Molecular Genetics in Non-Eukaryotes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
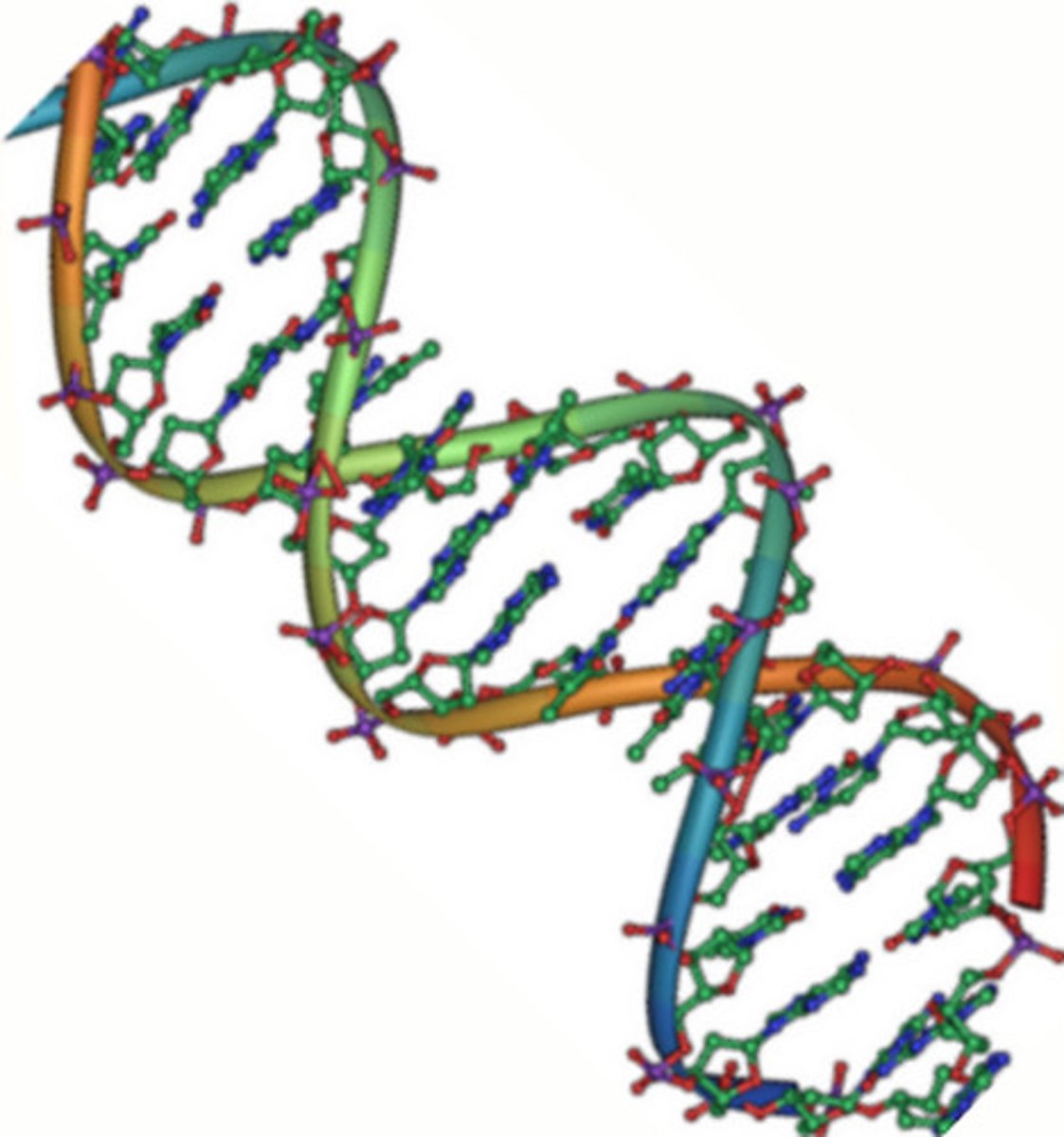
Which necessary part of a virus is RNA or DNA that can
be double or single-stranded?
nucleic acid
Which virus structure is a protein coat that encloses
the nucleic acid?
capsid
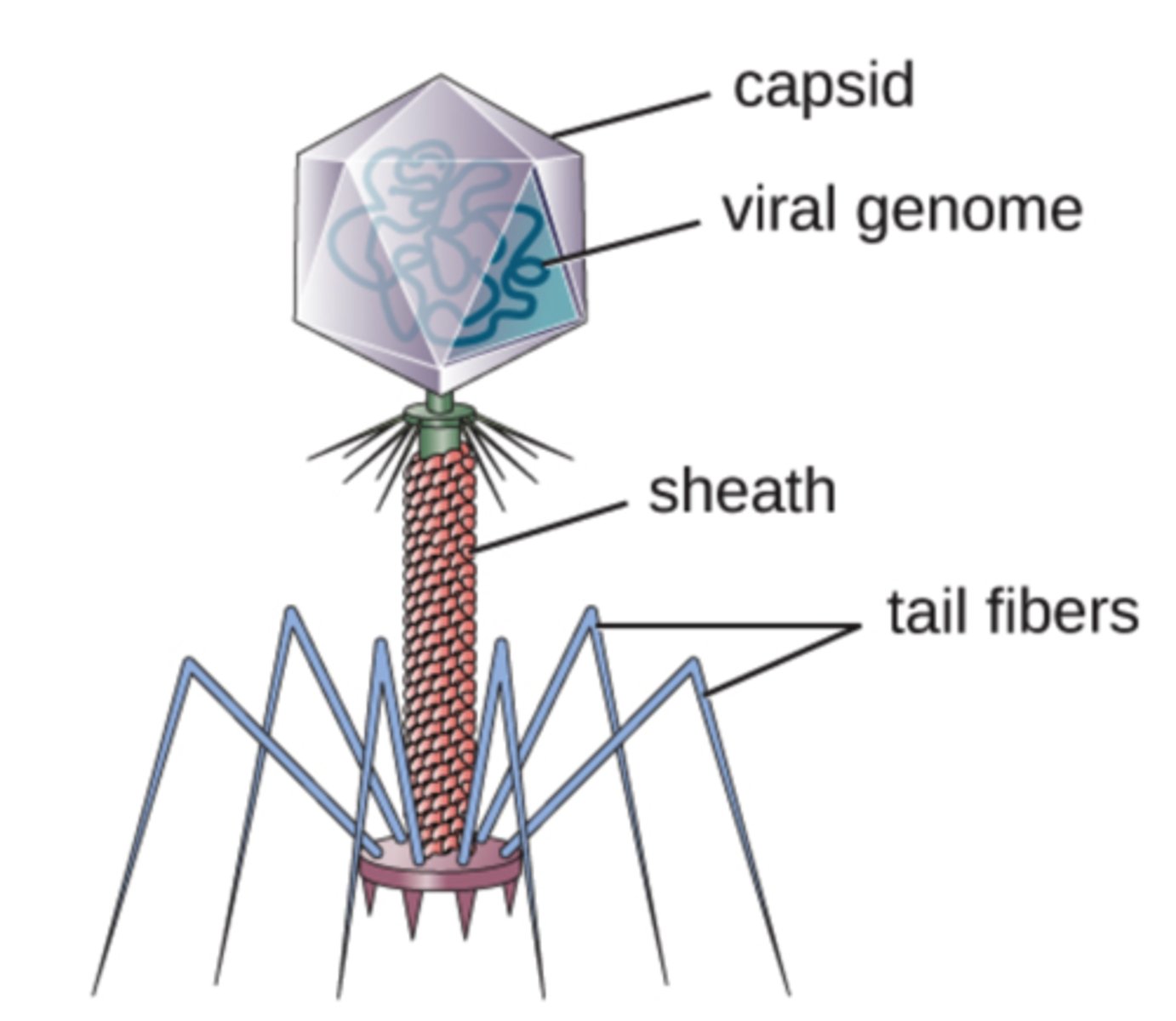
Which virus structures are proteins that are assembled to form the
capsid?
capsomeres
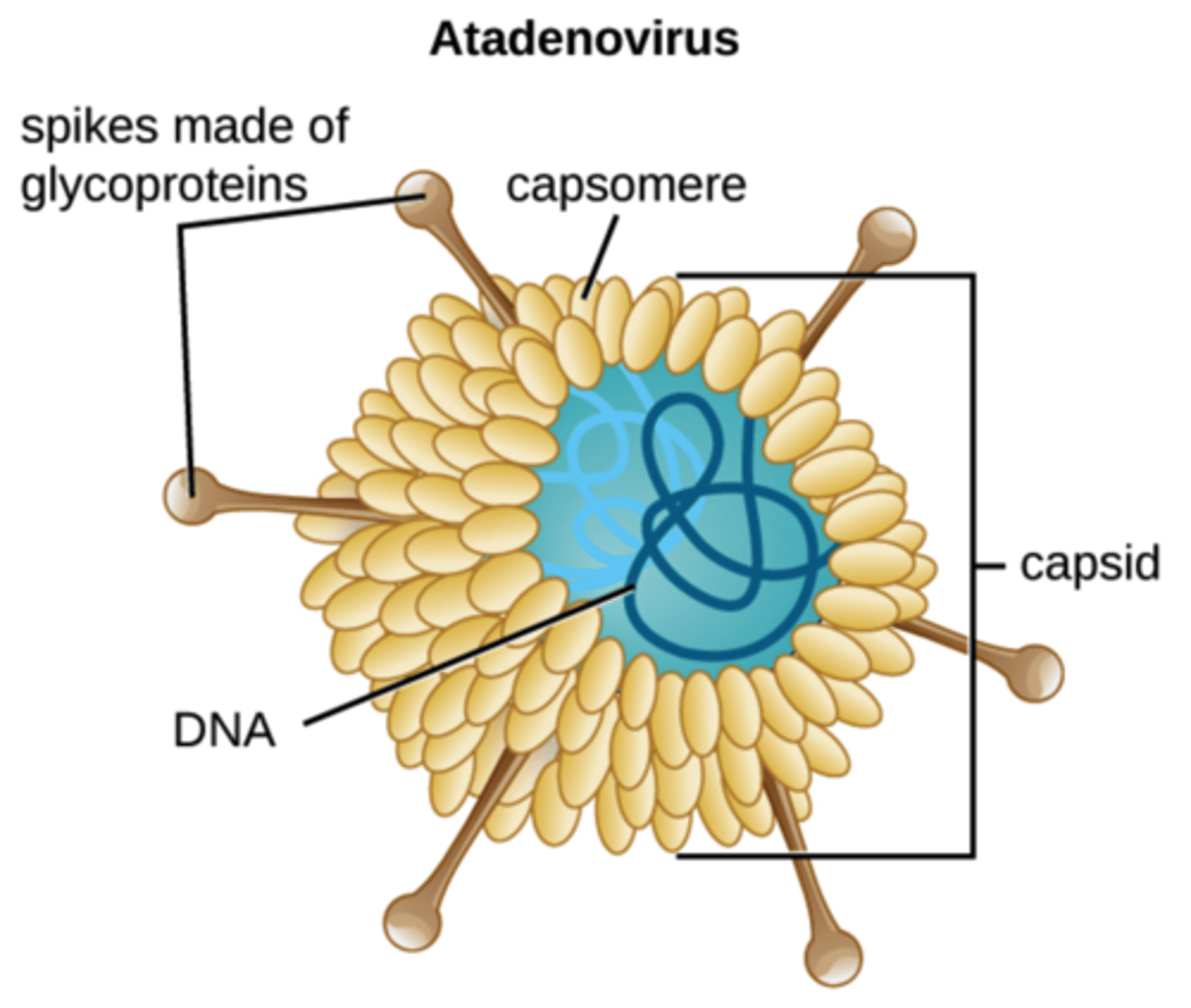
Which virus structure surrounds the capsids of some viruses?
viral envelope
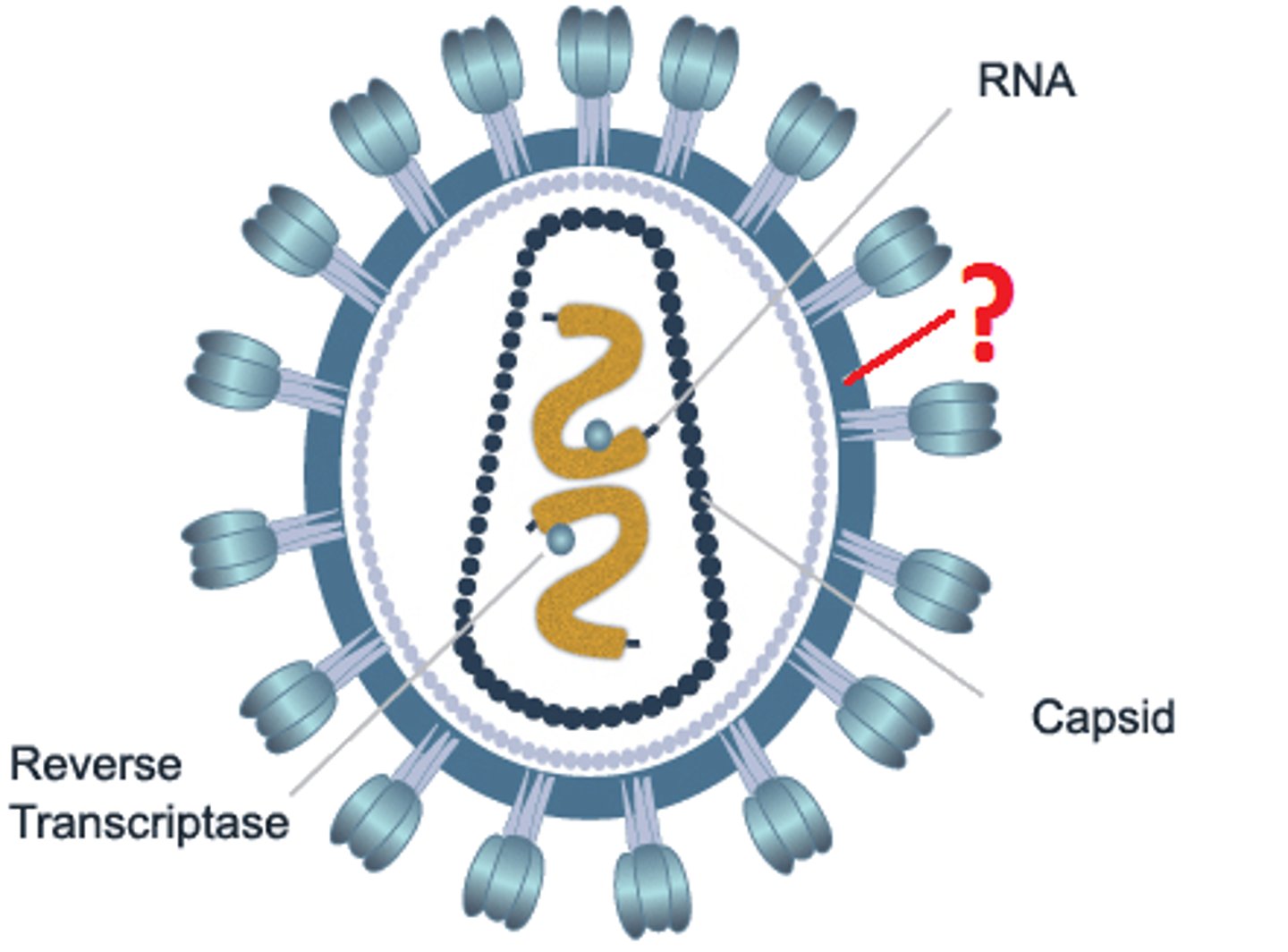
How are viral envelopes obtained?
a virus incorporates
phospholipids/proteins
from cell membrane of host
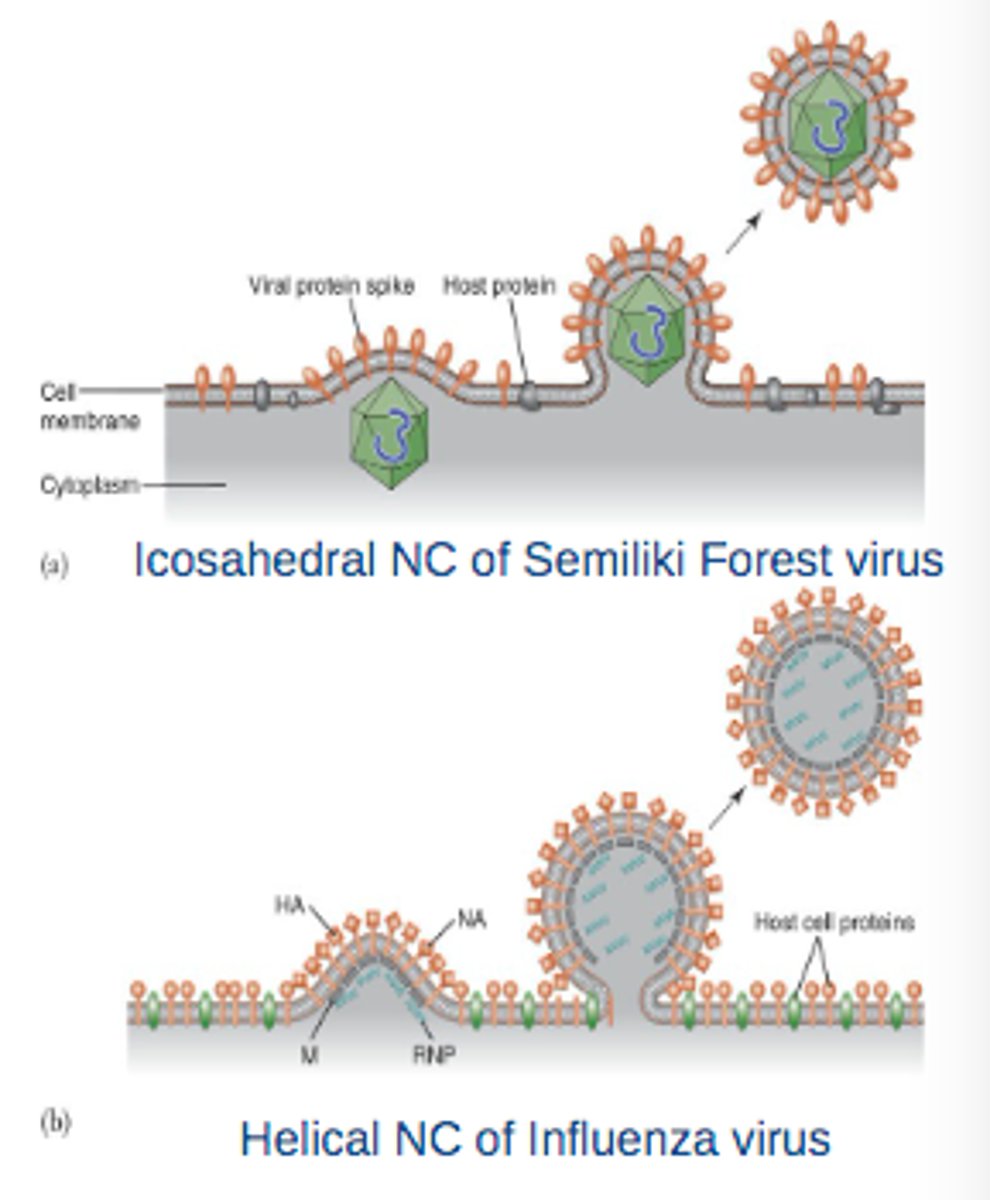
What is a virus that only attacks bacteria?
bacteriophage
What is a bacteriophage usually specific to?
a particular type of cell
What does a bacteriophage bind to?
host receptors
(Note: via viral surface proteins)
What is a term used to define the range of organisms or species a virus can attack?
host range
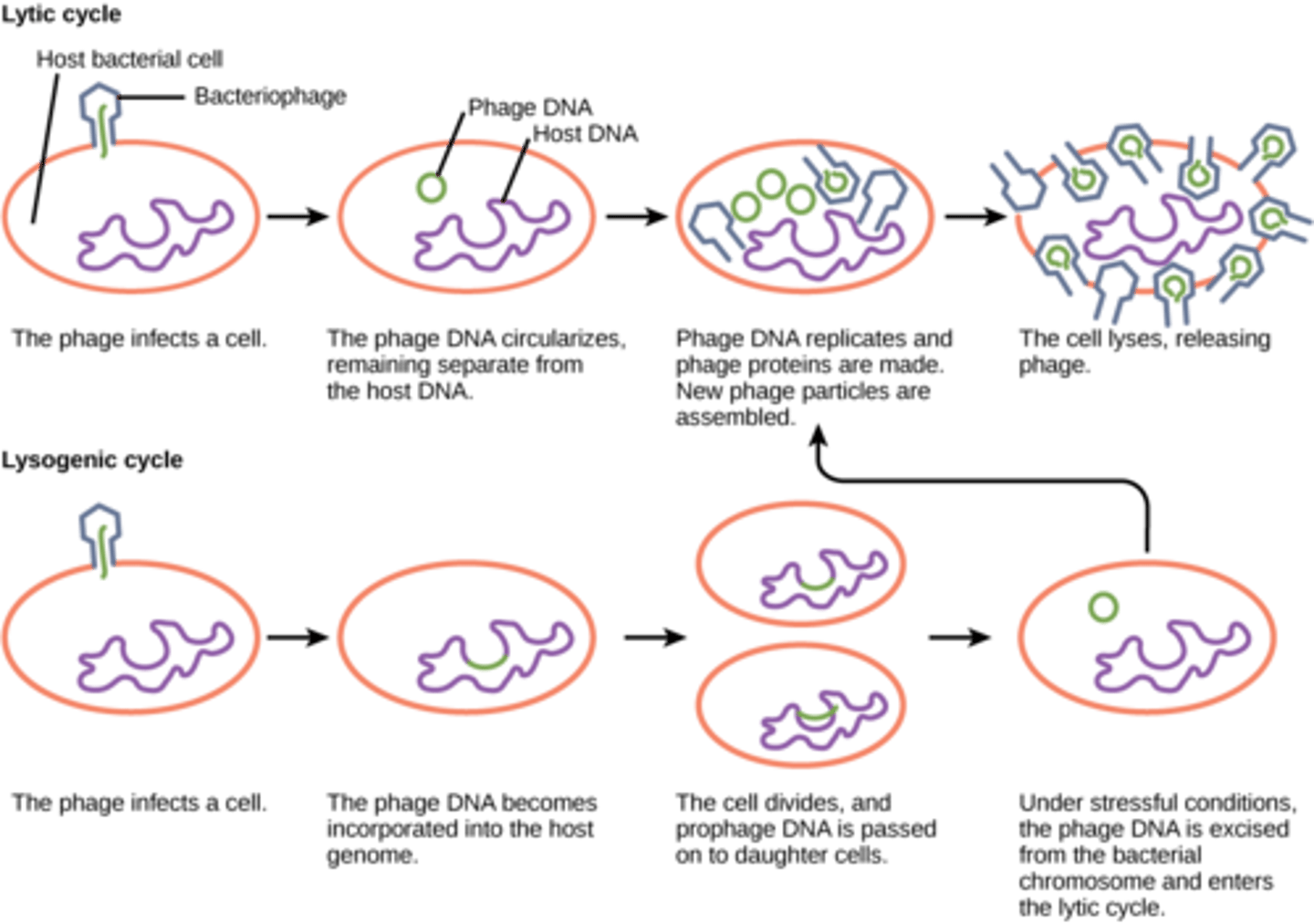
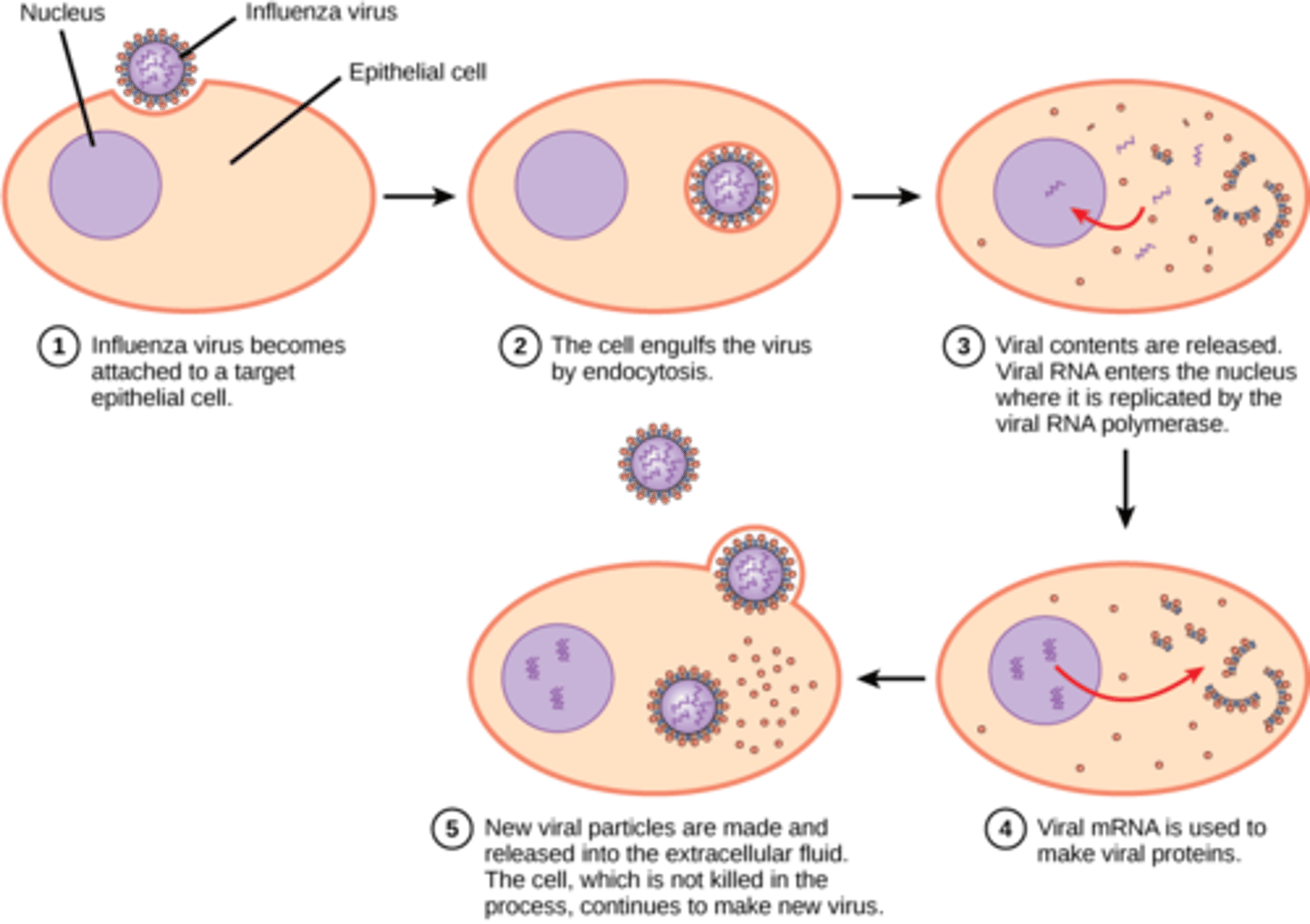
What viral reproduction cycle describes when a virus enters a cell, uses the host machinery to replicate, and bursts out of the cell?
lytic cycle
host machinery is used to create what building blocks of viruses?
nucleic acids and viral proteins
Which viruses replicate by first replicating DNA and forming new viral DNA?
DNA viruses
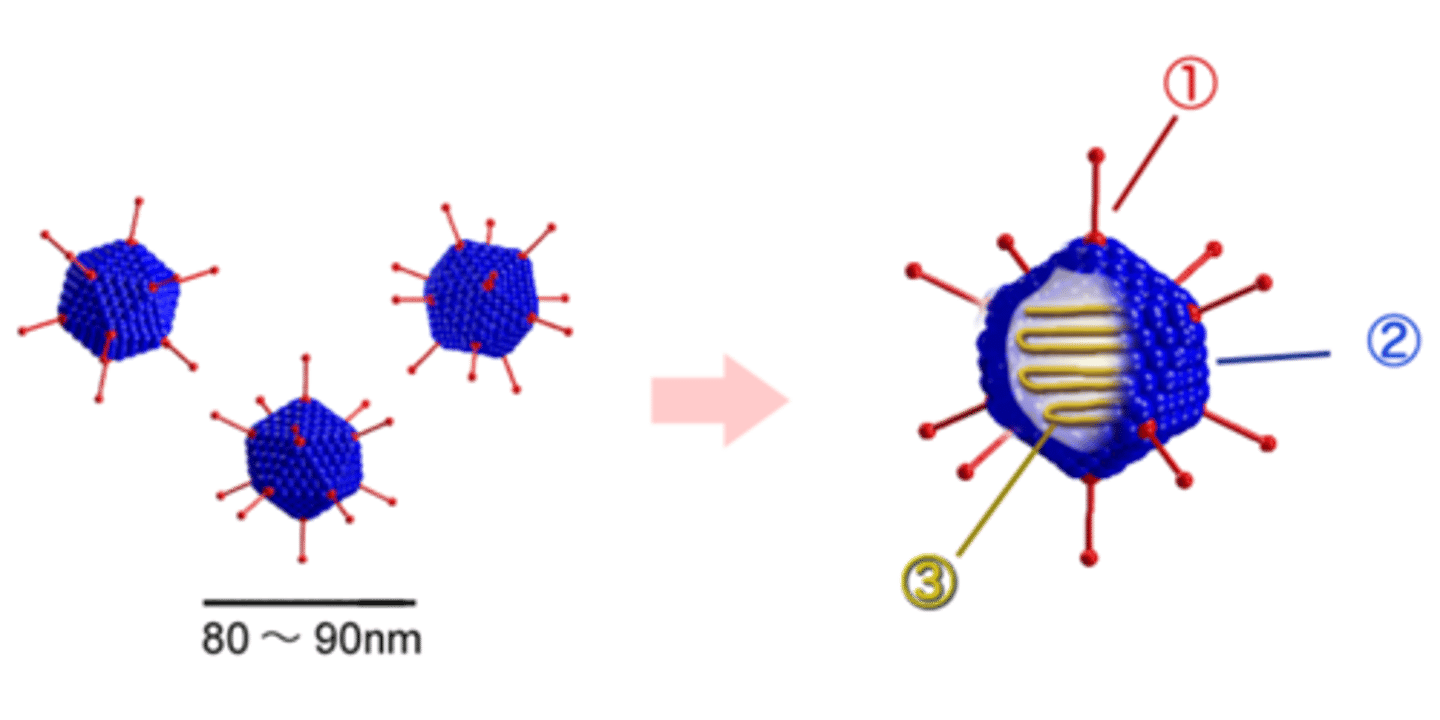
After DNA is replicated for DNA viruses, it is transcribed to make what molecules that combine with DNA to form new viruses?
viral proteins
Which virus contains RNA which serves as mRNA to be translated into proteins?
RNA virus
(Note: protein + RNA
assemble to form new
RNA viruses)
Which virus is a single-stranded RNA virus that uses reverse transcriptase to make a DNA complement of their RNA?
retrovirus
(Note: utilize host
replicating machinery)
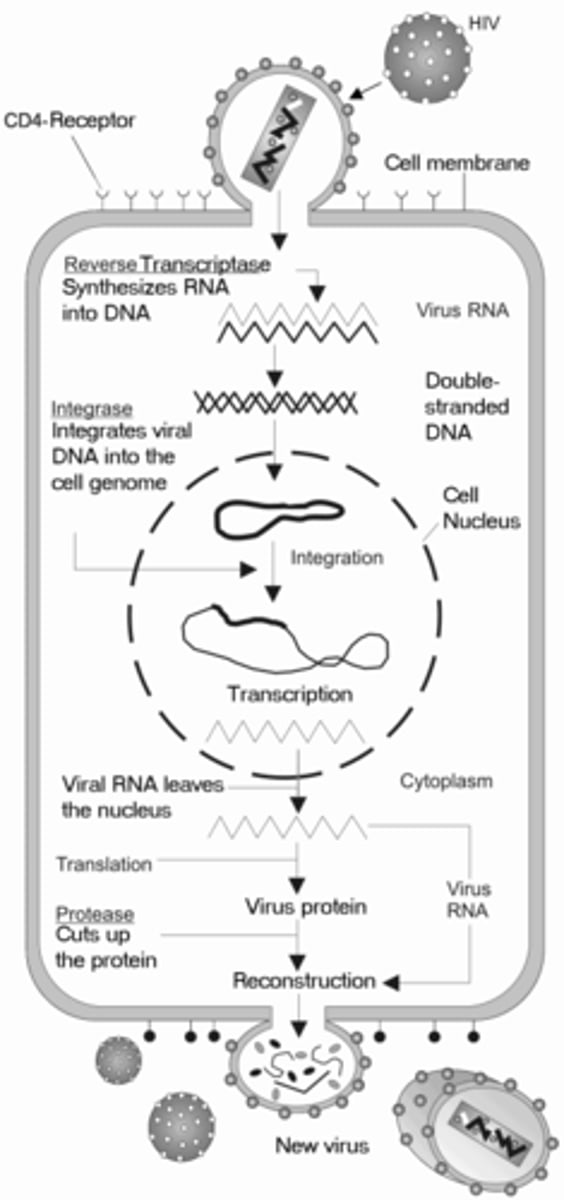
The DNA transcribed from retrovirus RNA can be used to complete which actions?
1. manufacture mRNA
2. enter lysogenic cycle
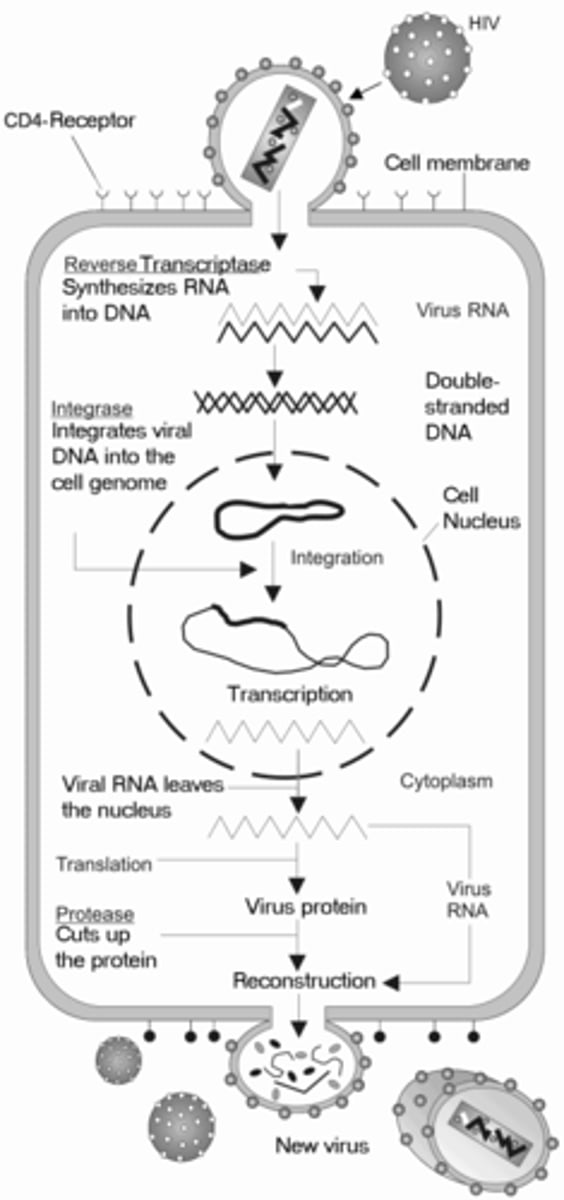
HIV is an example of which virus?
retrovirus
What viral cycle describes when viral DNA is incorporated into the DNA of the host cell?
lysogenic cycle
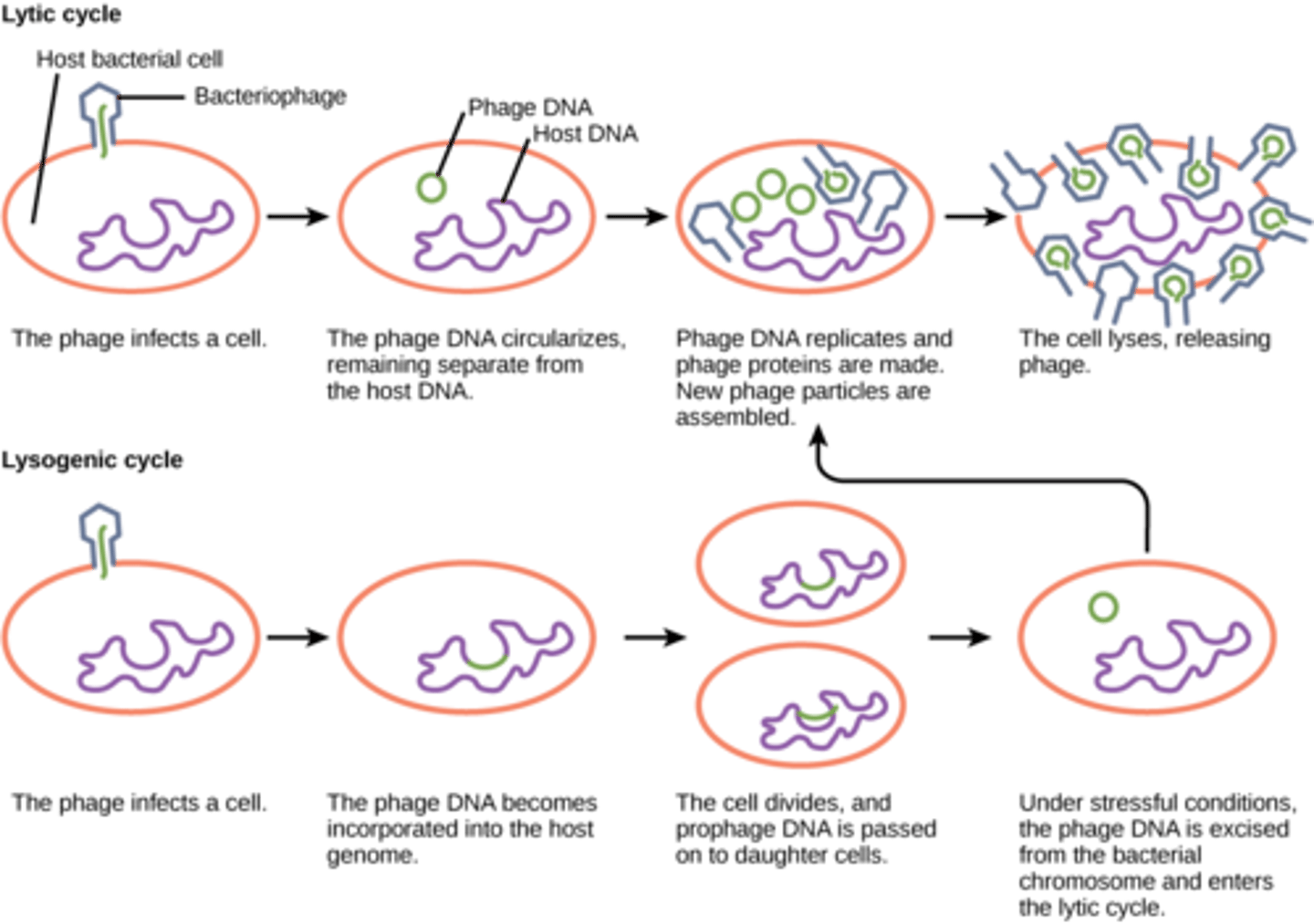
During which stage of the lysogenic cycle is the virus referred to as a provirus (prophage if bacteriophage)?
dormant stage
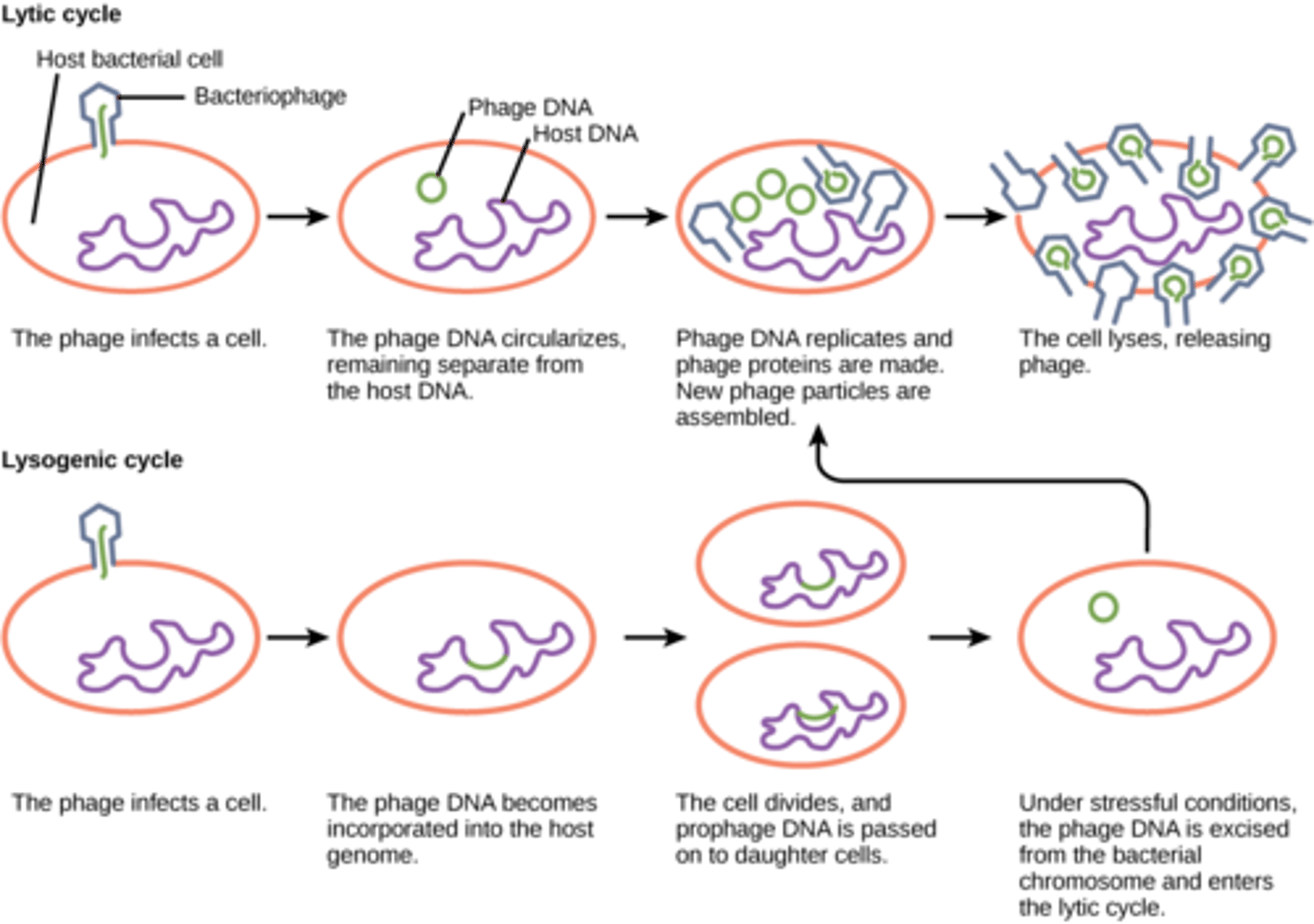
A virus in the dormant stage will remain inactive until what event?
external stimulus
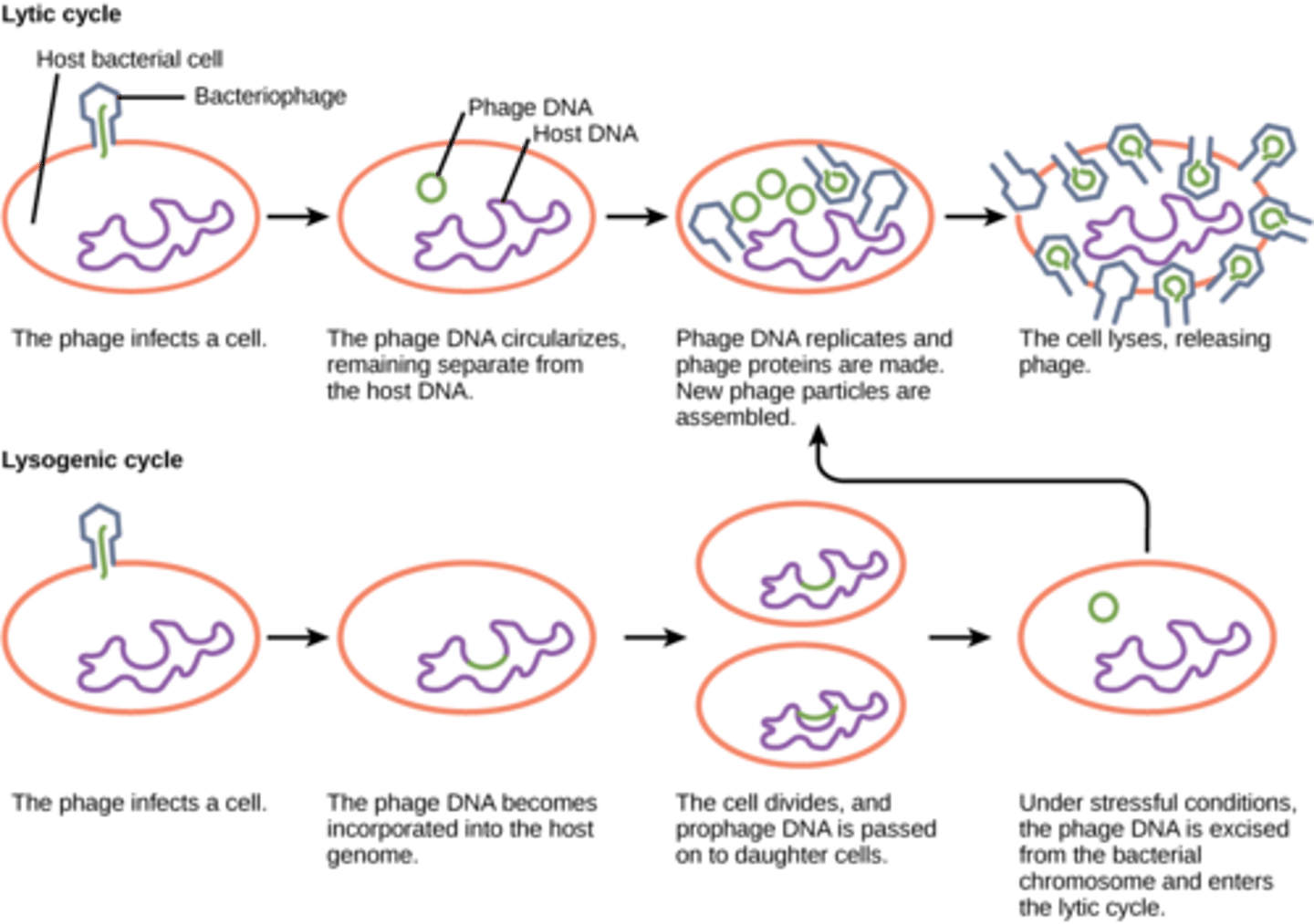
A virus in the lysogenic cycle will enter which cycle after receiving an external stimulus?
lytic cycle
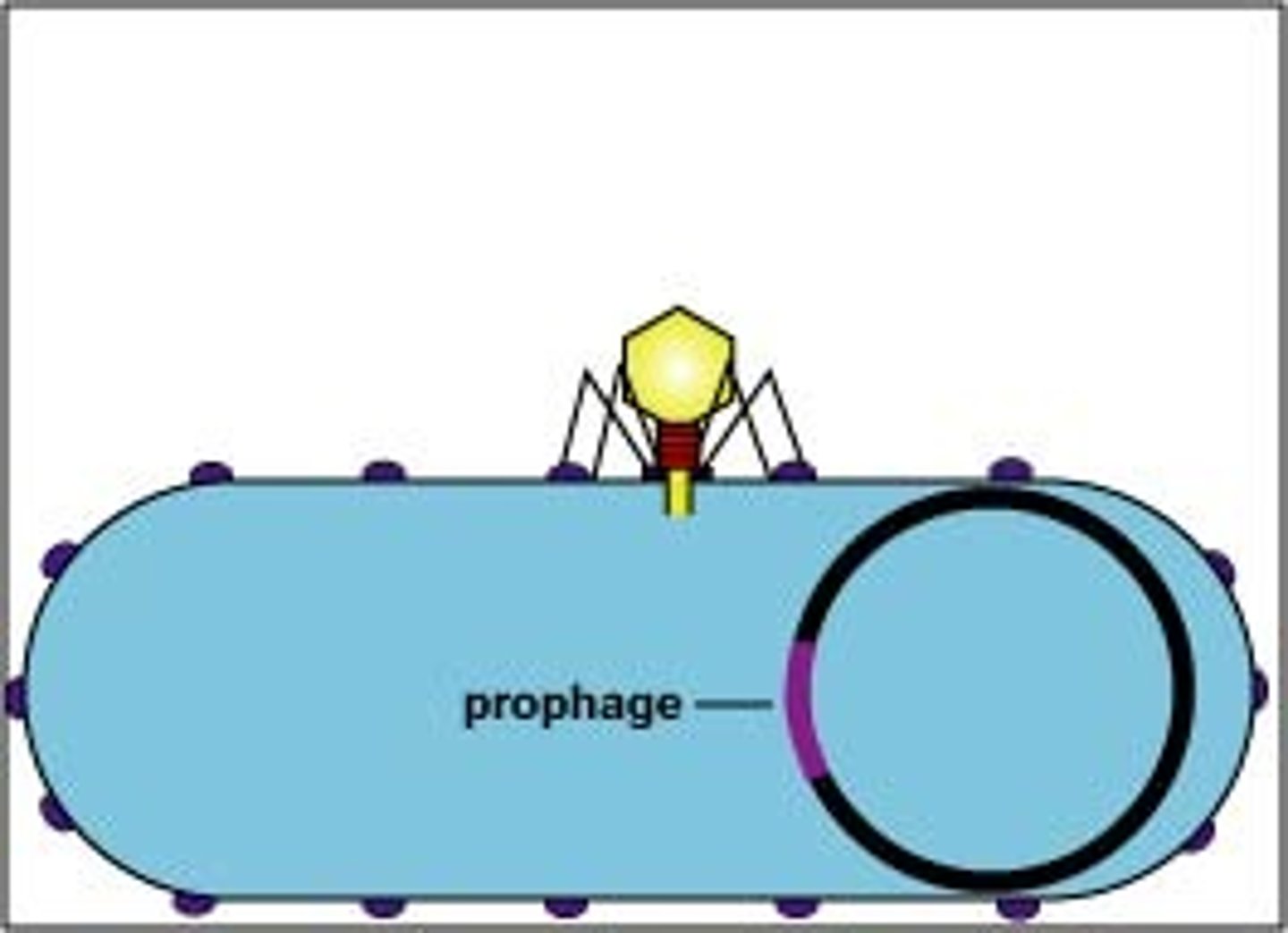
When a bacteriophage integrates itself into the host genome, what is it called?
prophage
(Note: not an episome!)
What are not viruses or cells, but are infectious, misfolded versions of proteins in the brain?
prions
(Note: prions are fatal)
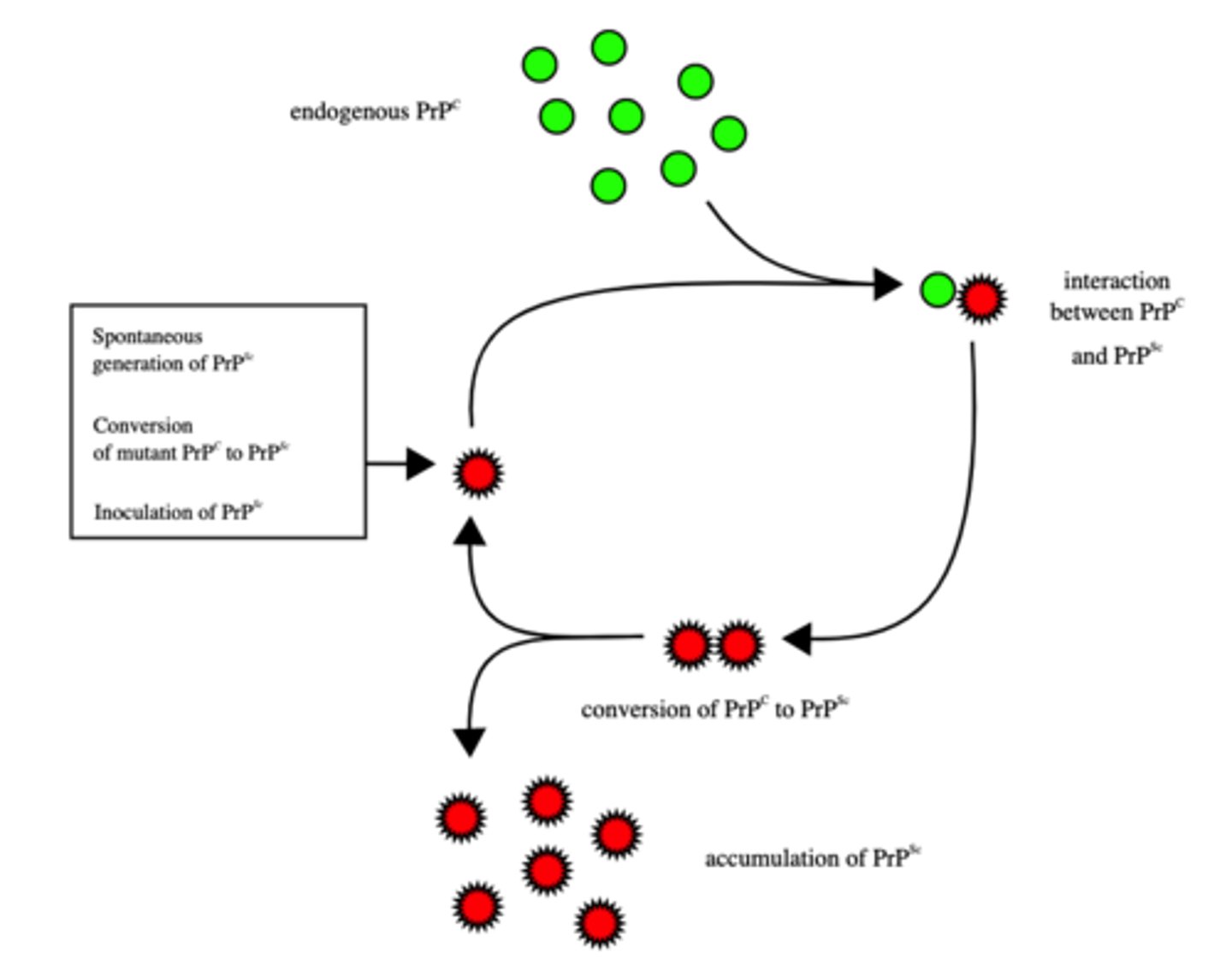
Prions have what effect on normal versions of proteins?
cause them to mis-fold also
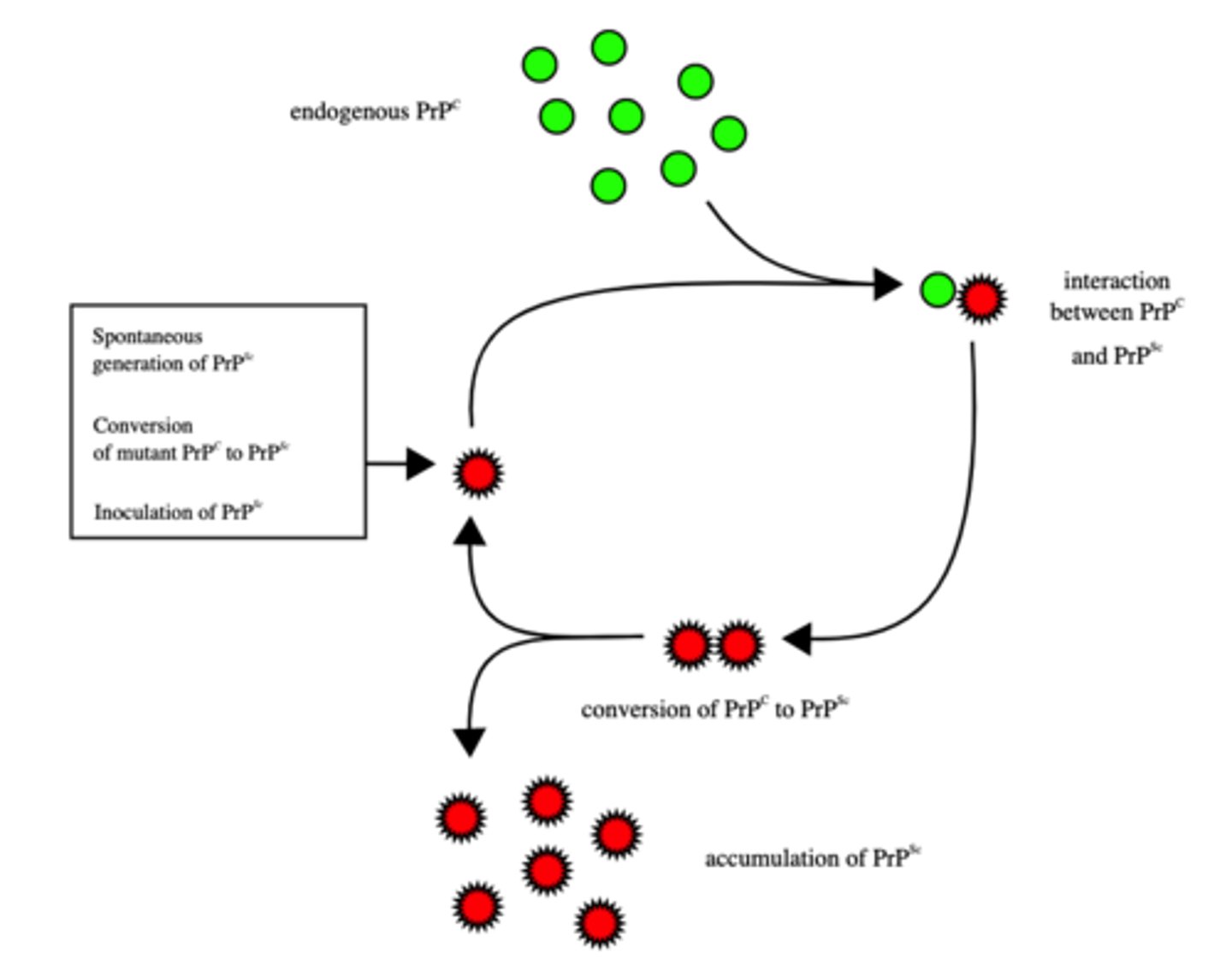
What are some common prion diseases?
1. mad cow disease
2. kuru
3. sheep scrapie
4. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
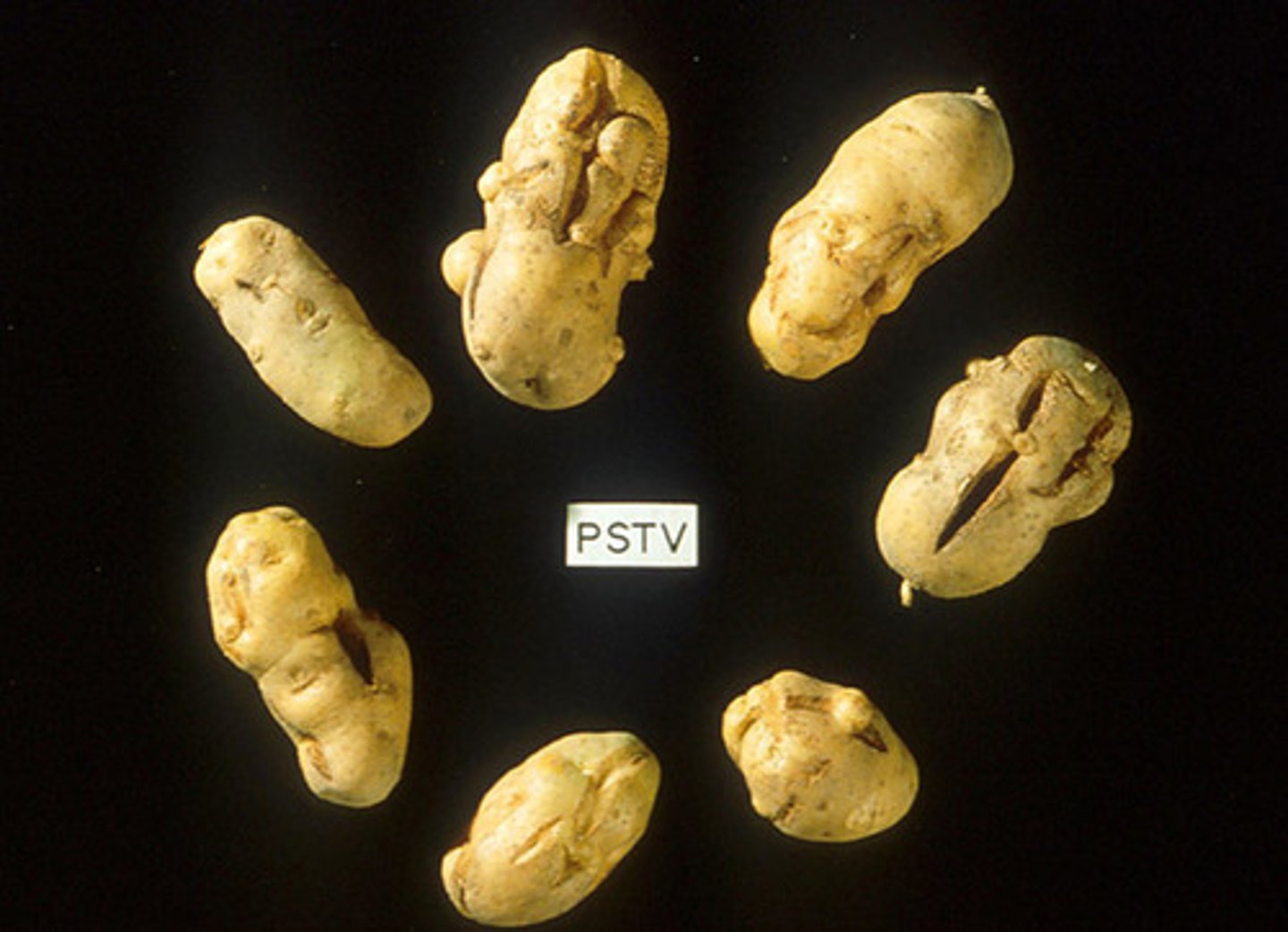
What are very small circular RNA molecules that infect plants?
viroids
(Note: even smaller
than viruses)

How do viroids replicate?
host enzymes
(Note: viroids do not encode for proteins)
What problems do viroids cause in plants?
cause errors in the
regulatory systems
of plant growth

What nucleic acid do bacteria possess?
circular,
double-stranded DNA
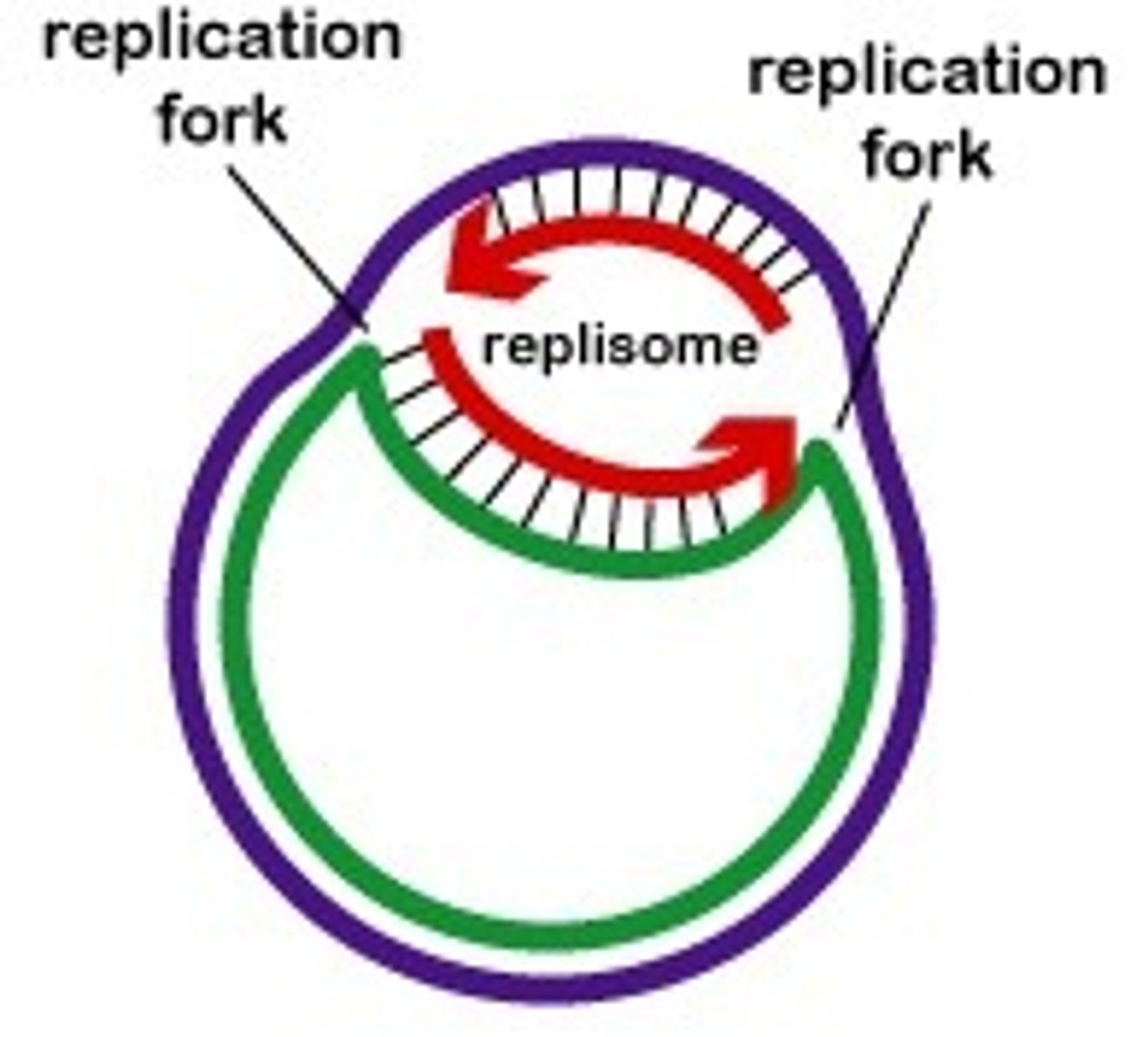
What is tightly condensed DNA in bacteria?
nucleoid
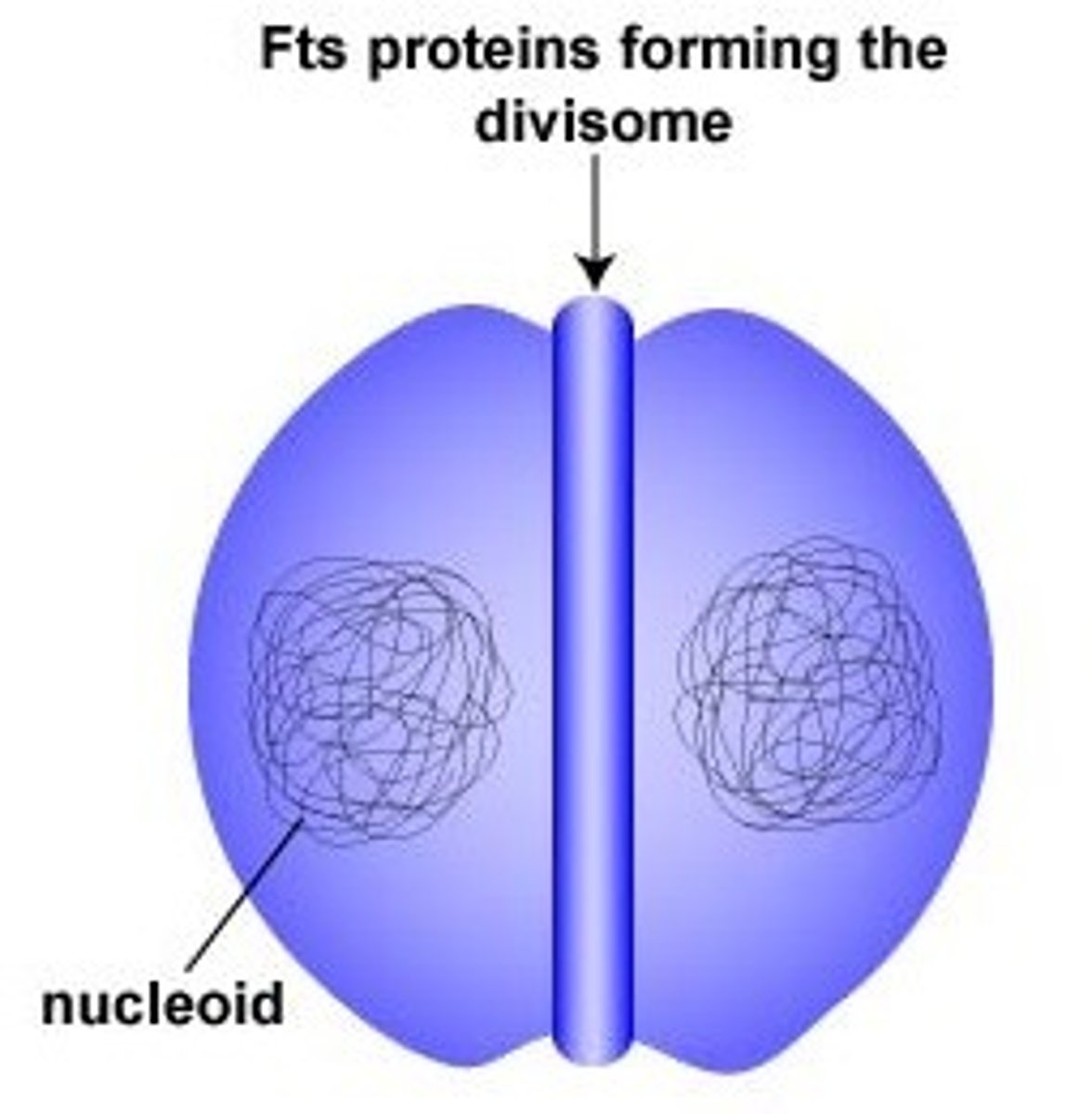
What is the replication method in bacteria in which the chromosome replicates and the cell divides into two genetically identical cells?
binary fission
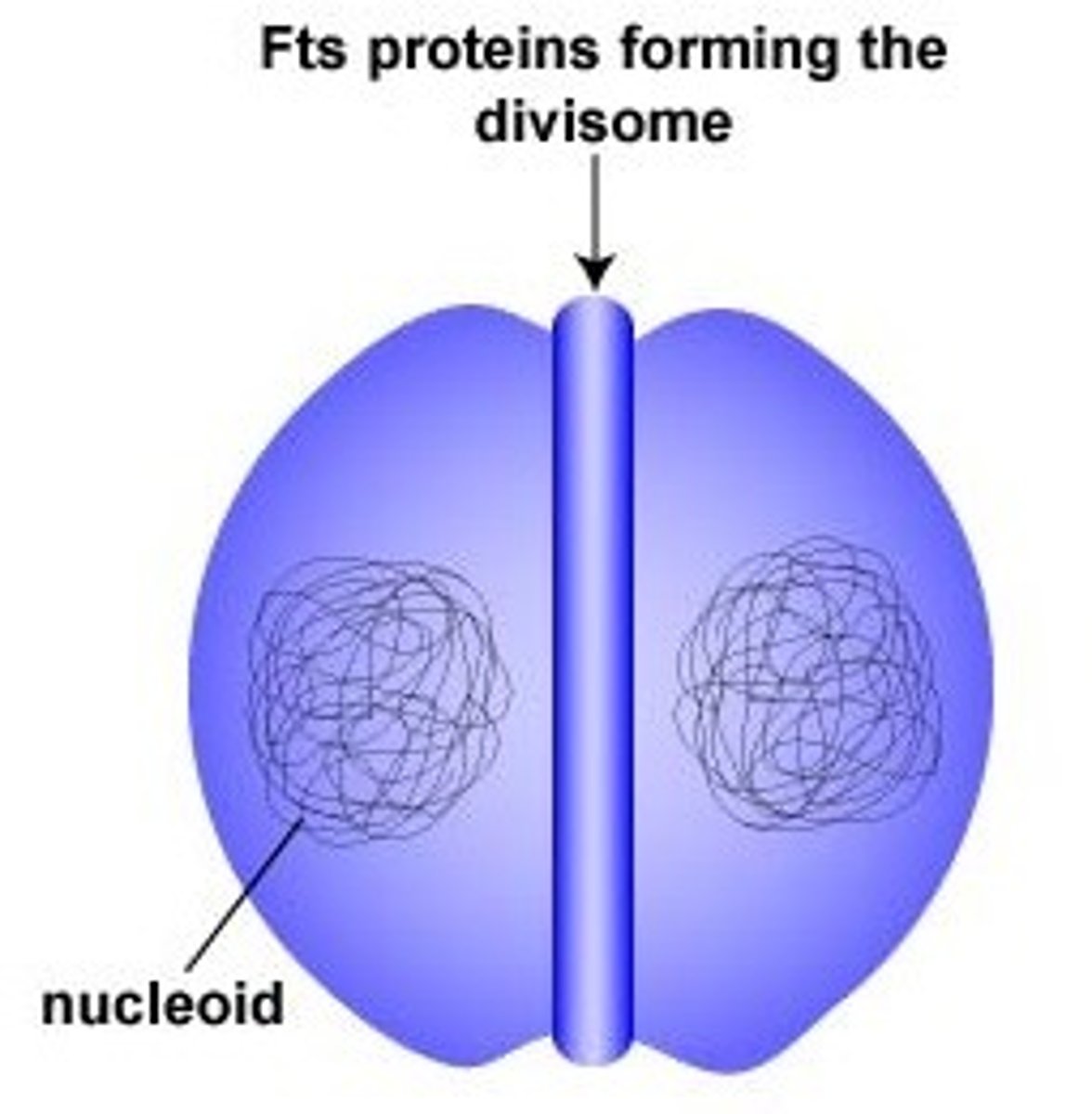
Because bacteria lack a nucleus, what other structures do they lack also?
1. microtubules
2. spindles
3. centrioles
What are plasmids that can incorporate into bacterial chromosomes?
episomes
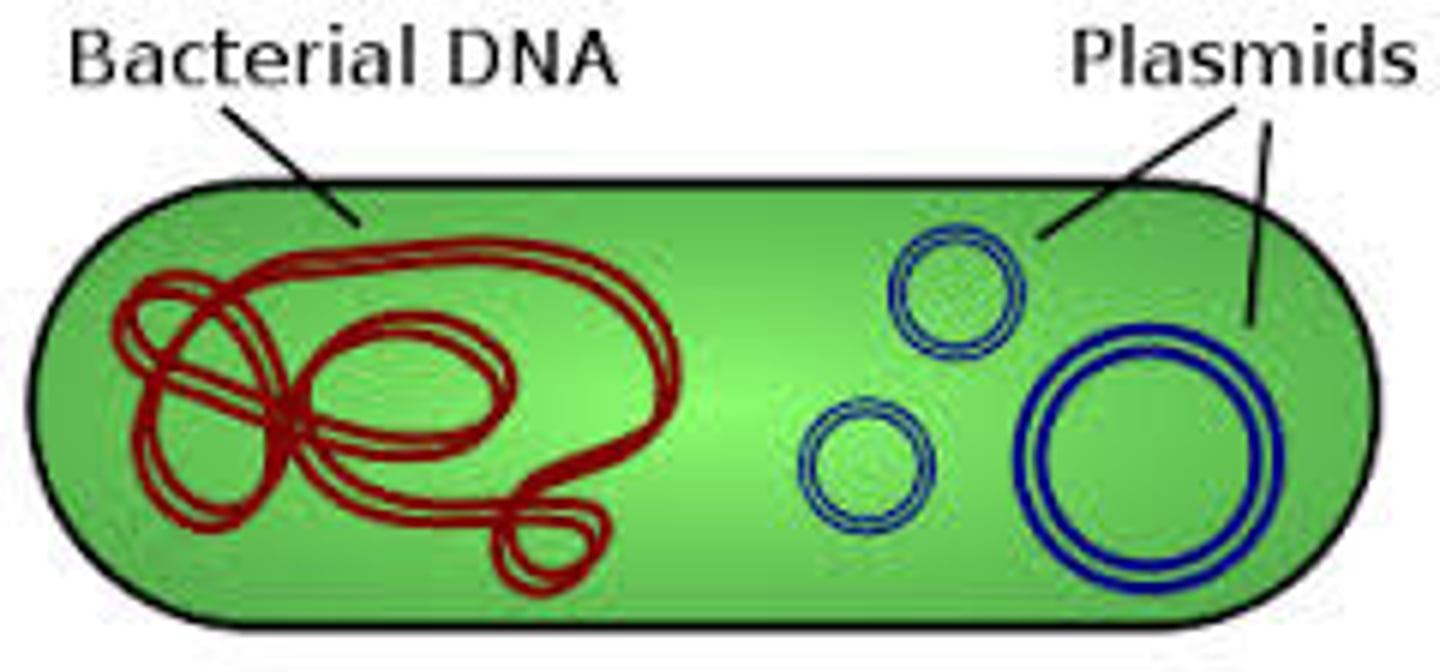
What are short, circular DNA outside of chromosomes that carry genes that are beneficial, but not essential for survival in bacteria?
plasmids
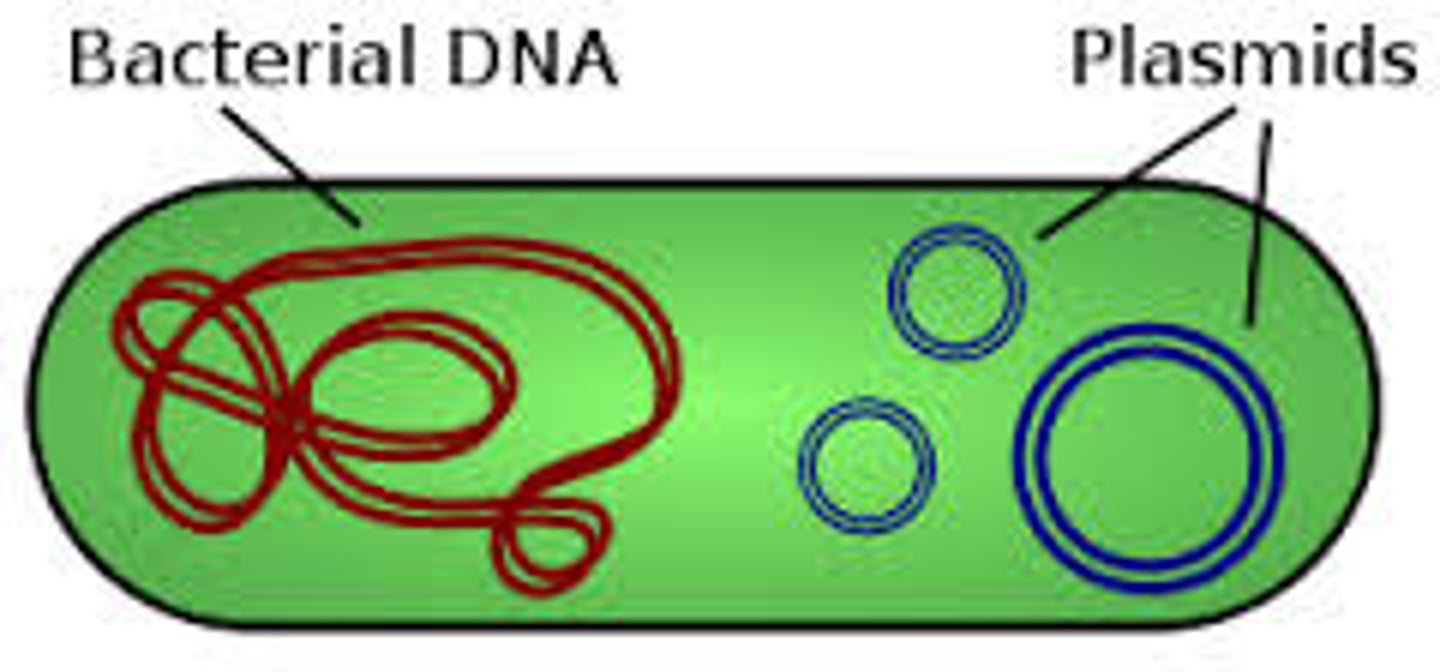
What adaptation are plasmids commonly associated with?
antibiotic resistance
what are the 3 main ways bacteria can exchange genetic information with each other or their surroundings?
1. conjugation
2. transduction
3. transformation
Which method of genetic exchange involves a donor bacteria producing a bridge (pilus) and connecting the recipient bacteria?
conjugation
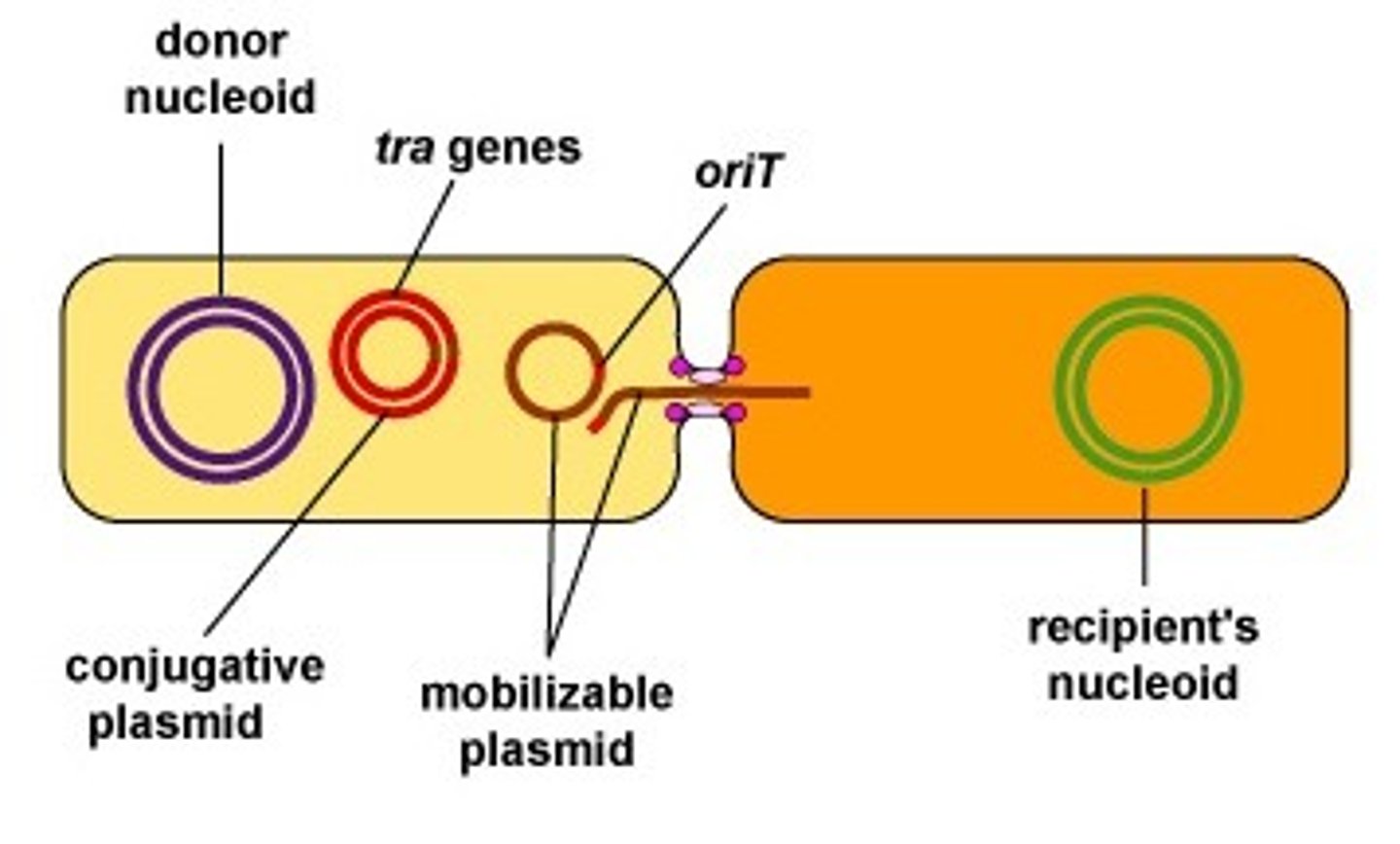
conjugation allows bacteria to exchange which genetic structures?
chromosomes or
plasmids
(Note: allows recombination
to occur)
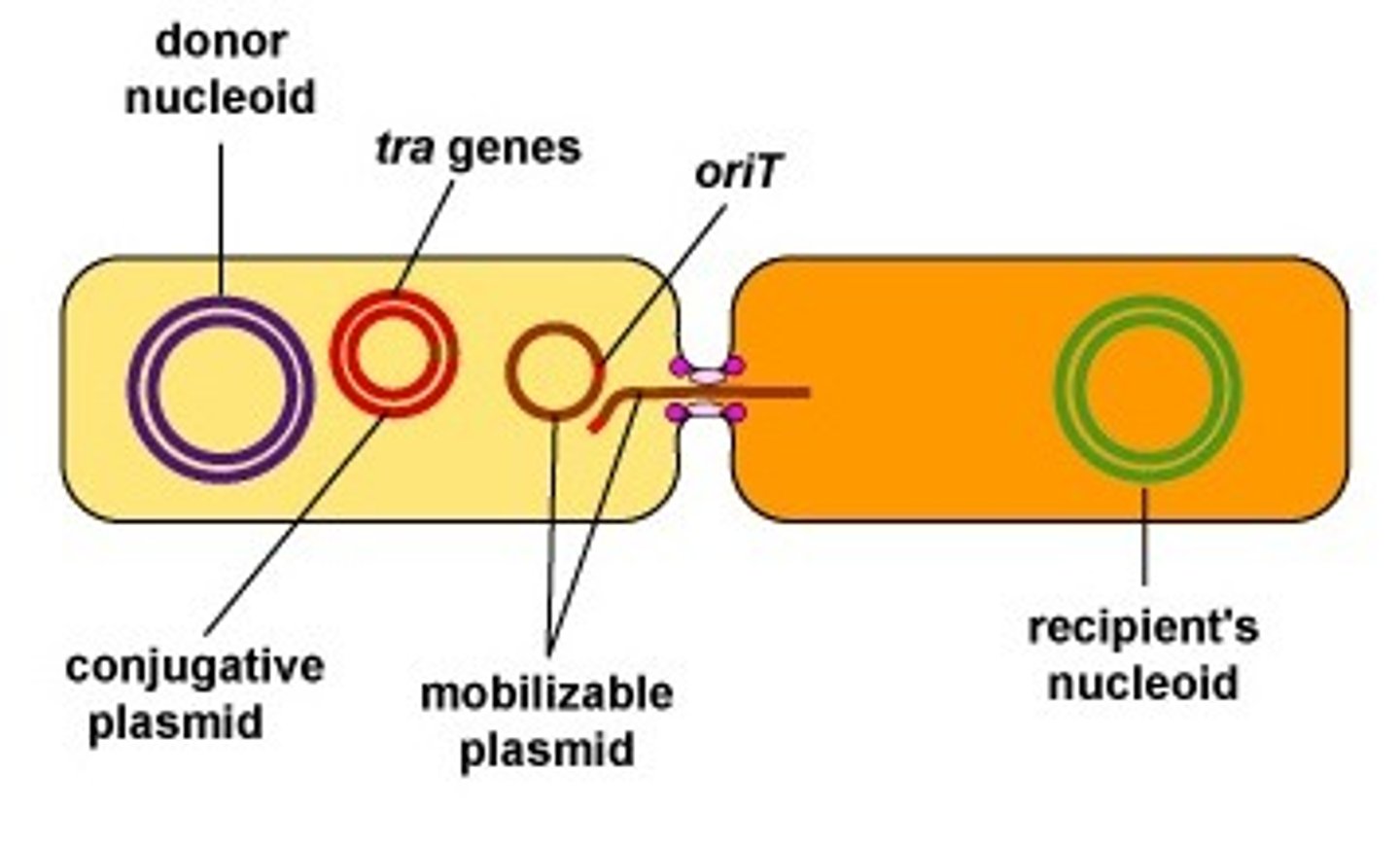
Which bacterial plasmid allows a pilus to form?
F plasmid
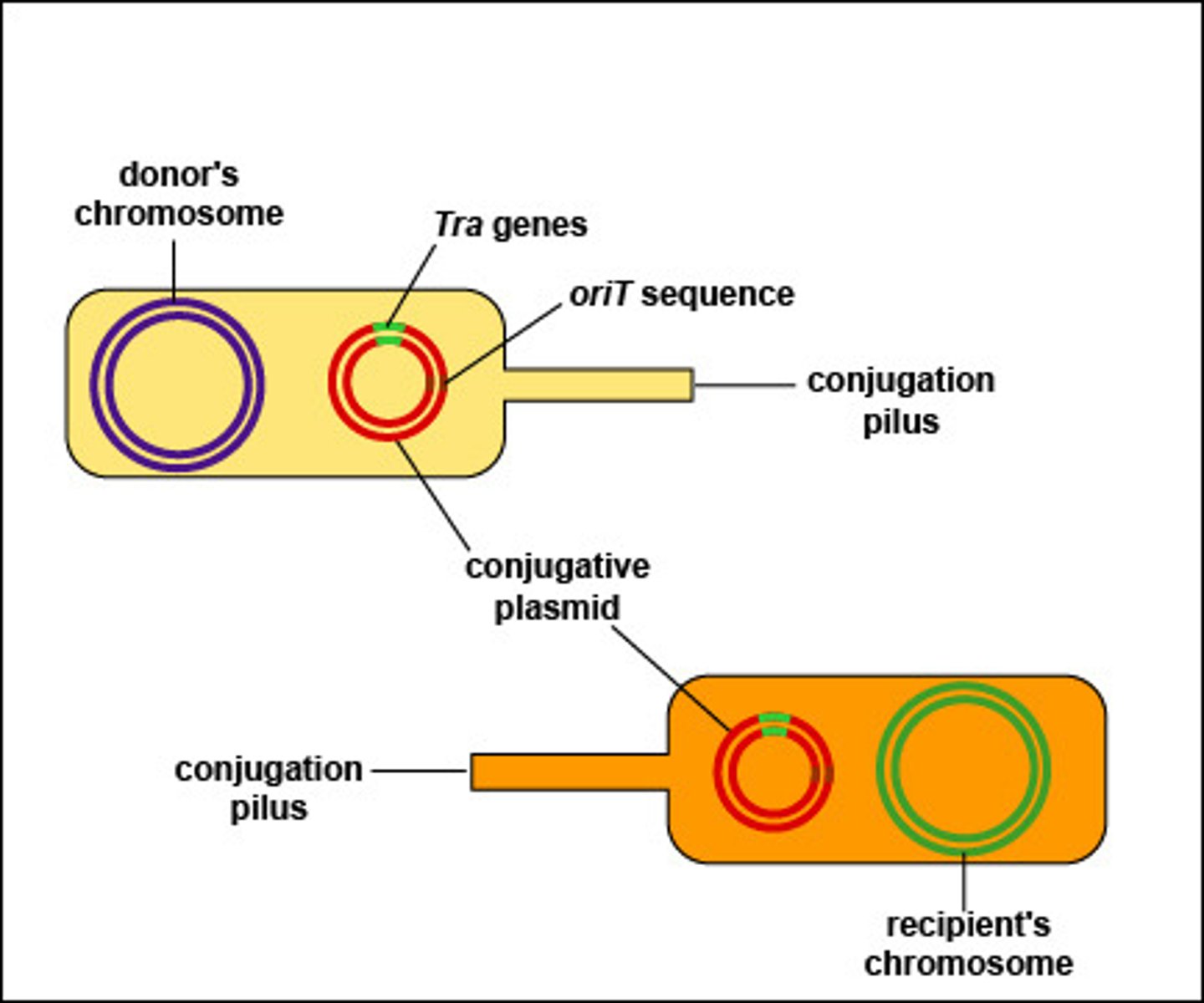
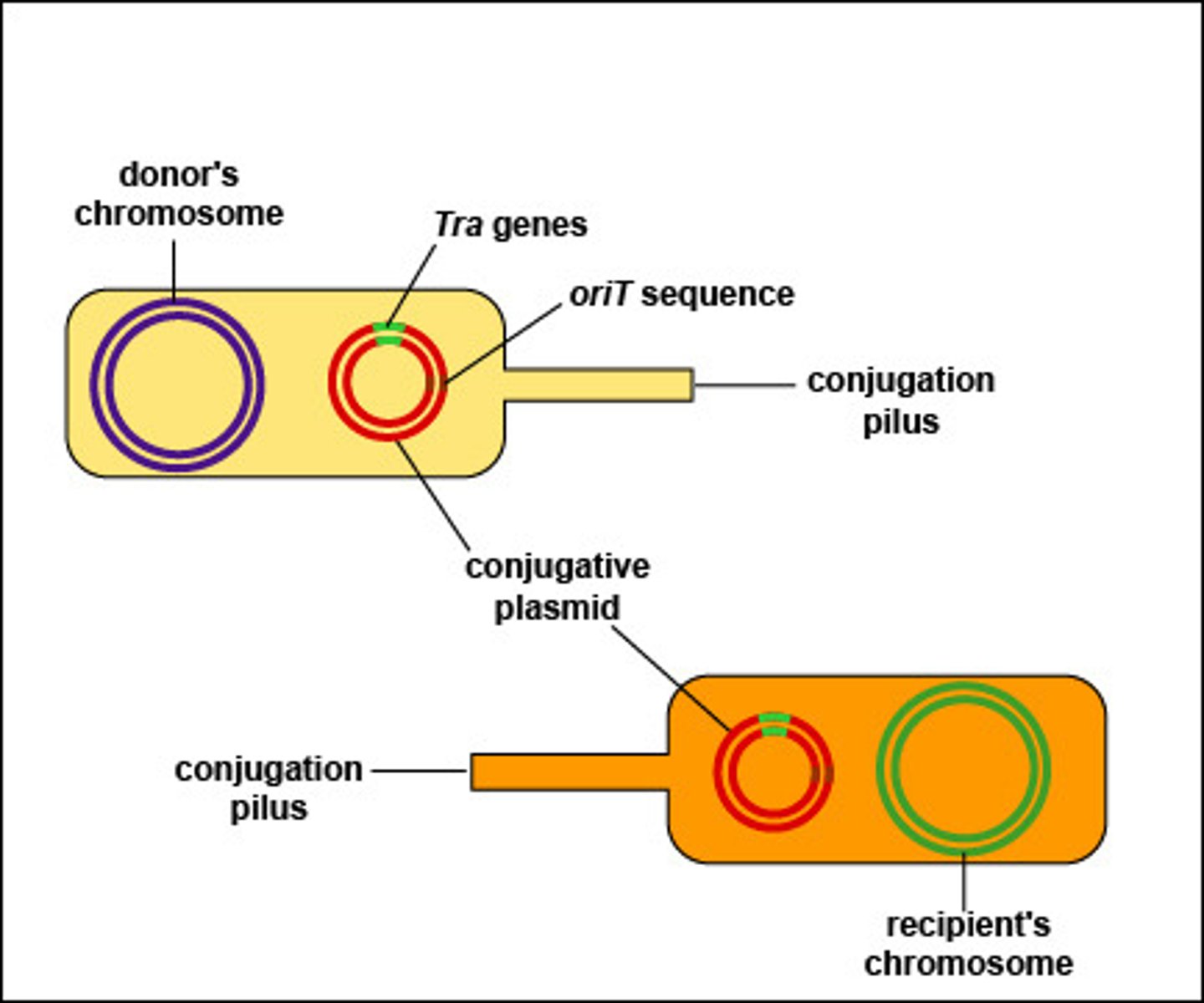
After a recipient bacteria receives an F plasmid what change does the plasmid undergo?
change to F+ plasmid
(Note: recipient bacteria
can now donate the plasmid)
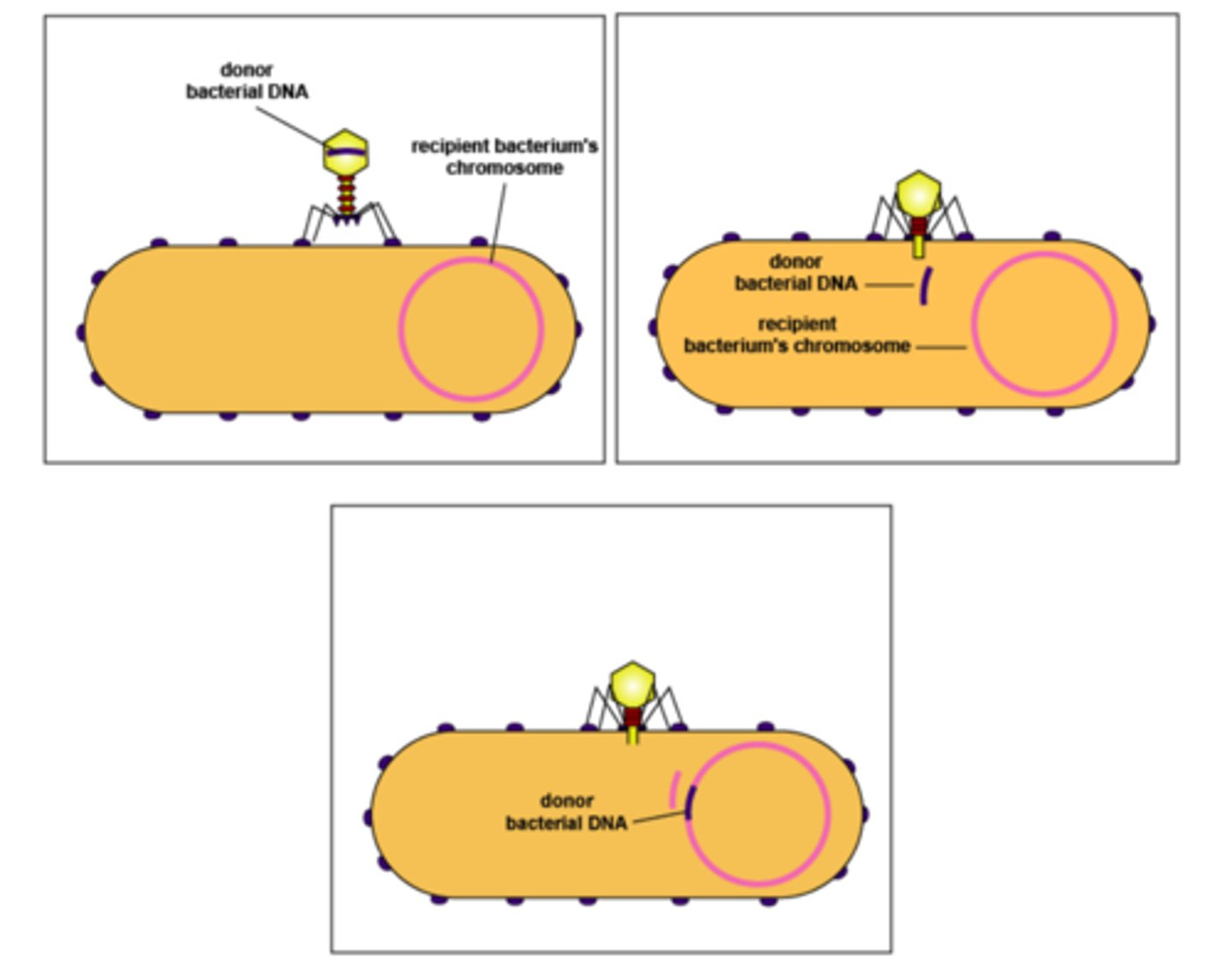
What method of genetic exchange in bacteria involves introducing DNA to a genome via virus?
transduction
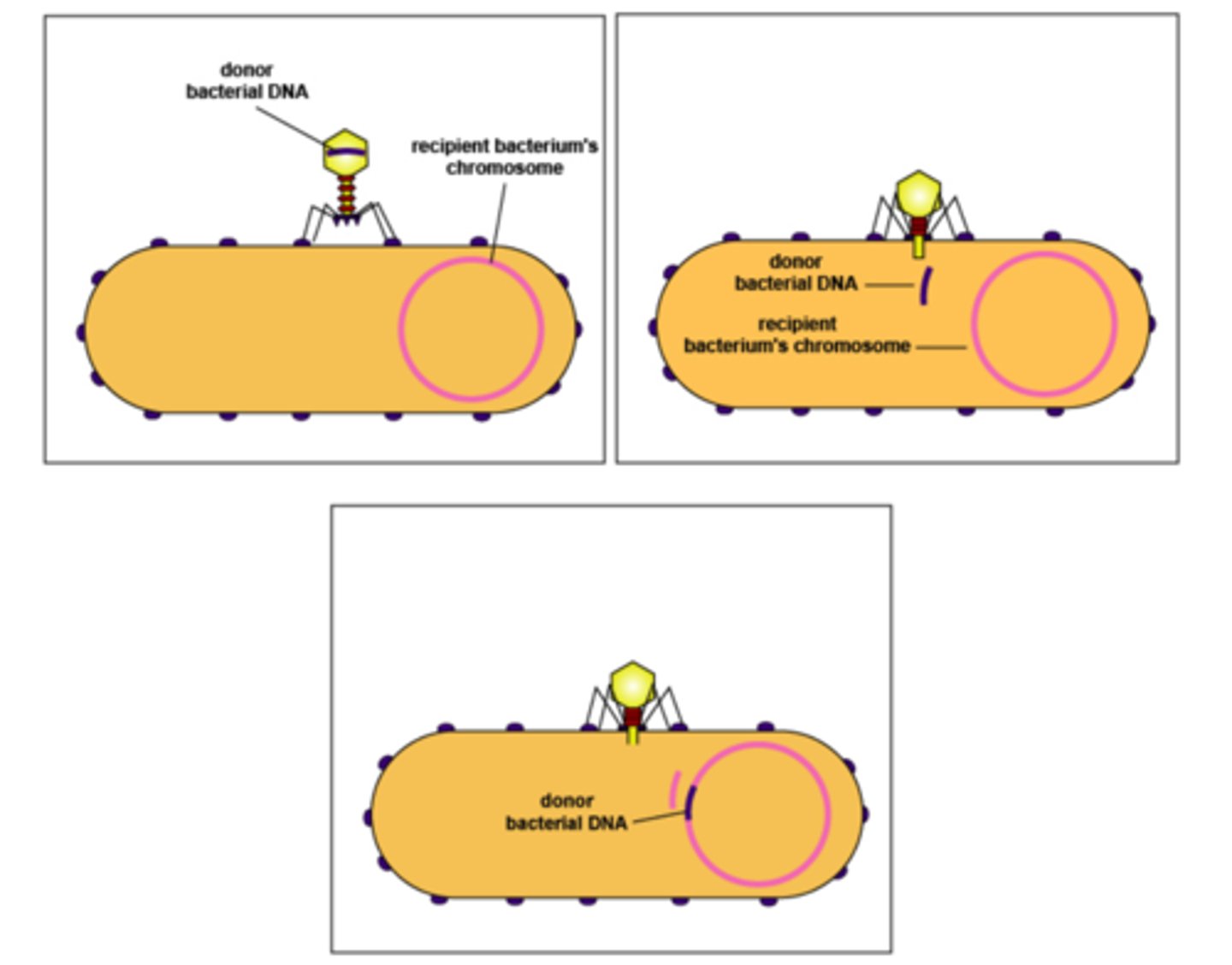
Within the host cell during transduction, what genetic information does newly synthesized viral DNA contain?
virus DNA and bacterial DNA
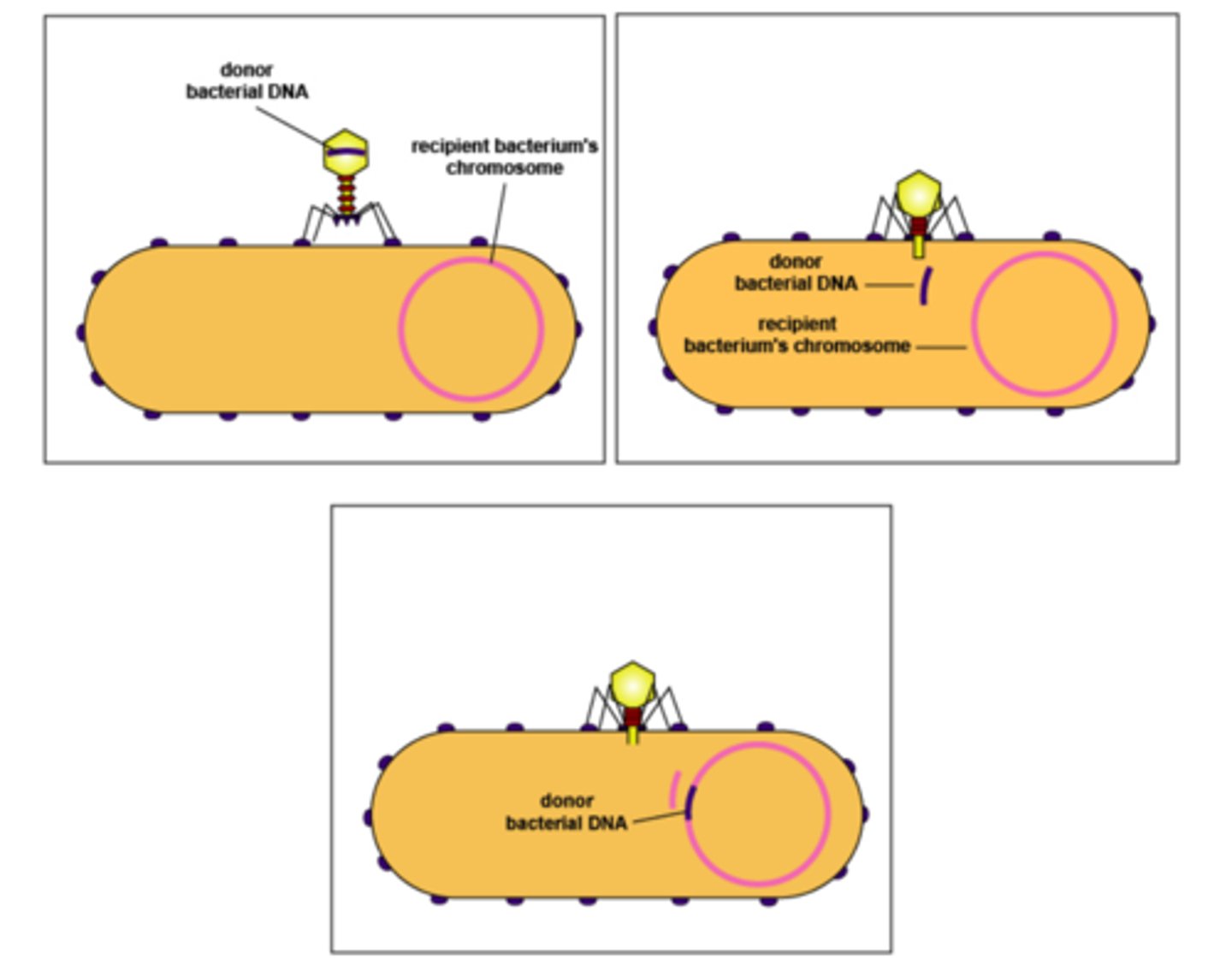
In transduction, how does it promote genetic variation when infecting a new host?
bacterial DNA from
virus can recombine
with resident DNA
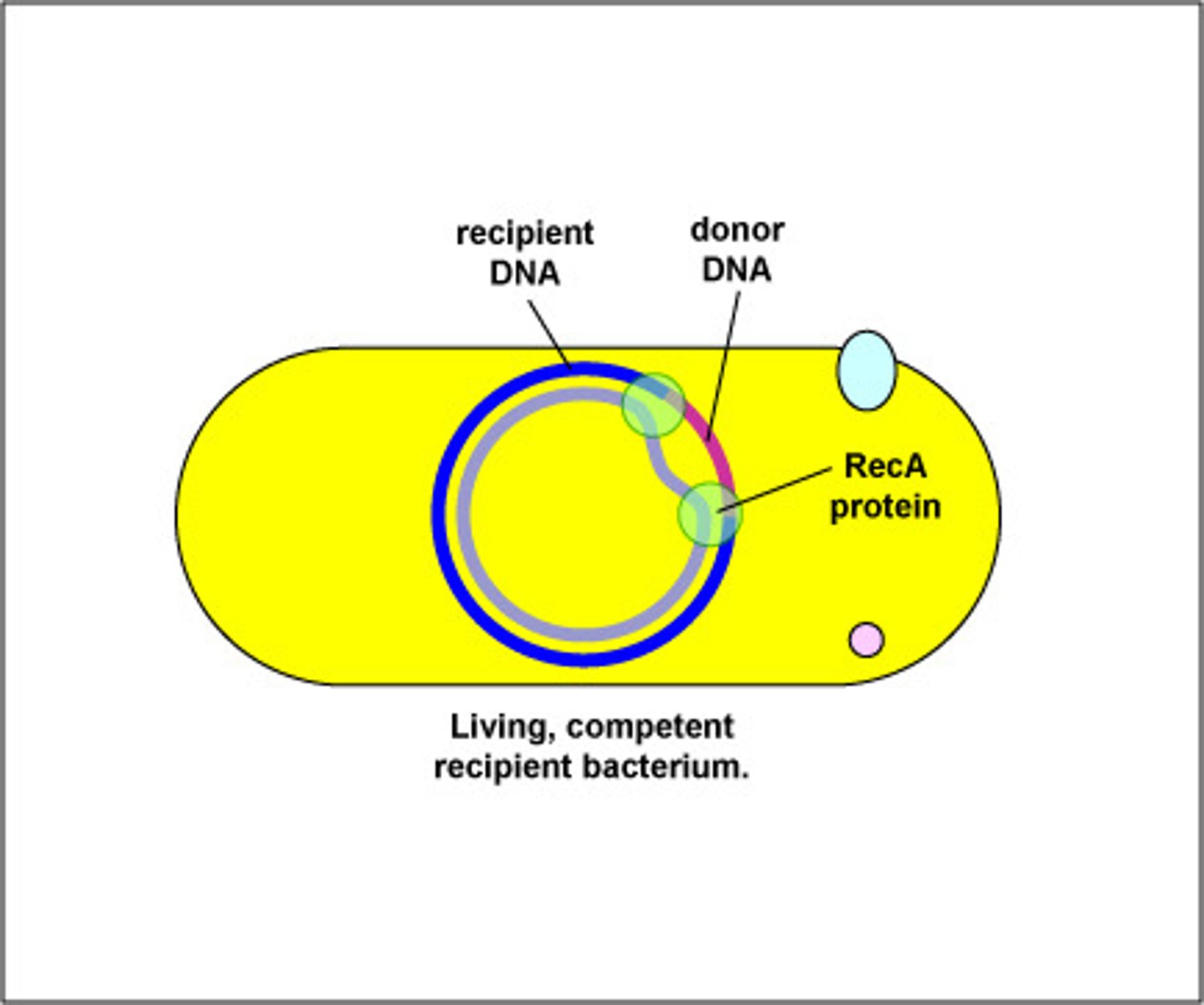
What method of genetic exchange in bacteria involves taking in DNA from surroundings and incorporating it into the genome?
transformation