disease+fungal species+mycotoxin)?
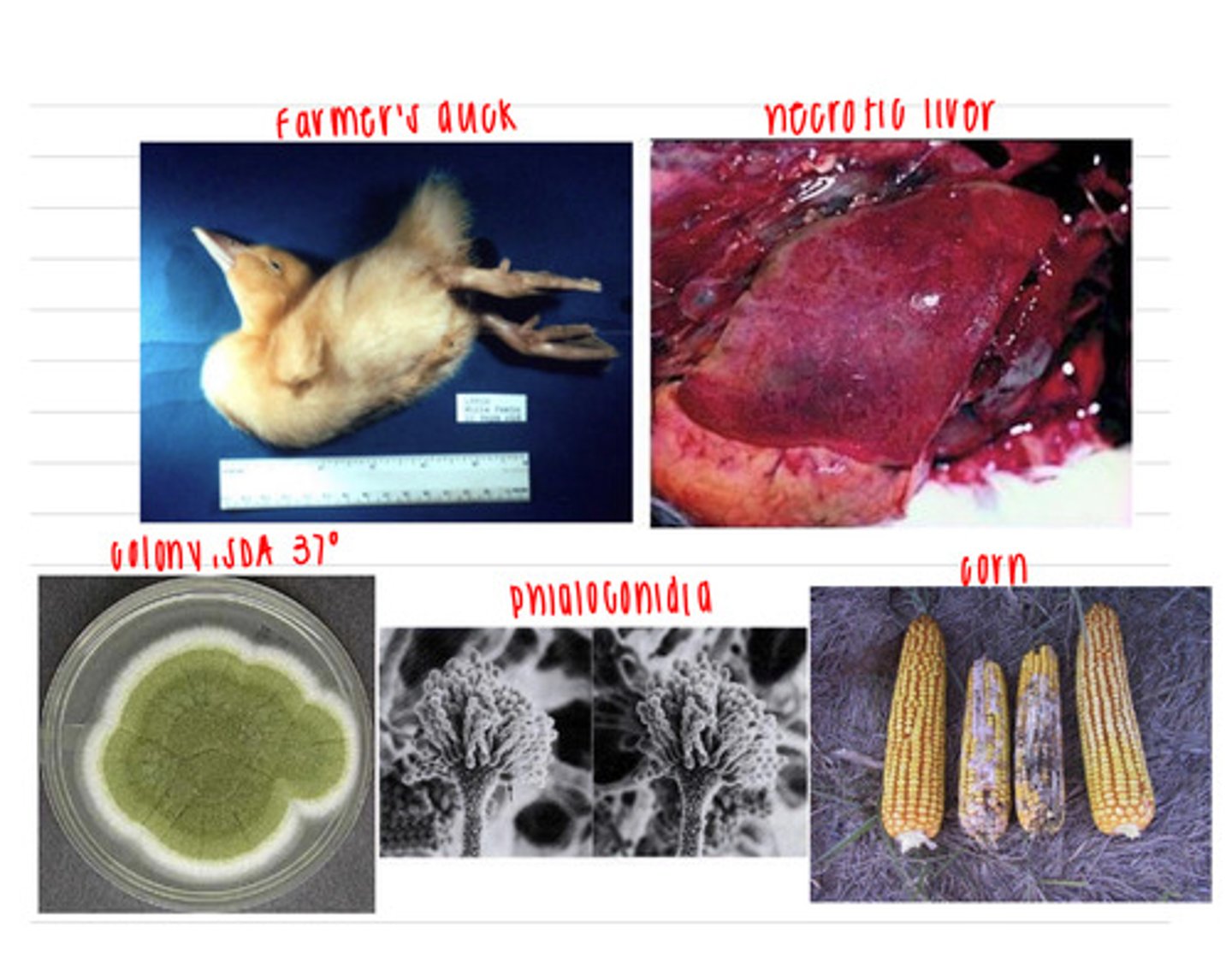
ataxia, opisthotonos (muscle spasms), and sudden death
what clinical signs are common in animals with acute aflatoxicosis?
the liver
what organ is mainly affected by aflatoxins?
aflatoxicosis OR tremorgenic mycotoxicosis
which disease is contracted by eating crops contaminated with Aspergillus flavus?
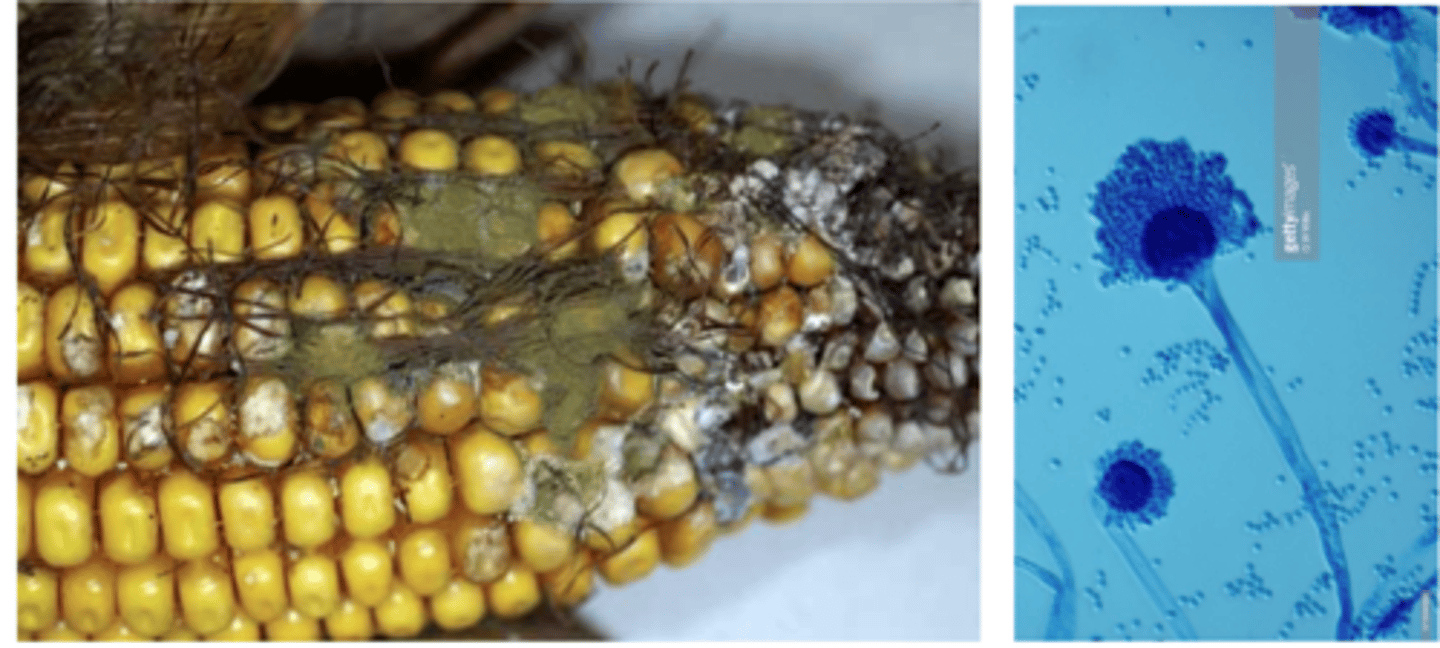

aflatoxin B1
a vet does a necropsy on a dog and removes the liver. if we know the dog had eaten some fungus infected crops, what can we guess was the mycotoxin that he was infected with?
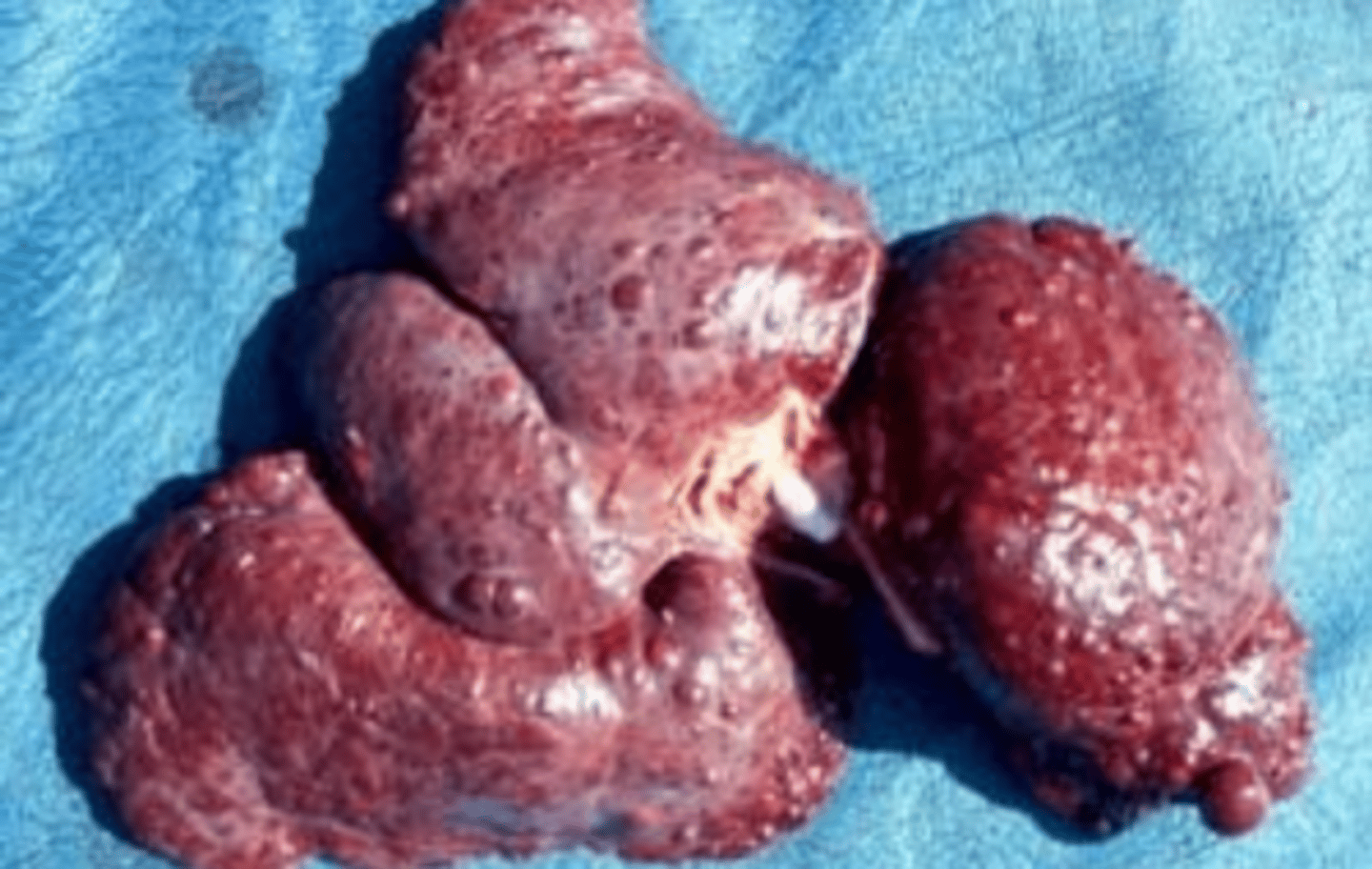
1. mycotoxic/equine leukoencephalomalacia
2. porcine pulmonary edema
Fumonisin toxicosis is a mycotoxicosis caused by the ingestion of the myotoxin fumonisin. 2 different diseases can be caused, depending on the animal it infects. what are the diseases?
Fusarium verticillioides
what fungal species causes fumonisin toxicosis?
equines- horses, donkeys, mules
mycotoxic leukoencephalomalacia is a type of fumonisin toxicosis that affects what animals?
mycotoxic leukoencephalomalacia
what disease is caused in equines when they ingest toxic Fusarium verticillioides?
neurological-
-inability to swallow
-weakness
-staggering
-circling
-depression
an equine with mycotoxic leukoencephalomalacia experiences what clinical symptoms?
liquefactive necrosis of the white matter of the cerebrum
when an equine ingests Fusarium verticillioides with the mycotoxin fumonisin, what is the affect in its body?
fumonisin
what mycotoxin causes liquefactive necrosis of the white matter of the cerebrum in equines?
the horse had mycotoxic leukoencephalomalacia (also known as equine encephalomalacia- ECEM) because it ate corn that had the fungal species Fusarium verticillioides, containing mycotoxin fumonisin
a man is concerned about his horse because it has been depressed, circling, weak, staggering, and cannot swallow his food. unfortunately, the horse dies before the vet can treat it, but the vet does a necropsy and finds areas of grey-brown malacia in the brain. he takes a sample and histologically observes liquefactive necrosis, congestion, and hemorrhages in the white matter of the cerebrum. what is the diagnosis? what is the probable cause?
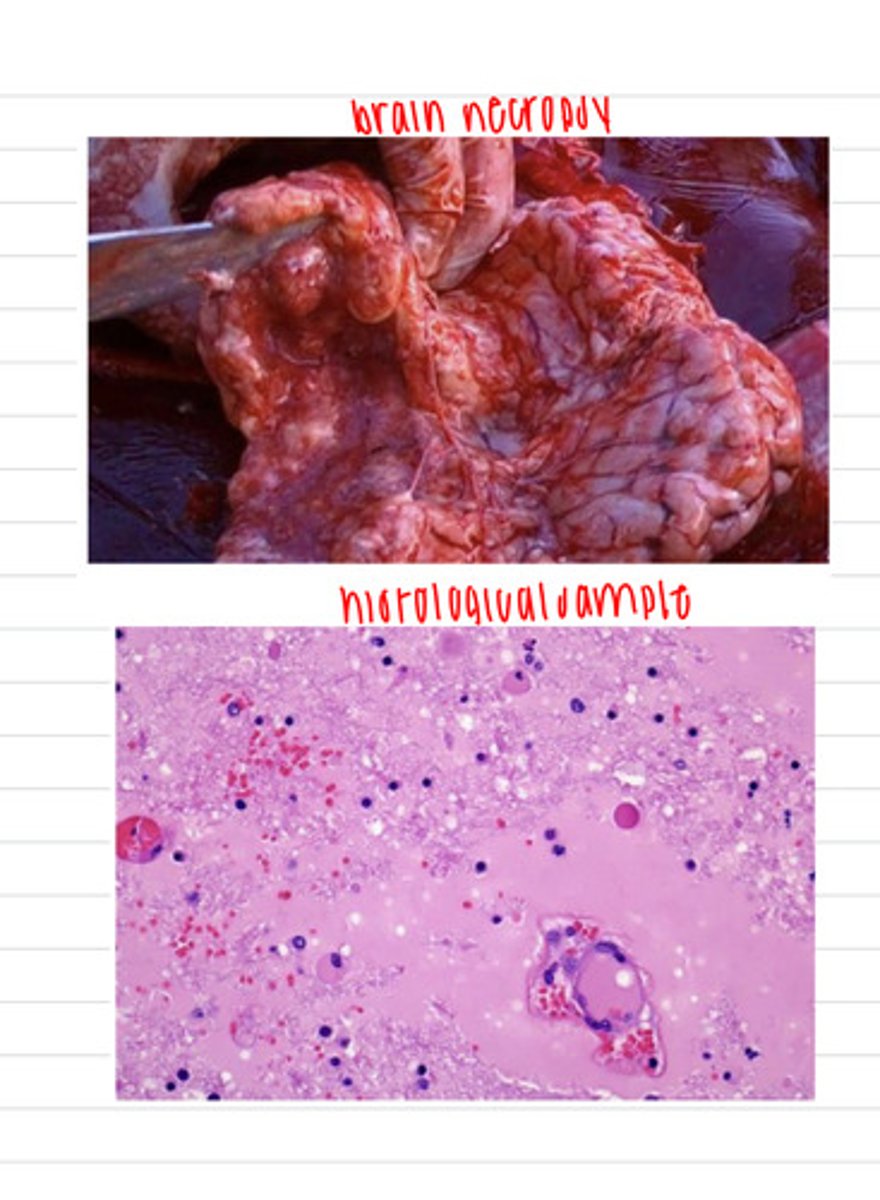
eating moldy corn (with Fusarium verticillioides)
how can an animal contract fumonisin toxicosis?
porcine pulmonary edema (PPE)
what disease do pigs get when they ingest Fusarium verticillioides with the mycotoxin fumonisin?
Fusarium verticillioides, mycotoxin fumonisin
what fungal species and mycotoxin causes porcine pulmonary edema?
-pulmonary hypertension
-fluid in the thorax (hydrothorax)
-interstitial pulmonary edema
=disease porcine pulmonary edema
what are the effects of a pig eating corn with Fusarium verticillioides and the mycotoxin fumonisin on the body?
-acute dyspnea
-cyanotic mucous membranes
-weakness
-recumbency- laying down
-abortion
-death within 24 hours of first symptom
what are the clinical signs of a pig with porcine pulmonary edema?
the disease is porcine pulmonary edema, which the pig contracted when it ate corn that had the fungal species Fusarium verticillioides growing on it. the mycotoxin is fumonisin.
a farmer brings in one of his pigs that has died. he says that the day before his death, he noticed the pig started to have trouble breathing, was weak, her mouth was turning blue, and she didn't want to stand up. the vet suspects a certain disease so takes out the pig's lungs to observe them and confirm his diagnosis because he sees interstitial pulmonary edema. what disease did this pig have, and what was the cause?
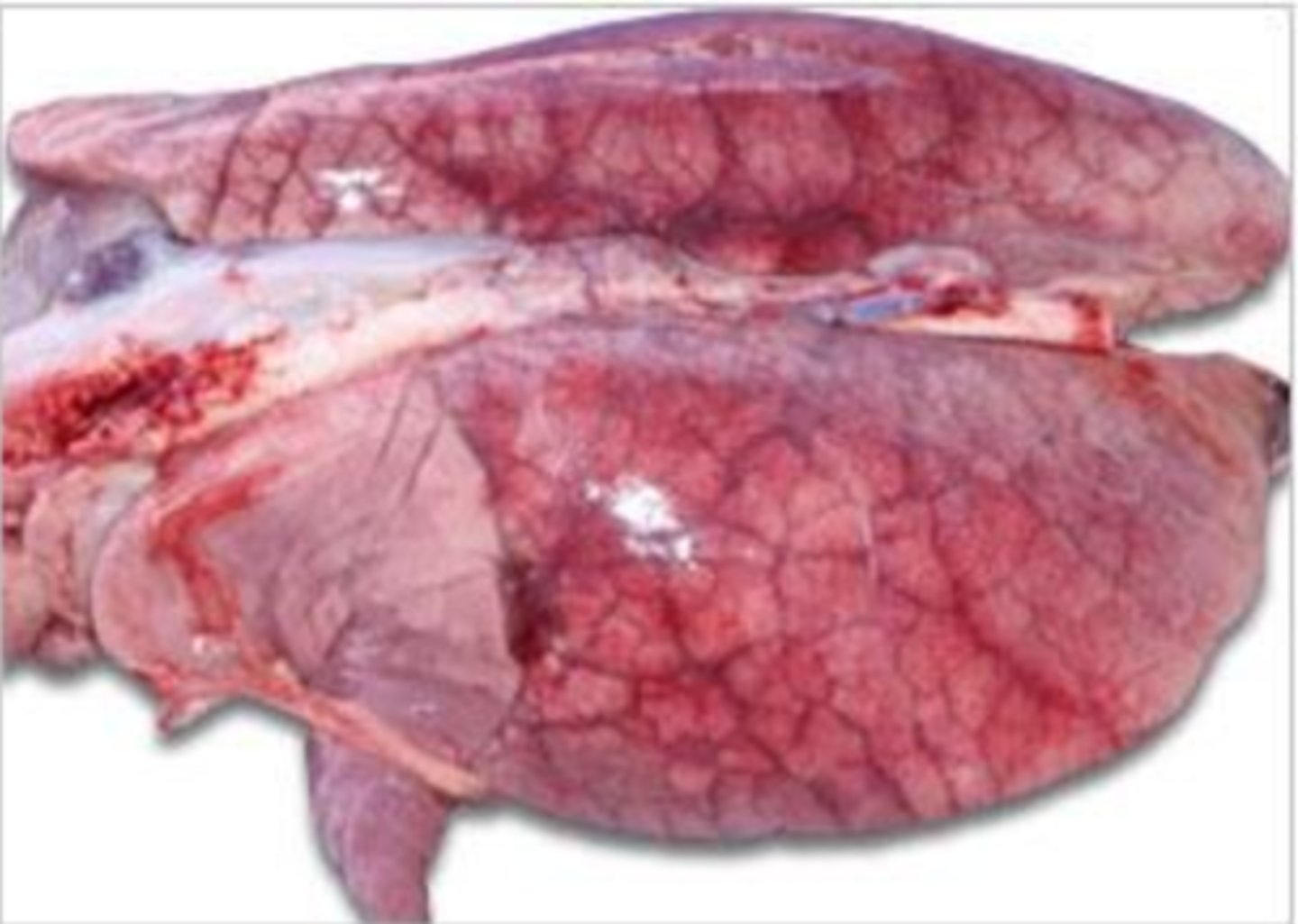
porcine pulmonary edema
when a pig ingests toxic Fusarium verticillioides, what type of fumonisin toxicosis does it get?
Equine Mycotoxic Leukoencephalomalacia
when a horse ingests toxic Fusarium verticillioides, what type of fumonisin toxicosis does it get?
domestic animals and humans
what animals can get the disease ergotism?
ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine
the ingestion of what mycotoxin causes ergotism?
Claviceps purpurea
what fungal species produces the mycotoxin ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine that causes ergotism?
ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine
Claviceps purpurea is a fungal species that grows in seeds and produces what mycotoxin?
seeds of rye grasses, rye, and barley
where does Claviceps purpurea grow and produce ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine?
-stimulation of adrenergic nerves that supply arteriolar smooth muscle
-inhibition of prolactin secretion
what are the 2 physiological effects on the body of the mycotoxin ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine?
convulsive ergotism-
-staggering
-convulsive episodes
-drowsiness
if an animal is exposed to a HIGH amount of the mycotoxin ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine, what are its clinical signs?
-persistent arteriolar constriction
-endothelial damage
-thrombosis
-ischemia (causing gangrene)
-swelling
-redness of extremities
if an animal is exposed to a LOW amount of the mycotoxin ergopeptide alkaloids/ergotamine over a long period of time, what are its clinical signs?
ergotamine/ergopeptide alkaloids
which mycotoxin produced by Claviceps purpurea grows in seeds?
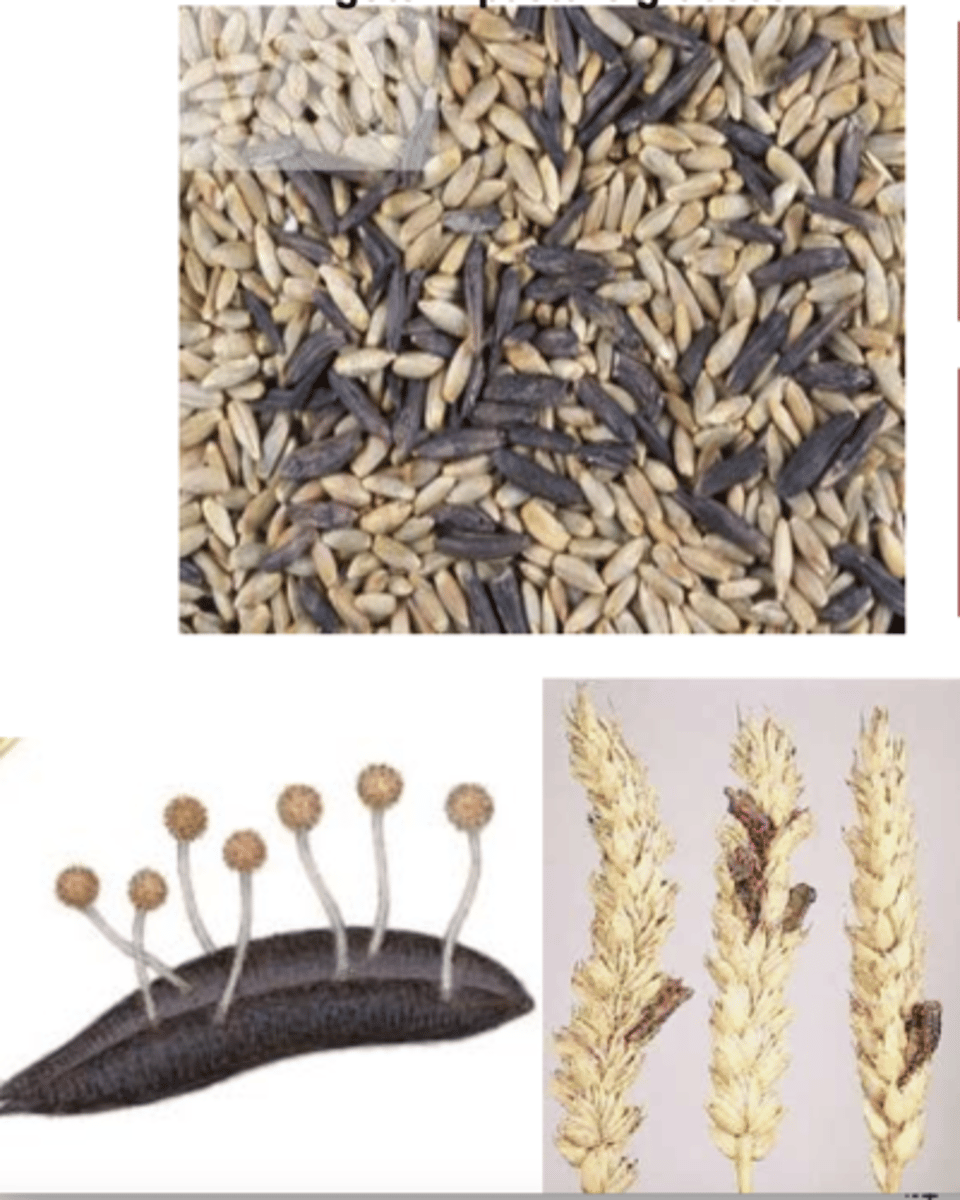

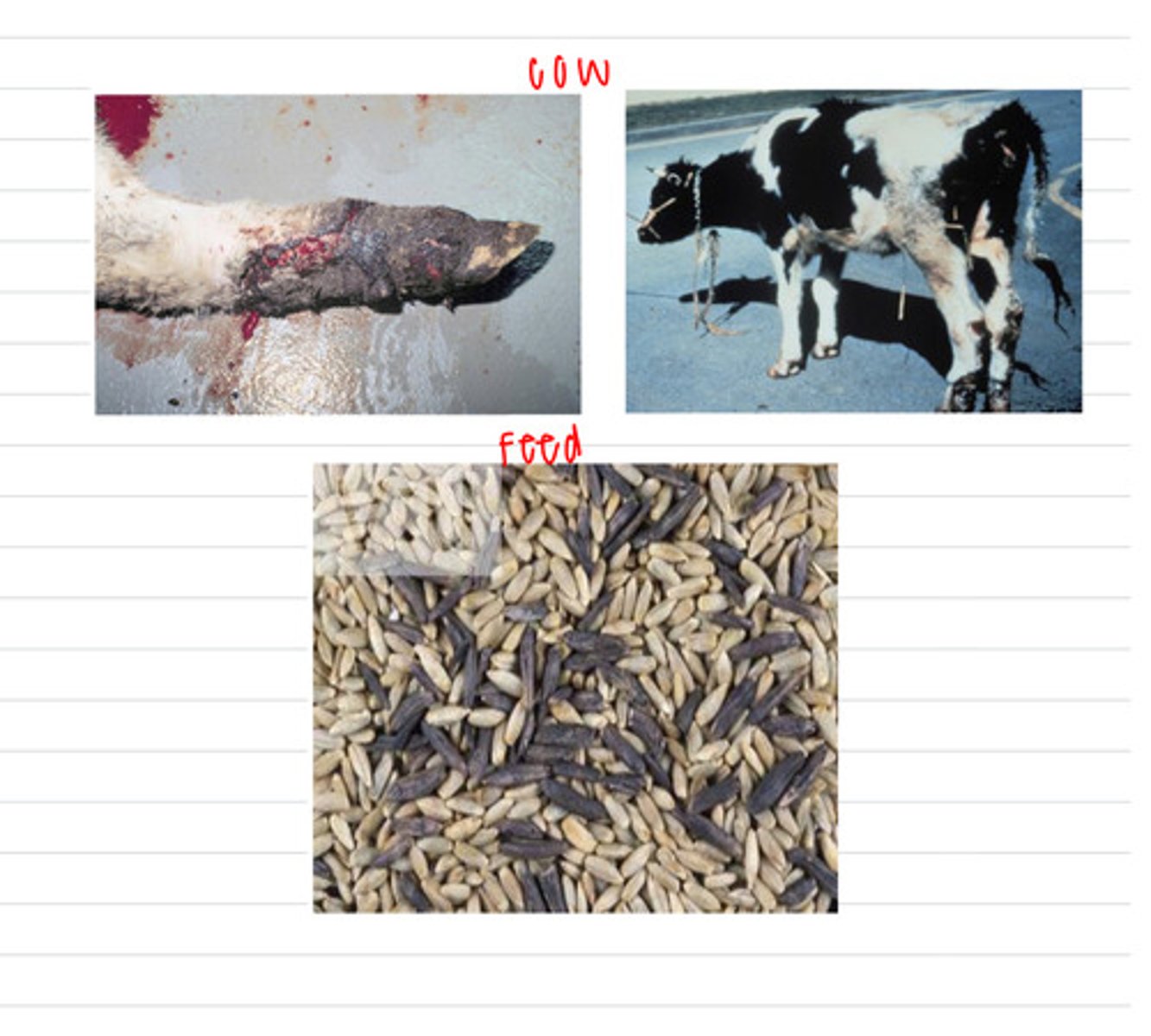
the cow has been eating seeds that have the fungus Claviceps purpurea growing inside, so it was infected by small amounts of the mycotoxin ergotamine/ergopeptide alkaloids. it has ergotism.
a cow comes to the vet with red, swollen, gangrene on its extremities. the farmer says it has been eating this feed:
what is the diagnosis?

the dog ate seeds with the fungus Claviceps purpurea, which produces the mycotoxin ergotamine/ergopeptide alkaloids. the dog has ergotism.
a woman went on a walk with her dog, where it ate a large amount of black rye seeds. shortly after, the dog started staggering and having convulsive episodes. what can we assume is the diagnosis?
ergotamine (produced by the fungus Claviceps purpurea)
which mycotoxin stimulates adrenergic nerves that supply smooth muscle and also inhibits prolactin secretion?
facial eczema
the mycotoxin sporidesmin produced by the fungus Pithomyces chartarum causes what disease?
it accumulates in the bile, causing necrosis, atrophy, and fibrosis of the liver and gallbladder. it also has a compound called phylloerythrin that is photodynamic, so the sun triggers lesions on the face: facial eczema.
describe the mechanism of the mycotoxin sporidesmin.
disease: facial eczema
fungus: Pithomyces chartarum
mycotoxin: sporidesmin
what disease do these animals have? what mycotoxin and fungal species causes it?
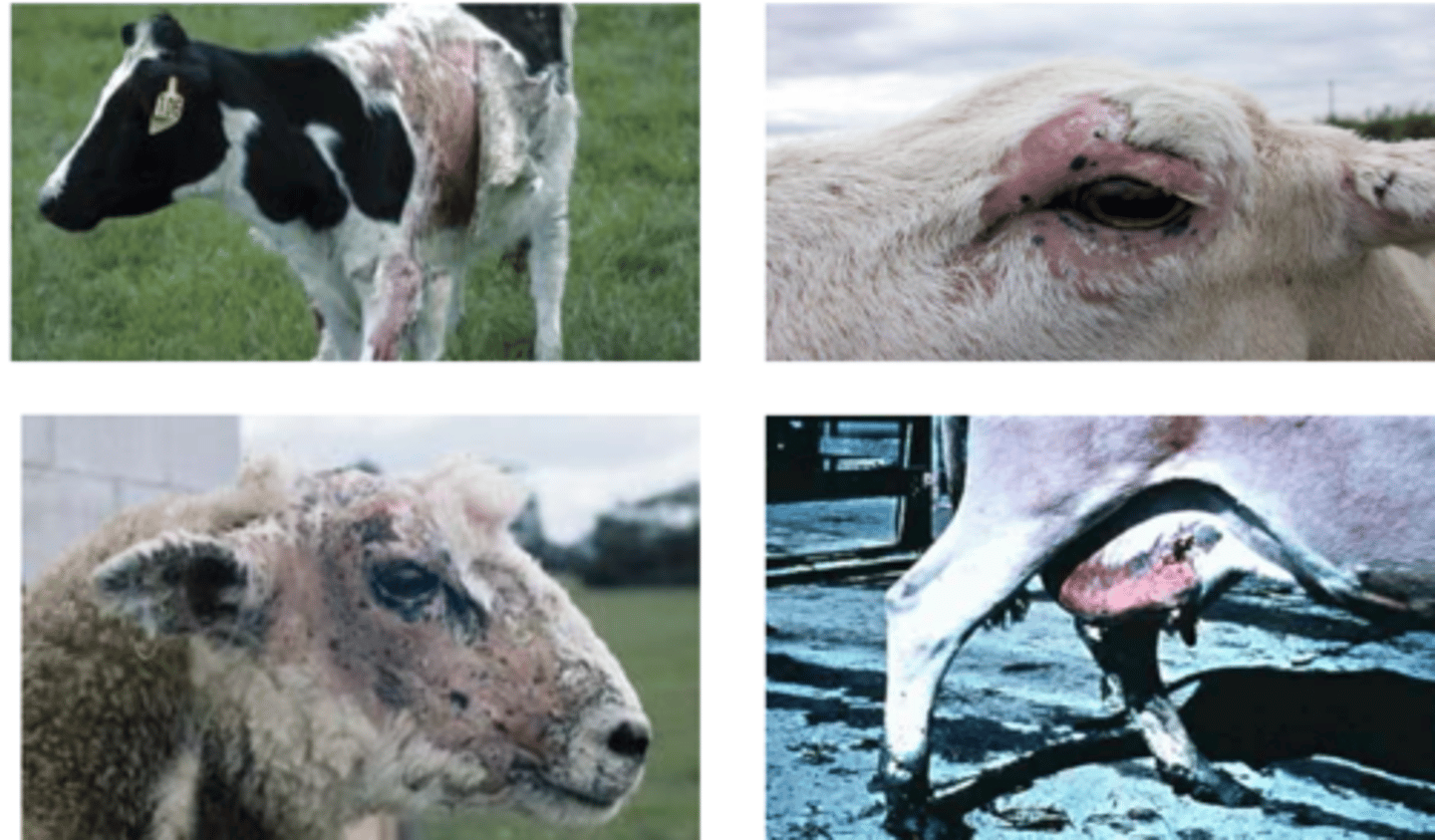

sporidesmin (produced by Pithomyces chartarum)
which mycotoxin has the photodynamic compound phylloerythrin?
ochratoxins, Aspergillus ochraceus and Penicillium vivridicatum
ochratoxicosis is a disease caused by the mycotoxin _________, which is produced by the fungus __________.
kidney
what is the target organ of ochratoxins?
on cereal grains- barley, oats, rye, wheat, corn
where do ochratoxin-producing Aspergillus ochraceus and Penicillium vivridicatum grow?
ochratoxicosis
which disease is nephratoxic?
-inappetence
-weight loss
-polydipsia and polyuria
what are the signs of a pig that has been infected with ochratoxins produced by Aspergillus ochraceus and Penicillium vivridicatum?
pigs and poultry
ochratoxicosis affects what 2 species?
-renal disease
-hepatic damage
-immunosuppression
-decreased growth rate, egg production, and egg quality
a chicken that ingests ochratoxins has these problems:
disease: ochratoxicosis
fungus: Aspergillus ochraceus and Penicillium vivridicatum
toxin: ochratoxins
a farmer notices his pig has lost his appetite, so he has lost lots of weight, and is also drinking and peeing a lot more than normal. what fungal species and mycotoxin probably caused this?
zearalenone
what toxin causes mycotoxic oestrogenism?
Fusarium graminearum
what fungus produces the mycotoxin zearalenone?
wheat
where does the fungus Fusarium graminearum grow, where it produces the mycotoxin zearalenone?
it gets the disease mycotoxic oestrogenism which causes prepubertral gilts:
-vulva edema
-hyperemia
-hypertrophy of mammary glands and uterus
-vaginal and rectal prolapse
what are the effects if a farm animal ingests zearalenone?
wheat with the fungus Fusarium graminearum, which produces the mycotoxin zealarenone, which causes the disease mycotoxic oestrogenism.
these pigs have most likely ingested what?
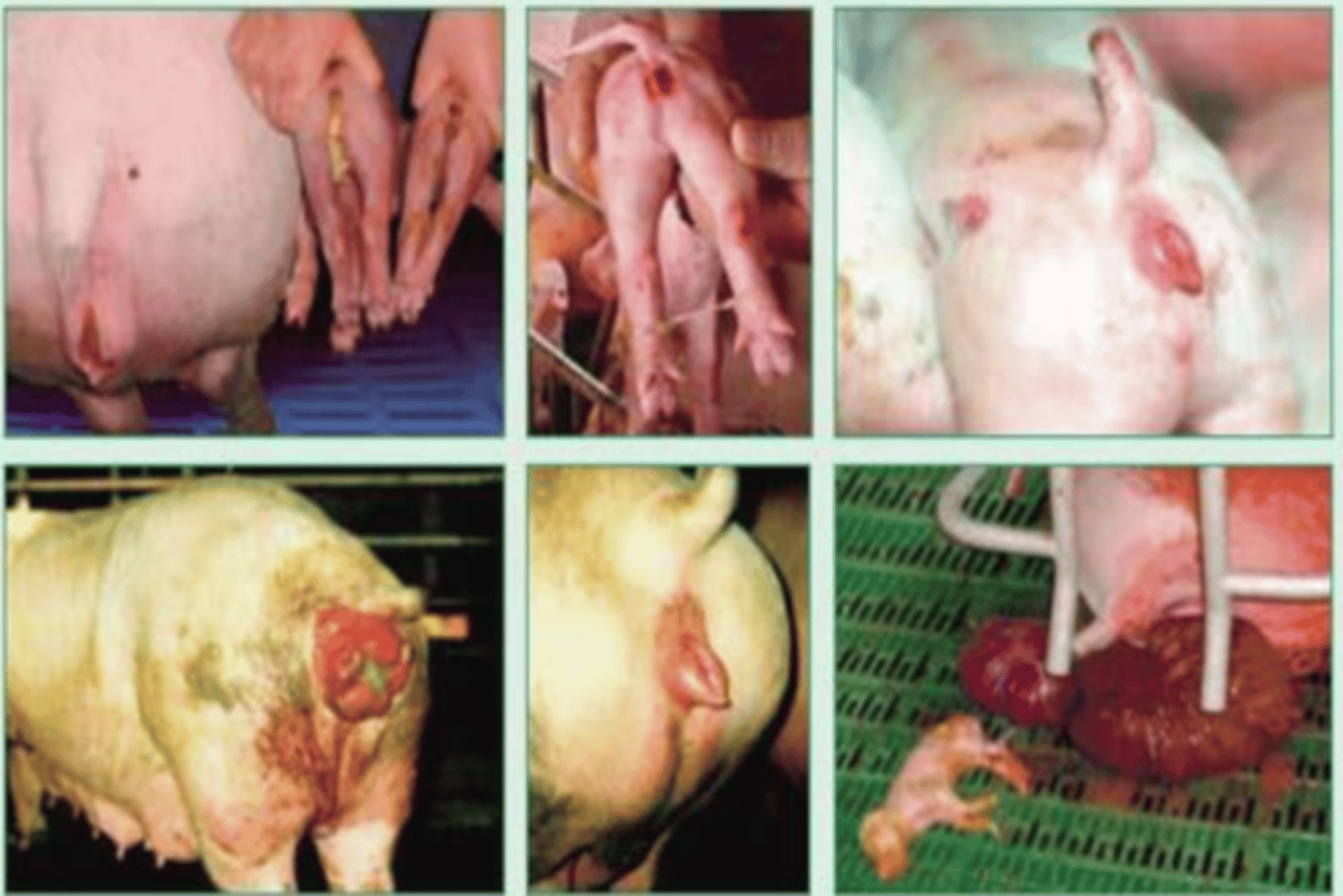
mycotoxic oestrogenism
what disease do these pigs have?
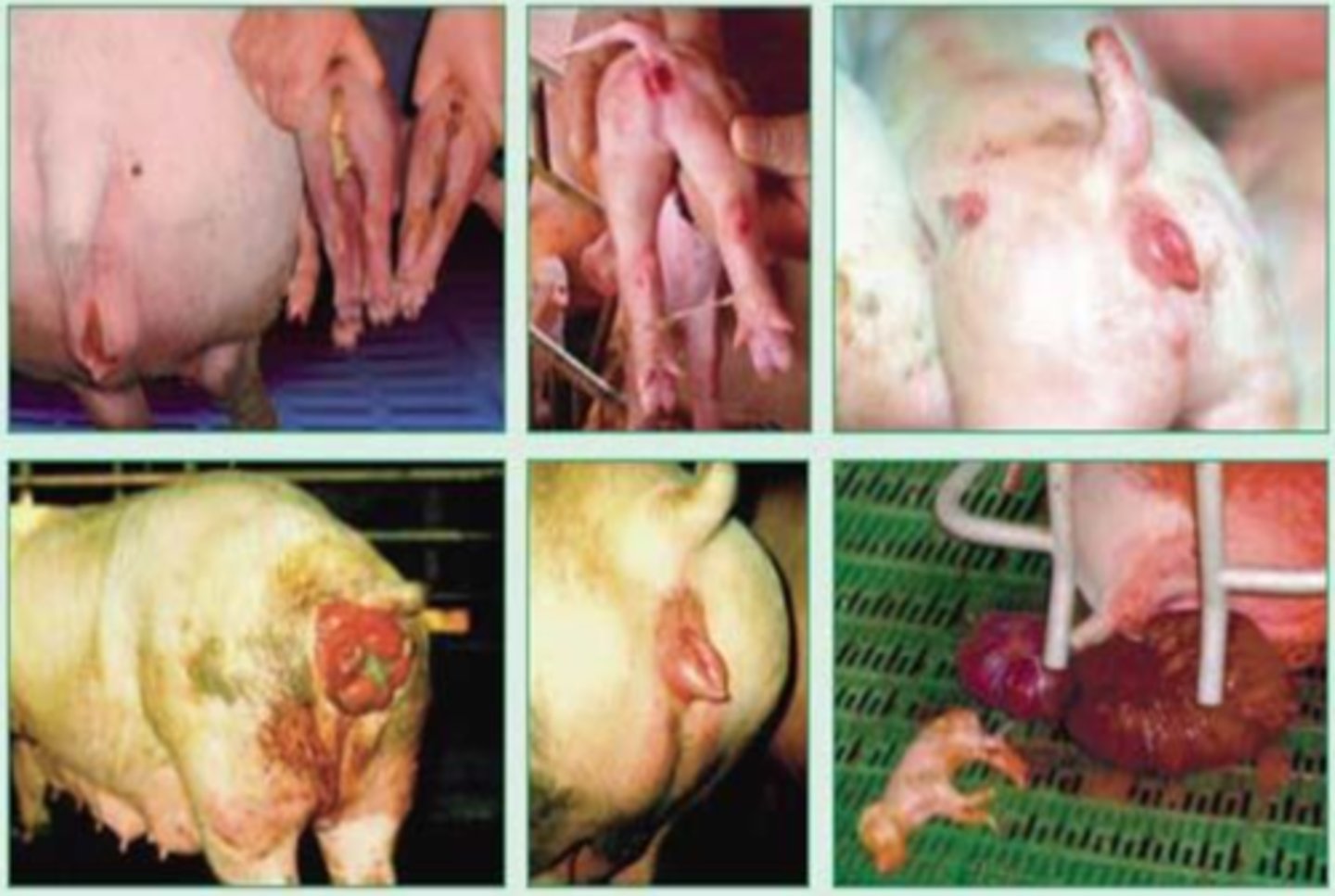
because the toxin zealarenone can be excreted in its milk, and a human that consumes this will contract the same disease
why is a cow infected with mycotoxic oestrogenism a health risk to humans?
penitrem A, Penicillum verrucosum, Penicillum crustosum, and Aspergillus flavus
the disease tremorgenic mycotoxicosis is caused by the mycotoxin _______, produced by the fungus _______
tremorgenic mycotoxicosis:
-muscle tremors
-rigidity
-seizures
-recumbency
-fainting
-unsteady movement
if the fungus species Penicillium verrucosum, Penicillium crustosum, and Aspergillus flavus produce the mycotoxin Penitrem A and it is ingested by an animal, what is the disease and the symptoms?
inhibits K+ channels in the smooth muscle
what is the physiological affect of the mycotoxin penitrem A?
penitrem A (produced by the fungi Penicillium verrucosum, Penicillium crustosum, & Aspergillus flavus)
which mycotoxin inhibits K+ channels in the smooth muscle, so causes muscle tremors, fainting, seizures, rigidity, etc?
Penicillium verrucosum, Penicillium crustosum, Aspergillus flavus
what 3 fungal species can produce penitrem A?
ochratoxicosis
which disease is nephrotoxic?