Normal Occlusion
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
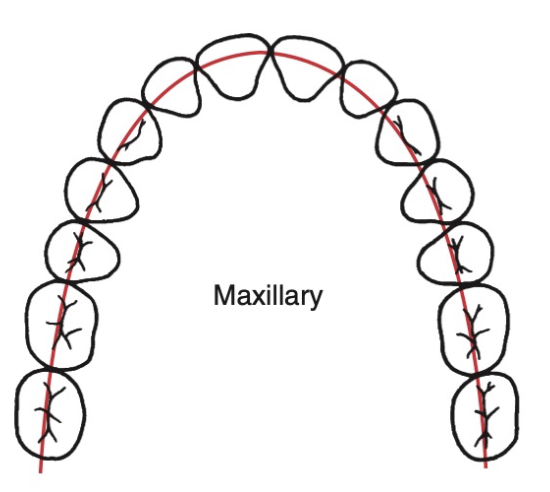
Line of Occlusion (Upper)
a smooth (catenary) curve passing through the central fossa of each upper molar and across the cingulum of upper canine and incisor teeth
Line of Occlusion (Upper)
Line of Occlusion (Upper): a smooth (catenary) curve passing through the ______ of each upper molar and across the cingulum of ________.
central fossa ; upper canine and incisor teeth
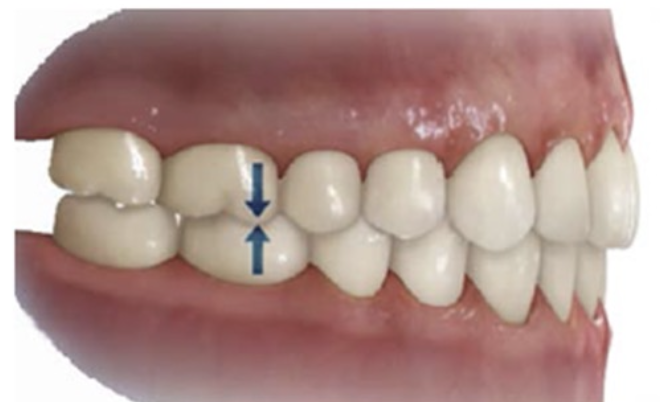
Normal Occlusion
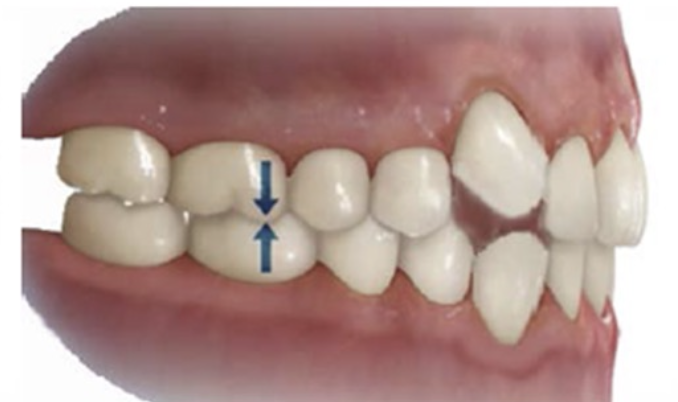
Class I Malocclusion
smooth (catenary) curve that runs along the buccal cusps and incisal edges of the lower teeth
Line of Occlusion (Lower)
Line of Occlusion (Lower): smooth (catenary) curve that runs along the _____ and incisal edges of the _____.
buccal cusps ; lower teeth
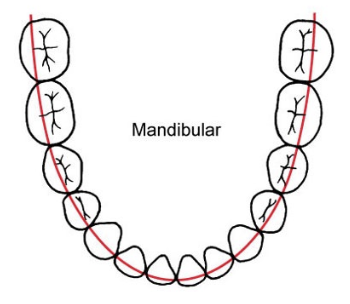
Line of Occlusion (Lower)
The perfect occlusion
Ideal Occlusion
Occlusion that never attained in nature
Ideal Occlusion
hypothetical goal for orthodontists
Ideal Occlusion
6 KEYS TO NORMAL OCCLUSION
1. Molar Relationship
2. Crown Angulation
3. Crown Inclination
4. Rotations
5. Spacing
6. Occlusal Plane
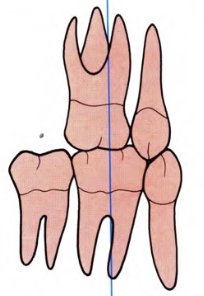
Impropert Molar Relationship
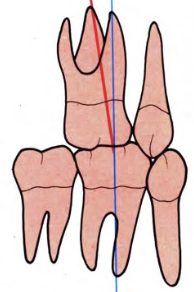
Improved Molar Relationship
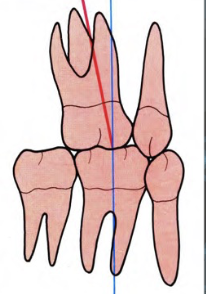
More Improved Molar Relationship
MBC of U6 occludes in the groove between mesial and middle cusps of L6
Propert Molar Relationship
Distal surface of DBC of U6 occludes with the mesial surface of MBC of L7
Proper Molar Relationship
He used 120 ortho cases with normal occlusions, that’s how he formulated the 6 keys to normal occlusion
Lawrence Andrews
How many cases did Lawrence Andrews used to arrive at the 6 keys to normal occlusion
120
long axis of the clinical crown (LACC)
Vertical line
center of long axis of clinical crown (LACC)
LA spot
mesiodistal tip
Crown Angulation
gingival portion of LACC is distal to the incisal portion
Crown Angulation
expressed in degrees (+ or -)
Crown Angulation
Give the reading: gingival portion of LACC is distal to the incisal portion
+ Reading
Give the reading: gingival portion of the LACC is mesial to the incisal portion
- Reading
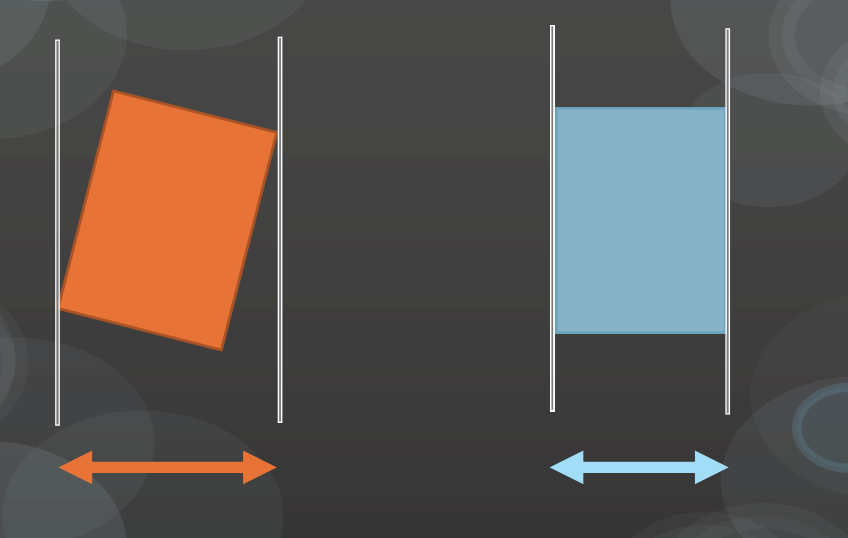
Crown Angulation
the degree of angulation depends on the ______
type of tooth
line passing through LA spots
horizontal plane reference
perpendicular to the horizontal plane
vertical plane reference
labiolingual or buccolingual inclination of LACC
Crown Incliantion
expressed as + or - degrees
Crown Inclination
What does the degrees in crown inclination represent
the angle formedby the line which is 90° to OP and a line tangent to the bracket site
Give the reading for crown inclination: gingival portion of the tangent line or of the crown is lingual to the incisal portion
+ Reading
Give the reading for crown inclination: gingival portion of the tangent line or of the crown is labial to the incisal portion
- Reading
Improperly inclined anterior crowns results in ___________
upper contact points being mesial
Properly inclined anterior crowns, contact points move ____
distally
spaces resulting from normally occluded posterior teeth and insufficiently inclined anterior teeth are often blamed on _______
tooth size discrepancy
for upper canine through molars lingual crown inclination in upper posterior teeth
CROWN INCLINATION Upper Posterior Teeth
constant/similar from canine thru second premolars
CROWN INCLINATION Upper Posterior Teeth
slightly more pronounced in molars
CROWN INCLINATION Upper Posterior Teeth
for lower canine through molars
CROWN INCLINATION Lower Posterior Teeth
lingual inclination progressively increases from canines through second molars
CROWN INCLINATION Lower Posterior Teeth
rotated premolars/molars = _________
occupy more space in the arch
contacts points are tight
Spacing
flat occlusal plane to slight curve of Spee
OCCLUSAL PLANE
_______ is best when occlusal plane is flat
intercuspation
results in more contained area for upper teeth, making normal occlusion impossible
Deep Curve of Spee
allows excessive space for each tooth to be intercuspally placed
Reverse Curve of Spee
contact of a tooth or teeth along the retruded path of closure
RETRUDED CONTACT POSITION (RCP)
initial contact of a tooth or teeth during closure around a transverse horizontal axis
RETRUDED CONTACT POSITION (RCP)
maximal intercuspal position (MIP)
INTERCUSPAL POSITION (ICP)
the complete intercuspation of opposing teeth independent of condylar position
INTERCUSPAL POSITION (ICP)
the best fit of the teeth regardless of condylar position
INTERCUSPAL POSITION (ICP)
a maxillo-mandibular relationship independent of tooth contact
CENTRIC RELATION (CR)
the condyles articulate in the anterior-superior position against the posterior slopes of the articular eminence
CENTRIC RELATION (CR)
the occlusion of opposing teeth when the mandible is in centric relation
CENTRIC OCCLUSION
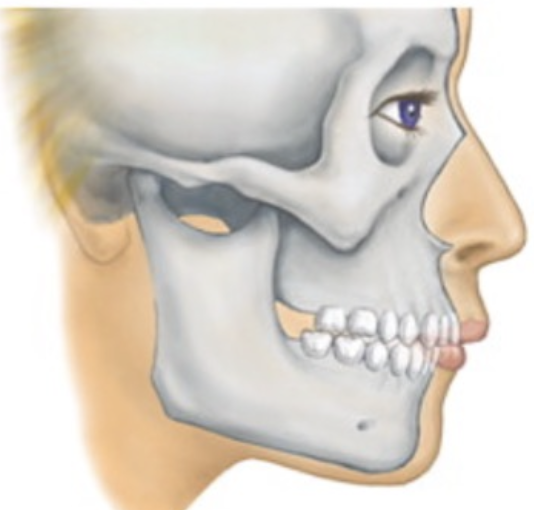
Centric Relation but not in centric occlusion
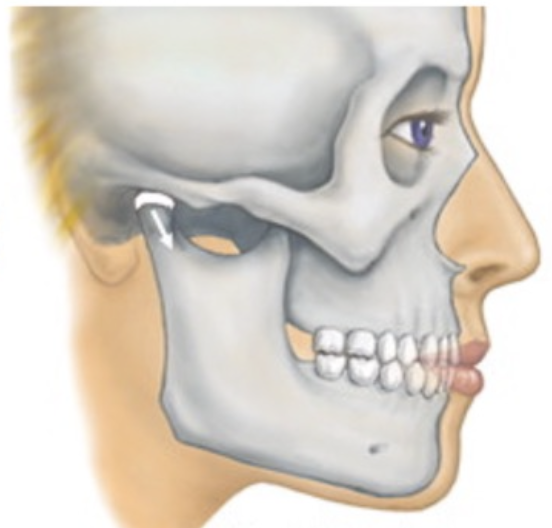
Centric occlusion but not in centric relation
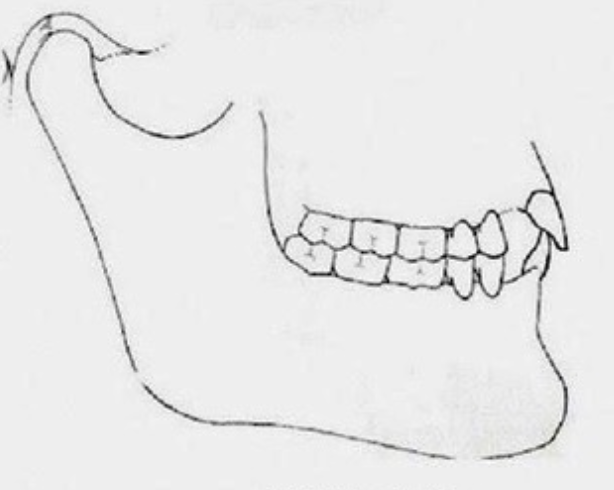
CR = CO
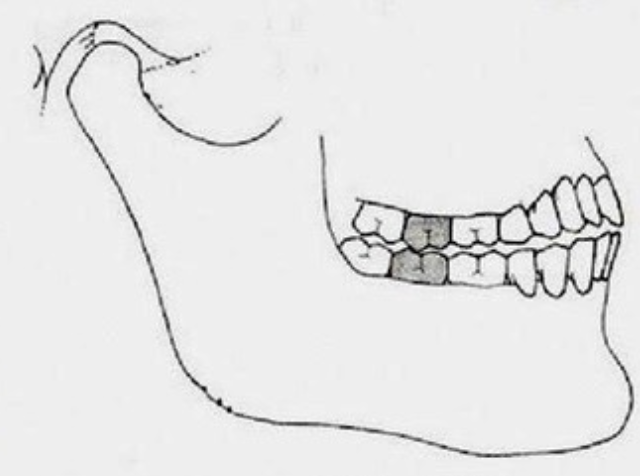
CR to CO Slide
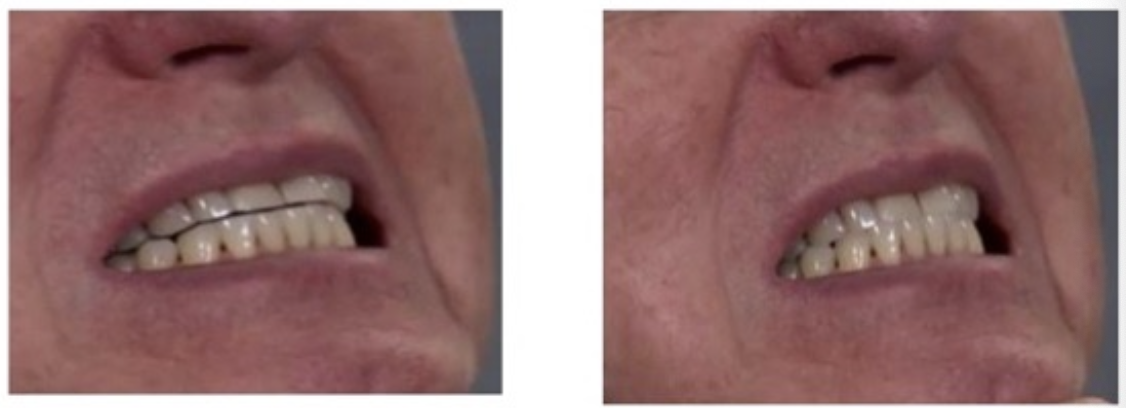
CR to MIP
a form of mutually protected articulation
CANINE GUIDANCE
horizontal and vertical overlap of canine teeth disclude the posterior teeth in the excursive mov’t of mandible
CANINE GUIDANCE
multiple contact relations between the maxillary and mandibular teeth in lateral movements on the working- side whereby simultaneous contact of several teeth acts as a group to distribute occlusal forces
Group Function
Group Function: multiple contact relations between the ______ in lateral movements on the working-side whereby simultaneous contact of several teeth acts as a group to distribute ______
maxillary and mandibular teeth ; occlusal forces
an occlusal scheme in which the posterior teeth prevent excessive contact of the anterior teeth in maximal intercuspal position, and the anterior teeth disengage the posterior teeth in all mandibular excursive movements.
MUTUALLY PROTECTED ARTICULATION
Teeth of the anterior and posterior dentitions protect each other during function
MUTUALLY PROTECTED ARTICULATION
MUTUALLY PROTECTED ARTICULATION:
an occlusal scheme in which the ______ prevent excessive contact of the anterior teeth in maximal intercuspal position, and the _____ disengage the posterior teeth in all mandibular excursive movements.
posterior teeth ; anterior teeth
CANINE GUIDANCE: horizontal and vertical overlap of ______ disclude the _____ in the excursive mov’t of mandible
canine teeth ; posterior teeth