Micro: Production externalities
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:38 AM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
1
New cards
When do negative externalities of production occur
When social costs (MSC) are greater than private costs (MPC)
2
New cards
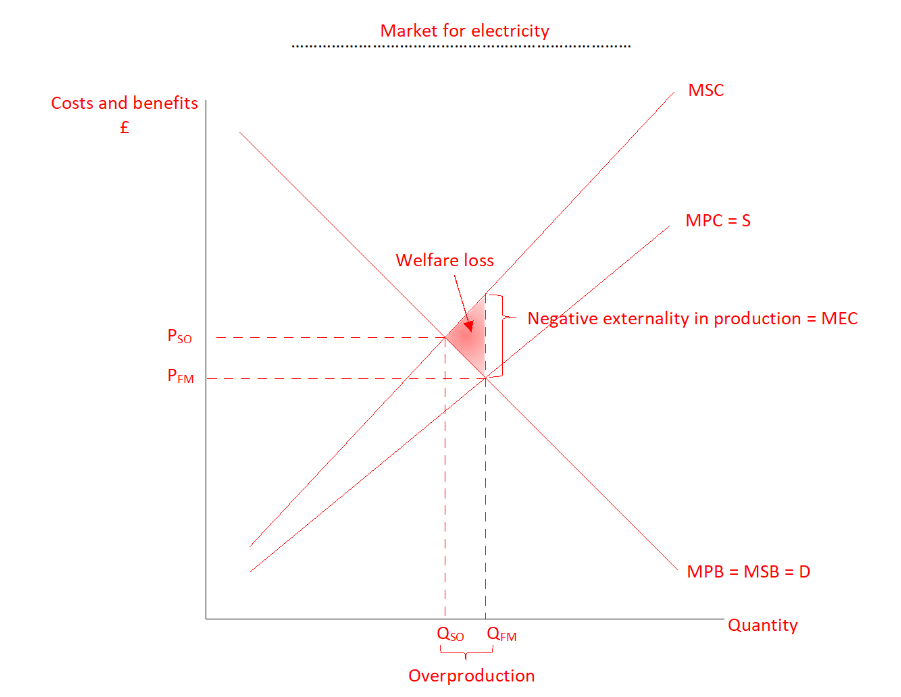
Model a negatuve externality in production
3
New cards
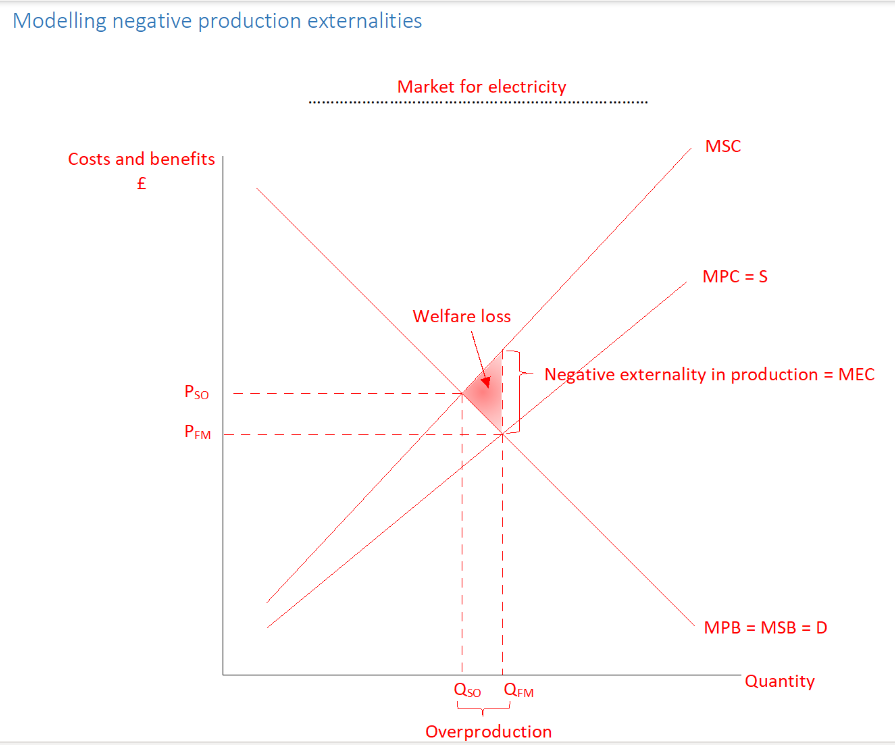
Where is the free market equilibrium
S=D, MPC=MPB, Pfm, Qfm
4
New cards
Where is social welfare maximised
MSC=MSB, Qso=Pso
5
New cards
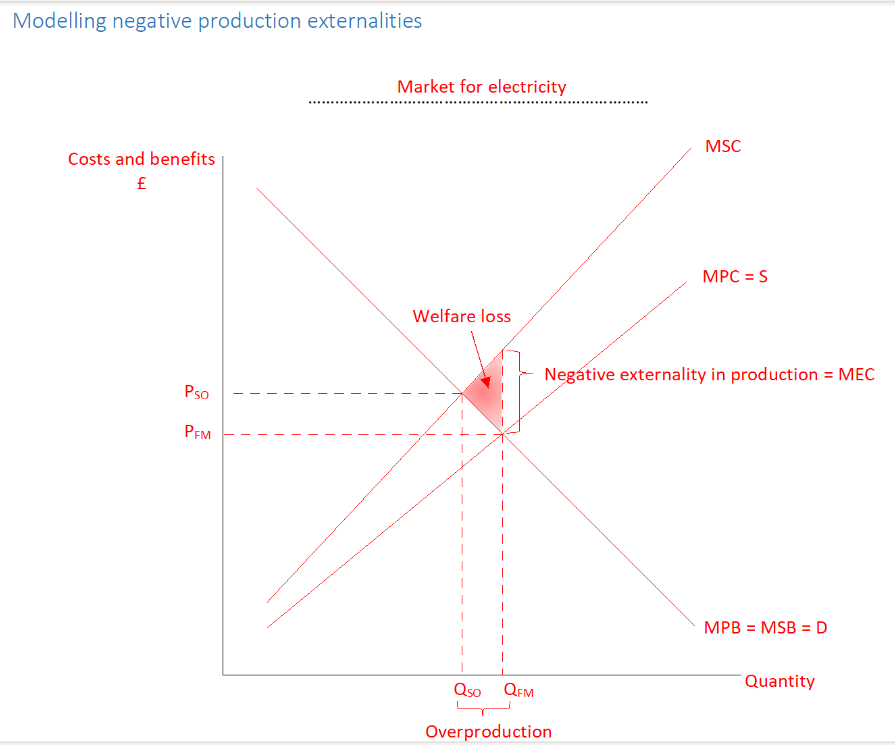
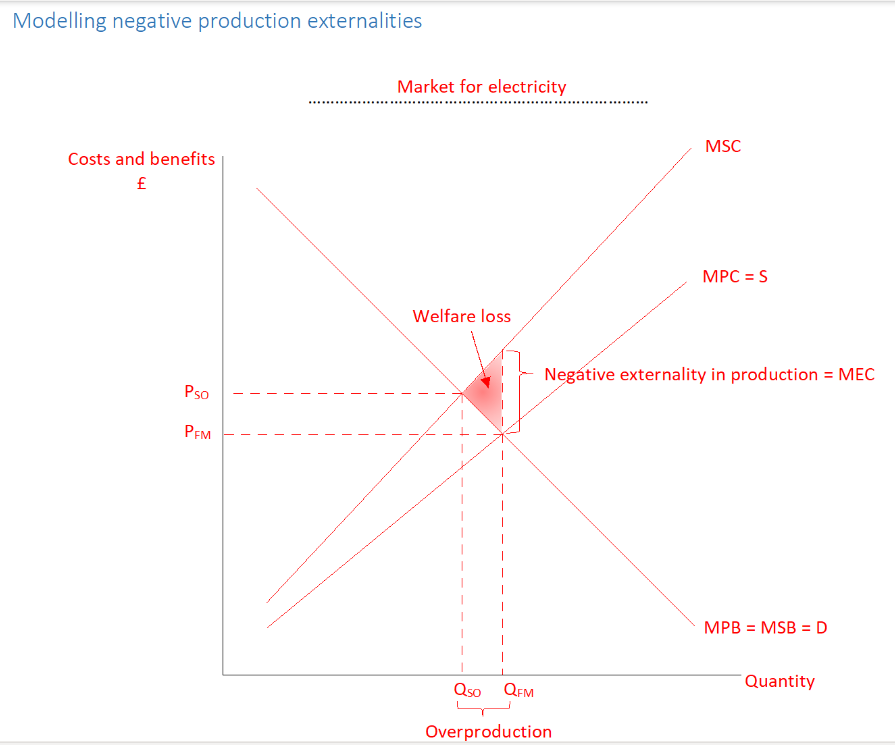
Why is there market failure with negative exteranilities in production
Market forces results in too much electricity being produced (Qfm-Qso), electricity becomes too cheap (pso-Pfm) to bring about socially optimum level of consumption
6
New cards
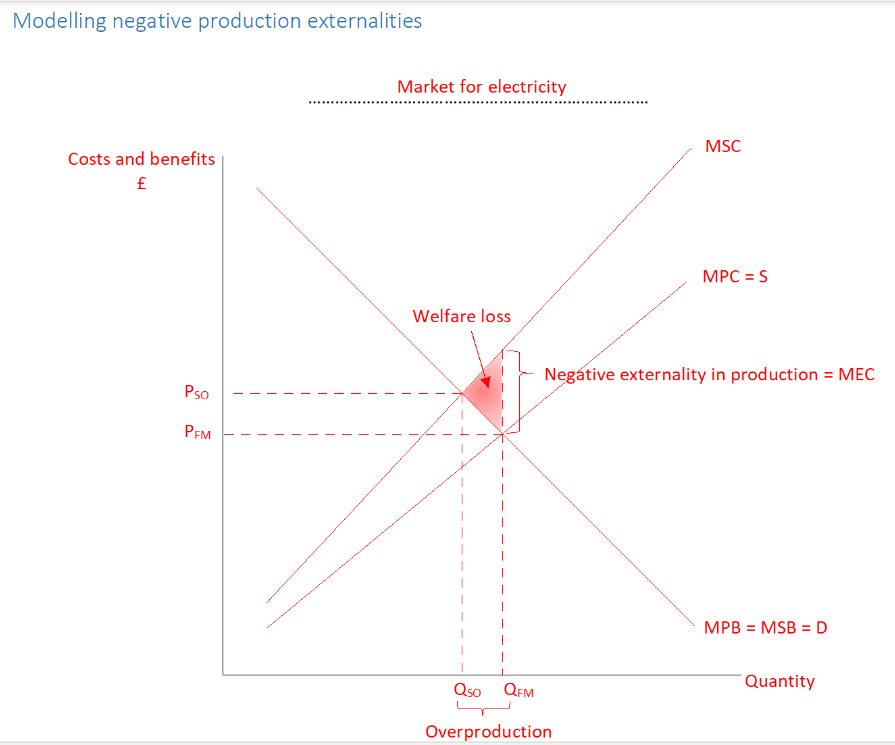
Why is there a triangle of welfare loss in negative externalities in production
for units of output Qso-Qfm, the social cost of producing each unit of electricity is greater than the benefit derives from each unit produced, society would be better off if these units weren’t produced
7
New cards
When do positive production externalities occur
When Private costs (MPC) are greater than Social costs (MSC)
8
New cards
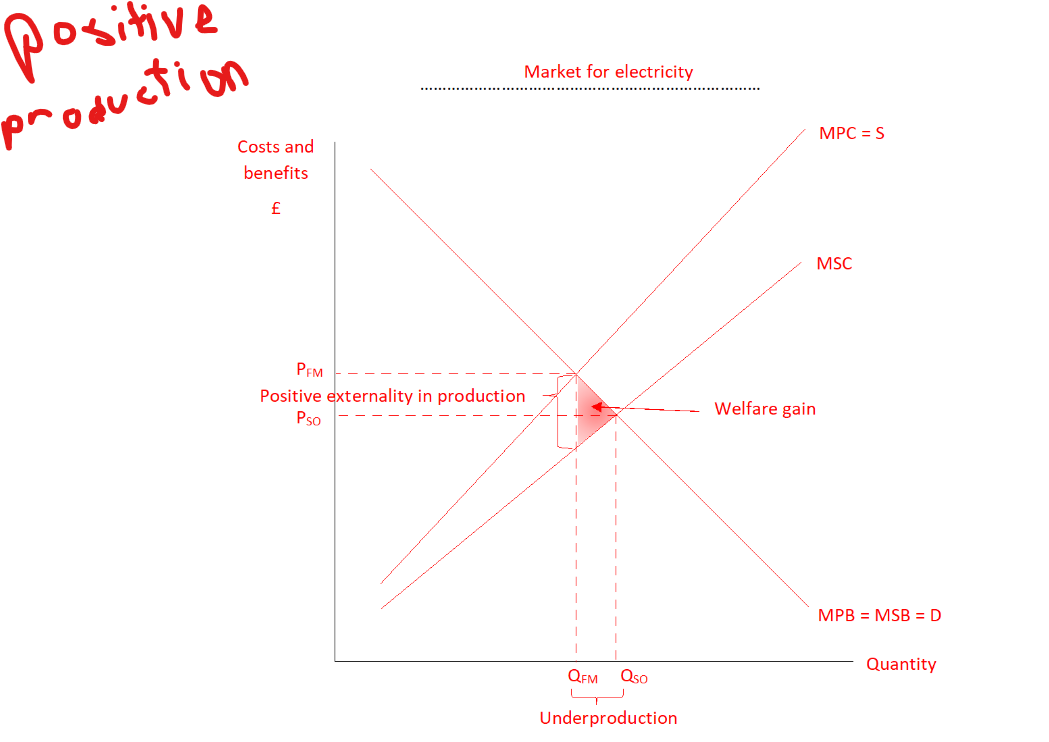
Model a positive production externality
9
New cards
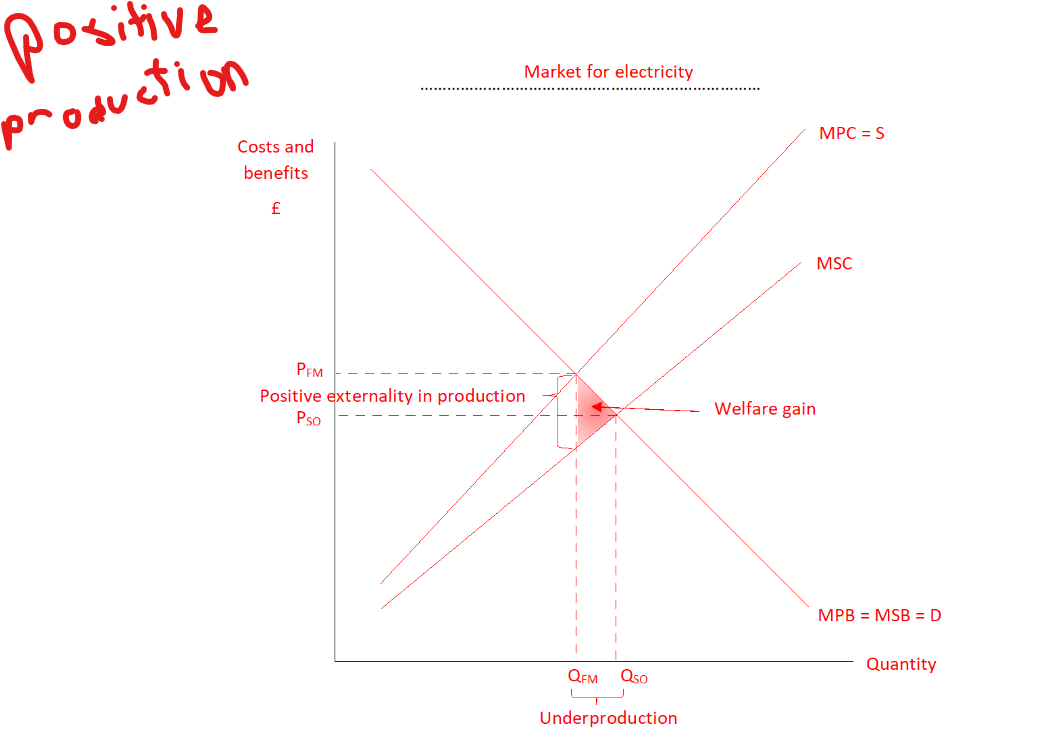
Where is the free market equilibrium in positive production externalities
S=D, MPC=MPB, Pfm=Qfm
10
New cards
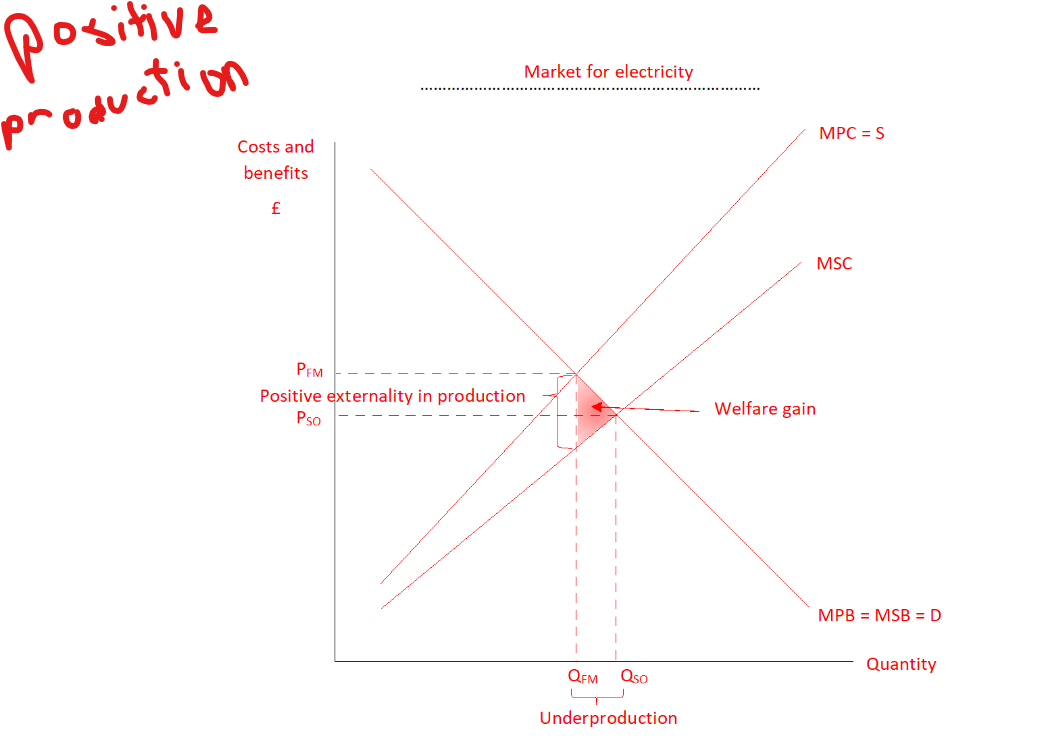
Where is social welfare maximised in a positive production externality
MSC=MSB, Pso=Qso
11
New cards
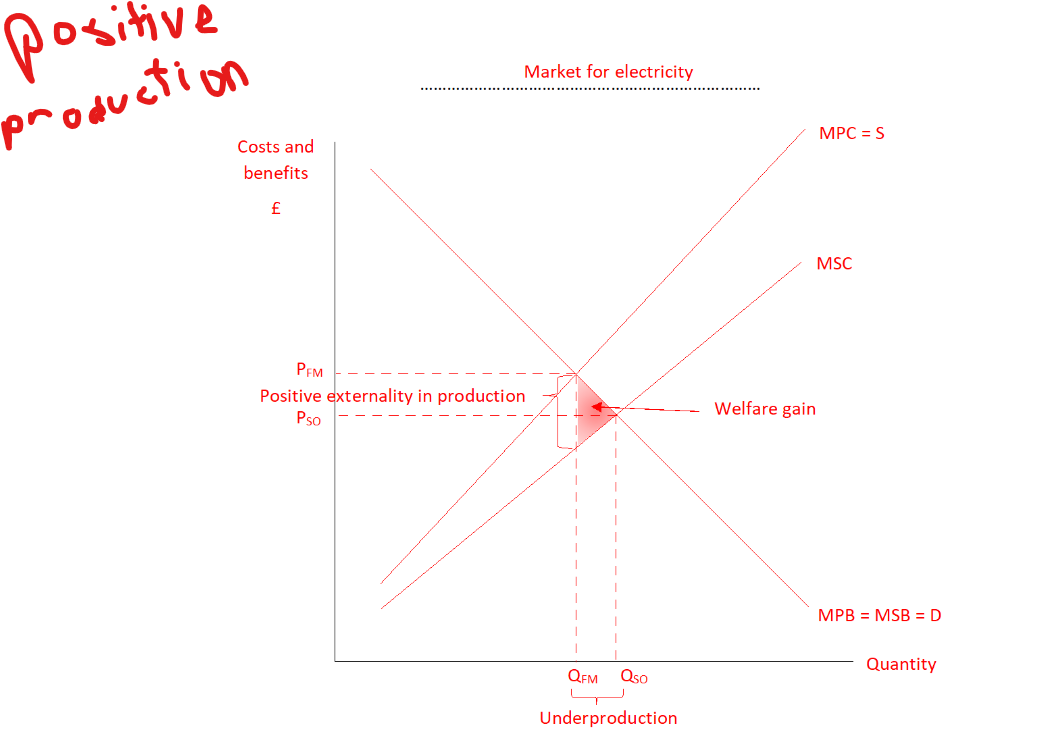
Why is there market failure in a positive production externality
Market forces result in too little electricity being produced (Qso-Qfm), electricity becomes too expensive (Pfm-Qso) to bring about socally optimum level of consumption
12
New cards
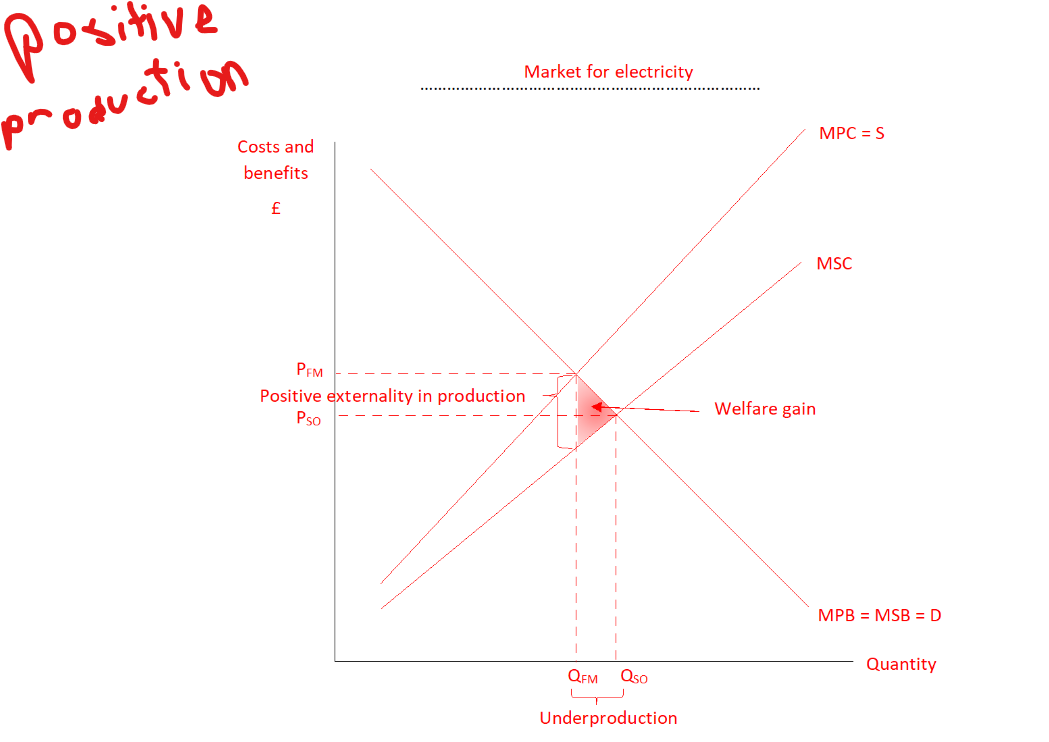
Why is there a triangle of welfare gain in positive production externalities
For Units of output Qfm-Qso the social benefit of producing each unit of electricity is greater than the cost society incurs from each unit produced, society would be better off if these units were produced.
13
New cards
Define externalities
third party spill over effect
14
New cards
Define government intervention
an action carried out by the government that affects the market with the objection of changing the free market equilibrium
15
New cards
Define market failure
when the price mechanism fails to allocate scarce resources efficiently leading to a net social welfare loss
16
New cards
Why are negative production externalities an example of market failure
true costs of production are under-reflected, leads to underpriced output, causes allocative function of prices to fall in that too much of good gets produced and consumed
17
New cards
Define an indirect tax
tax levied on the producers of goods and services
18
New cards
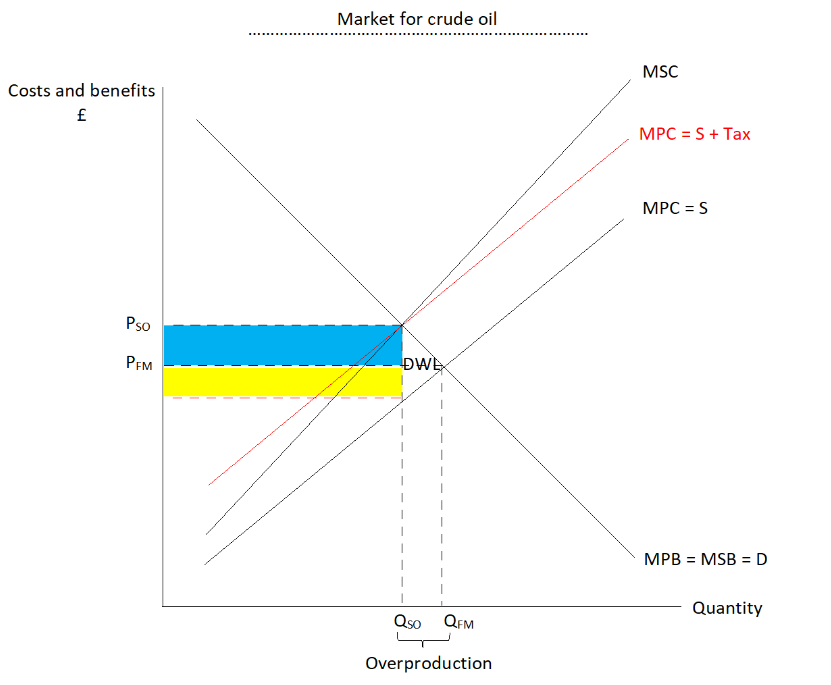
model an ad velorem tax on a negative production externality
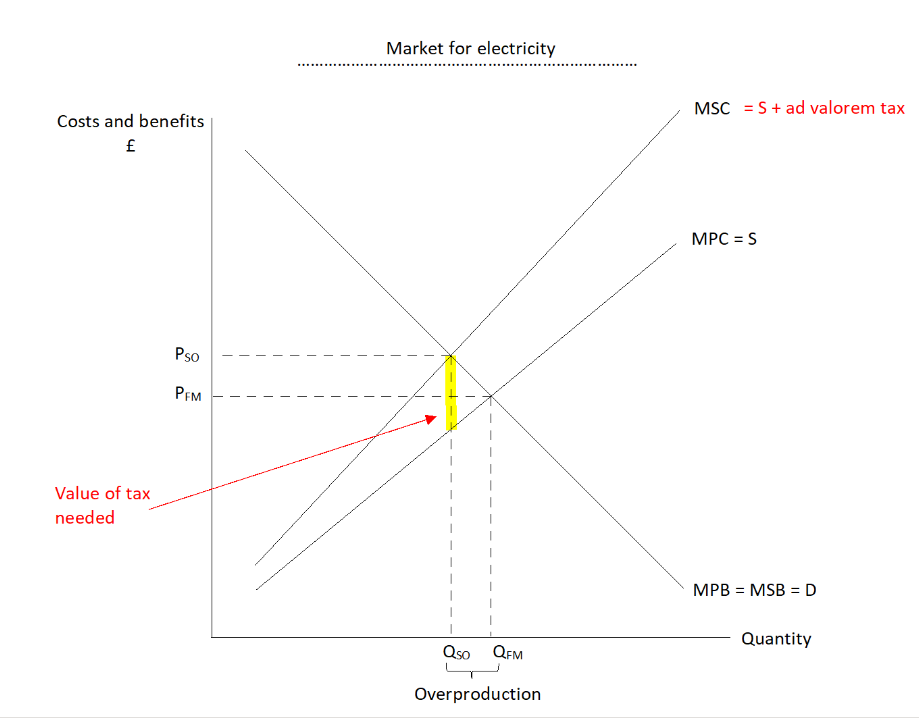
19
New cards
Model a direct tax on a negative production externality