Computer Systems Arcutecture
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Who was the first programmer?
Ada Lovelace
What does the IR (Instruction register do?
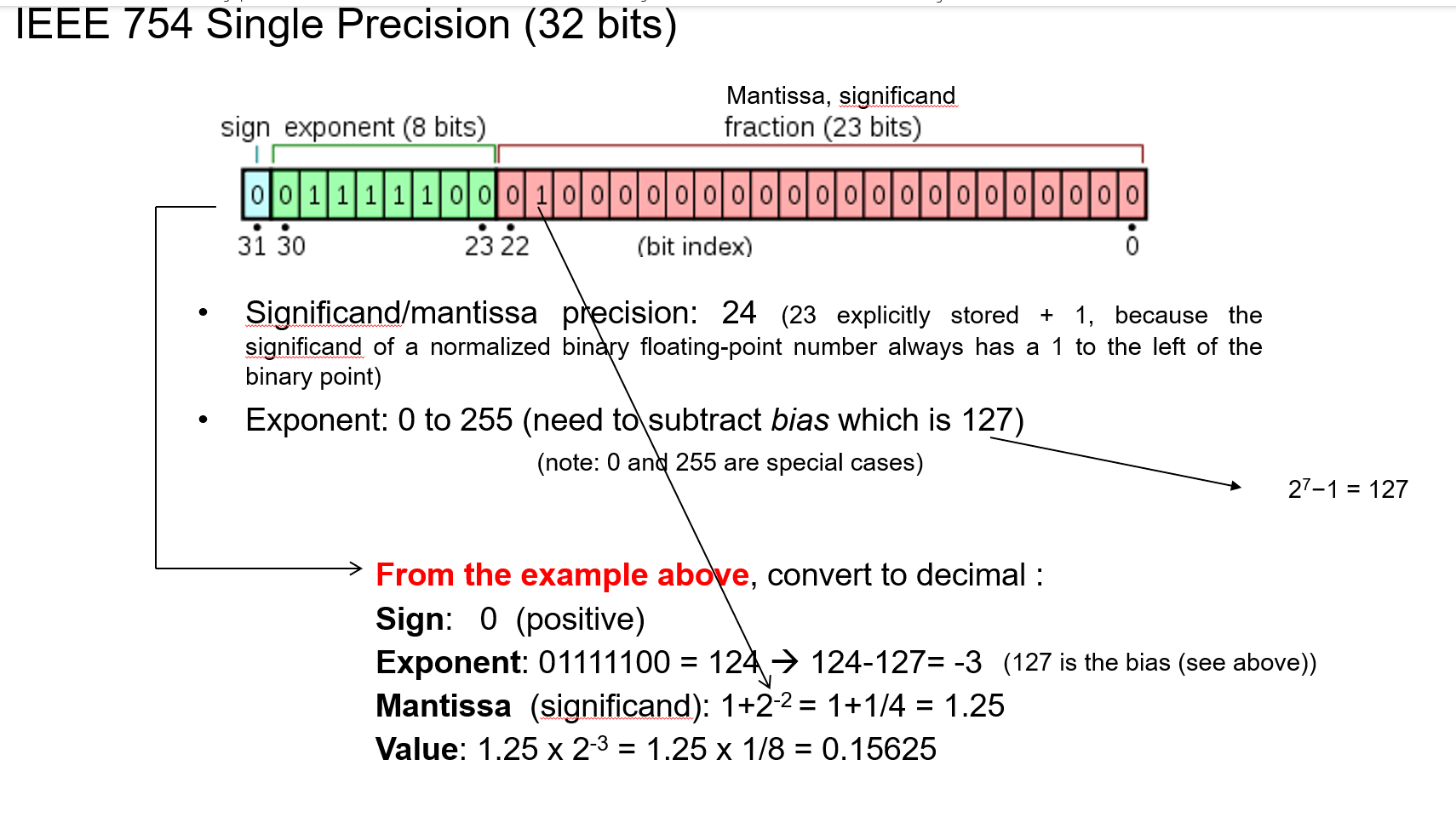
What must you do to the exponent 8 bit in single precision to decimal conversion & why?
Actual = Given - 127
How does the fetch-execute cycle work?
What does the program counter do?
Special register in the CPU that keeps track of the memory address of the next instruction to be executed. It ensures the CPU knows where it is in the program.
Where are the PC and IR found?
Both are in the control unit.
What does abstraction mean?
The concept of hiding lower-level details of a system and exposing only the essential features or interfaces needed for higher-level operations.
Is the ALU automatic?
No, operands & operations must be supplied in the correct sequence by the control unit
What does ALU stand for?
Arithmetic (and) logic unit
What does the control unit do?
Orchestrates the execution of instructions for the ALU
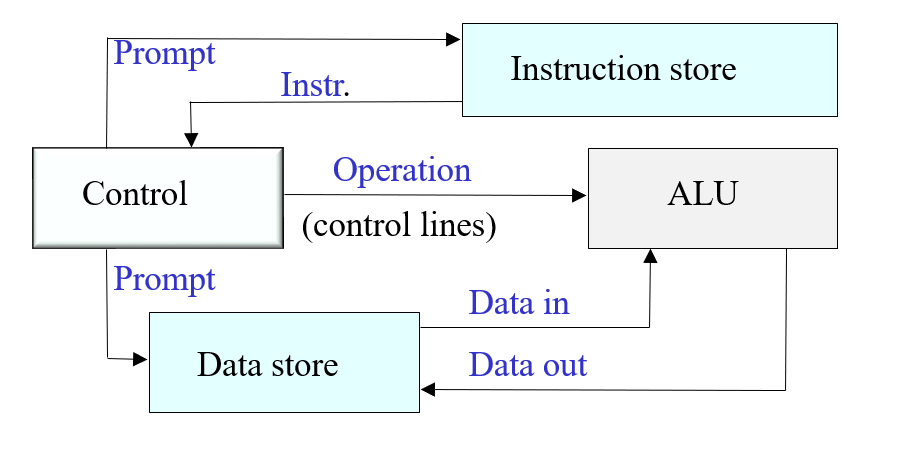
What is the form of the data that is processed by von Neumann architecture?
Digital (binary)
What are the defining features of the von Neumann architecture?

Where is data stored in the von Neumann architecture?
Data store unit, which is combined with the instruction store in a single store
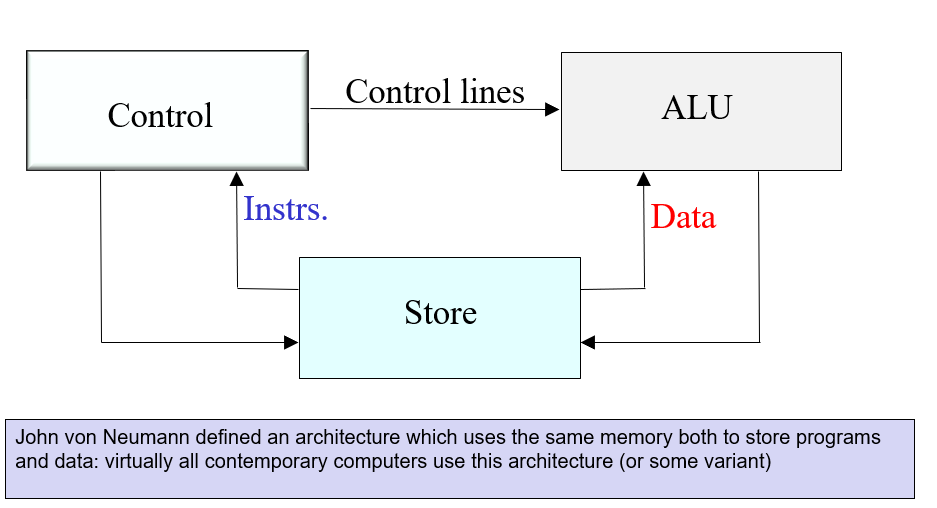
Where do the operation information come from?
From the instruction store (in the main memory) which also stores the data store
How does the control unit work? (3-word cycle)
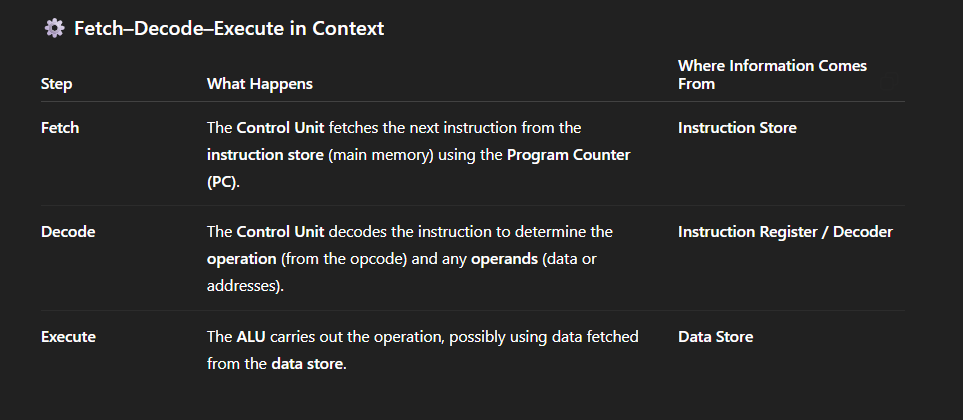
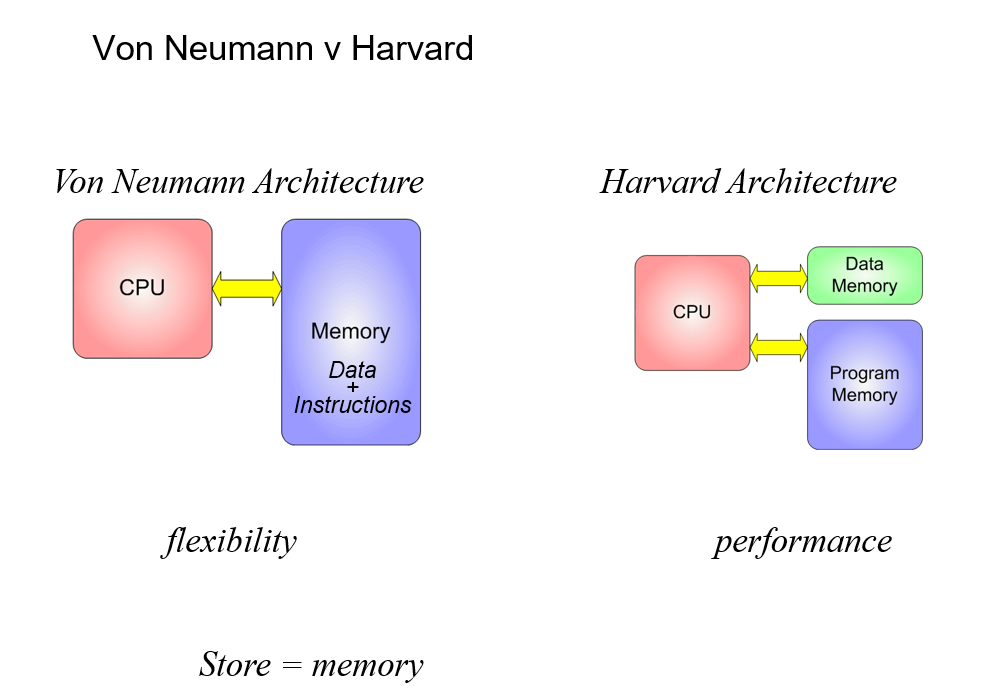
Difference between Harvard & von Neumann?
Separates stores of data and instructions, allowing the CPU to access both simulaneously.
What is a microcontroller?
A device with ALU, control unit, I/O & memory. Usually uses Harvard Architecture

When is Harvard Architecture used?
Microcontrollers
Sophisticated high-performance processors which exploit the parallel of fetching instructions & data at the same time
What are the 5 main components of von Neumann architecture?\
What are buses?
A set of physical wires or communication pathways that carry data, addresses, and control signals between different parts of a computer system — mainly the CPU, memory, and input/output (I/O) devices.
What does the control unit enable?
Automation
What is the von Neumann bottleneck?
The limitation on data transfer speed between the CPU and main memory, because both program instructions and data share the same communication path
Benefit of cache?
Reduce the time the CPU spends waiting for data from the slower main memory.
How does cache work?
Cache holds a copy of recently used data or instructions from main memory.
The original data remains in main memory; the cache just keeps a faster, nearby copy.
When the CPU accesses memory:
Cache hit: CPU uses the copy in cache.
Cache miss: CPU fetches data from main memory, also storing a copy in the cache for future access.
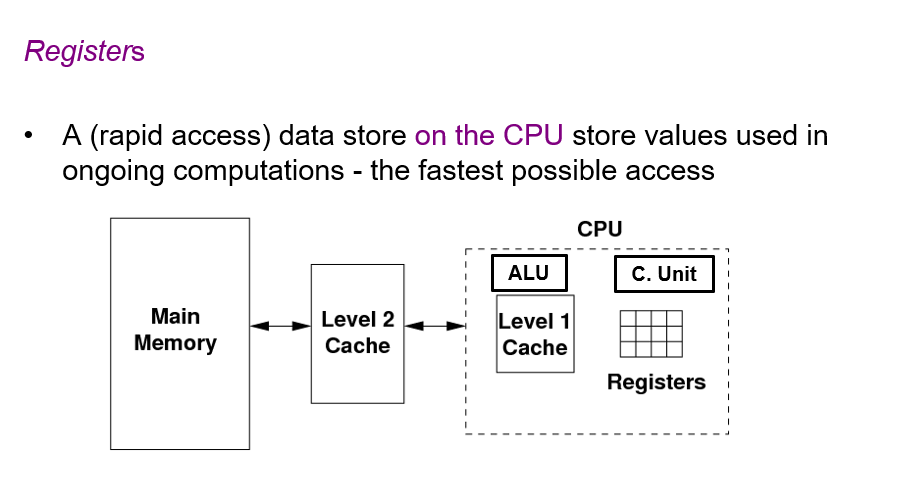
What are registers?
Registers are small, very fast storage locations located inside the CPU.
They are the fastest type of data store
What is a uniprocessor?
A single central processing unit (CPU) that executes instructions one at a time.
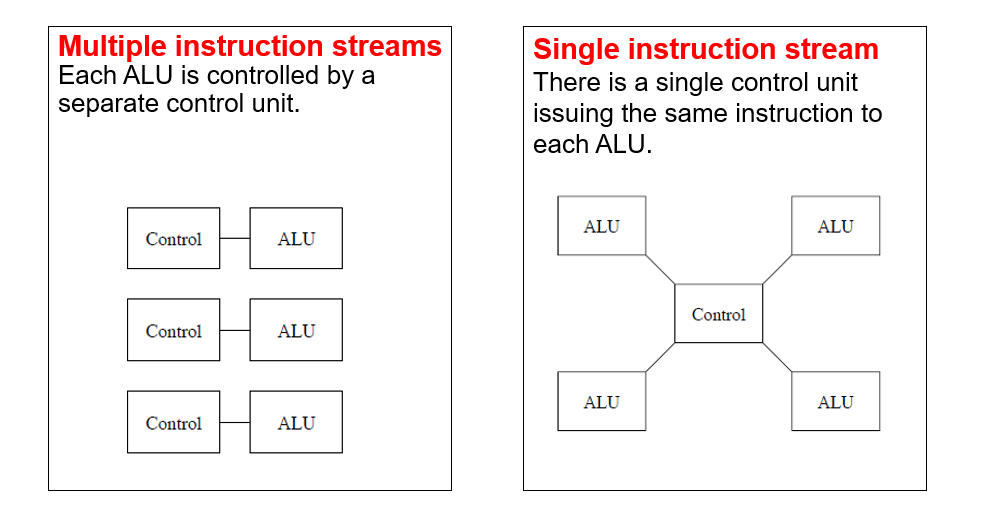
What are the 2 control architectures for multiprocessors?
What is an array?
Contiguous (unbroken sequence) collection of elements of the same data type. Can be accessed directly using an index or subscript

What is Flynn’s Taxonomy?
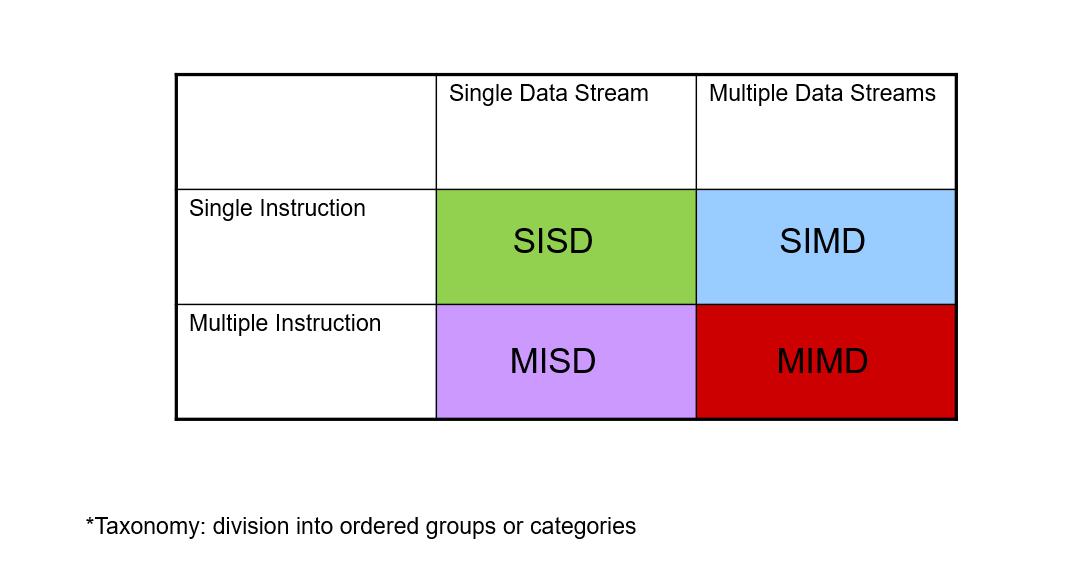
What are the 4 different types of parallel processing?
/watch?v=MJ-ettBDJqQ
What are the 2 types of memory architecture?
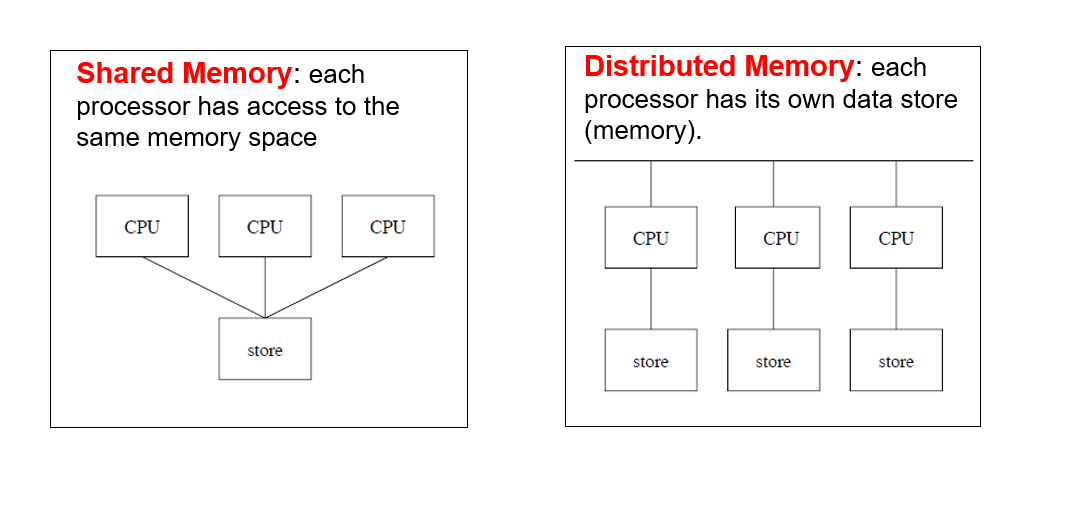
Benefits/Cons to shared/distributed memory?
Shared is an efficient use of space, but leads to memory-to-CPU bottlenecks & cache coherence issues.
Distributed easy to scale up, but communication between processors is indirect and inefficient (message passing)
What is cache coherence?
When multiple caches store copies of the same memory location, any change made by one processor must be visible to all other processors. Shared memory can become a problem unless solved with “coherence protocols”.
What are some solutions to both shared and distributed memory architectures?

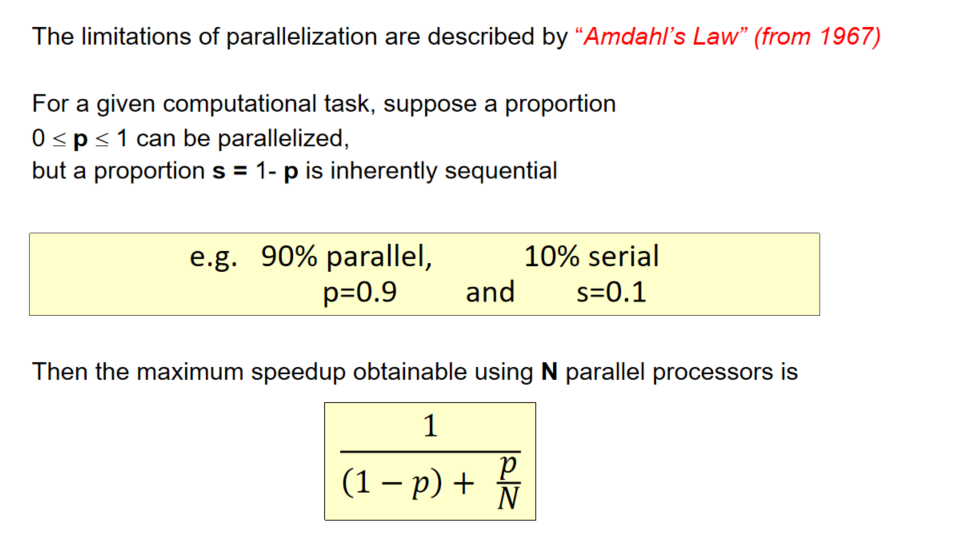
What is Amdahl’s law?
P is the proportion of the program that can be run in parallel. N is the number of parallel parts
How to convert numbers to different bases?
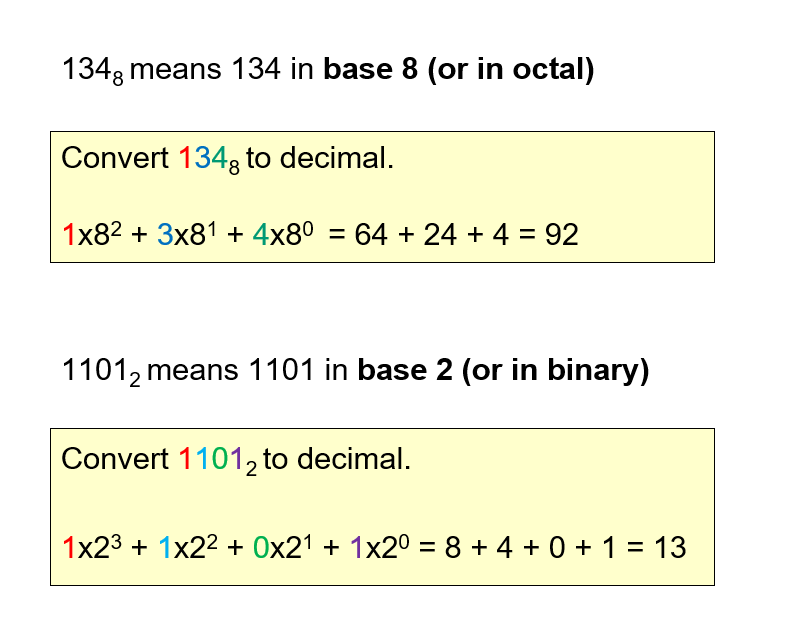
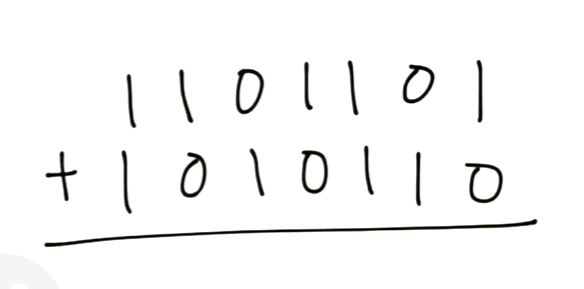
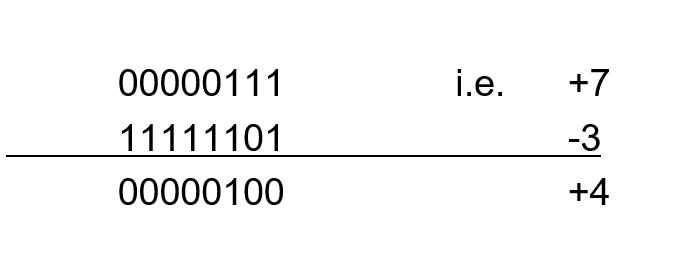
How to add this?
Where are bytes stored?
In memory cells
What is a store?
A collection of cells, each cell has an address (usually positive integers)
How are addresses numbered?
Addresses are numbered from 0 to (m-1) for a store with m cells.

What is sequential memory access?
You must go through earlier data to reach later data.
Magnetic tape is the classic example of sequential access storage.
If you want to read record #90, the drive has to start at the beginning and move through records 1 → 2 → 3 ... → 90.
What is a flip-flop?
A flip-flop is like a tiny memory cell that:
Can hold either 0 or 1.
Remembers its state even when input changes — until told to change again.
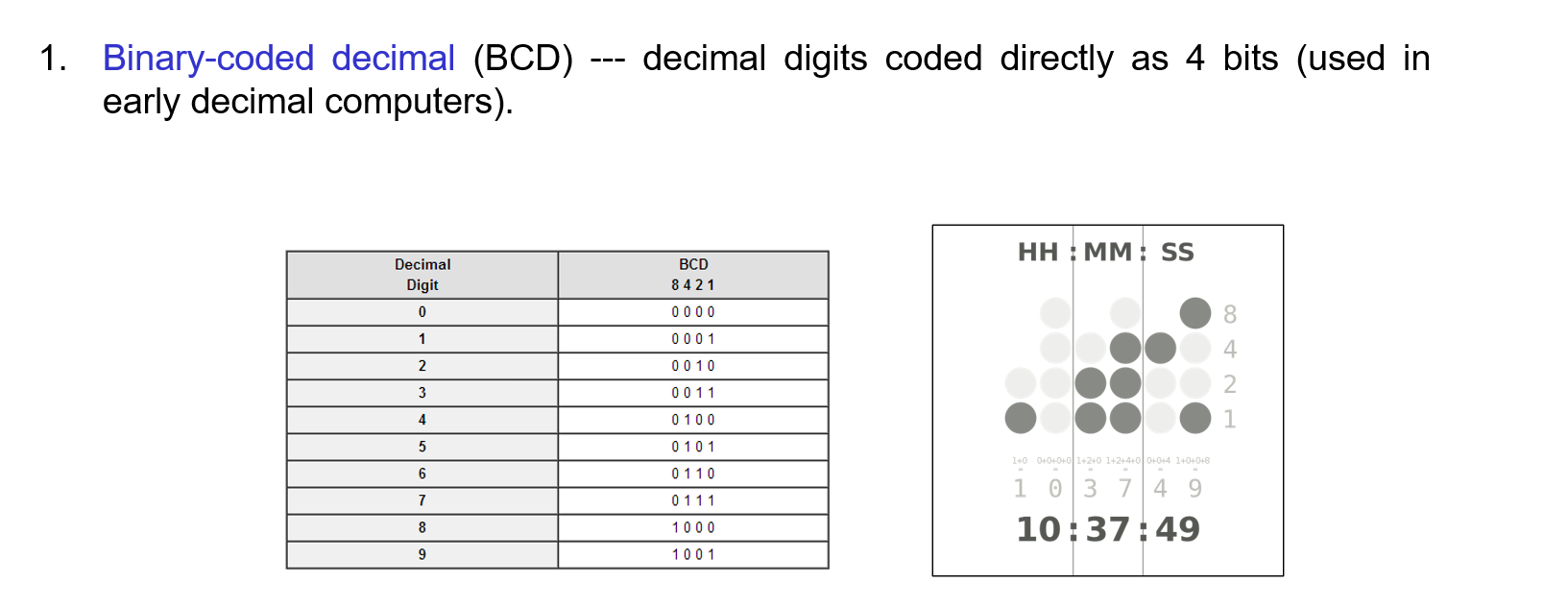
What is binary-coded decimal?
How do you represent negative integers in binary? (Using one’s complement)
First bit represents sign of integer:
0 = positive
1 for negative
e.g: 0111 1111 is +127
1111 1111 is -127
Only 255 values are represented in a cell.(since 0000 0000 and 1000 0000 both represent 0! (0 and -0)
How does 2’s complement system work?
Invert all bits (change 0 → 1, 1 → 0).
Add 1 to the result.
Benefit of using 2’s complement system?
There is only 1 way to represent 0, so not 256 possible data representations, not 255 like in 1’s complement.
How do you add 2 data points represented with 2’s complement?
Just like normal!
What is a mantissa?
The part of a floating-point number which represents the significant digits of that number.
How to convert IEEE standard to decimal?
DOnt forget there is always a 1 at the front. All of this just represents the significant digits.