02 - Hypothalamus-Pituitary Axis (HPA)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
hypothalamus-pituitary axis (HPA)
integration bridges nervous and endocrine systems for whole-body coordination
hypothalamus → part of brain that receives input from nervous system
pituitary gland → responds to hypothalamic signals by secreting hormones that act on other endocrine organs
hypothalamus connection to anterior and posterior pituitary
anterior pituitary → hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system
hormones secreted by hypothalamus travel a short distance to stimulate pituitary for release of tropic hormones
posterior pituitary → neural connection (neurohypophysis)
hormones synthesized in hypothalamus and directly transported down axons
posterior pituitary
neural connection mainly from supraoptic nuclei in hypothalamus to posterior pituitary
hormones release from “nerve” terminals
hormones synthesized in supraoptic nuclei, released from posterior pituitary
transport involves neurophysins also produced in hypothalamus
anterior pituitary
portal circulation
hypothalamus synthesizes hypothalamic releassing hormones in paraventricular nucleus
pituitary releases tropic hormones
integration
localized circulation maintains pulsatile timing due to limited volume and single pass
peptide hormone secretion
stored in membrane granules
released by exocytosis with Ca2+ influx
degraded by liver and kidney
hormone groups of anterior pituitary
glycoproteins → FSH, LH, TSH, hCG
alpha units produced in excess, with unique beta units for specificity
rate-limiting production
somatomammotropin → GH, PRL, hCS
growth promoting
adenocorticotropin → ACTH, ⍺,β-MSH, LPH, β-endorphin
arise from same pro-hormone, pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC)
found in anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes
glycoprotein hormones of anterior pituitary
all share common alpha chain but have unique residues in beta chains (rate-limiting for synthesis)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
luteinizing hormone (LH)
thyroid hormone (TSH)
placental human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
endocrine disorders
multiple controls on hormone secretion
primary → endocrine gland
secondary → pituitary gland
tertiary → hypothalamus
negative feedback peripheral
secondary from peripheral target tissue feedback, where modulation of secretion is determined by hypothalamic control
peripheral target organs limit stimulation of pituitary by hypothalamus
feedback occurs both at hypothalamus and directly on pituitary
negative feedback is usually long-loop feedback
may be short-loop feedback of hormone on pituitary
EXCEPTION — prolactin is subject to little peripheral feedback
open loop control
may be affected by other hormones, such as estrogen
anterior pituitary regulation
primarily from CNS and secretory control from hypothalamic releasing factors
tonic effects of hypothalamus on pituitary
allows for integration of both internal and external environment → feedforward regulation
often provides information for a set-point, maintained by peripheral factors
often release of hypothalamic factors occurring in bursts
affect synthesis and secretion of pituitary hormones
secondary messengers may be cAMP or phosphatidylinositol (PI) turnover to increase Ca2+ for hormone release
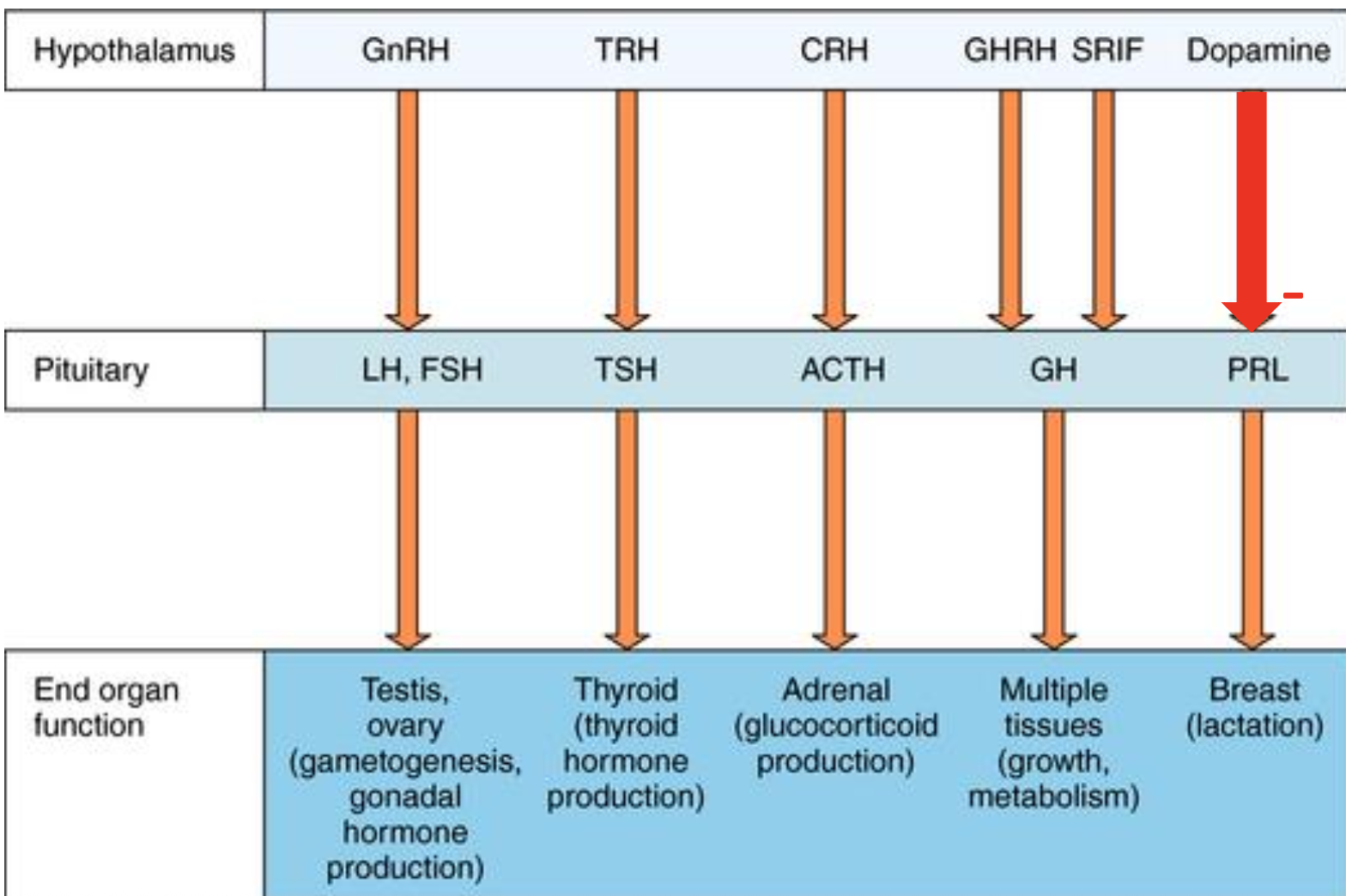
hypothalamic factors controlling anterior pituitary
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GRH) → stimulates FSH and LH release
thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) → stimulates TSH release
effect modulated by thyroid hormone
stimulates PRL release
corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) → stimulates ACTH, β-LPH, and β-endorphin
growth hormone inhibitory hormone (GHIH, somatostatin) → inhibits GH release
may inhibit TSH release
prolactin inhibitory hormone (PIH) and dopamine → inhibits PRL release, which is tonically active
major factor responsible for PRL release
other influences on secretion/synthesis
other hormones may affect control
pattern of secretion varies with time
none of pituitary hormones are subject to constant release
often diurnal patterns, may be light/dark or day/night
often secondary to hypothalamic factors
pattern is not sinusoidal release but consists of multiple spiking patterns
mean rhythm may be generated altering frequency of burst activity