Pharmacology - Final Exam
A patient newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism receives a prescription for a thyroid hormone replacement drug. The nurse assesses for which potential contraindication to this drug.
A. Infection
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Liver disease
D. Recent myocardial infarction
D. Recent myocardial infarction
A patient with hypothyroidism is given a prescription for levothyroxine. When the nurse explains that this is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone, he states that he prefers to receive more natural forms of drugs. What will the nurse explain to him about the advantages of levothyroxine?
A. It has a stronger effect than the natural forms.
B. Levothyroxine is less expensive than the natural forms.
C. The synthetic form has fewer adverse effects on the gastrointestinal tract.
D. The half-life of levothyroxine is long enough to permit once-daily dosing.
D. The half-life of levothyroxine is long enough to permit once-daily dosing.
1/359
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
360 Terms
A patient newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism receives a prescription for a thyroid hormone replacement drug. The nurse assesses for which potential contraindication to this drug.
A. Infection
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Liver disease
D. Recent myocardial infarction
D. Recent myocardial infarction
A patient with hypothyroidism is given a prescription for levothyroxine. When the nurse explains that this is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone, he states that he prefers to receive more natural forms of drugs. What will the nurse explain to him about the advantages of levothyroxine?
A. It has a stronger effect than the natural forms.
B. Levothyroxine is less expensive than the natural forms.
C. The synthetic form has fewer adverse effects on the gastrointestinal tract.
D. The half-life of levothyroxine is long enough to permit once-daily dosing.
D. The half-life of levothyroxine is long enough to permit once-daily dosing.
The order reads, give Levothyroxine 200mg PO once every morning. Which action by the nurse is correct?
A. Give the medication as ordered.
B. Change the dose to 200mcg because that is what the prescriber meant.
C. Hold the drug until the prescriber returns to see the patient.
D. Question the order because the dose is higher than 200mcg.
D. Question the order because the dose is higher than 200mcg.
During a teaching session for a patient on antithyroid drugs, the nurse will discuss which dietary instructions.
A. Using iodized salt when cooking.
B. Avoiding foods containing iodine.
C. Restricting fluid intake to 2500 milliliters per day.
D. Increasing intake of sodium and potassium containing foods.
B. Avoiding foods containing iodine.
A patient who is taking propylthiourscil for hyperthyroidism wants to know how this medicine works. Which explanation by the nurse is accurate?
A. It promotes the formation of thyroid hormone.
B. It slows down the formation of thyroid hormone.
C. It destroys overactive cells in the thyroid gland.
D. It inactivates already existing thyroid hormone in the bloodstream.
B. It slows down the formation of thyroid hormone
A 19-year-old student was diagnosed with hypothyroidism and has started thyroid replacement therapy with Levothyroxine. After one week, she called the clinic to report that she does not feel better. Which response from the nurse is correct?
A. It will probably require surgery for a cure to happen.
B. The full therapeutic effects may not occur for several weeks.
C. Is possible that you did not take your medication as instructed?
D. Let's review your diet. It may be causing absorption problems.
B. The full therapeutic effects may not occur for several weeks.
A patient newly diagnosed with hypothyroidism has received a prescription for thyroid replacement therapy. The nurse will instruct the patient to take this medication at which time of the day?
A. In the morning
B. With the noon meal
C. With the evening meal
D. At bedtime
A. In the morning
When reviewing the laboratory values of a patient who is taking antithyroid drugs, the nurse will monitor for which adverse effect.
A. Decreased glucose levels
B. Decreased white blood cell count
C. Increased red blood cell count
D. Increased platelet count
B. Decreased white blood cell count
A patient has been taking Levothyroxine for more than one decade for primary hypothyroidism. Today she calls because she has a cousin who can get her the same medication in a generic form from a pharmaceutical supply company. Which is the nurse's best advice?
A. This would be a great way to save money.
B. There's no difference in brands of this medication.
C. This should never be done. Once you start with a certain brand, you must stay with it.
D. It's better not to switch brands unless we check with your doctor.
D. It's better not to switch brands unless we check with your doctor.
A patient has a diagnosis of primary hypothyroidism. Which statement accurately describes this problem?
A. The hypothalamus is not secreting thyrotropin-releasing hormone, TRH, therefore thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH, is not released from the pituitary gland.
B. The pituitary gland is dysfunctional and is not secreting TSH.
C. The abnormality is in the thyroid gland itself.
D. The abnormality is caused by an insufficient intake of iodine.
C. The abnormality is in the thyroid gland itself.
A 19-year-old woman has been diagnosed with hypothyroidism and has started thyroid replacement therapy with levothyroxine. After six months, she calls the nurse to say that she feels better and wants to stop the medication. Which response by the nurse is correct?
A. You can stop the medication if your symptoms have improved.
B. You need to stay on the medication for at least one year before a decision about stopping it can be made.
C. You need to stay on this medication until you become pregnant.
D. Medication therapy for hypothyroidism is usually lifelong and you should not stop taking the medication.
D. Medication therapy for hypothyroidism is usually lifelong and you should not stop taking the medication.
Levothyroxine has been prescribed for a patient with hypothyroidism. The nurse reviews the patient's current medications for potential interactions. Which of these drugs or drug classes interact with levothyroxine? Select all that apply.
A. Phenytoin
B. Estrogens
C. Beta Blockers
D. Warfarin
E. Penicillins
F. Iron Supplements
• A. Phenytoin – Increases metabolism of levothyroxine, reducing its effectiveness.
• B. Estrogens – Can increase thyroid-binding globulin, which may lower free thyroid hormone levels.
• D. Warfarin – Levothyroxine enhances the effects of warfarin, increasing bleeding risk.
• F. Iron Supplements – Reduce absorption of levothyroxine and should be taken several hours apart.
The nurse is giving morning medications. The medication administration record has an order for levothyroxine 88mcg PO. The drug dispensing cabinet contains levothyroxine tablets in milligram strings instead of micrograms. Calculate the milligram equivalent dose of 25mcg.
88/1000 = 0.088
The nurse is administering insulin Lispro and will keep in mind that this insulin will start to have an effect within which time frame?
A. 15 minutes
B. 1-2 hours
C. 80 minutes
D. 3-5 hours
A. 15 minutes
When teaching about hypoglycemia, the nurse will make sure that the patient is aware of the early signs of hypoglycemia, including which of these?
A. Hypothermia and seizures
B. Nausea and diarrhea
C. Confusion and sweating
D. Fruity acetone odor to the breath
C. Confusion and sweating
The nurse is teaching a group of patients about self-administration of insulin. What content is important to include?
A. Patients need to use the injection site that is the most accessible.
B. If two different insulins are ordered, they need to be given in separate injections.
C. When mixing insulins, the cloudy, such as NPF insulin, is drawn up into the syringe first.
D. When mixing insulins, the clear, such as regular insulin, is drawn up into the syringe first.
D. When mixing insulins, the clear, such as regular insulin, is drawn up into the syringe first.
When monitoring a patient's response to oral anti-diabetic drugs, the nurse knows that which laboratory result would indicate a therapeutic response.
A. Random blood glucose level 180 mg/DL
B. Blood glucose level of 50 mg/DL after meals
C. Fasting blood glucose level of 92 mg/DL
D. Evening blood glucose level below 80 mg/DL
C. Fasting blood glucose level of 92 mg/DL
A 75-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes has recently been placed on Glipizide. She asks the nurse when the best time would be to take this medication. What is the nurse's best response?
A. Take this medication in the morning, 30 minutes before breakfast.
B. Take this medication in the evening with a snack.
C. This medication needs to be taken after the midday meal.
D. It does not matter what time of day you take this medication.
A. Take this medication in the morning, 30 minutes before breakfast.
A patient who has type 2 diabetes is scheduled for an oral endoscopy and has been NPO, nothing by mouth, since midnight. What is the best action by the nurse regarding the administration of her oral anti-diabetic drugs?
A. Administer half the original dose.
B. Withhold all medications as ordered.
C. Contact the prescriber for further orders.
D. Give the medication with a sip of water.
C. Contact the prescriber for further orders
The nurse is reviewing instructions for a patient with type 2 diabetes, who also takes insulin injections as part of the therapy. The nurse asks the patient, What should you do if your fasting blood glucose is 44mg/DL? Which response by the patient reflects a correct understanding of insulin therapy?
A. I will call my doctor right away.
B. I will give myself the regular insulin.
C. I will take an oral form of glucose.
D. I will rest until the symptoms pass.
C. I will take an oral form of glucose.
The nurse is teaching patients about self-injection of insulin. Which statement is true regarding injection sites?
A. Avoid the abdomen because absorption there is irregular.
B. Choose a different site at random for each injection.
C. Give the injection in the same area each time.
D. Rotate sites within the same location for about one week before rotating to a new location.
D. Rotate sites within the same location for about one week before rotating to a new location.
Which action is most appropriate regarding the nurse's administration of a rapid-acting insulin to a hospitalized patient?
A. Give it within 15 minutes of mealtime.
B. Give it after the meal has been completed.
C. Administer it once daily at the time of the midday meal.
D. Administer it with a snack before bedtime.
A. Give it within 15 minutes of mealtime.
After starting treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus 6 months earlier, a patient is in the office for a follow-up examination. The nurse will monitor which laboratory tests to evaluate the patient's adherence to the antidiabetic therapy over the past few months.
A. Hemoglobin levels
B. Hemoglobin A1c level
C. Fingerstick fasting blood glucose level
D. Serum insulin levels
B. Hemoglobin A1c level
A patient in the emergency department was showing signs of hypoglycemia and had a finger sick glucose level of 38 MgDL. The patient has just become unconscious. The nurse will anticipate which action to be next.
A. Having the patient eat glucose tablets
B. Having the patient consume fruit juice, a non-diet soft drink or crackers
C. Administering intravenous glucose 50% dextrose
D. Calling the lab to order a fasting blood glucose level
C. Administering intravenous glucose 50% dextrose
The nurse is preparing to administer insulin intravenously. Which statement about the administration of intravenous insulin is true?
A. Insulin is never given intravenously.
B. Only regular insulin can be administered intravenously.
C. Insulin aspart or insulin lispro can be administered intravenously, but there must be a 50% dose reduction.
D. Any form of insulin can be administered intravenously at the same dose as that is ordered for subcutaneous administration.
B. Only regular insulin can be administered intravenously.
A patient with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD, and type 2 diabetes has been treated for pneumonia for the past week. The patient has been receiving intravenous corticosteroids as well as antibiotics as part of his therapy. At this time, the pneumonia has resolved, but when monitoring the blood glucose levels, the nurse notices that the level is still elevated. What is the best explanation for this elevation?
A. The antibiotics may cause an increase in the glucose levels.
B. The corticosteroids may cause an increase in the glucose levels.
C. The patient's type 2 diabetes has converted to type 1.
D. The hypoxia caused by the COPD causes an increased need for insulin.
B. The corticosteroids may cause an increase in the glucose levels.
The nurse knows to administer Acarbose, an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, at which time?
A. 30 minutes before breakfast.
B. With the first bite of each main meal.
C. 30 minutes after breakfast.
D. Once daily at bedtime.
B. With the first bite of each main meal.
A patient has been diagnosed with metabolic syndrome and is started on the biguanide metformin. The nurse knows that the purpose of the metformin in this situation is which of these?
A. To increase the pancreatic secretion of insulin
B. To decrease insulin resistance
C. To increase blood glucose levels
D. To decrease the pancreatic secretion of insulin
B. To decrease insulin resistance
When administering morning medications for a newly admitted patient, the nurse notes that the patient has an allergy to sulfa drugs. There is an order for the sulfonylurea glipizide glue control. Which action by the nurse is correct?
A. Give the drug as ordered 30 minutes before breakfast.
B. Hold the drug and check the order with the prescriber.
C. Give a reduced dose of the drug with breakfast.
D. Give the drug and monitor for adverse effects.
B. Hold the drug and check the order with the prescriber.
The nurse is reviewing a patient's medication list and notes the sitagliptin, or Januvia, is ordered. The nurse will question an additional order for which drug or drug class.
A. Glitazone
B. Insulin
C. Metformin
D. Sulfonylurea
B. Insulin
The nurse is teaching a review class to nurses about diabetes mellitus. Which statement by the nurse is correct?
A. Patients with type 2 diabetes will never need insulin.
B. Oral anti-diabetic drugs are safe for use during pregnancy.
C. Pediatric patients cannot take insulin.
D. Insulin therapy is possible during pregnancy if managed carefully.
D. Insulin therapy is possible during pregnancy if managed carefully.
The nurse is teaching a group of patients about management of diabetes. Which statement about basal dosing is correct?
A. Basal dosing delivers a constant dose of insulin.
B. With basal dosing, you can eat what you want and then give yourself a dose of insulin.
C. Glargine insulin is given as a bolus with meals.
D. Basal bolus dosing is the traditional method of managing blood glucose levels.
A. Basal dosing delivers a constant dose of insulin.
When teaching a patient who is starting metformin, which instruction by the nurse is correct?
A. Take metformin if your blood glucose level is above 180 mgDL.
B. Take this 60 minutes after breakfast.
C. Take the medication on an empty stomach one hour before meals.
D. Take the medication with food to reduce gastrointestinal GI effects.
D. Take the medication with food to reduce gastrointestinal GI effects.
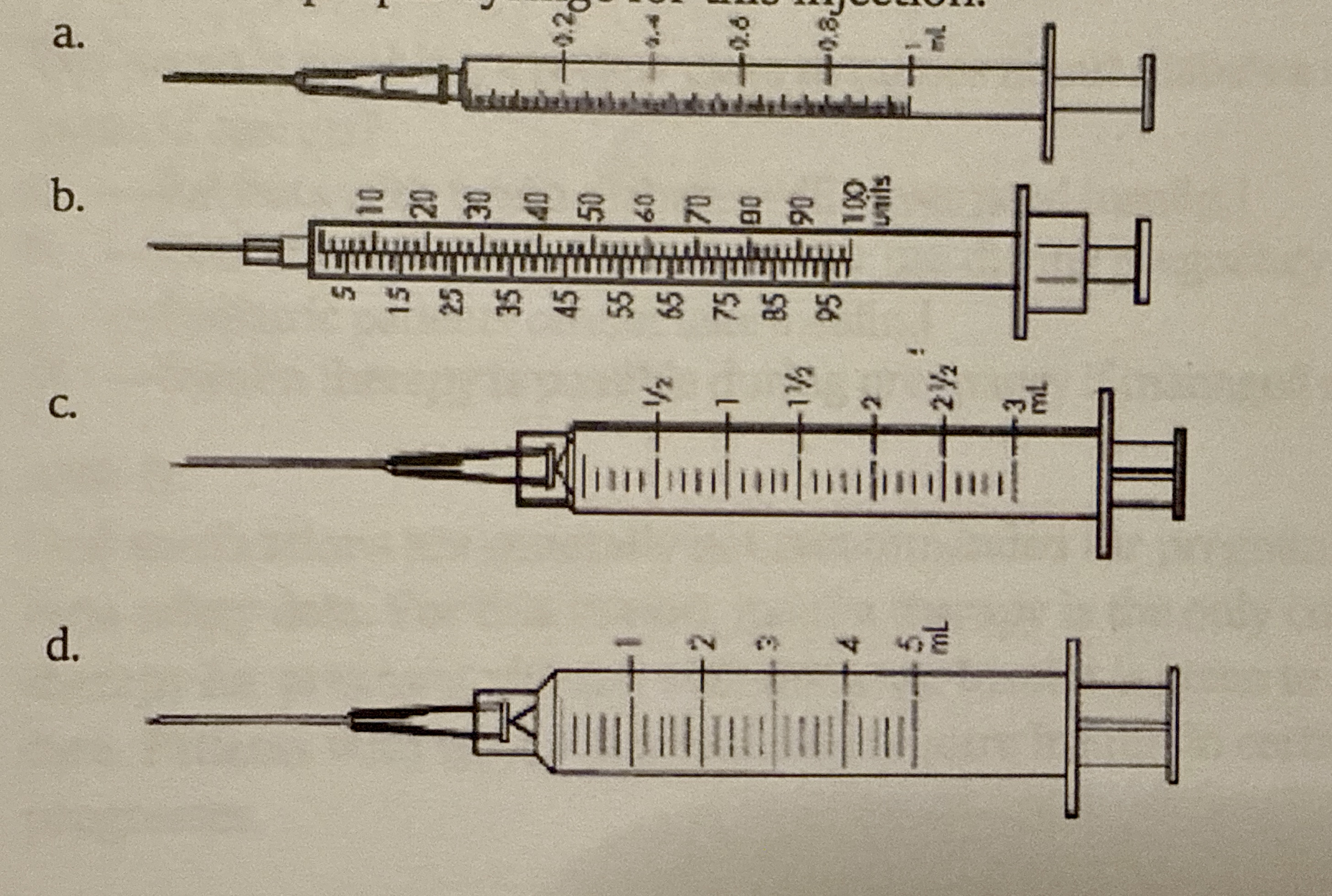
The insulin order reads, give 15 units insulin glargine sub-Q every evening after dinner. Choose the proper syringe for this injection.
b. — the insulin syringe labeled in units (up to 100 units)
A patient is taking a sulfonylurea medication for a new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. When reviewing potential adverse effects during patient teaching, the nurse will include information about which of these effects. Select all that apply.
A. Hypoglycemia
B. Nausea
C. Diarrhea
D. Weight gain
E. Peripheral edema
• A. Hypoglycemia – a common adverse effect due to increased insulin secretion
• B. Nausea – a possible gastrointestinal side effect
• D. Weight gain – due to increased insulin activity promoting fat storage
A patient will be taking U-500 insulin. The nurse is reviewing the use of this drug. Which of these statements are true? Select all that apply.
A. U-500 insulin is 5 times stronger than U-100 insulin.
B. U-500 insulin syringes must be used when giving U-500 insulin.
C. U-500 syringes can deliver 500 units of insulin.
D. Each line on a U-500 syringe measures 5 units of U-500 insulin.
E. U-500 insulin delivers a smaller dose of insulin in a single injection.
A. U-500 insulin is 5 times stronger than U-100 insulin.
B. U-500 insulin syringes must be used when giving U-500 insulin.
D. Each line on a U-500 syringe measures 5 units of U-500 insulin
The nurse is administering an adrenal drug to a patient. Which action by the nurse is appropriate for this patient?
A. Administering oral adrenal drugs on an empty stomach to maximize absorption.
B. Rinsing the oral cavity after using corticosteroid inhalers.
C. Administering the corticosteroids before bedtime to minimize adrenal suppression.
D. Discontinuing the medication immediately if weight gain of 5 pounds or more in one week occurs.
B. Rinsing the oral cavity after using corticosteroid inhalers
A patient will be starting therapy with a corticosteroid. The nurse reviews the prescriber's orders and notes that an interaction may occur if the corticosteroid is taken with which of these drug classes?
A. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
B. Antibiotics
C. Opioid analgesics
D. Antidepressants
A. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
A patient is concerned about the body changes that have resulted from long-term prednisone therapy for the treatment of asthma. Which expected effect of this drug therapy would cause a change in the patient's appearance?
A. Weight loss
B. Weight gain
C. Pale skin color
D. Hair loss
B. Weight gain
A patient is taking fludrocortisone for Addison's disease, and his wife is concerned about all of the problems that may occur with this therapy. When teaching them about therapy with this drug, the nurse will include which information?
A. It may cause severe postural hypotension.
B. It needs to be taken with food or milk to minimize gastrointestinal upset.
C. The medication needs to be stopped immediately if nausea or vomiting occurs.
D. Weight gain of 5 pounds or more in one week is an expected adverse effect.
B. It needs to be taken with food or milk to minimize gastrointestinal upset.
When monitoring a patient who is taking a systemically administered glucocorticoid, the nurse will monitor for signs of which condition?
A. Dehydration
B. Hypokalemia
C. Hyponatremia
D. Hypoglycemia
B. Hypokalemia
A glucocorticoid is prescribed for a patient. The nurse checks the patient's medical history knowing that glucocorticoid therapy is contraindicated in which disorder?
A. Cerebral edema
B. Peptic ulcer disease
C. Tuberculous meningitis
D. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
B. Peptic ulcer disease
A patient who has been on long-term corticosteroid therapy has had surgery to correct an abdominal hernia. The nurse keeps in mind that which potential effect of this medication may have the most impact on the patient's recovery.
A. Hypotension
B. Osteoporosis
C. Muscle weakness
D. Delayed wound healing
D. Delayed wound healing
The nurse is reviewing therapy with glucocorticoid drugs. Which conditions are indications for glucocorticoid drugs? Select all that apply.
A. Glaucoma
B. Cerebral edema
C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
D. Organ transplantation
E. Varicella
F. Septicaemia
B. Cerebral edema
C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
D. Organ transplantation
The nurse expects that a patient is experiencing under-secretion of adrenocortical hormones. When which conditions are found upon assessment, select all that apply.
A. Dehydration
B. Weight loss
C. Steroid psychosis
D. Increased potassium levels
E. Increased blood glucose levels
F. Decreased serum sodium levels
A. Dehydration
B. Weight loss
D. Increased potassium levels
F. Decreased serum sodium levels
A patient has been admitted for an exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and will be receiving methylprednisolone 30 mg intravenously every 6 hours. The medication is available in 40 mg ml vials. Identify how many milliliters will the nurse draw up for this dose. Do not round your answer.
0.75 mL
The nurse is providing teaching for a patient who is to receive progestin therapy. Which statement is correct to include in the teaching session?
A. If you miss a dose, double up on the next dose.
B. There's no need to be concerned about breast lumps or bumps that occur.
C. Be sure to report any weight gain of 5 pounds or more per week.
D. Take the medication on an empty stomach to enhance absorption.
C. Be sure to report any weight gain of 5 pounds or more per week.
The nurse recognizes that use of estrogen drugs is contraindicated in which patient?
A. A patient who has atrophic vaginitis.
B. A patient who has inoperable prostate cancer.
C. A woman who has just given birth and wants to prevent postpartum lactation.
D. A woman with a history of thrombophlebitis.
D. A woman with a history of thrombophlebitis.
A patient is being treated for secondary amenorrhea. The nurse expects which drug to be used to treat this problem.
A. Methylergonavine
B. Estradiol Transdermal
C. Raloxifene
D. Medroxyprogesterone
D. Medroxyprogesterone
The nurse is teaching a patient about the adverse effects of fertility drugs such as clomiphene. Which is a potential adverse effect of this drug?
A. Headache,
B. Drowsiness,
C. Dysmenorrhea,
D. Hypertension.
A. Headache,
A patient is receiving oxytocin to induce labor. During administration of this medication, the nurse will also implement which action?
A. Giving magnesium sulfate along with the oxytocin.
B. Administering the medication in an intravenous bolus.
C. Administering the medication with an IV infusion pump.
D. Monitoring fetal heart rate and maternal vital signs every two hours.
C. Administering the medication with an IV infusion pump.
The nurse is reviewing the use of uterine tocolytics such as indomethacin or indocin. Which statement best describes the indication for these drugs?
A. Prevention of preterm labor in the 15th week of pregnancy.
B. Prevention of preterm labor in the 22nd week of pregnancy.
C. Stimulation of contractions in prolonged labor.
D. Stimulation of ovulation as part of infertility treatments.
B. Prevention of preterm labor in the 22nd week of pregnancy.
A 51-year-old woman will be taking Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators, SERMs, as part of treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis. The nurse reviews potential contraindications, including which condition?
A. Hypocalcemia
B. Breast cancer
C. Stress fractures
D. Venous thromboembolism
D. Venous thromboembolism
During a follow-up visit, a patient who has been on estrogen therapy admits that she has continued to smoke cigarettes. The nurse will remind the patient that smoking while on estrogen may lead to an increase in which of these conditions?
A. Incidence of nausea.
B. Risk for thrombosis.
C. Levels of triglycerides.
D. Tendency to bleed during menstruation.
B. Risk for thrombosis.
When considering the various types of contraceptive drugs, the nurse is aware that which type most closely duplicates the normal hormonal levels of the female menstrual cycle?
A. Monophasic
B. Biphasic
C. Triphasic
D. Short-acting
C. Triphasic
A woman visits a health center requesting oral contraceptives. Which laboratory test is most important for the nurse to assess before the patient begins oral contraceptive therapy?
A. Complete blood count
B. Serum potassium level
C. Vaginal cultures
D. Pregnancy test
D. Pregnancy test
The nurse is providing patient teaching about the oral bisphosphonate alendronate (fosamax). Which statement by the patient indicates a good understanding of when this drug should be taken?
A. I will take it in the evening just before bedtime.
B. I will take it in the morning with an 8-ounce glass of water.
C. I will take it with the first bite of the morning meal.
D. I will take it between meals on an empty stomach.
B. I will take it in the morning with an 8-ounce glass of water.
A woman is preparing for a 10-hour trans-Pacific flight. She has been taking the S-E-R-M raloxifene for 6 months. The nurse will provide which instructions to this patient.
A. She needs to stop taking the drug at least 72 hours before the trip.
B. She must remember to take this drug with a full glass of water each morning.
C. She will not take the drug while traveling on the plane.
D. No change in how the drug is taken will be needed.
A. She needs to stop taking the drug at least 72 hours before the trip.
The nurse recognizes that the risk of osteoporosis is higher in an individual with which risk factor?
a. Whites or Asians
b. Blacks
c. History of participation in active sports
d. Obesity
a. Whites or Asians
A patient who is taking the bisphosphonate alendronate has been instructed to lie flat in bed for two days after having ophthalmic surgery. Which intervention is appropriate at this time?
A. She will continue to take the alendronate with water.
B. She cannot take the alendronate until she can sit up for 30 minutes.
C. She can take the medication with breakfast.
D. She will stop taking the medication 72 hours before her surgery.
B. She cannot take the alendronate until she can sit up for 30 minutes.
The nurse is preparing to administer the contraceptive form of medroxyprogesterone. What route is appropriate?
A. Subcutaneous
B. Intramuscular
C. Vaginal
D. Transdermal
B. Intramuscular
A patient wants to try an oral soy product to relieve perimenopausal symptoms. The nurse will assess the patient's medication history for which potential drug interaction.
A. Thyroid replacement therapy.
B. Oral anticoagulant therapy.
C. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
D. Beta blockers.
A. Thyroid replacement therapy.
The nurse is administering oxytocin. Which situation is an indication for the use of oxytocin?
A. Decreased fetal heart rate and movements.
B. Stimulation of contractions during labor.
C. Cervical ripening near term in pregnant patients.
D. To reverse premature onset of labor.
B. Stimulation of contractions during labor.
An older adult female patient is receiving the progestin drug Megestrol. Which is the most likely reason Megestrol is ordered for this patient?
A. Migraine headaches
B. Osteoporosis
C. Appetite stimulant
D. Reduction of hot flashes
C. Appetite stimulant
The nurse is providing patient education for a patient taking an oral contraceptive. Which drugs may cause interactions with oral contraceptives? Select all that apply.
A. Cefalexin
B. Guafenisin
C. Warfarin
D. Ibuprofen
E. Theophylline
A. Cefalexin
C. Warfarin
E. Theophylline
A patient is to receive medroxyprogesterone deproprovera 700 mg weekly, intramuscularly as part of palliative therapy for endometrial cancer. The medication is available in vials of 400 mg per mL. Identify how many mL will the nurse draw up and administer with each injection. Record your answer using one decimal place.
1.8 mL
A patient is to receive testosterone therapy via a transdermal patch. He asks the nurse, I'd rather take a pill. Why am I getting a patch? Which response by the nurse is correct?
A. The patch reduces the incidence of side effects.
B. If you don't take the patch, you will have to have injections instead.
C. The patch allows for better absorption of the medication.
D. You will only have to change the patch weekly.
C. The patch allows for better absorption of the medication.
When a male patient is receiving androgen therapy, the nurse will monitor for signs of excessive androgens, such as
a. fluid retention,
b. dehydration,
c. restlessness,
d. visual changes.
a. fluid retention,
A patient is receiving Finasteride for treatment of benign prosthetic hyperplasia. The nurse will tell him that a possible effect of this medication is
A. alopecia,
B. increased hair growth,
C. urinary retention,
D. increased prostate size.
B. increased hair growth,
The nurse is reviewing orders for a female patient and notes an order for the androgen testosterone. Based on this finding, which of these is correct?
A. The patient has fibrocystic breast disease
B. The patient has hereditary angioedema
C. The patient has inoperable breast cancer
D. The order is incorrect and needs to be clarified
C. The patient has inoperable breast cancer
A 21-year-old male athlete admits to using androgenic steroids. The nurse tells him that which of these is a possible adverse effect of these drugs.
A. Liver Damage
B. Renal Failure
C. Heart Failure
D. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
A. Liver Damage
During the administration of Finasteride, the nurse must remember which important precaution.
A. It must be taken on an empty stomach.
B. It must not be handled by pregnant women.
C. It is given by deep intramuscular injection to avoid tissue irritation.
D. The patient needs to be warned that alopecia is a common adverse effect.
B. It must not be handled by pregnant women.
A 73-year-old male patient is in the clinic for a yearly physical and is asking for a prescription for sildenafil. He has listed on his health history that he is taking a nitrate for angina. The nurse is aware that which problem may occur if sildenafil is taken with a nitrate.
A significant increase in pulse rate,
B significant decrease in blood pressure,
C increased risk of bleeding,
D reduced effectiveness of the sildenafil.
B significant decrease in blood pressure,
The nurse is reviewing the medication list of a patient who will be starting androgen therapy. Which drug classes, if taken with androgens, may have an interaction with them?
A. Oral anticoagulants,
B. Nitrates,
C. Beta blockers,
D. Proton pump inhibitors.
A. Oral anticoagulants,
A 63-year-old male patient is scheduled for a physical examination, and he tells the nurse that he wants to start taking a vitamin formula that includes saw palmetto for prostate health. Which is the nurse's best response?
A. I've heard many good things about saw palmetto
B. It's not a good idea to start herbal therapy at your age
C. There are very few adverse effects with saw palmetto therapy
D. The doctor will need to do a PSA blood test and a digital rectal exam first.
D. The doctor will need to do a PSA blood test and a digital rectal exam first.
The nurse notes in a patient's medication history that the patient is taking the synthetic androgen danazoll. Indications for danazoll include which conditions? Select all that apply.
A. Endometriosis
B. Decreased sexual libido
C. Postpartum breast engorgement
D. Fibrocystic breast disease in women
E. Hereditary angioedema
F. Metastatic breast cancer
A. Endometriosis
D. Fibrocystic breast disease in women
E. Hereditary angioedema
The nurse is instructing a male patient about application of transdermal testosterone gel. Which body location is preferred for this medication? Select all that apply.
A. Shoulders.
B. Thigh.
C. Scrotum.
D. Abdomen.
E. Upper arms.
A. Shoulders.
D. Abdomen.
E. Upper arms.
A patient will be receiving testosterone cypionate, 400 mg, intramuscularly every 4 weeks. The medication is available in a 200 mg per mL strength. Identify how many mL will the nurse draw up for each injection.
2 mL
A nurse is teaching a patient newly diagnosed with congestive heart failure (CHF). Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
A. “I will weigh myself every morning before breakfast.”
B. “I should avoid taking my diuretic before bedtime.”
C. “I can stop taking my beta blocker if I feel fine.”
D. “I’ll try to limit my salt to no more than 2,000 mg a day.”
C. “I can stop taking my beta blocker if I feel fine.”
Which of the following symptoms would the nurse most likely observe in a patient with left-sided heart failure?
A. Peripheral edema
B. Jugular vein distention
C. Shortness of breath when lying down
D. Hepatomegaly
C. Shortness of breath when lying down
A patient taking lisinopril for CHF reports muscle weakness and palpitations. Which lab value should the nurse assess first?
A. Sodium
B. Potassium
C. Calcium
D. Magnesium
B. Potassium
Which instruction should the nurse give to a patient prescribed furosemide?
A. “Take your medication at night so it lasts while you sleep.”
B. “Skip your medication on days you feel tired.”
C. “Record your weight each morning using the same scale.”
D. “Take potassium supplements with this medication.”
C. “Record your weight each morning using the same scale.”
The nurse is reviewing the medication list of a CHF patient. Which combination should the nurse question?
A. Metoprolol and insulin
B. Lisinopril and potassium chloride
C. Losartan and furosemide
D. Carvedilol and atorvastatin
B. Lisinopril and potassium chloride
A Hispanic male patient with newly diagnosed CHF asks about his risk factors. What is the best response by the nurse?
A. “There are no ethnic risk factors for CHF.”
B. “Your ethnicity may be linked to increased left ventricular mass.”
C. “Only African Americans are at increased risk for CHF.”
D. “Gender and ethnicity don’t affect your heart failure.”
B. “Your ethnicity may be linked to increased left ventricular mass.”
Which dietary selection made by a patient with CHF indicates they understand their diet instructions?
A. Grilled chicken with brown rice and steamed broccoli
B. Ham and cheese sandwich with potato chips
C. Fried chicken with macaroni and cheese
D. Canned soup and saltine crackers
A. Grilled chicken with brown rice and steamed broccoli
The nurse is explaining stages of CHF. Which stage corresponds with structural heart changes but no symptoms?
A. Stage A
B. Stage B
C. Stage C
D. Stage D
B. Stage B
A nurse is teaching a patient about beta blockers. Which statement by the patient demonstrates understanding?
A. “I can stop this medication once my heart rate normalizes.”
B. “This medication will increase my energy right away.”
C. “I should avoid this medication if I have asthma.”
D. “This medication replaces my need for diet changes.”
C. “I should avoid this medication if I have asthma.”
A patient with advanced CHF is classified as Stage D. What would the nurse expect in this patient’s treatment plan?
A. Annual checkup with no medications
B. Lifestyle changes only
C. Medications with symptom management
D. Possible mechanical support or transplant consideration
D. Possible mechanical support or transplant consideration
A nurse would like to assist Americans in improving their health. Which strategy would be most beneficial to improve the health of the American public?
A. Encourage Americans to stop smoking.
B. Lobby for state-of-the-art magnetic resonance imaging machines in all hospitals.
C. Provide free medications for Americans.
D. Offer free condoms to teenagers.
A. Encourage Americans to stop smoking.
A nurse is using a health education component when teaching about smoking cessation. Which of the following actions is the nurse implementing?
A. Setting a quit date for people in a smoking cessation class.
B. Providing education regarding the benefits of smoking cessation.
C. Allowing smokers to participate in a smoking cessation program only if they use the patched nicotine replacement system.
D. Encouraging attendees of a smoking cessation program to participate in a research study.
B. Providing education regarding the benefits of smoking cessation.
Any combination of planned experiences based on sound theories that provide individuals, groups, and communities the opportunity to acquire the information and skills needed to make quality health decisions is known as Health
A. Promotion,
B. Counseling,
C. Education,
D. Knowledge.
C. Education,
An overweight woman joins a support group to help her lose weight. During her first session, the nurse explains the components of a healthy diet and discusses with the woman how she can eat out and still maintain a healthy diet. She asks the woman what her goal is and emphasizes that she herself is the key to success. What is the nurse promoting through the use of this strategy?
A. Communication
B. Values
C. Advanced Planning
D. Empowerment
D. Empowerment
Which of the following illustrates that the objectives of health education and counseling are being met?
A. Diabetic who attends a diabetes education program.
B. Diabetic who watches a video about self-administration of insulin.
C. Diabetic who starts taking his medications regularly.
D. Diabetic who is admitted in diabetic ketoacidosis.
C. Diabetic who starts taking his medications regularly.
Which of the following illustrates that the objectives of health education and counseling have been met?
A. Asthmatic who has a decrease in emergency department visits
B. Asthmatic who has been prescribed an albuterol inhaler
C. Asthmatic who attends an asthma education program
D. Asthmatic who visits the emergency department with an exacerbation
A. Asthmatic who has a decrease in emergency department visits
A teenager who lives at home with her parents and school-aged brother has been diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. Which of the following would be the most appropriate teaching goal for this family?
A. Increased energy level.
B. Improved coping.
C. Enhanced self-esteem.
D. Facilitated family conversation.
B. Improved coping.
A teenager who lives at home with her parents and school-aged brother has been diagnosed with anorexia nervosa. Which of the following would be the most appropriate teaching goal for this teenager?
A. Increased energy level.
B. Improved coping.
C. Enhanced self-esteem.
D. Accomplished activities of daily living.
C. Enhanced self-esteem.
A nurse is using the Health Belief Model as a framework when developing a community action campaign to increase the percentage of the population who receives the influenza vaccine. Which of the following considerations will need to be made?
A. How empowerment can be used to motivate community members
B. How modeling can be used in the community to increase public awareness
C. Perceived susceptibility in the community about getting influenza
D. Perceived stage of behavior change that exists in the community
C. Perceived susceptibility in the community about getting influenza
Which of the following emphasizes that an individual's belief in being personally capable of performing the behavior is required to influence one's own health?
A. Social Cognitive Theory
B. Self-Efficacy Theory
C. Health Belief Model
D. Trans-Theoretical Model
A. Social Cognitive Theory
A nurse is counseling a teenager who smokes one pack of cigarettes a day. The teenager states he likes to smoke with his friends and does not recognize the connection between his smoking and his asthma. When planning an intervention for this person, the nurse must first recognize that the teenager is in the
A. Pre-contemplation stage of change,
B. Preparation stage of change,
C. Action stage of change,
D. Maintenance stage of change.
A. Pre-contemplation stage of change,
An overweight woman is in the preparation stage of change. Which of the following interventions would be the most appropriate for the nurse to implement?
A. Inform her of the health risks associated with being overweight.
B. Prepare her for the setbacks.
C. Develop a low-calorie, low-fat diet with her so she can follow it at home.
D. Praise her for her recent success.
C. Develop a low-calorie, low-fat diet with her so she can follow it at home.