Global test 2 Hammurabi's code - China
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Harappan civilization
Ancient settlements in the Indus River Valley (at a site known as Harappa)
Geography of the Indian Subcontinent
landmass with india pakistan and bangladesh
tall mountain ranges
desert to the east
narrow strip of tropical land along coast
monsoons flooding dry summer
Indus Vally Civilization
influenced an area larger then mesopotamia or Egypt
brick building built one a grid system
plumbing and sewage system
Two cities Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro
Aryans arrive in India
crossed into the inus river vally
Originallynomadic people who kept herds of animals (PASTORALISTS), but eventually settled down to farm.
created the vedic civlization
had rajahs as warior chiefs
Hinduism
from aryan costumes and oral traditions
not just a religion, it is a PHILOSOPHY OF LIFE, DEATH, SOCIETY, AND EXISTENCE
no single founder or single religuos text (closest to it is the vadas texts)
Brahman
Everything in the universe is part of the unchanging, all-powerful spiritual force
Vishnu
the preserver
Shakti
the female divine, who is believed to be ruthless against evil
Moksha
goal of life union with brahman
Dharma
the religious and moral duties of an individual
ahimsa
nonviolence main belief
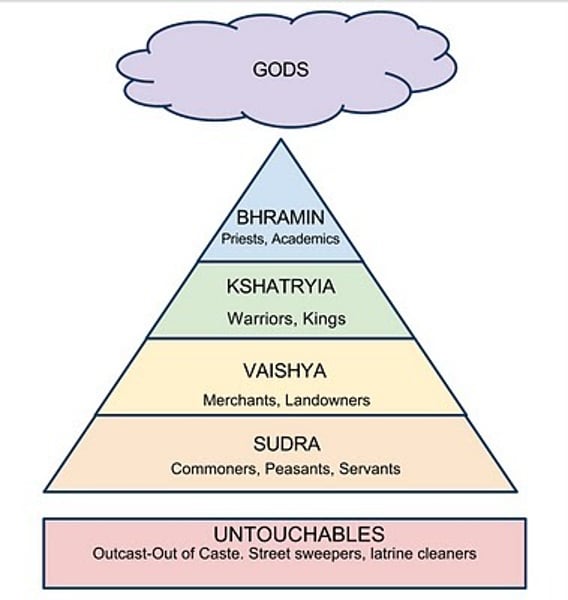
caste system
rigid social hierarchy
assigned everyone a place that you can't intermingle of leave
4 basic castes
Story of Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama was a real prince and heir to a throne in India in mid-500s BCE
He began to MEDITATE (engage in concentration, to think deeply) and sought ENLIGHTENMENT (higher knowledge than is found on earth
main principles of buddhism
physical world is an illusion
pain is cause by attatchment to this world
bodhi (wisdom) comes when you let go
nirvana state of enlightenment
rencarnation
4 noble truths
8 fold path
buddhism spreads
The Buddha garnered many followers throughout his life
After his death his followers collected his teachings into a sacred text called the Tripitaka, or "Three Baskets of Wisdom."
Missionaries and traders spread Buddhism across India to many parts of Asia. Gradually, Buddhism split into two major schools: Theravada (thehr uh vah duh) Buddhism and Mahayana (mah huh yah nuh) Buddhism
These schools became sects (or subgroups) of Buddhism
Ashoka empire
india was conqured at 3000 BC by CHANDRAGUPTA MAURYA
Strong central government
Well organized bureaucracy (System of government)
Strong army
Harsh rule
Secret police
Women warriors guarded his palace
King Ashoka
military leader
the emipire reached it peak
waged war
eventually became Buddhist
applied their principles of nonviolence and cooperation throughout his empire.
People of other religions were permitted to worship freely
Edicts of Ashoka
first translatable indian document
preached love and tolerance
carved onto stone piler in major cities
Fall of Asoka
after asoka died the rulers fought each other and were stupid causing 5 centuries of war
Geography of China
Isolated by natural barriers such as mountains deserts rain forest and oceans cause Ethnocentrism
Yellow River
started Chinease civilization flows West to East has loess (Fine windblown yellow soil) which caused it to overflow and people had to learn irragation
Shang Dynasty
dominated the yellow river vally
controlled northern China and fought off Nomads from the North Steppes and Western desert
Many accomplishments
writing
jewelry of wood, ivory, and jade
artisans used bronze
Ruled until 1122 B.C.E when they were overthrown by the Zhou
had clans that ruled were they didn't
Zhou Dynasty
the longest lasting Chinese dynasty, increased china's territories
Mandate of Heaven
divine right to rule
Religion in Shang Dynasty
afterlife
ancestors were venerated
ANCESTOR WOESHIP
spirits influnced life
Questions (and answers) to spirits were recorded on animal bones and tortoise shells known as ORACLE BONES.
Then, a hot poker would be thrust into the bone, and it would crack. Priests would "read" the cracks to divine (tell) the answers given by the spirits.
Dynastic Cycle
the rise and fall of dynasties
Rulers were good they kept the Mandate of Heaven
Rulers became corrupt or weak they lose the Mandate of Heaven
Replaced by another ruling family
Life in Zhou China
Feudalism
local lords controlled their own regions but owed military service to the ruler.
Production of food increased (terrace farming)
Coined money
Built roads and canals
Improved trade
Astronomers observed Halley's Comet, studied the movements of planets, and recorded eclipses of the sun.
Calendar- 365 and ¼ days
Bronze making
SILK
Warring States Period
time of warfare between regional lords following the decline of the Zhou dynasty in the 8th century B.C.E.
Confucius
born to a poor family
had a government job at 50 but lost it do to infighting
philosopher
Confucianism
focus on contemporary problems
ethical not spiritual issues
philosophy
5 basic relationships
taught in a time of turmoil and believed that leaders should do better and that government jobs should be allowed to be had by the poor
spread after his death
Chinese rulers would base their governments on Confucian ideas. The State Philosophy
Only scholars educated in Confucian thought could become government officials.
daoism
from the term path or way
dao controlled the universe
The Way of Virtue is the primary work expressing the Daoist understanding of the Way. The author was Laozi (LOW-DZUH).
we can begin to understand the Way by observing how nature works, though we must be careful not to impose human desires on our observations.
Legalism
Based on the teachings of Hanfeizi (Han Fei
rejected the Confucian idea that people would follow the example of a good ruler. Instead, he insisted that the only way to achieve order was to pass strict laws and impose harsh punishments.
philosophy
The nature of man is evil. His goodness is acquire
Qin Shi Huangdi
First Emperor of the Qin State
Conquered the other warring states
Unified China
Believed in Legalist Philosophy
shi huangdi as a ruler
Feudalism abolished
Noble families forced to live in the capital city
Land divided among peasants (though they had to pay high taxes)
Weights and measures were standardized to promote unity
Uniformity in Chinese writing
Workers repaired and extended roads and canals to strengthen the transportation system
Legalism
Teracotta Army
collection of seven thousand life-sized sculptures made from pottery in the tomb of Shi Huangdi that would help in the afterlife buried the workers alive so know one would know where it was
Great Wall of China
several walls joined along China's border
built be solider and convicts
for deafness
used by the military to communicate
fall of shi haungdi
death the dynasty struggled to keep control.
The policies of the dynasty were not well liked.
Han Dynasty in China golden age
centralized government.
golden age of china
Expansionism
policy of increasing the amount of territory a government holds
emperor wudi
expanded the empire, acquiring new lands.
Revival of Confucian learning
made Confucianism the official philosophy of his government.
adopted the idea that Civil Servants (Government officials) would gain their position through merit.
Meritocracy
government by people who show best effort and merit (as opposed to simply being born a royal or being a favorite of the king).
Silk Road
trade route
main traded item was silk
transported by camels
4000 miles
promoted cultural diffusion
land and sea
Golden age of china achievements
Advances in Science and Medicine
Acupuncture
Technology
PAPER
Population eventually reached 60 million
Salt and Iron were so valuable the government held a monopoly (complete control) on the production
how the government wanted people to assimilate
Move farmers to the newly conquered areas (and give them Confucian schooling)
Encourage intermarriage
Newly conquered people were also taught Chinese ideas and sent to Confucian schools.
social structure of han dynasty
1. emperor 2. local kings and governers 3. scholars 4 peasents and farmers 5 artisans and merchants 6 siolders 7 slaves
Fall of Han Dynasty
Warlords (local military rulers) gained power
Canals and roads fell into disrepair
A series of natural disasters
Once the fall of the dynasty occured China was no longer unified.
Unification lasted 400 years
Invaders from the north (over the Wall) created their own states
lasting impact of the han dynasty
Confuscian ideas within the government would last 2,000 years
he bar in which future dynasties would try to reach
Subcontinent
Land mass that is a distinct part of a continent
Monsoon
A seasonal wind.
SANSKRIT
Aryan's first writing system
Shiva
destroyer
Karma
the belief that all actions determine a person's fate in the next life
Hammurabi's Code
First written set of laws 282 laws split into criminal and civil laws
First Empire
Akkad
King Hammurbi
king of Babylon) got the Sumerian city-states under his control.
Nile River
flows south to north
floods
empties into a delta (triangular area of marshland formed by deposits of silt at the mouth of some rivers)
drinking water and food
irrigation
silt
transportation
led to Egypt becoming a nation
Upper and lower
regions of Egypt
Cataracts
Waterfalls in the Nile are called
Nation
a group of diverse people and places divided under one government
Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, New Kingdom
3 periods of eygpt
Dynasty
ruling family
Egypt government
1. pharaoh 2. vizier3. specfic departments 4. scribes
ra
sun god
osiris
god of the dead
Isis
goddes of motherhood and wives
Mummification
used to perverse bodies after death
Egyption Religion
polytheistic
pharaoh was a living god who would rule after death
pyramids were built for the pharaohs
Egypt social structure
1.Pharaoh
2.government offiacals (priests)
3. artisans merchants and scribes
4.peasants
Hyroglifics
writing system of eygpt
Papyrus
paper
astronomy in Egypt
12 months each 30 days
advancemnts of egypt
wriings
paper
astronomy
math
medicine
Atman
essential self
Fielial Piety
respect for ones parents above all else