BME211 Week 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Biomechanics
The study of the mechanics of living organisms, focusing on how forces interact with the body’s structures.
Cardiovascular Biomechanics
The study of the mechanical function and forces of the cardiovascular system, including the heart, blood vessels, and blood flow.
Heart
A muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body via the circulatory system.
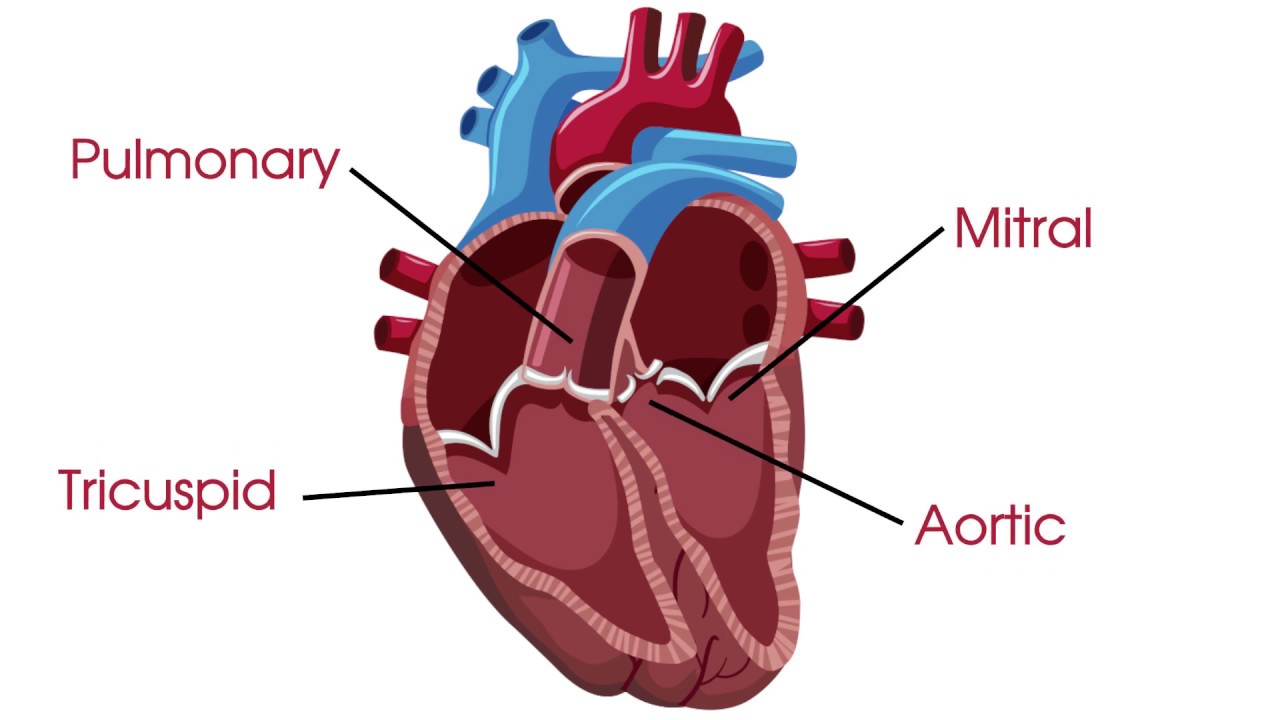
Valves
Structures in the heart that ensure one-way blood flow, preventing backflow between chambers.
Diastole
The phase when the heart relaxes and fills with blood.
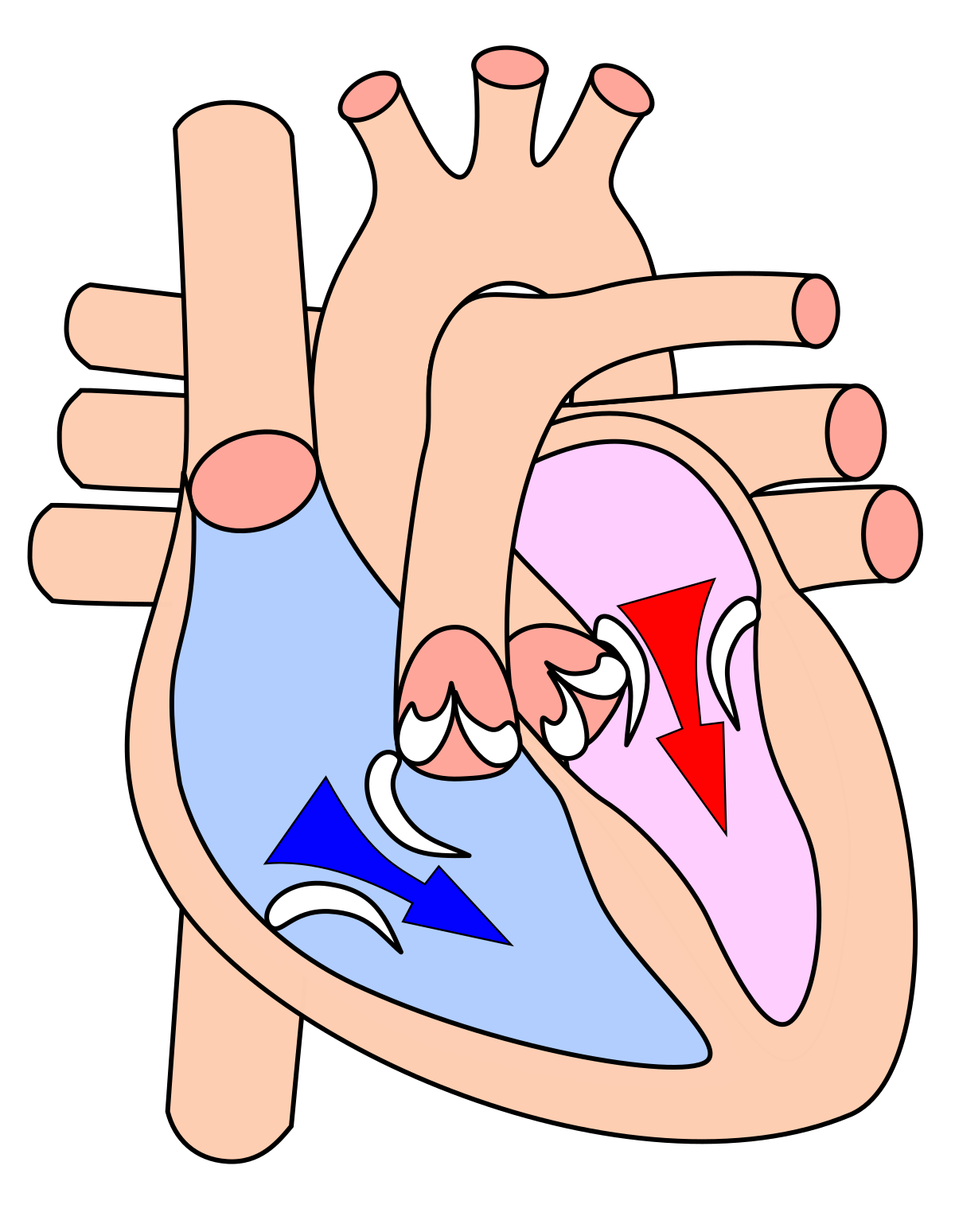
Systole
The phase when the heart contracts and pumps blood out.
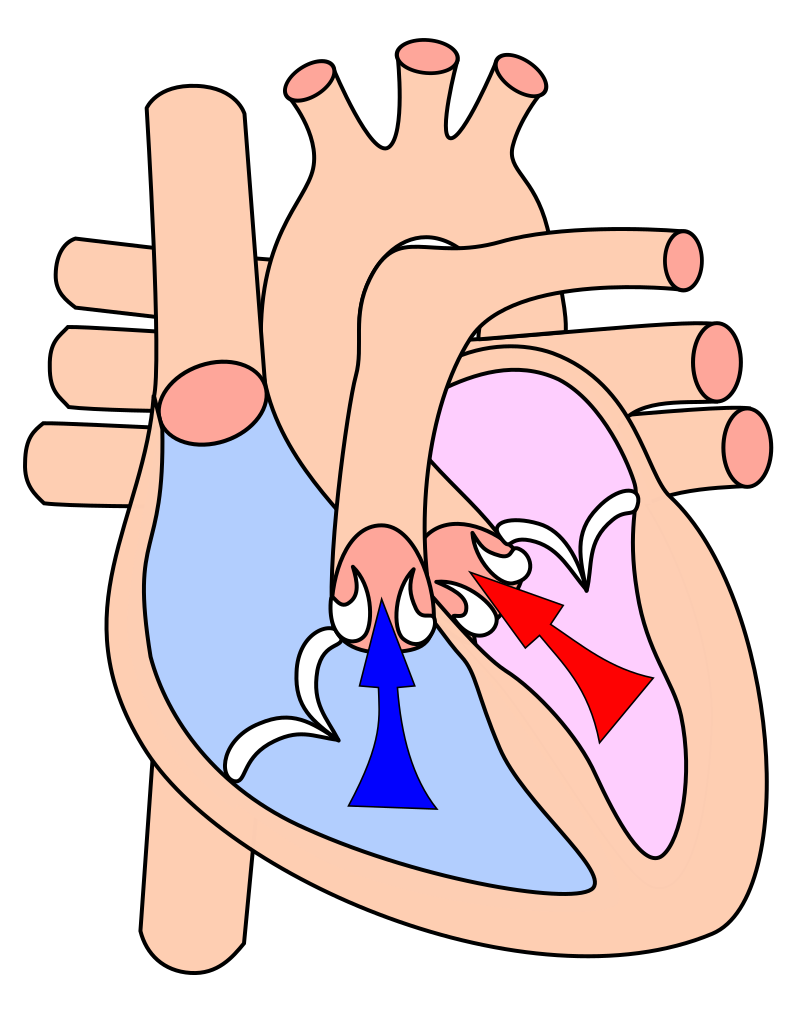
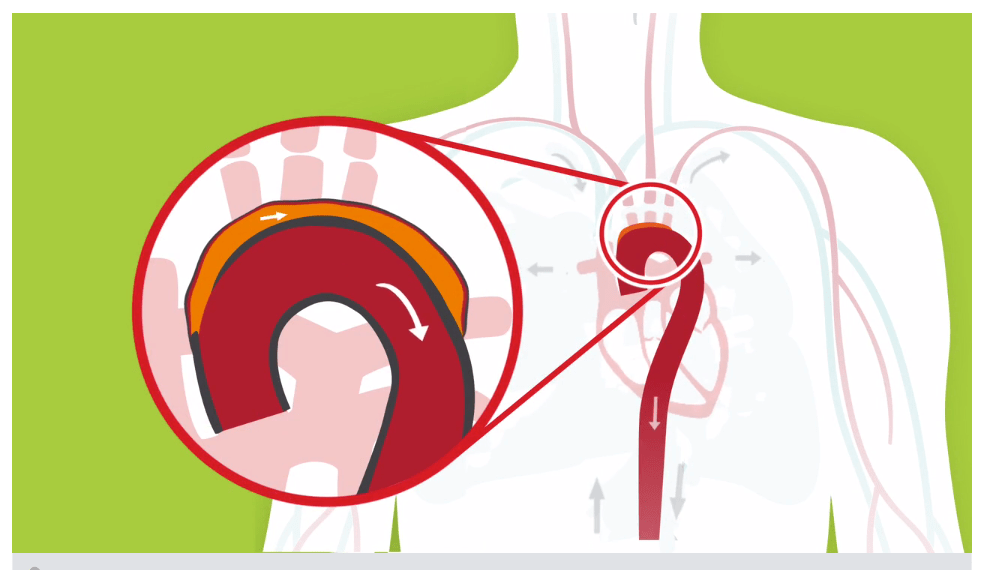
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, carrying oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
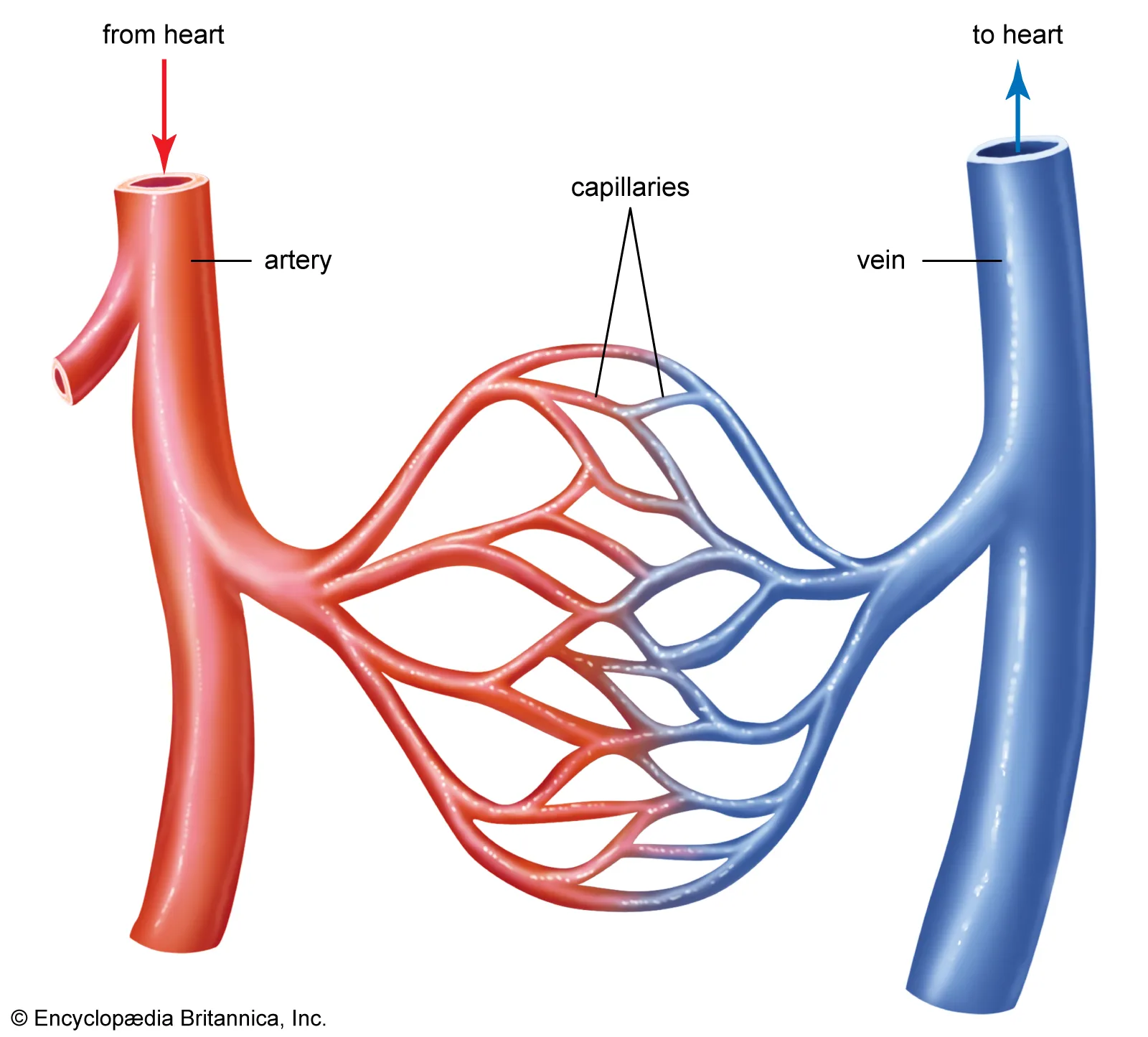
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart.
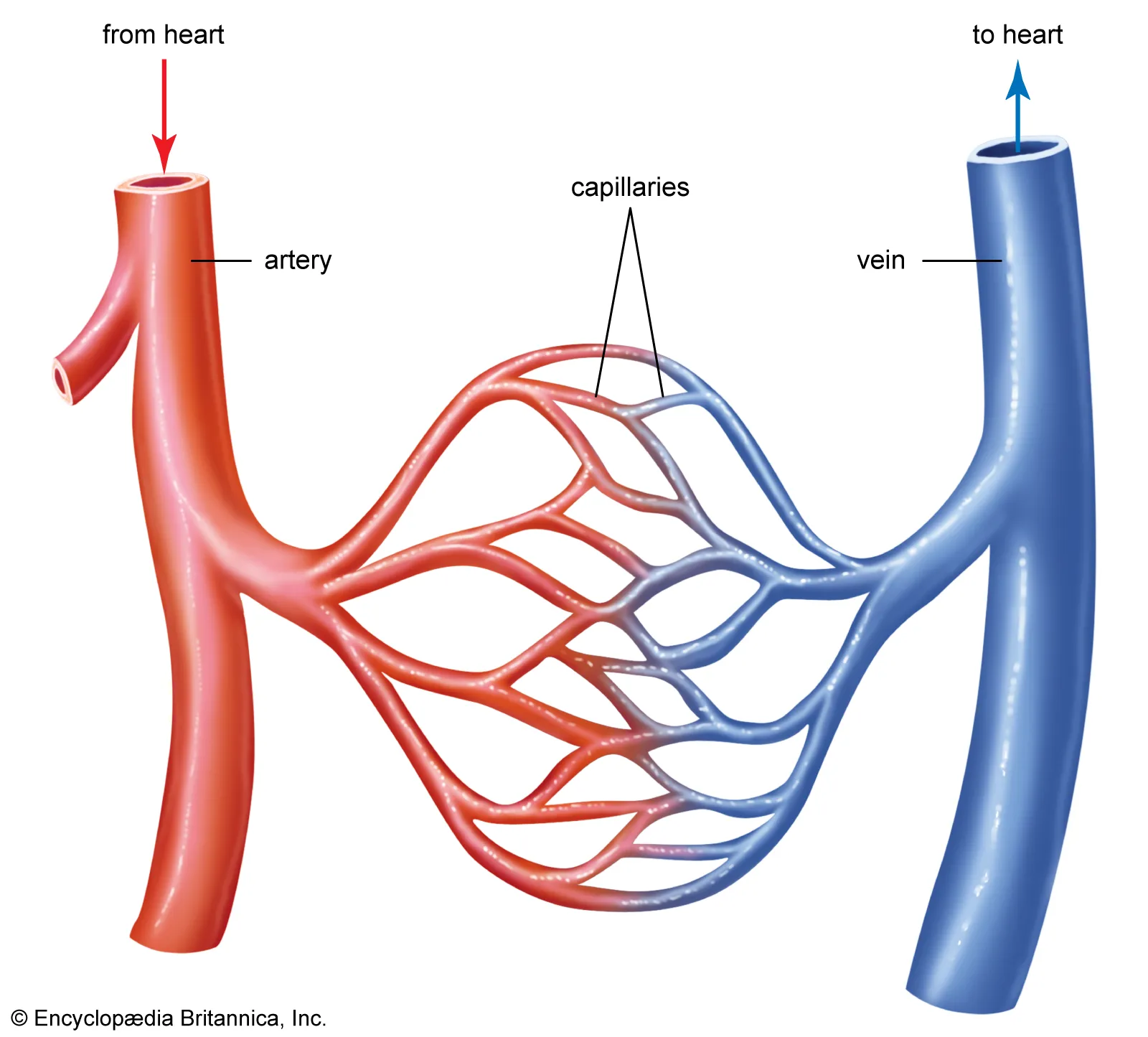
Capillaries
Tiny blood vessels where gas, nutrient, and waste exchange occur between blood and tissues.
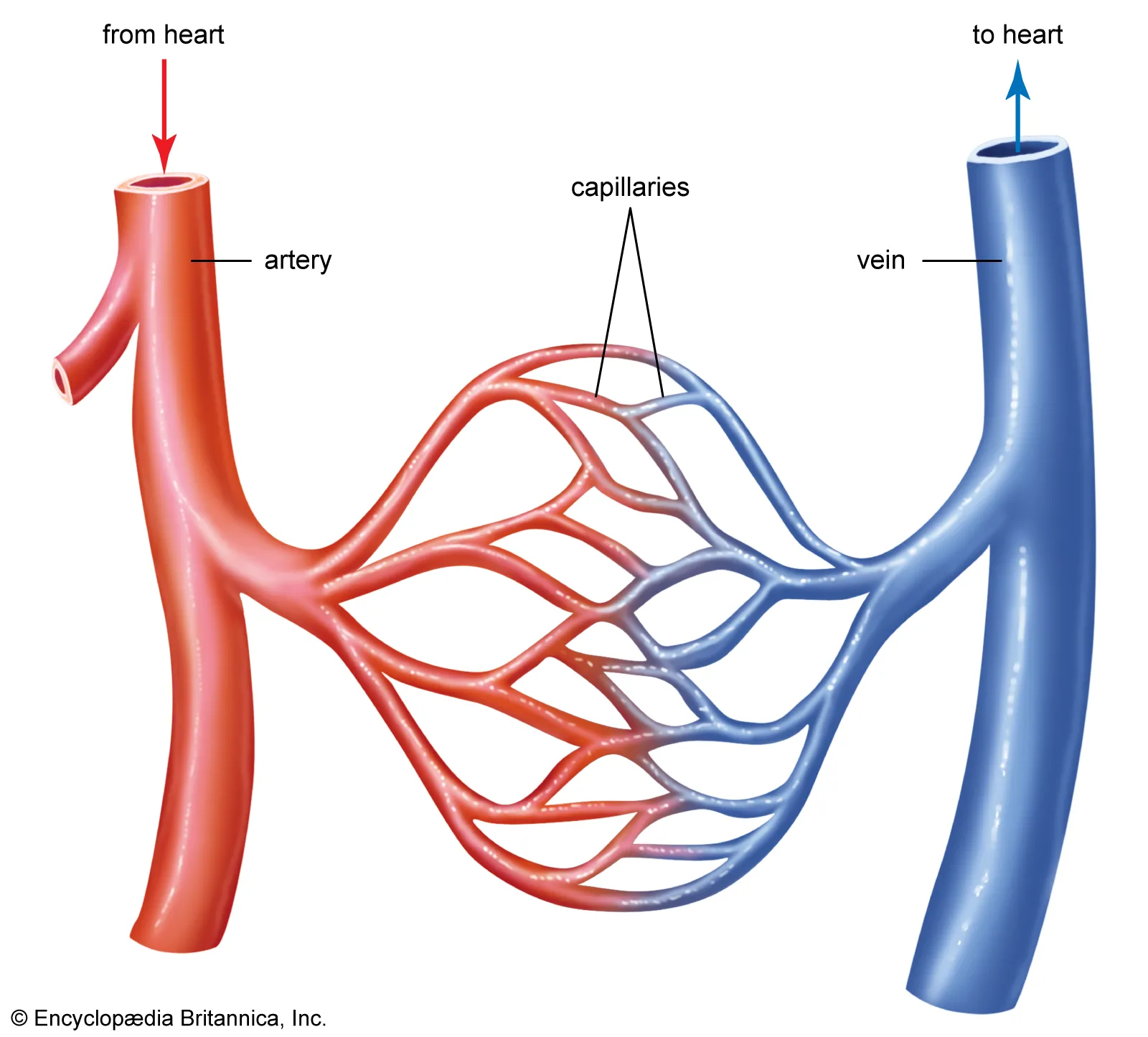
Veins
Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
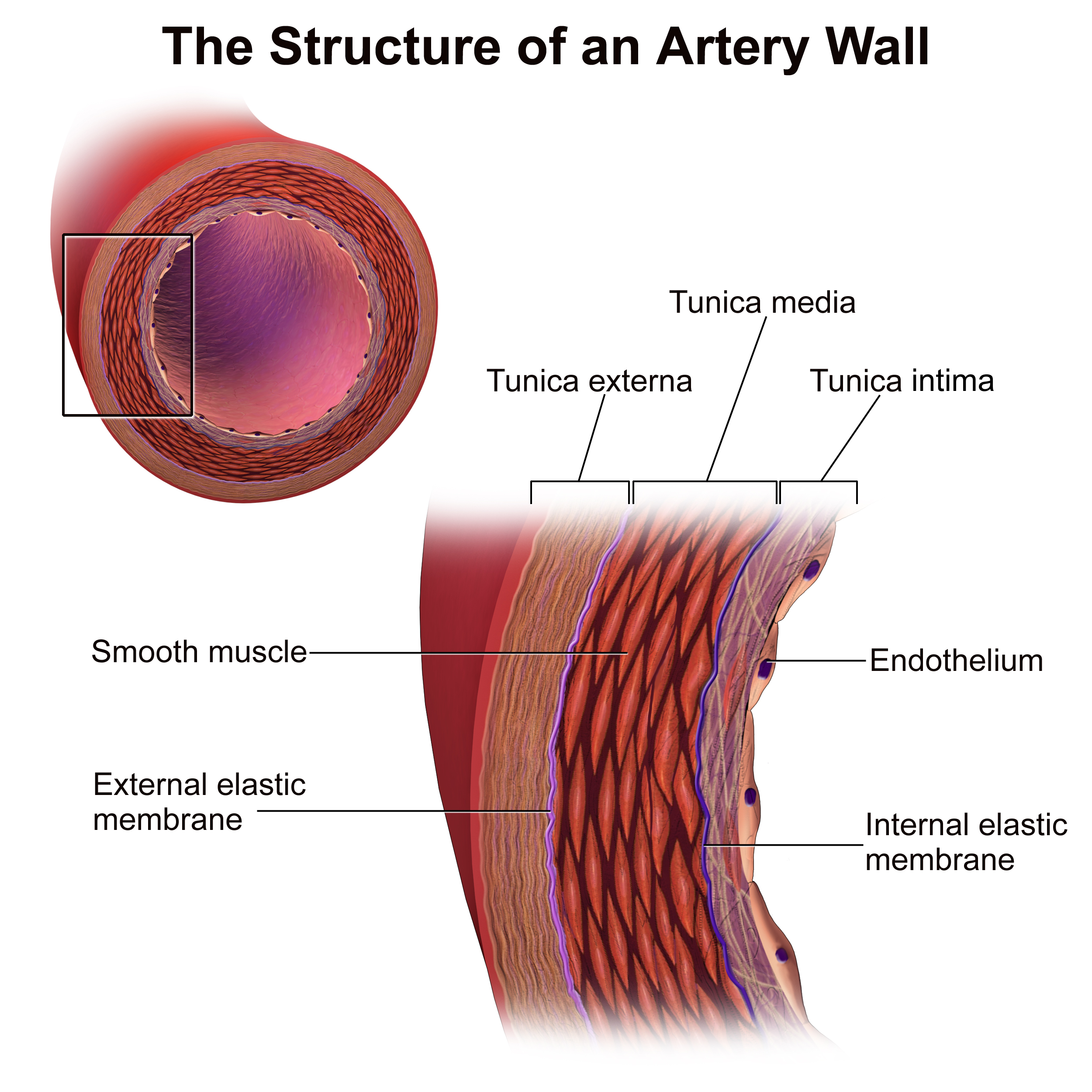
Vessel Structure
The layers of blood vessels, including intima, media, and adventitia.
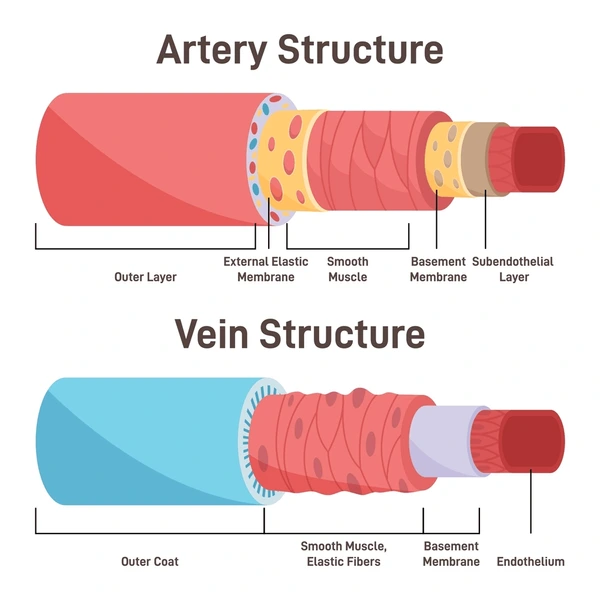
Intima
The innermost layer of a blood vessel, in direct contact with blood.
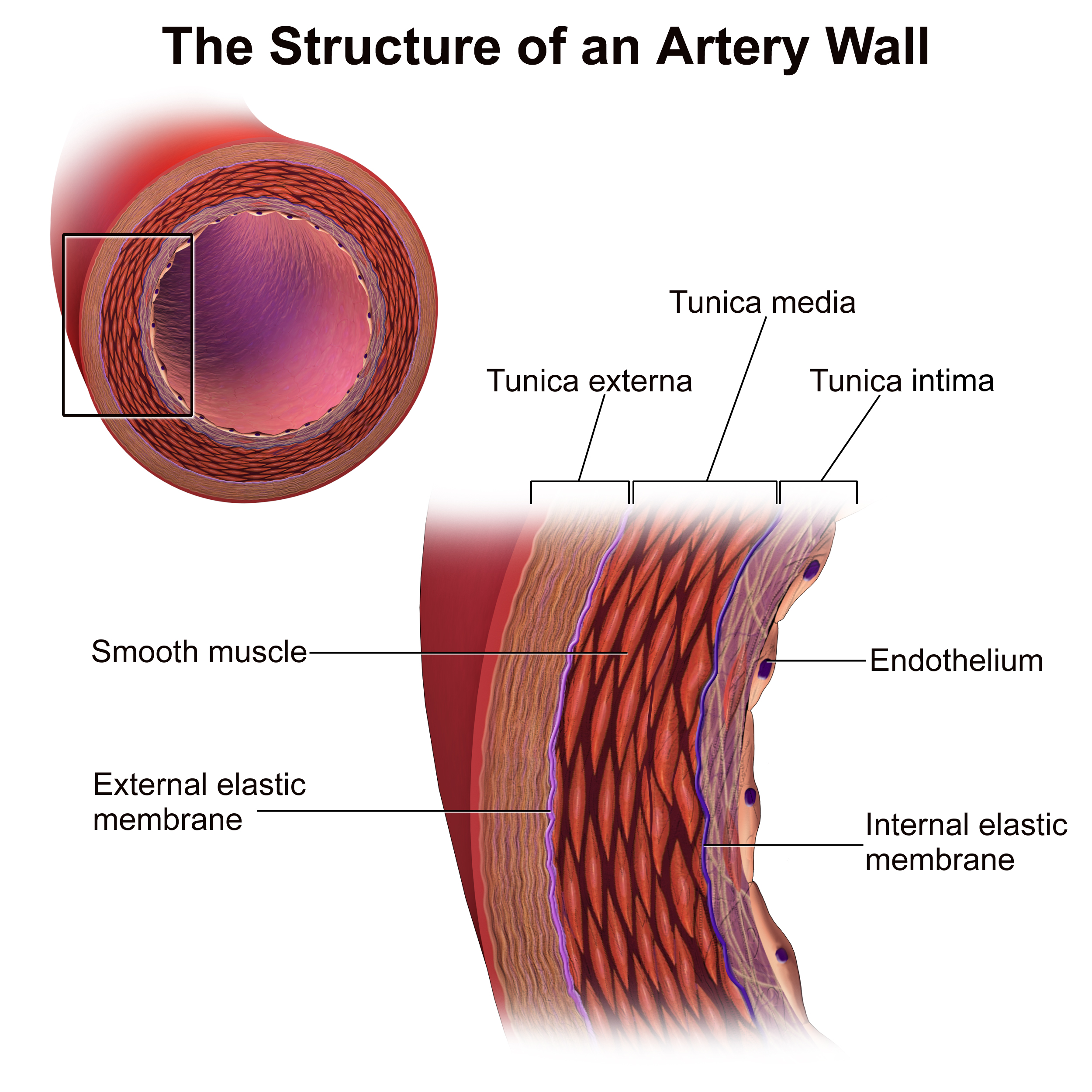
Media
The middle layer of a blood vessel, mostly smooth muscle, controls vessel diameter.
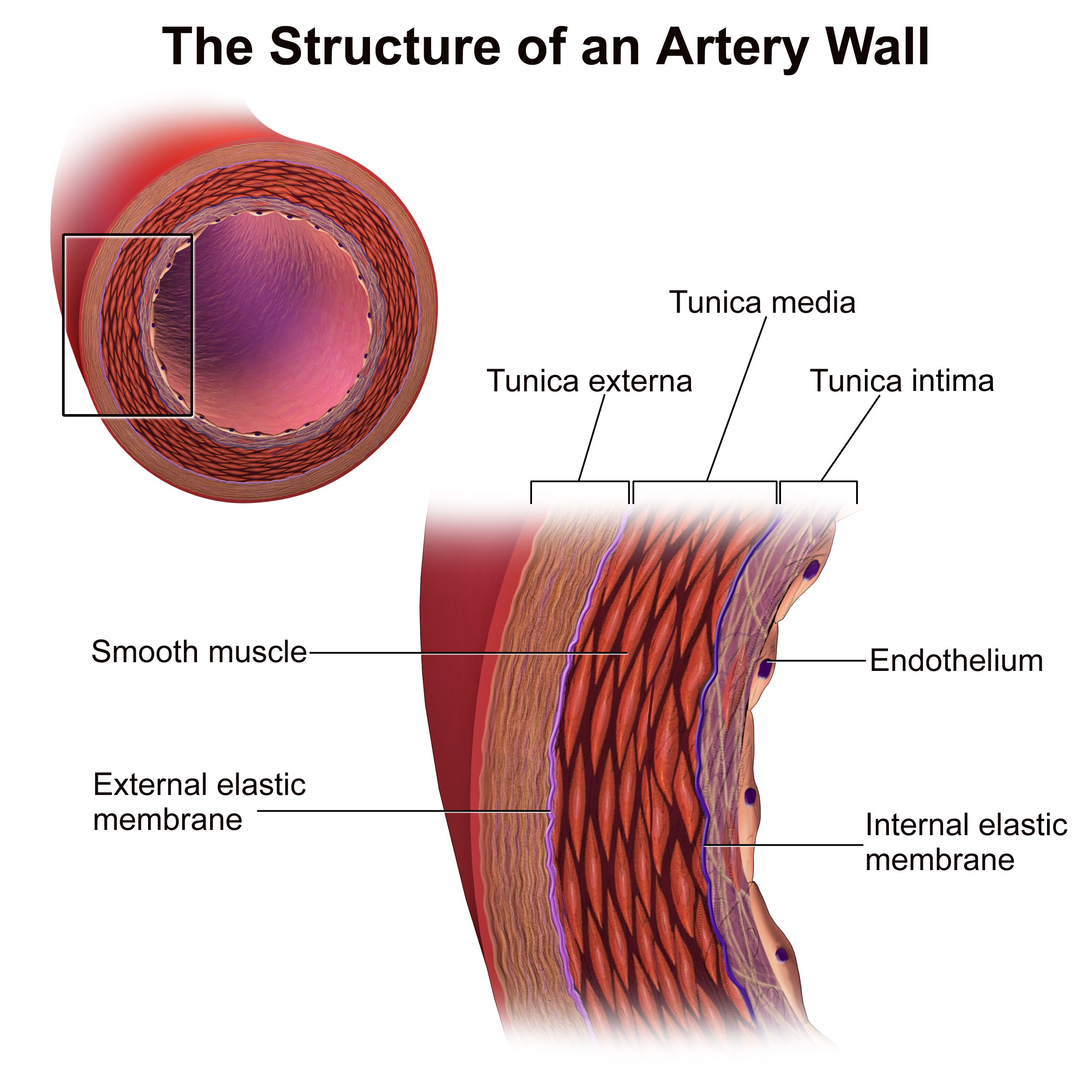
Adventitia
The outermost layer of a blood vessel, providing structural support.
Vessel Composition
The materials that make up blood vessel walls, including elastin and collagen.
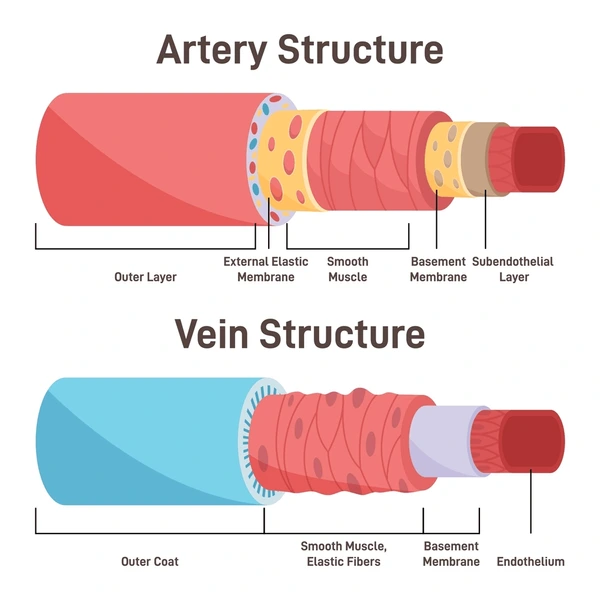
Elastin
A protein that provides elasticity, allowing vessels to stretch and recoil.
Collagen
A protein that provides strength and structure to the vessel walls.
Blood Constituents
The components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma.
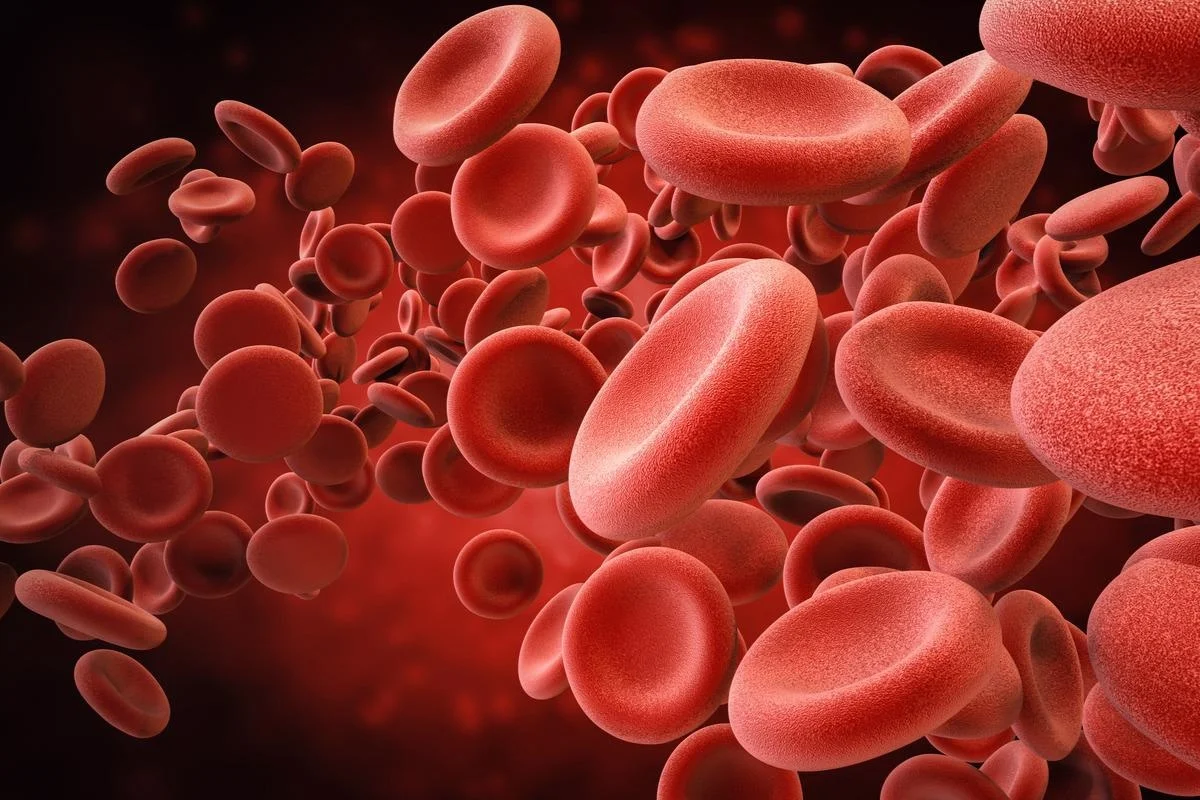
Red Blood Cells
Cells that transport oxygen in the blood.
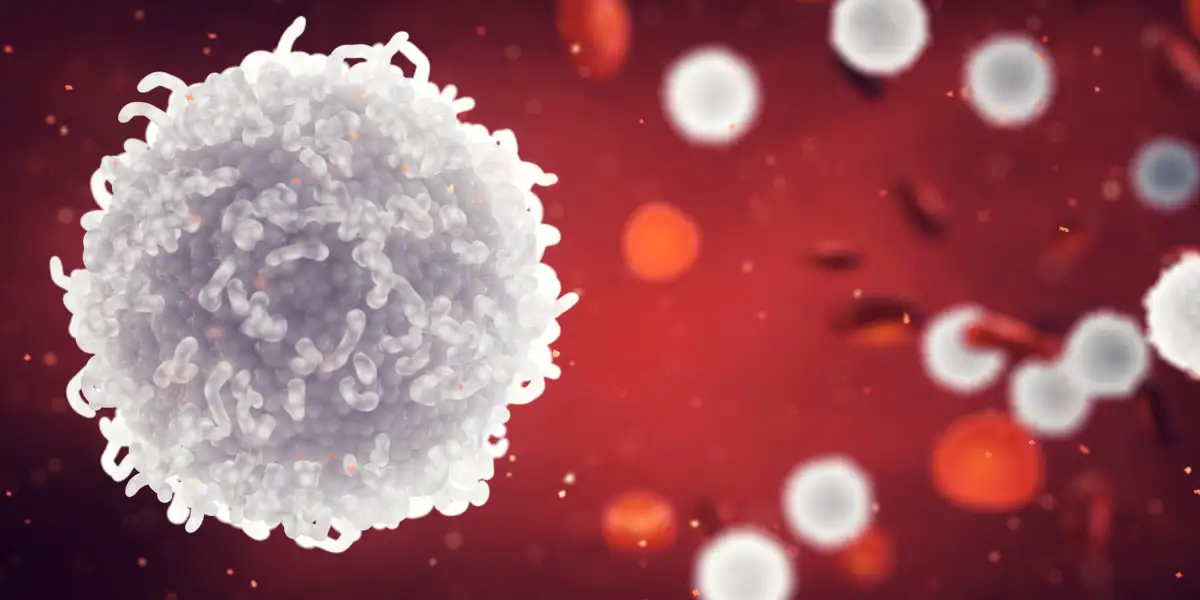
White Blood Cells
Cells that fight infections in the body.
Platelets
Cell fragments that help in blood clotting.
Plasma
The liquid component of blood that carries cells, nutrients, and waste.
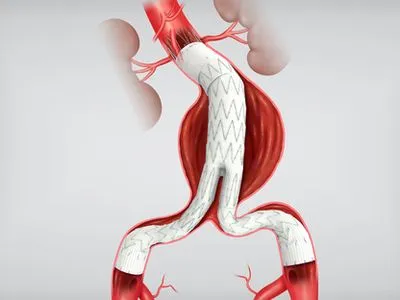
Aortic Endograft
A minimally invasive device used to reinforce a weakened aorta, commonly used in treating aneurysms.
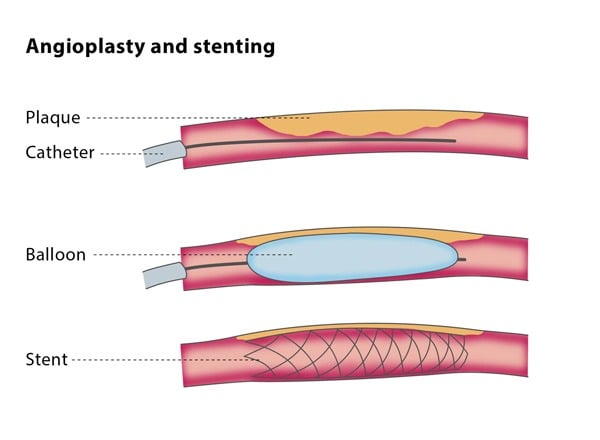
Angioplasty and Stenting
Procedures to open narrowed arteries using a balloon (angioplasty) and keep them open with a stent (a small mesh tube).