PSYCH EXAM 2
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 4-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
Sounds
vibrations cause by the compression of air molecules that propagate as an acoustic wave
psychological definition: the experience of hair cells in our inner ear reacting to these acoustic waves
conscious
momentary and controllable
subconcious
(easily) accessible
describes our awareness of internal and external
eg: pain, hunger, thrist, emotions and thoughts
selective attention
process that controls awareness and preparedness to response to stimuli
helps to not overwhelm individual and select what is important
cocktail party effect
attention is shifted when you hear your name mentioned
eg: disrupts original attention (failure of selective attention)
stroop effect
delay in reaction time between reading words while trying to name the font colour
congruent and incongruent stimuli
measures a persons selective attention capacity and skills (processing speed)
sleep
state of low levels of physical activity and reduced sensory awareness
wakefullness
high levels of snesory awanress, thought and behavoir
states of conciousness
sleep
wakefulness
intoxication
daydreaming
unconsciousness (anesthesia)
circadian rythm
Biological rhythm over 24hrs
sleep wake cycle
heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, body temp
the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
brains clock mechanism
located in hypothalamus
light sensitive neurons in retina provide information to SCN, synching it to the outside world
melatonin
important regulator hormone for sleep-wake schedule
released by the pineal gland
stimulated by darkness
pineal gland
endocrine structure located inside the brain
releases melatonin
chronotype
individual differences in circadian patterns
eg: night owls and morning larks
Sleep regulation
brain’s control of switching between sleep and wakefulness and coordinating this cycle with the outside world.
jet lag
mismatch between our internal circadian cycles and enviroment
symptoms include: fatigue, sluggishness, irritability and insomnia
rotating shift work
persistent feelings of exhaustion and agitation
results in sleeping problems, depression and anxiety
common in health care workers
slept debt
induvial without sufficient amount of sleep on a daily basis
symptoms: decreased alertness, mental efficiency
amount of sleep since invention of electric light has declined
sleep reccomendation
0-3 months: 14-17 hours
4-11 months: 12-15 hours
1-2 years: 11-14 hours
3-5 years- 10-13 hours
6-13: 9-11 hours
14-17: 8-10 hours
18-25: 7-9 hours
26-64: 7-9 hour
≥65 years: 7-8 hours
sleep deprivation
assosicated with obesity, depression, increased levels of stress hormone and blood pressure
halluciantions, cognative imparment, risk of heart disease, growth suppression, risk of type 2 diabetes, impared immune system
Sleep rebound
sleep-deprived individual will fall asleep more quickly during subsequent opportunities for sleep.
areas of brain in sleep-wake cycles
thalamus
regulate slow wave sleep
hypothalamus
SCN
pons
REM
hormones in sleep
melatonin- pineal gland
regulate biological rhythms and immune system
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)- pituitary gland
important in reproductive system
luteinizing hormone (LH)
important in reproductive system
growth hormone- pituitary gland
physical growth
hypothesis for sleep (evolutionary psychology)
restore recourses expanded throughout the day
sleep patterns evolved as an adaptive response to predators to sleep in safe areas
reduce risk of predators
cognative function of sleep
benifit memory formation
creative thinking
processing emotional information
beta waves
while awake
highest frequency & lowest amplitutde
13-30hz
REM
rapid eye movement
brain waves similar to wakefulness
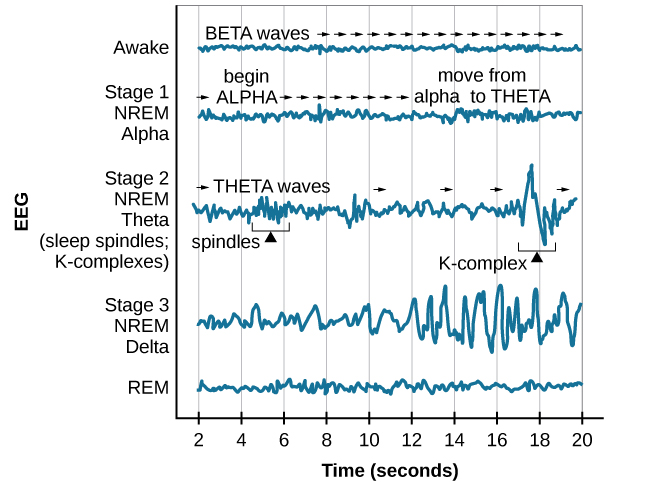
stage 1: NREM
drifting off to sleep/transitional
slowdown in respiration and heartbeat
begins ALPHA
move to THETA waves after 12 SECONDS
alpha waves
stage 1 NREM
drifting off to sleep/relaxed
8-12hz
Theta waves
low frequency (4-7hz), higher im amplitude
NREM: stage 2
body in deep relaxation
K- complex present: high amplitude pattern of brain activity in reaction to environmental stimuli
theta waves dominate but interrupted by rapid burst of high frequency brain waves
may be important for learning and memorization
NREM: stage 3 sleep
deep sleep
lowest frequency - 3hz
highest amplitude delta waves
individuals do not feel refreshed if woken up during this stage
REM sleep
rapid eye movement
brain waves similar to when awake
no voluntary muscle movement
learning and memory
REM rebound: induvial with lost rem sleep will spend more time in this stage
freud on dreams
dreams access the unconious
gain insight into problems in life
manifest content
content and storyline of a dream
freud
latent content
hidden/implicit meaning of a dream
freud
collective unconscious
symbols in dreams similar for all people regardless of culture or location
Rosalind Cartwright: dreams
dreams simply reflect important life events to dreamer
Alan Hobson
activation-synthesis theory of dreaming
brain trying to synethsize/make sense of neural activity during REM
Lucid dreaming
aspects of wakefullness maintained in a dream state
person is aware they are dreaming and can control the content
insomnia
long delayes between bed time and sleep
person may wake up
3x a week for a month
anxiety, tiredness
treatment to insomia
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
stress management
medication
limit stimulant drugs (caffine)
should seek professional help
sleepwalking-somnambulism,
complex behaviors when asleep
wandering to driving
common during slow wave sleep
treatment success is questionable
REM sleep behavoir disorder (RBD)
muscle paralysis dosent occour in REM sleep
high lebels of phsycial activity during sleep, disturbing dreams
kicking, punching, scratching, yelling
degenerative diseases: Parkinsons
treated w anti anxiety meds
restless leg syndrome
uncomfortable sensation in legs when falling asleep
relived by moving legs
assosiated with kidney diseases and diabetes
night terrors
senese of panic accompanied by screams or trying to escape from enviroment
no reccolection of events
occour during NREM
sleep apnea
breathing stops for 10-20 seconds, increase fatige
common in overweight people
loud snoring
obstructive sleep apnea: airway blocked during sleep
central sleep apnea: disruption in signals sent from brain that regulate breathing cause periods
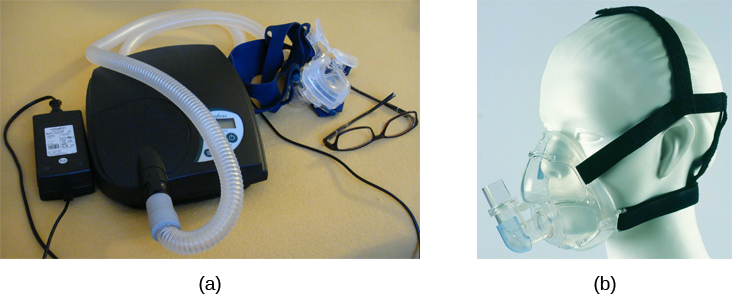
continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP)
treatment for sleep apnea
mask over nose
pumps air into persons airways, forcing them to remain open
SIDS: sudden infant death syndrome
breathing stops infant dies
under 12 months boys higher risk
risk factors: premature birth, smoking, hyperthermia
infants should sleep on back
Narcolepsy
person falls aleep whenever
reduced levels of hypocretin in brain
cataplexy: muscle weakness/paralysis
triggered by arousal, stress, excitemnet
treated with stimulant drugs
Physical dependence
bodily functions changes
withdrawl
eg: needing za to sleep
psychological dependence
emotional dependance to drug
use to relieve psychological distress
tolerance
linked to psycological dependance
needs more druh to acheive same experince
can lead to dangerous intake/death
withdrawl
negative symptoms when not using drug
withdrawal from sedatives= unpleasant agitation/arousal
can develop tolerance and withdrawal from NOT abused drugs
DSM-5
substance use disorder as a compulsive patter on drug use
types of stimulants
cocaine, amphetamines
Adderall
MDMA
increased heart rates, alertness, death
types of sedative-hypnotics: depressants
alcohol
barbiturates
benzodiazepines: xanex
decreased heart rate, relaxation, memory loss, decreased heart rate, death
types of opiates
opium, heroin, fent, morphine, oxy, viocdin, meth and other pain relivers
decreased pain, pupil constriction, decreased respitory (can lead to death)
sleepiness, euphoria
types of hallucinogens
marijuana
LSD
peyote
DMT
ketamine
mild to intesne perceptual changes based on drug
depressants
depressant: alcohol
suppresses central nervous system activity
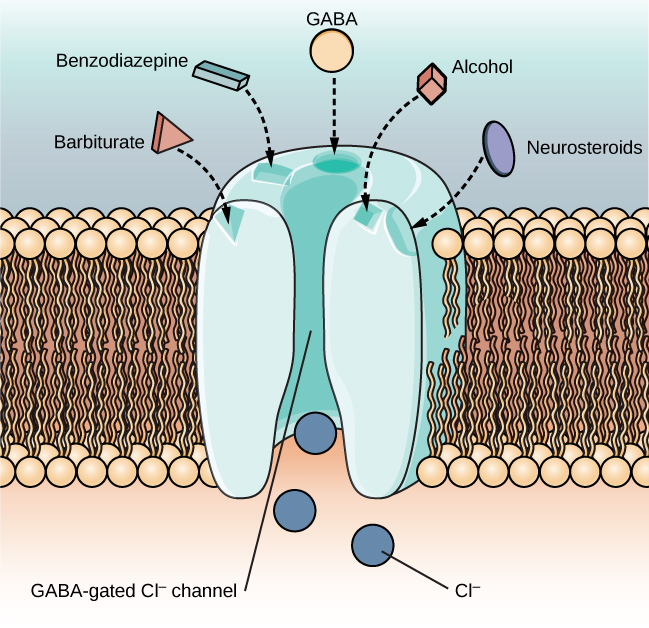
agonists of the gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter system
has a quieting effect treating anxiety
binding of depressants in GABA-fated Cl- channel allows negatively charged chloride ions into neurons cell body. pushes neuron away from firing= quieting effect on brain
fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD)
pregnant person consuming alcohol
baby born with a cluster of birth defects
stimulants- Amphetamines
MDMA, nicotine, caffeine, bath salts
increase levels of neural activity
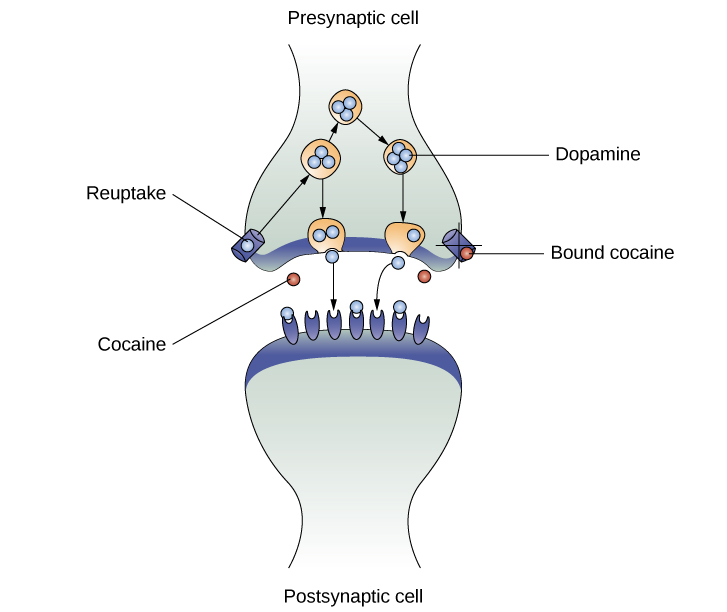
agonists of dopamine neurotransmitter system, blocking reuptake of dopamine in neuronal synapse
prescribed for ADHD
caffine
increase alertness
antagonizing adenosine activity
neurotransmitter that promotes sleep
Nicotine
highly addictive
interacts with acetylcholine receptors
neurotransmitter in motor neuron, plats a role in arousal and reward mechanisms
hypnosis
state of extreme self-focus and attention, minimal attention is given to external stimuli
can be used to enhance memory, skill, alter thoughts/perception of patients
helps depression, anxiety and smoking cessation
Patient must be relaxed and open to hypnosis
meditation
focusing on a single target (breath or sound) to increase awareness of the moment
goal is a relaxed awareness and focus
helps reduce blood pressure, stress, sleep, mood, anxiety
methadone
synthetic opioid that is less euphorigenic than heroin- used to manage withdrawal symptoms in opiate users
parasomnia
one of a group of sleep disorders characterized by unwanted, disruptive motor activity and experiences during sleep
sensation
when sensory information is detected by a sensory receptor
transduction
The conversion from sensory stimulus energy to action potential
Absolute threshold
the minimum amount of stimulus energy that must be present for the stimulus to be detected 50% of the time
how dim can a light to be detected 50% of the time
strong enough to excite sensory receptors and sense nerve impulse to brain
subliminal messages
a message below the threshold for consious awarness
controversy about messages in music, advertising etc
just noticeable difference/ difference threshold
how much difference in stimuli is required to detect a difference between them
changes depending on stimulus intensity
eg: changing volume of music until able to hear the difference in volume
perception
the way sensory information is organized, interpreted and consiously experinced
bottom up processing
sensory information from a stimulus in the environment driving a process
uses data to interpret new meaning
eg: hearing a glass breaks causing analysis
eg: learning a new word with no knowledge of that
top- down processing
knowledge and expectations driving a process
based on prior knowledge
eg: understanding a word despite a typo, as long as the first and last letter are the same
sensory adaptation
not perceiving stimuli that are present for extended peroids of time
eg: not seeing your nose because your nose blocks it out
eg: not hearing a fan after some time
attention
plays a key role in determing our perception from our enviroment
eg: tuning out the music at a party when talking to a friend
eg: gorilla experiment with ball

Inattentional blindness
failure to notice something that is visible because the person was not paying attention
experiment: not seeing a car cut you off in traffic because you are texting
signal detection theory
ability to determine a stimuli when it is embedded in a distracting environment
eg: mother hearing quiet murmur from baby but not other sounds when she is sleeping
eg: detecting a siren in a busy street
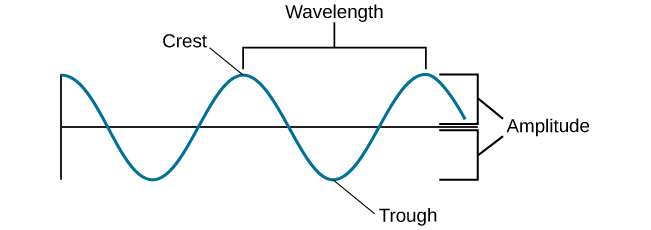
amplitude
distance from center line to the top/crest OR center to bottom/trough
wavelength
length of a wave from one peak(crest) to the next

frequency
number of waves that pass a point in a given time
expressed in hertz (hz)
longer wavelength: lower frequency
shorter: high frequency
visible specturm
portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans can see
wavelenghts from 380 to 740nanometers
honeybees can see light in ultraviolet waves
snakes can see infared
light waves
for humans: assosiated with perception of colour
red is longer wavelength- violet is shortest
soundwaves
frequency of a sound is associated with the sounds pitch
high frequency= high pitch, low freuq= low pitch
audible range of sound is 20 to 20,000 Hz
chickens have limited audible range from 125 to 2000hz
sound volume
loudness is associated with amplitude of sound wave
high amp= loud sounds
loudness measured in decibles (dB)
typical conversation= 60dB
concert = 120 dB
timbre
a sounds purity affected by frequency, amplitude, and timing of sound waves
cornea
transparent covering over the eye
involved in focusing light waves that enter the eye
pupil
small opening in eye which light passes through
size can change due to amount of light
dialted pupil= less light
constricted pupil= lots of light
iris
controls the pupils size
the coloured part of the eye
lens
after light passes into pupil, it does into the lens
can change shape to aid in focusing light from near or far objects
lens focuses images in the back of the eye- fovea
fovea
part of the retina- light sensitive lining of the eye
contains photoreceptor cells (cones): light detecting cells
cones
specialized types of photoreceptor cells
bright light conditions
provide spatial resolution and ability to perceive color
type of photoreceptor
low/dim light conditions
perception of movement
night blindness: if rods do not transform light into nerve impulse effectively
optic nerve
axons from the retinal ganglion cells converge and exit through the back of the eye to form the optic nerve
carries visual information from the retina to the brain
blind spot
point in visual field we cannot see
optic chiasm
optic nerves from each eye merge below the brain in the optic chiasm
information from right visual field is sent to the left vise versa
visual processing inside of the brain
sent to the occipital lobe for processing
what pathway: object recognition and identification
where/how pathway: location in space and interaction with visual stimulus
trichromatic theory of colour vision
all colours in spectrum created by combination of red, blue and green