Chapter 14-Therapies
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Psychoanalysis
A method of therapy developed by Freud that asserts clinical symptoms are from unconscious conflicts rooted in childhood
Psychodynamic approaches
Approaches that derive from psychoanalysis
less frequent/intensive
face-to-face
relief from symptoms & insight
Interpersonal therapy (IPT)
Focuses on helping clients improve their current relationships
Humanistic approaches
approaches that center around the idea that people must take responsibility for their lives and actions
Client-centered therapy
Assumes everyone has a tendency toward growth which can be facilitated through acceptance and being genuine from the therapist
Motivational Interviewing
A brief, non-confrontational therapy meant to change specific problematic behaviors
Gestalt therapy
Help patients integrate inconsistent aspects of themselves into a whole by increasing awareness
challenging the client and working through how they act in situations
Behavioral approaches
eliminate unwanted behaviors
promote desired behavior
lower unwanted emotional responses
Exposure therapies
Type of behavioral therapy, helps clients face their fears
In Vivo
facing a fear in real life
Behavior modification techniques
Behaviors can be reinforced (type of behavioral therapy)
Token economy
positive behaviors are rewarded with literal tokens/objects
Ex. star chart
Contingency management
uses rewards/positive behaviors to incentivize behavior
Ex. recovering addicts receive rewards for hitting milestones
Cognitive approach
A family of therapeutic approaches based on the idea that maladaptive behaviors arise due to errors in thinking
Rational emotive behavior therapy
therapist behavior changes patients irrational belief
Cognitive therapy
Change patients habitual modes of dysfunction about themselves, their situation, and their future
Negative cognitive triad
A model of depression that describes the negative thoughts and beliefs that people feel about themselves and the word
negative views of the world
negaitve views of themsleves
negative views of themselves
Cognative restructiuring
Techniques for changing a person’s maladaptive beliefs or interpretations
Cognitive behavior therapy
Focuses on changing patients habitual interpretations of the world and ways of behaving
“New wave” therapies
focus on acceptance and commitment, mindfulness
Typical Antpsychotics
Blocks dopamine
lowers positive schizophrenia symptoms
Tardive dyskinesia
Atypical antipsychotic
block dopamine more selectively
alter serotonin transmission
Serotonin
Happiness and mood regulation
Dopamine
Temporary sense of pleasure, reward, and motivation
Norepinephrine
Regulates stress reactions, arousal, attention
Antidepressants- Early
Monoamine Oxide Inhibitor (MAOI)
breakdown of dopamine, serotonin, Norepinephrine
Tricyclic antidepressant
blocks reuptake of serotonin and Norepinephrine
Antidepressants-later
Selective serotonin Reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
Prozac, Celexa, paxil
Serotonin and Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI)
Effexor
“Atypical antidepressants”
Norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor
Reuptake inhibitor
Prevents reabsorption of neurotransmitters, increases levels and makes them more avaliable for body use
Mood stabalizer
Manic, mixed, and depressive states, used to treat bipolar disorder
Anti-Anxiety medication
Anxiolytic
Benzodiazepine
beta blocker
Anxiolytic
Drug that alleviates anxiety symptoms
Benzodiazepine
Facilitates inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA
addictive
rebound effect
Beta blocker
controls autonomic arousal
Psychosurgery
surgical destruction of specific brain areas
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
using small electrical currents to induce a brief seizure in the brain to treat mental illness
Deep brain stimulation
implanting small electrodes in the brain as an attempt to treat mental illness
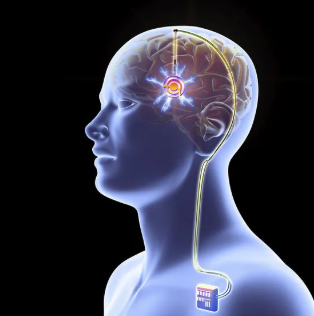
Vagal nerve stimulation
electrically stimulating the vagal nerve with a small battery powered implant
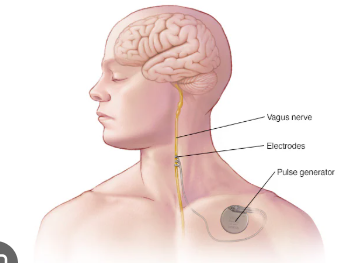
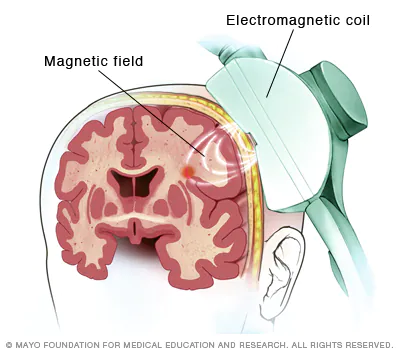
Repetative Transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS)
using magnetic pulses to treat conditions
Dialectic behavior therapy (DBT)
An electrical therapy for treating BPD that involves elements of cognitive, behavioral, humanistic, and psychodynamic approaches